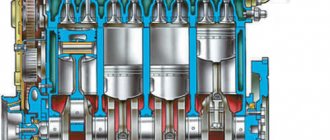
Peugeot launched the production of engines designated HDi or High-pressure Direct Injection (direct injection under high pressure) in 1998. Engines with a volume of 1.6 liters appeared only in 2003 and already belonged to the second generation HDi. Therefore, the manufacturer has already eliminated some of the errors, but not all. Details below.
1.6HDI
A little history
Peugeot is far from new to the development of diesel engines. They were the first in the world to install a diesel engine in a passenger car. This was the experimental Peugeot Torpedo in 1921. Since then, the company has not stood still. Now Peugeot diesel engines are used by such famous automobile brands as Ford, Jaguar, Volvo, Land Rover and Mitsubishi.
Diesel units of the DV family are manufactured at the SMAE (Societe Mecanique Automobile de l'Est) plant in France. The highly computerized and technologically advanced plant allows the production of one new engine almost every 20 seconds, with minimal human intervention.
The HDi system is a direct injection of fuel into the combustion chamber under high pressure. This technology improves engine performance, reduces fuel consumption and reduces vibration and noise. In comparison with the “classic” diesel engine, the design of the engine has become more complicated and is not without weak points and expensive parts. With each new generation, the manufacturer makes changes to the design and produces various modifications. Therefore, the DV6 series of diesel engines are installed on many modern cars.
Brief history of the Peugeot concern (Peugeot SA)
The Peugeot concern (Peugeot SA), the largest private automobile manufacturing company in France, has a history dating back to the 15th century, when the first mentions in chronicles of prominent representatives of this glorious family appeared.
Armand Peugeot
The family's transition from agriculture to industry took place in 1810, when two Peugeot cousins converted one of their flour mills into a metalworking enterprise. Over several decades, the factory has mastered a wide range of various household metal products and tools, the most famous of which are coffee and spice mills.
By the 80s of the 19th century, the Peugeot family business had developed into one of the largest industrial enterprises in France and exported beyond its borders.
During this period, bicycles appeared in Europe and began to quickly gain popularity. The grandson of the founder of the Peugeot brand, Armand (1849-1915), enthusiastically began to develop this new branch of the business, and soon Peugeot bicycles became predominant in France and remain so today.
But the era of the automobile was approaching. In 1889, Armand Peugeot, together with a great enthusiast of steam engines, Leon Serpollet, produced the three-wheeled steam carriage "Serpollet-Peugeot", which in the same year became an exhibit at the Paris World Exhibition, and in 1890 made a run from Paris to Lyon. But the era of steam engines was not long.
At this time, the Panhard-Levassor company was already building carriages with gasoline engines under license from the German Daimler. Emile Levassor was a friend of Armand Peugeot and once introduced him to Gottlieb Daimler. This meeting decided the future fate. Not without the support of E. Levassor, in 1891 the first car with a two-horsepower two-cylinder Daimler engine was released.
Since 1892, Peugeot launched mass production of 10 types of cars with different bodies, with power ranging from 1.5 to 4 hp. In 1895, about 130 cars were produced.
Being a very energetic and enterprising man, Armand Peugeot soon realized the importance of the emerging interest in automobile races and competitions for advertising his cars at that time. Therefore, when the newspaper Le Petit Journal organized the “great motor rally” Paris - Rouen, he was one of the first to apply. On June 22, 1894, the first car race in the history of motorsport took place.
The first of 102 crews to reach the finish line of the 126-kilometer run was the six-seater steam engine “de Dion Bouton and Trepardou”, having spent 5 hours and 40 minutes on the run. Two Peugeots and a Panhard finished behind him. After consulting, the panel of judges made an unexpected verdict - the prize should be awarded to petrol Peugeots, as more advanced and progressive vehicles. The following year, Peugeot again took the prize.
This is how the history of the famous automobile brand Peugeot began, which today is part of the PSA Peugeot-Citroen industrial group and produces a wide range of magnificent modern cars.
A large number of purposeful and energetic people are subconsciously ready to become individual entrepreneurs and are looking for information on, for example, how to open their own business in Donetsk. But finding high-quality and up-to-date information on this issue is not so easy. The best source of information will be a law firm in a particular region, which, in addition to information, can offer registration services.
Generations and modifications
Since the manufacturer missed the 1.6-liter capacity in the first generation of the HDi family, the history of the DV6 begins immediately with the second.
Second generation
The first version of the 1.6 HDi was released in 2003. Motors designated DV6TED4 and DV6ATED4 were installed on Peugeot/Citroen cars until 2011. And the modification DV6BTED4 was intended for commercial vehicles and was used until 2015 inclusive.
All engines used the Common Rail fuel system from Bosch, the service life of which is very dependent on the frequency of replacing the fuel filter. The motor with the index DV6TED4 has two varieties:
- 9HZ – without particulate filter for EURO 3;
- 9HY – version with FAP filter for EURO 4.
The tables below present the main technical characteristics of the Peugeot 1.6 HDi DV6 series engines.
| 1.6 HDI second generation | |||
| Factory index | DV6TED4 | DV6ATED4 | DV6BTED4 |
| Volume | 1560 cm³ | ||
| Fuel system | Common Rail | ||
| Power | 109 hp | 90 hp | 75 hp |
| Torque | 240 Nm | 205 - 215 Nm | 175 - 185 Nm |
| Cylinder block | R4 aluminum | ||
| Block head | 16v aluminum | ||
| Cylinder diameter | 75 mm | ||
| Piston stroke | 88.3 mm | ||
| Compression ratio | 18.0 | 17.6 — 18.0 | |
| Intercooler | There is | No | |
| Hydraulic compensators | There is | ||
| Timing drive | belt and chain | ||
| Phase regulator | No | ||
| Turbocharging | VGT | Yes | |
| Volume and type of oil | 3.75 liters 5W-30 | 3.85 liters 5W-30 | 3.8 liters 5W-30 |
| Ecology | Euro 3/4 | EURO 4 | EURO 4 |
| Motor life* | 240,000 km | 220,000 km | 300,000 km |
*subject to compliance with maintenance regulations
Third generation
Motors of this generation have been installed in parallel with the second since 2009. The cylinder head has changed significantly; it now has an eight-valve design. The fuel equipment has also been improved. It can be of two types:
- Bosch – with electromagnetic injectors;
- Continental (Siemens) – with piezo injectors.
