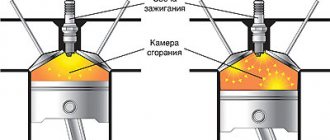
One of the important factors in the operation of an internal combustion engine is the compression in its cylinders, which indicates the maximum pressure value when the internal combustion engine is idling. Individual engine models require different compression levels. What compression should be in gasoline and diesel engines will be discussed in the article below.
Among car owners, compression is considered a diagnostic factor that allows one to assess the performance of the car’s engine and the condition of the piston group.
The compression indicator is the value of the pressure in the cylinders of a car, which the piston creates at its top point at the end of the compression stroke. The units for measuring engine compression are atmosphere, bar, kg/cm2 and MPa. High compression in the cylinders protects the crankcase from excessive gases, thus all gases are directed to perform useful work. At the same time, fuel and oil consumption is reduced, and accordingly, engine power and efficiency are increased. With low compression, the power of the internal combustion engine decreases, the dynamics of the vehicle deteriorate and fuel consumption increases. Not very experienced car owners sometimes confuse the concept of “compression” with the concept of “compression ratio”, but, in fact, these are different things. Compression
is the maximum air pressure in the combustion chamber at the end of the compression stroke.
The compression ratio of an engine
is the ratio of the total volume of the cylinder to the volume of the combustion chamber. Compression ratio. On a forced engine, depending on the final task, the compression ratio can vary significantly, reaching values of 11 - 11.5. All this is aimed at extracting maximum power from a motor of a specific size. The higher the compression ratio, the higher the power density. True, this will inevitably reduce the service life and sharply increase the risk of problems with the engine when refueling with low-quality fuel. One refueling with questionable fuel can quickly kill a “stressed” engine. So, when boosting the engine, you won’t be able to save on the quality of gasoline. Therefore, when tuning an engine, the compression ratio does not increase very significantly, usually in order to switch to a brand of gasoline that is next to the one already used in terms of octane number.
In principle, indirectly, the value of the compression ratio can be judged by the brand of gasoline used - you can drive an AI-80 with a compression ratio of 9.0, and an AI-92 - up to 10.0 (provided that the gasoline meets the declared characteristics). Raising the compression ratio is a complex process that requires precise calculations and very highly qualified mechanics. Therefore, it is highly not recommended to do this yourself. Compression, as mentioned above, is the pressure in the cylinder. This is why compression depends on the compression ratio (the pressure in a smaller volume will always be greater, i.e., as the compression ratio increases, the compression increases). By the amount of compression, you can preliminarily judge the condition of the piston.
List of parts responsible for the engine compression level
When the fuel mixture pressure is from 15 to 30 atmospheres, the following elements receive the greatest load:
- cylinder head gasket;
- piston;
- cylinder body;
- intake and exhaust valves;
- compression rings.
All of the listed parts of the gas distribution mechanism experience repeated loads resulting from the effects of high temperature and pressure. Wear of any of these elements affects compression, engine power and its economic characteristics.
Why is compression needed at all?
And here everything is simple - after fuel is injected into the cylinder, the valve closes, the piston moves upward, compressing the fuel (compression ratio). At the top point, a spark is supplied, the compressed fuel ignites, thereby pushing the piston down (thus spinning the engine).
If there is no compression (or it is very low), then all this created pressure will simply leave the cylinder (through a leak, usually these can be worn or burnt valves, or worn engine rings). The engine will work very poorly, or will not work at all; an engine overhaul (major repair) will be needed.
Thus, engine compression is a very important indicator, and directly affects the proper operation of the engine. It works in tandem with the compression ratio, but they are not the same thing! You need to know this.
And now a useful video on how to measure compression.
And today that’s all I have, this is what I hope is an easy to understand article. Read our AUTOBLOG.
Similar news
- DOHC engine
- What is engine torque
- What is VAG? We study the intricacies of German business
Pressure in diesel and gasoline engines
Due to differences in the design of diesel engines and gasoline engines, different compression is observed in the engine cylinders. The pressure standard for diesel engines is twice as high as for gasoline engines. This is due to the need for higher operating pressure to produce a diesel fuel flash.
What value should the diesel compression be? A diesel engine can only be started when a pressure in the cylinders exceeds 22 atmospheres. The optimal compression value for diesel engines is in the range of 28–32 atmospheres. This level is possible due to the high technology and complexity of the motor design.
The compression of a gasoline engine characterizes the level of pressure at idle speed of the power unit. The amount of pressure depends on the make and model of the car.