All engines began to be equipped with particulate filters.
| 1.6 HDI third generation | |||
| Factory index | DV6CTED | DV6DTED | DV6ETED |
| Volume | 1560 cm³ | ||
| Fuel system | Common Rail | ||
| Power | 110 - 115 hp | 90 - 92 hp | 75 hp |
| Torque | 270 Nm | 230 Nm | 220 Nm |
| Cylinder block | R4 aluminum | ||
| Block head | 8v aluminum | ||
| Cylinder diameter | 75 mm | ||
| Piston stroke | 88.3 mm | ||
| Compression ratio | 16.0 | ||
| Intercooler | There is | No | |
| Hydraulic compensators | There is | ||
| Timing drive | belt | ||
| Phase regulator | No | ||
| Turbocharging | VGT | Yes | |
| Volume and type of oil | 3.85 liters 5W-30 | 3.8 liters 5W-30 | 3.75 liters 5W-30 |
| Ecology | EURO 4/5 | ||
| Motor life* | 240,000 km | 250,000 km | 300,000 km |
*subject to compliance with maintenance regulations
Fourth generation
Modern engines that have been installed on new cars since 2014. They differ from the previous ones with an even more complex fuel system and new Blue HDi technology (exhaust gas purification system). Thanks to the latter, DV6 diesel engines were able to “squeeze” into strict EURO 6 environmental standards.
| 1.6 HDI fourth generation | |||
| Factory index | DV6FCTED | DV6FDTED | DV6FETED |
| Volume | 1560 cm³ | ||
| Fuel system | Common Rail | ||
| Power | 120 hp | 100 hp | 75 hp |
| Torque | 300 Nm | 250 Nm | 230 Nm |
| Cylinder block | R4 aluminum | ||
| Block head | 8v aluminum | ||
| Cylinder diameter | 75 mm | ||
| Piston stroke | 88.3 mm | ||
| Compression ratio | 16.0 | 16.7 | 16.0 |
| Features of internal combustion engines | BlueHDi | ||
| Hydraulic compensators | There is | ||
| Timing drive | belt | ||
| Phase regulator | No | ||
| Turbocharging | VGT | Yes | |
| Volume and type of oil | 4.5 liters 5W-30 | ||
| Ecology | EURO 5/6 | ||
| Motor life* | 220,000 km | 240,000 km | 250,000 km |
*subject to compliance with maintenance regulations
First generation[ | ]
| Peugeot 308 T7 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total information | |||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturer | Peugeot | ||||||||||||||||||
| Years of production | 2007–present | ||||||||||||||||||
| Assembly | Sochaux, France Mulhouse, France Wuhan, China Villa Boche, Argentina Rosva, Kaluga region, Russia Jakarta, Indonesia | ||||||||||||||||||
| Design | |||||||||||||||||||
| Platform | PSA PF2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Engine | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| 1.6VTi | |||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën | ||||||||||||||||||
| Type | EP6, petrol | ||||||||||||||||||
| Volume | 1598 cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum power | 88–90 kW | ||||||||||||||||||
| Configuration | in-line, 4-cylinder. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinders | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Valves | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Environmental standards | EURO-IV | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinder diameter | 77 mm | ||||||||||||||||||
| Piston stroke | 86 mm | ||||||||||||||||||
| Supply system | Distributed injection | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1.6 THP | |
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën |
| Type | EP6DT, petrol |
| Volume | 1598 cm3 |
| Maximum power | 103–129 kW |
| Configuration | in-line, 4-cylinder. |
| Cylinders | 4 |
| Valves | 16 |
| Environmental standards | EURO-IV |
| Cylinder diameter | 77 mm |
| Piston stroke | 86 mm |
| Supply system | Direct injection, turbocharging |
| 1.6 THP-200 | |
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën |
| Type | EP6DTX, petrol |
| Volume | 1598 cm3 |
| Maximum power | 147 kW (200 hp) |
| Configuration | in-line, 4-cylinder. |
| Cylinders | 4 |
| Valves | 16 |
| Environmental standards | EURO-IV |
| Cylinder diameter | 77 mm |
| Piston stroke | 86 mm |
| Supply system | Direct injection, turbocharging |
| 1.6 HDi | |
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën |
| Type | DV6, diesel |
| Volume | 1560 cm3 |
| Maximum power | 66–82 kW |
| Configuration | in-line, 4-cylinder. |
| Cylinders | 4 |
| Valves | 16 |
| Environmental standards | EURO-V |
| Cylinder diameter | 75 mm |
| Piston stroke | 88 mm |
| Supply system | Common Rail, turbocharged |
| 2.0 HDi | |
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën |
| Type | DW10, diesel |
| Volume | 1997 cm3 |
| Maximum power | 100–120 kW |
| Configuration | in-line, 4-cylinder. |
| Cylinders | 4 |
| Valves | 16 |
| Environmental standards | EURO-V |
| Cylinder diameter | 85 mm |
| Piston stroke | 88 mm |
| Supply system | Common Rail, turbocharged |
| Type | mechanical |
| Number of steps | 5 |
| manual 6-speed | |
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën |
| Model | ML6C, twin shaft |
| Type | mechanical |
| Number of steps | 6 |
| automatic 4-speed | |
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën |
| Model | AL4 (AT8), hydromechanical, shaftless |
| Type | automatic |
| Number of steps | 4 |
| automatic 6-speed | |
| Manufacturer | Aisin Warner |
| Model | ML6C, hydromechanical, shaftless |
| Type | automatic |
| Number of steps | 6 |
| robotic 6-speed | |
| Manufacturer | PSA Peugeot Citroën |
| Model | EGS®, twin shaft, single clutch |
| Type | robotic |
| Number of steps | 6 |
Compared to its predecessor, the Peugeot 307, the new car has become a little wider, with the same track, and a little lower, which has led to an increase in internal volume. The front end of the car has been slightly redesigned to meet the more stringent EuroNCAP requirements. The power structure of the body has also changed, in which the number of elements made of high-strength steels has increased, while the torsional rigidity of the body has increased by 25%. This made it possible to exclude the upper roof panel from the overall power structure of the body, and install a panoramic glass roof instead. In addition, the range of diesel engines and gearboxes has been expanded, and the range of petrol engines has been completely updated.
Changes also affected the interior, in particular, its basic equipment and the quality of the materials used were improved, and the number of airbags was increased to six[1].
A 5-door hatchback and a 2-door coupe-convertible are available on the Russian market[2].
Gasoline engines[ | ]
From the very beginning of the production of the 308, the first among all PSA concern cars received the next generation of fundamentally new design four-cylinder engines, developed by the concern for further use on all its cars of segments B, C, D: a VTi type motor with multipoint injection and throttleless intake, and a type THP with direct injection and turbocharging.
In 2010, based on the results of three years of production and operation, both engines were slightly modernized. The modernization affected individual elements of the engine without serious intervention in the overall design. The control firmware has also been adjusted. Simultaneously with the modernization, the PSA concern released a third engine - THP 200 hp, combining the features of the VTi engine with the features of the THP motor.
All three engines are assembled on a common aluminum cylinder block, with a chain drive of a 16-valve twin-shaft timing belt and hydraulic compensators in the valve drive. There are no balance shafts. The engine cooling system uses a variable displacement water pump and an electronically controlled thermostat. The design differences between the three motors are in the timing device, power supply and control systems.
Motor VTi[ | ]
A traditional power system is used - multipoint injection. The gas distribution mechanism implements the possibility of complex control of the intake and exhaust phases according to such parameters as the lift height of the intake valves, the width of the intake phase, the shift of the intake and exhaust phases. The phase shift is carried out by hydraulic phase shifters located on the intake and exhaust camshafts and operating independently of each other.
Thrust control is carried out by changing the lifting height of the intake valves while simultaneously changing the width of the intake phase, by means of a special cam shaft acting on the intake valves through a pusher system. This allows the engine to operate in the vast majority of operating modes without the participation of the throttle valve, which is always in the fully open position. At the time of entering the market, the engine complied with the Euro-4 environmental class.
It is produced and installed on the 308 in two displacement options - 1.4 and 1.6 liters. Both options are structurally identical and differ only in the height of the cylinder block. 1.4VTi variants:
- index EP3 - in the 2007 version - 95
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 5-speed manual transmission only. - index EP3C - in the 2010 version - 98
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 5-speed manual transmission only.
1.6VTi variants:
- index EP6 - in the 2007 version - 120
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 5-manual gearbox, 4-automatic gearbox. - index EP6C - in the 2010 version - 120/125
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 5-manual gearbox, 4-automatic gearbox.
Motor THP[ | ]
Power system - direct fuel injection (Direct Inject), turbocharging (Twin Scroll turbocharger). There is an electric fuel pump in the gas tank, and a single mechanical injection pump that feeds the common fuel rail, located on the cylinder head and driven by the intake camshaft.
The gas distribution mechanism uses a hydraulic phase shifter only on the intake camshaft. The valve lift height and intake phase width are not adjustable. Thrust control is carried out by a traditional throttle valve in the intake tract.
Thanks to the Twin Scroll turbocharger, the exhaust gas flows from two cylinders operating in series do not interfere with each other at the end/beginning of the exhaust stroke, which leads to more efficient cleaning of the cylinders and more efficient operation of the turbocharger. And direct fuel injection allows you to run on lean mixtures, which has a positive effect on fuel economy. At the time of entering the market, the engine complied with the Euro-4 environmental class. Available in only one volume option - 1.6 liters.
Execution options:
On the 308, one way or another, all possible versions of the engine were installed in terms of power from 140 to 175 hp.
- index EP6DT - with a basic turbocharger in the 2007 version - 140/150
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 6-manual gearbox, 5-manual gearbox, 4-automatic gearbox. - index EP6CDT - with a basic turbocharger in the 2010 version - 150/156/163
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 6-manual gearbox, 6-automatic gearbox. - index EP6DTM - with an enlarged turbocharger in the 2007 version - 175
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 6-speed manual transmission only.
Motor THP-200[ | ]
Power system - direct fuel injection (Direct Inject), turbocharging (Twin Scroll turbocharger) similar to a THP engine. The gas distribution mechanism and traction control are similar to the VTi engine. In terms of the general level of design and performance characteristics in 2010, the engine was one of the most advanced units in its class in the world. At the time of entering the market, it complied with the Euro-5 environmental class.
Execution options:
- index EP6CDTX - in the 2010 version - 200
hp, equipped with gearboxes: 6-speed manual transmission only.
Diesel engines[ | ]
During the production process, the 308 was equipped with the second and third generation of HDi diesel engines. HDi motors are PSA's own development for all its cars in the B segment and above. All HDi engines are united by a common concept - Common Rail injection, turbocharging. Each generation was represented on the 308 by two engines from the list: 1.6 HDi and 2.0 HDi.
Both engines of different sizes within each generation have practically no common parts, but are comparable in the engineering solutions used. Motors of different generations but of the same volume are built on an identical cylinder block of the same displacement and dimensions, but differ significantly in individual engineering solutions, which determine whether the motor belongs to each generation.
The second generation of HDi engines was installed on the 308 from the beginning of the model's production until the end of 2010. The third generation of HDi engines was installed from the beginning of 2010 and by the beginning of 2011 it completely replaced the previous one.
Engine 1.6 HDi II[ | ]
- Working volume - 1560 cm³.
- Compression ratio - 17.5
Aluminum cylinder block with forged crankshaft. Aluminum block head. Sixteen-valve, two-shaft timing belt, with a combined belt-chain drive and hydraulic compensators in the valve drive. There are no balance shafts. The location of the turbocharger is in front of the engine in the direction of travel of the car.
It was offered in two versions: basic with a variable geometry turbocharger; simplified with a fixed geometry turbocharger. Honeywell turbochargers. Both versions of the motor have an identical Bosch power system with six-hole electromagnetic injectors and a system operating pressure of 1750 bar. Also, the remaining working parts of the engine are completely identical, including the intercooler, control system, and exhaust system.
Exhaust system - two-component neutralizer and particulate filter (in the version for countries with environmental standards Euro-4 and lower, the particulate filter may be absent). Ecological class - Euro-4. Consumer differences between motors are in power and torque level. Execution options:
- 9HZ - 109
hp with particulate filter - 9HY - 109
hp without particulate filter - 9HV - 90
hp with particulate filter - 9HX - 90
hp without particulate filter
Engine 1.6 HDi III[ | ]
- Working volume - 1560 cm³.
- Compression ratio - 16.0
Aluminum cylinder block with forged crankshaft. Aluminum block head. Eight-valve single-shaft timing belt, with toothed belt drive and hydraulic compensators in the valve drive. There are no balance shafts. The location of the turbocharger is in front of the engine in the direction of travel of the car.
It was offered in two versions: basic with a Honeywell variable geometry turbocharger; simplified with a Mitsubishi fixed geometry turbocharger. In addition to turbochargers, the engines differ in power supply systems: Continental with piezoelectric nozzles with seven holes and a working pressure in the system of 2000 bar; Bosch with electromagnetic-type injectors with eight holes and a system pressure of 1900 bar. Otherwise the motors are identical.
Exhaust system - two-component neutralizer and particulate filter (in the version for countries with environmental standards Euro-4 and lower, the particulate filter may be absent). Ecological class - Euro-5.
Compared to previous generation engines, in order to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions, the compression ratio was lowered to 16.0, an exhaust gas recirculation system was used, the diameter of the combustion chamber in the piston was increased, intake losses were reduced and the level of turbulence of air flows was reduced.
As a result, despite the transition from a sixteen-valve design to a simpler eight-valve design, both versions of the engine had increased power throughout the entire speed range (with maximum power shifted to lower speeds), and the noise level was reduced.
Execution options
- Index DV6CTED4, model 2009 - 112
hp. It is equipped with gearboxes: 5-speed manual transmission, 6-speed manual transmission, 6-speed manual transmission. - Index DV6DTED4, model 2009 - 92
hp. Equipped with gearboxes: 5-speed manual transmission only.
Engine 2.0 HDi II[ | ]
- Working volume - 1997 cm³.
- Compression ratio - 17.6
- Boost pressure - 1.25-1.35 Bar.
The cylinder block is cast iron, linerless. The block head is aluminum. An intake manifold with dual ports of different lengths for each of the pair of intake valves. Honeywell variable geometry turbocharger. Particulate filter. The motor has a version for countries with cold climates.
The motor was developed by the PSA concern in 2002 as the next new generation of diesel engines, for further use on cars of the C and D segments and under the Euro-4 engine environmental class. For the PSA concern, this was the first sixteen-valve diesel engine with electronically controlled Common Rail injection and a variable geometry turbine.
From the very beginning of the production of the 308, the engine was installed on the car in the original version of 2003. In various markets, the engine was offered with a power of 136-140 hp. In 2009, the engine was upgraded to a higher environmental class Euro-5. The vast majority of engine parts have undergone technological and structural modernization. All attachments were also replaced, including the turbocharger. The motor received new control firmware. The maximum power was increased to 163 hp, the power at medium speed was increased, and the noise level was reduced. In 2010, simultaneously with the base one, a motor derated to 150 hp was offered to the market.
Execution options:
- Index DW10BTED4, model 2003 - 136/140
hp. depending on the firmware. It is equipped with gearboxes: 6-speed manual transmission, 6-automatic transmission.
Engine 2.0 HDi III[ | ]
- Working volume - 1997 cm³.
- Compression ratio - 16.0
The cylinder block is cast iron, linerless. The block head is aluminum. An intake manifold with dual ports of different lengths for each of the pair of intake valves. Honeywell variable geometry turbocharger. Particulate filter.
Execution options:
- Index DW10CTED4, model 2009 - 163
hp. It is equipped with gearboxes: 6-speed manual transmission, 6-automatic transmission. - Index DW10DTED4, model 2010 - 150
hp. It is equipped with gearboxes: 6-speed manual transmission, 6-automatic transmission.
Gearboxes[ | ]
- 5-speed manual transmission
in-house developed by PSA. It was also installed on model 307. - The 6-speed manual gearbox
was developed for PSA by Borg Warner, is capable of working with engines with a torque of up to 400 Nm, is highly reliable and has clear, short lever strokes. - The 4-speed automatic transmission
was developed by PSA in collaboration with Renault in 2001 for gasoline engines up to 2 liters in volume. The Peugeot 308 uses the third (since 2007) and fourth (since 2011) modification of the box. - The 6-speed automatic transmission
was developed for PSA by the Japanese company Aisin Warner in 2005.
Both automatic transmissions are structurally hydromechanical automatic transmissions of the shaftless type, on planetary gearboxes with a torque converter. Both boxes are adaptive (according to the driver’s driving style), and also have a manual control system similar to Tiptronic®-Porsche (gear changes are carried out by longitudinal movement of the lever according to the scheme first widely used on Porsche cars: in this case, downshifting is done by pushing the lever to the rear non-locking position ; and increasing the gear by pushing the lever to the front non-locking position).
- The 6-speed robotic gearbox, type EGS
, was developed independently by PSA in 2007 in collaboration with Borg Warner (shafts and gears) and Magnetti Marelli (control electronics).
A two-shaft gearbox of a mechanical type on gears with synchronizers, with one clutch and electro-hydraulic actuators. On compact-class cars, this is the only gearbox among all robots with one clutch, developed from scratch: the box does not have a donor of units and mechanisms among the other boxes used by PSA, but on the contrary, it itself is a donor for six-speed manual gearboxes. Compared to a six-speed manual transmission, the weight of the robot is only 15 kilograms more. At the time of its creation, it was perhaps the lightest production six-speed gearbox operating in automatic mode. In terms of adaptability to the specific requirements of the driver in motion, it is at the level of the best automatic transmissions in the world. However, changing gears, due to the presence of only one clutch, occurs with a break in the power flow, which is accompanied by some push. Due to its design, it is extremely reliable, not prone to overheating and slipping. PSA states that in its creation, all the positive experience of the concern’s cars participating in motorsport was used: Peugeot - in the World Endurance Championship, Citroen - in the World Rally Championship [ source not specified 705 days
]. The gearbox can also be controlled using the steering wheel switches.
Chassis[ | ]
Front-wheel drive, with a transverse power unit. It is the simplest and most common design: front suspension - MacPherson type, lower L-shaped arm; rear suspension - torsion beam, springs. Despite the somewhat primitive nature of the suspension, the car has a quite acceptable level of comfort, and handling can be assessed as very good.
The car can be equipped with the latest generation ESP, which adequately combats the car's drift to the outside of the turn when speeding up and at the same time allows it to take turns with a slight skid.
The rear suspension beam provides a steering effect on surfaces with a high coefficient of adhesion. The effect of steering appears when braking on an arc as the car is pulled into the corner. When the brake pedal is abruptly released, the opposite effect is observed - the car moves to a larger radius.)
Security[ | ]
The following systems are standardly used as active safety elements on the 308:
- Anti-lock brakes (ABS)
. 8th generation. - Electronic Brake Force Distribution (EBD)
. Four-circuit pressure regulator in the brake line of each wheel, depending on the static and dynamic longitudinal and lateral loads on the wheels during braking. Allows you to brake in turns of any radius. - Emergency Brake Assist (AFU)
. Pressure booster in the brake line in case of emergency braking.
Optionally used systems:
- Dynamic stabilization (ESP)
. 8th generation, has its own processor, spatial position sensor and transverse and longitudinal acceleration sensors. It is able to combat both the drift of the car to the outside of the turn and dampen the amplitude of the skid. - Anti-slip (ASR)
. Included in the previous one. - Assistance when starting on a slope
. Only on cars with a 1.6HDi diesel engine and a robotic gearbox.
Passive[ | ]
| 35 | |||
| Child | 39 | ||
| A pedestrian | 19 | ||
| Model tested: Peugeot 308 1.6 diesel (5 doors) (2007) | |||
| 36 | |||
| Child | 34 | ||
| A pedestrian | 12 | ||
| Model tested: Peugeot 308 1.6 (convertible) (2008) | |||
Restyling[ | ]
The model update was announced by Peugeot in May 2011. Almost immediately, the updated version was presented at the Geneva Motor Show. In fact, the changes affected only the external design of the front of the car. The bumper, fenders, hood, lighting, and individual external decorative elements were changed. Some of the external lighting equipment was switched to LEDs. No structural changes were made to the body and chassis. Structural changes to the interior and equipment were also not made. The automatic transmission has been updated. AT8 is installed instead of AL4. The new box has a ZF torque converter. Accordingly, the operating modes of the torque converter have been changed, which undoubtedly improved the operation of the automatic transmission as a whole. The planetary part of the automatic transmission remains unchanged.
Simultaneously with the restyling, Peugeot launched a so-called “micro-hybrid” version with an e-HDi diesel engine, a start-stop system and supercapacitors to save energy. In Russia, the updated version has been available since July 1, 2011.
Security[ | ]
The restyled 308 passed the EuroNCAP safety test in 2013:
| Euro NCAP[5] | |||
| overall rating | |||
| 92% | 79% | 64% | 81% |
| adult passenger | child | a pedestrian | active safety |
| Model tested: Peugeot 308 1.6 diesel, Level 2, LHD (2013) | |||
Sales in Russia[ | ]
Sales of the model officially started in March 2008. Modifications were proposed: 5-door hatchback, 5-seater station wagon, 7-seater station wagon. Since 2010, a 4-seater coupe-convertible has been added. The 3-door hatchback was not offered on the Russian market through official sales channels.
The representative of the PSA concern in Russia, the official importer, rather chaotically shuffled the power units that could be ordered during the sales period of the model. During the entire period of sales, only two remained unchanged: 1.6VTi with a five-speed manual transmission and 1.6VTi with a four-speed automatic. Diesels, turbo engines and all three six-speed gearboxes were absent from the offer at various times. Turbo engines were not officially sold in 163, 175 and 200 hp versions. With. The 1.4VTi engine was also not sold. The 2.0HDi diesel was sold only in 2008-2009 and only in the 136 hp version. With. The robotic box, despite general positive reviews, was sold only in 2009-2010. The six-speed automatic has only been sold since 2011. A six-speed manual transmission was offered with the 1.6HDi diesel. The reasons for this were not officially disclosed.
Initially there were three fixed configurations: “Comfort Pack”, “Premium” and “Premium Pack”. Subsequently, the “Sport” package was introduced, which included some new decorative elements and was very close to the average “Premium Pack” package. After restyling in 2011, the names of the three main trim levels changed to “Access”, “Active” and “Allure” while maintaining the “Sportium” trim level. The coupe-convertible was supplied in only one highest configuration - “Felin”.
With each passing year of sales, the volume of additional options offered was cut, and each trim level received slightly cheaper interior elements.
Since 2010, the assembly of the most popular 120-horsepower modifications of the model from vehicle kits has started at the PSA concern plant in Kaluga. All Russian cars received the Russian Pack option package: additional protection for the engine compartment from below, a high-capacity battery, and suspension for difficult conditions. The value of these options is ambiguous: the car has become a little higher and a little softer, but has lost controllability. In 2012, production of this model was discontinued. Among the features: approximately 90% of cars sold are with 120-horsepower VTi engines; approximately 50% are in medium trim levels (“Premium”, “Sportium”, “Active”).
Cars built on the 308[ | ]
For developing markets, Peugeot offers two additional models:
- 408 (sedan) - wheelbase 2710 mm
- 308 (sedan) - standard wheelbase
Both models are built on the basic 308 platform, using suspension components and a subframe. Equipped with engines of the previous generation from Peugeot 307: 1.6 110 hp. and 2.0 148 hp, paired with a five-speed manual transmission and a four-speed automatic transmission. Suspension for severe conditions is used.
The overall level of performance and options on the 408 is consistent with those in Europe. Leather interior, navigation and multimedia can be ordered. The panoramic glass roof has been replaced by a sliding sunroof. The level of options for the 308 sedan is limited and corresponds to the basic version of the European 308, expanded with individual inexpensive options. Both cars are offered in important non-European markets for Peugeot, such as China and South America. In 2011, there were plans to organize production of the 308 sedan model at the plant in Kaluga for Russia.
Based on the 308, a two-seater RCZ coupe was also built, structurally entirely built on the Peugeot 308 chassis and having power units from the general list.
Gallery[ | ]
- 308 3 doors
- 308 5 doors
- 308 SW/Break
- 308 CC
- 308 RCZ
Weaknesses and strengths
The overall reliability and service life of the DV6 series units is at a high level. But, unfortunately, you won’t be able to drive for years without looking under the hood. During the modernization process, the manufacturer eliminated some shortcomings, but the complication of the design brought new ones. Let's look at the weak points of each motor in the series, since knowing about them, you can easily prevent breakdowns. Let's start in order.
DV6TED4
The most powerful of the second generation line, but this does not prevent the engine from being economical. In 2008, a record was even recorded for the Guinness Book of Records - 3.13 liters of diesel fuel per 100 km, using a Peugeot 308 1.6 HDi.
DV6TED4
This version is equipped with a more complex and expensive variable geometry turbine (VGT). It is especially sensitive to low-quality or dirty oil. To extend the “life” of this important part, it is necessary to clean or change the coarse filter mesh more often. It is installed in the fitting of the oil supply tube to the turbine (this fitting is screwed into the engine block). When the filter becomes clogged, the turbine begins to “starve”, and then its shaft and bearing bushings wear out very quickly.
But the Garrett GT15 turbine also has advantages:
- good traction from the bottom;
- fast turbine response, no “turbo lag”;
- Overboost effect – short-term increase in boost to increase torque by +20 Hm;
- optimal fuel consumption.
Garrett GT 15
The internal combustion engine is demanding on the quality of diesel fuel, so in our area problems often arise with the EGR and FAP filter. In 99% of cases, the problem is solved by removing these “extra” spare parts and reflashing the engine control unit.
The DV6TED4 version with index 9HY (with a particulate filter) has a pneumatic metering device with two dampers. It is often the cause of engine oil leaks. Cracks in the housing or through seals allow oil to drip directly onto the alternator and belt. Therefore, the problem must be resolved promptly.
DV6ATED4
It differs from the previous modification by turbocharging. The turbine here is simple, with a bypass valve, manufactured by MHI (Mitsubishi). This affected the power - 90 hp, but potentially reduced service costs. The last statement is controversial, since it largely depends on the regularity and quality of car maintenance.
On this engine, the index 9HZ means the presence of a particulate filter, and 9HV means the absence. The entire second-generation 1.6 HDi range uses a Common Rail fuel system with a high-pressure pump and electromagnetic injectors.
DV6ATED4
One of the weak points of the engine is the copper washers under the fuel injectors. They may burn out over time. Then the gases from the combustion chamber will break into the injector wells and form soot and carbon deposits there. The same problem can arise due to loosening of the injector mounting studs. There is only one way out - replacing the washers and tightening the studs with a torque wrench.
The timing drive in the second generation of DV engines is combined. It consists of a belt and chain. The chain connects two camshafts and tends to stretch over time. A clear sign of stretching is “chirping” from under the valve cover. The factory replacement interval for the belt and chain is 240 thousand km. But sometimes, due to stretching, you have to cut the period in half.
DV6BTED4
This unit was installed only on commercial Peugeot Partner and Citroen Berlingo. The motor, derated to 75 horsepower, is designed for traction loads. Perhaps due to this, the resource of the DV6BTED4 is higher than that of more powerful options. Mileage of 300+ thousand km without “surgical” intervention is quite common.
DV6BTED4
DV6CTED
Representative of the third generation of DV motors. The manufacturer has simplified the cylinder head. Returned to a simpler eight-valve, single-cam version. This scheme is simpler and more reliable, but there is one drawback - the engine sluggishly picks up speed. The French solved this problem by modernizing the piston group:
- new alloy pistons - harder and lighter, with internal cooling;
- graphite rings were placed on the “skirt” of the pistons to reduce friction and eliminate temperature “sticking”;
- toroidal-spherical combustion chamber - allows you to burn the mixture more completely due to three-dimensional mixing.
The design with a single camshaft made it possible to abandon the combined timing system, leaving only a toothed belt, without a chain.
DV6CTED
Traditionally, the most powerful version in the DV6C series is equipped with a variable geometry turbine, the rest with a regular one. The fuel system is now available in two versions. Familiar from the previous generation Bosch with electromagnetic injectors and Siemens (Continental) with piezo injectors. The first option can be repaired and restored, but the piezo injectors will have to be replaced with new ones, starting from $300 apiece.
But the aluminum cylinder block with cast iron liners is quite repairable. There are even three repair sizes at quite reasonable prices.
DV6DTED
With an eight-valve cylinder head and a conventional turbo, the DV6D is potentially a very reliable engine. A power of 90 horsepower may not seem enough, but 240 Hm of torque is quite enough for normal city driving.
The main problems remain common to the entire family of engines: all kinds of engine oil leaks, burnt-out injector washers and a clogged particulate filter. The internal combustion engine designated DV6DTED M is a modification reduced in environmental terms to Euro 4.
DV6DTED
DV6ETED
Traditional in the line, the derated version for commercial vehicles. The letter "M" at the end of the engine code means there is no particulate filter. A more preferable option, from a purchasing point of view, is one with fewer problems.
DV6ETED
DV6FCTED
In the fourth generation, the DV6FC motor has not changed structurally. The main innovation was the introduction of the BlueHDi system. Its main task is to reduce CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. Since September 2020, all Peugeot diesel vehicles are equipped with BlueHDi. This allows them to comply with Euro VI environmental standards, but adds additional difficulties when operating the vehicle.
For the system to function properly, it is necessary to regularly refill the special AdBlue fluid. It loosens solid particles and allows them to be burned in the particulate filter at a lower temperature. The original fluid is quite expensive (from $100 per canister), and a poor-quality replacement can damage the entire system.
DV6FCTED
In fact, BlueHDi only affects the environment. But the car's computer brain won't allow you to drive normally without fluid or with a faulty BlueHDi system. Errors and warnings will be constantly displayed, the engine may “go” into emergency operation.
In commercial vehicles, the DV6FCTED engine is derated to 115 hp.
DV6FDTED
Since 2020, it has been installed on almost the entire model range of the French concern. A regular turbine, but BlueHDi is a must. Compared to the previous generation, the power of the DV6FD has increased by 10 hp. (100 versus 90), and for “commerce” it was reduced to 95 forces.
In the fourth generation, the oil bath has increased, and now 4.5 liters of 5W30 engine oil are required for replacement. But improvements to the fuel system made it possible to reduce fuel consumption by an average of 0.5 liters per “hundred”.
DV6FDTED
DV6FETED
Even the youngest in the line, DV6FE, did not escape the fate of e-HDi, so you will have to regularly add the additive. These engines are available not only for the commercial Berlingo and Partner, but also for the Peugeot 208/2008 and Citroen C3.
In the new series of engines, the fuel system is installed mainly with expensive piezo injectors. Therefore, potential problems with this unit depend on the mileage of the car. Usually, problems do not arise until 150-200 thousand mileage.
DV6FETED
Features of the sedan
Cars with affordable prices and excellent technical characteristics are valued not only in the CIS countries, but also in Russia. To satisfy all the wishes of Russian buyers, the French concern Peugeot-Citroen created the model 408. It is known where the Peugeot 408 is produced, now let’s talk in more detail about the capabilities of this car. This car model cannot be called small; it can easily be classified as a D-class. Thanks to the increase in the dimensions of the car, the inside of the sedan has become much more comfortable and spacious. The dimensions of the Peugeot 408 are 4337 mm × 4703 mm × 1505 mm. Our compatriots are very fond of this car model; the owners speak especially positively about the car’s engine.
The Peugeot 408 sedan is equipped with a 150-horsepower turbocharged engine with a volume of 1.6 liters. The car's suspension is also excellent. Despite the quality of Russian roads, this nimble sedan copes with all obstacles and potholes with a bang. In addition to an engine with a power of 150 horsepower, Russian buyers can purchase a sedan with a 1.6-liter gasoline unit producing 110 horsepower, or an engine with the same volume, but with a power of 120 horsepower. A turbodiesel consumes five liters of fuel per hundred kilometers, while gasoline units consume a little more - 8.2 liters. The car is offered with both a 5-speed manual and automatic transmission. The volume of the luggage compartment of the car is 560 liters.
But by folding the rear seats, you will be able to increase it. The luggage compartment has its own “zest”. Where the Peugeot 408 is produced, a plastic cover for the front bumper grille is placed there. The manufacturer recommends that owners use this part in the winter. It will protect the engine compartment from snow, sand, and dirt. It also helps the engine warm up faster. Since the body is galvanized, the manufacturer provides a 12-year guarantee against corrosion.
Service Features
On any modification of the Peugeot 1.6 HDi engine, in order to change the oil filter, you will have to remove the air supply pipe to the turbine. Therefore, after servicing, be sure to check the tightness of the pipe. If there is a “suction” of dirty air, the turbocharger will soon fail. The fuel filter is located near the engine shield - also not the most convenient place to replace it.
If the turbine could not be saved, then when replacing it, be sure to follow the following procedures:
- clean or simply throw away the coarse mesh;
- blow/clean the oil heat exchanger;
- remove any coke or carbon deposits in the oil pan and under the valve cover;
- change the oil supply tube, preferably the latest model - completely copper;
- change engine oil.
All these procedures are necessary to prevent solid particles from entering the turbine. If “garbage” remains in the engine, the new turbocharger may work for several hundred kilometers and fail again.
What cars were DV6 series engines installed on?
The tables present models of the PSA Peugeot Citroën automaker, linked to a specific engine type and broken down by year. Motors of the DV6 series are also installed on other brands of machines, but attachments and most parts are not interchangeable.
| 1.6 HDI second generation | |||||
| DV6TED4 | DV6ATED4 | DV6BTED4 | |||
| Brand, model | Years of manufacture | Brand, model | Years of manufacture | Brand, model | Years of manufacture |
| PEUGEOT | |||||
| 206 | 2003 — 2005 | 207 | 2006 — 2010 | Partner I | 2005 — 2008 |
| 207 | 2006 — 2011 | 307 | 2006 — 2008 | Partner II | 2008 — 2015 |
| 307 | 2004 — 2008 | 308 | 2007 — 2010 | ||
| 308 | 2007 — 2011 | Partner | 2003 — 2010 | ||
| 3008 | 2009 — 2011 | ||||
| 5008 | 2009 — 2011 | ||||
| 407 | 2004 — 2011 | ||||
| Partner | 2008 — 2010 | ||||
| CITROEN | |||||
| C2 I | 2007 — 2009 | C3 I | 2005 — 2009 | Berlingo I | 2008 — 2015 |
| C3 I | 2006 — 2009 | C3 II | 2009 — 2010 | ||
| C3 II | 2009 — 2011 | C4 I | 2004 — 2010 | ||
| C4 I | 2004 — 2010 | Xsara Picasso | 2006 — 2010 | ||
| C5 I | 2004 — 2008 | Berlingo I | 2006 — 2008 | ||
| C5 II | 2008 — 2010 | Berlingo II | 2008 — 2010 | ||
| Berlingo | 2008 — 2015 | ||||
| Xsara Picasso | 2004 — 2010 | ||||
| 1.6 HDI third generation | |||||
| DV6CTED | DV6DTED | DV6ETED | |||
| Brand, model | Years of manufacture | Brand, model | Years of manufacture | Brand, model | Years of manufacture |
| PEUGEOT | |||||
| 207 | 2011 — 2012 | 207 | 2010 — 2013 | Partner | 2009 — 2015 |
| 208 | 2012 — 2015 | 208 | 2012 — 2015 | ||
| 2008 | 2013 — 2014 | 2008 | 2013 — 2015 | ||
| 308 | 2011 — 2013 | 301 | 2012 — 2015 | ||
| 3008 | 2011 — 2015 | 308 I | 2010 — 2013 | ||
| 408 | 2010 — 2014 | 308 II | 2013 — 2015 | ||
| 4008 | 2012 — 2017 | Partner II | 2010 — 2015 | ||
| 508 | 2010 — 2012 | ||||
| 5008 | 2011 — 2015 | ||||
| Partner | 2010 — 2015 | ||||
| CITROEN | |||||
| C3 | 2011 — 2013 | C3 II | 2010 — 2014 | Berlingo | 2009 — 2015 |
| DS3 | 2010 — 2014 | DS3 | 2010 — 2014 | ||
| C4 | 2010 — 2015 | C4 II | 2010 — 2014 | ||
| C4 Picasso | 2011 — 2015 | C4 Picasso | 2013 — 2015 | ||
| C4 Aircross | 2012 — 2017 | C4 Cactus | 2014 — 2015 | ||
| DS4 | 2011 — 2015 | C-Elysee | 2012 — 2016 | ||
| C5 | 2010 — 2015 | Berlingo II | 2010 — 2015 | ||
| DS5 | 2011 — 2015 | ||||
| Berlingo | 2010 — 2015 | ||||
| 1.6 HDI fourth generation | |||||
| DV6FCTED | DV6FDTED | DV6FETED | |||
| Brand, model | Years of manufacture | Brand, model | Years of manufacture | Brand, model | Years of manufacture |
| PEUGEOT | |||||
| 208 | 2015 - present | 208 | 2015 - present | 208 | 2015 - present |
| 308 | 2014 - present | 2008 | 2015 — 2018 | 2008 | 2015 - present |
| 3008 I | 2015 — 2016 | 301 | 2016 - present | Partner | 2015 — 2018 |
| 3008 II | 2016 — 2017 | 308 | 2015 - present | ||
| 5008 I | 2015 — 2017 | 3008 | 2016 - present | ||
| 5008 II | 2017 — 2018 | 5008 | 2017 - present | ||
| Partner | 2015 — 2018 | Partner | 2015 — 2018 | ||
| Traveler | 2016 — 2018 | Traveler | 2016 — 2018 | ||
| CITROEN | |||||
| C3 Aircross | 2017 - present | C3 II | 2015 — 2016 | C3 II | 2015 — 2016 |
| DS3 | 2014 — 2016 | C3 III | 2016 - present | C3 III | 2016 - present |
| C4 II | 2015 — 2018 | C3 Picasso | 2015 — 2017 | Berlingo II | 2015 — 2018 |
| C4 Picasso | 2015 - present | C3 Aircross | 2017 - present | ||
| Berlingo | 2015 — 2018 | C4 II | 2015 — 2018 | ||
| Spacetourer | 2016 — 2018 | C4 Picasso | 2015 - present | ||
| C4 Cactus | 2015 - present | ||||
| C-Elysee | 2016 - present | ||||
| Berlingo | 2015 — 2018 | ||||
| Spacetourer | 2016 — 2018 | ||||
| D.S. | |||||
| 3 | 2016 - present | ||||
| 4 | 2015 - present | ||||
| 5 | 2015 - present | ||||
| OPEL | |||||
| Crossland X | 2017 - present | ||||
| Grandland X | 2017 - present |