How much should the compression be in a gasoline engine? For carburetor engines, the compression rate is calculated using a special formula. The calculation is based on the compression ratio specified in the technical documentation and the coefficient, the value of which is determined by the gasoline engine’s belonging to a certain group.
For example, this coefficient for a four-stroke engine with a spark discharge in the spark plug is 1.2–1.3. Normal compression of a gasoline engine should be slightly above ten atmospheres.
Low compression can be caused by using low-quality oil, failure to change the lubricant, or frequent driving at high speeds.
If symptoms such as increased fuel and oil consumption or decreased traction appear, it is necessary to diagnose the engine. To identify the causes, it is not necessary to disassemble the engine; it is enough to measure the compression in the cylinders.
Compression table for gasoline cars is normal
Compression indicators in VAZ cars, provided that all systems and assemblies are in working order:
- VAZ 2106-2107 - compression 11 kg/cm2.
- VAZ 2109 - compression 11 kg/cm2.
- VAZ 2110 - compression 12 kg/cm2.
- VAZ 2112 - compression 12.6 kg/cm2.
Compression in gasoline engines of some other vehicle models from different manufacturers:
Description of pressure measurement
Compression measurements are performed on a warm engine. Checking the pressure in each cylinder is done on your own if you have a measuring device. Compression is measured using a special tool - a compression meter.
When choosing a measuring device, special attention must be paid to its threaded tip, which must be suitable for screwing it in instead of spark plugs.
To diagnose the motor, you must perform the following steps:
- Remove the spark plug from one cylinder.
- Install the measuring device in place of the removed spark plug.
- Turn the crankshaft using the starter.
- Record the instrument reading.
- Measure the pressure in all cylinders and then record the data.
- Compare the results obtained.
- Add some machine oil to the pistons.
- Crank the engine with the starter without inserting the spark plugs.
- Re-measure compression in cylinders.
To obtain real diagnostic results, compression should be measured at a crankshaft speed of 200–250 rpm.
These measures are carried out to identify a malfunction in one of the cylinders. A significant increase in pressure indicates damage to the piston or piston rings. If the pressure remains unchanged, therefore, the breakdown has affected the elements of the cylinder head or its gasket.
Self-compression test
Before measuring compression in the engine cylinders, check the battery (must be fully charged) and the serviceability of the starter (provides at least 200 rpm), otherwise the measurements may be inaccurate. The engine is warmed up to 80-90°C, after which it is ready for testing.
The compression measurement procedure is carried out in the following order:
- Remove the power wires from the spark plugs.
- The candles are screwed in and laid out, marking them so that after measurement they can be screwed into place. Sometimes car enthusiasts only unscrew the spark plug of the cylinder they are going to check; in this case, accurate readings will not be obtained. This is due to the creation of pressure in the remaining cylinders, which prevents the crankshaft from turning at the required number of revolutions.
- The wires are disconnected from the low-voltage coils for safety, so that accidental breakdown does not occur.
- With a manual pump, the fuel hose is disconnected to prevent fuel from being supplied to the cylinders. With an electric pump, pull in its relay, or remove the wires from the injectors.
- The compression gauge is installed in the spark plug hole and held tightly (with a rubber tip).
- The person sitting behind the wheel presses the gas pedal and turns the starter until the needle stops moving.
- The device readings are recorded and reset.
- The procedure is carried out similarly for other cylinders.
- After completing the measurements, everything is assembled in the reverse order, and you can analyze the results obtained.
Factors affecting engine pressure
The results of compression measurements often differ from each other, even if all the parts involved in the gas distribution are working properly. The following conditions influence the pressure in the cylinders:
- the amount of incoming air masses;
- crankshaft rotation speed;
- engine temperature;
- motor oil viscosity.
If you have problems starting and power is lost, the engine needs careful professional diagnostics. Repair and restoration work must be entrusted to experienced specialists. Extending the life of the engine and maintaining normal compression depends on a competent and attentive attitude to the engine.
What conclusions can be drawn from the results of compression measurements?
In books on the technical operation of domestic cars, factories prescribe the lowest permissible compression limits that are possible when operating vehicles. One of the most important conditions is the minimum difference in size between the cylinders. If the wear of the cylinders and parts is the same, then the values will be approximately the same. For example: in the first cylinder the compression is 10.8 kgf/cm2, and in the other three from 12.3 to 12.5 kgf/cm2. A large run-up indicates a malfunction, although the compression values are normal. The difference between the largest and smallest values should not exceed 1 kgf/cm2.
What to do if the compression is too low?
The pressure in the cylinders of an internal combustion engine can drop for various reasons: piston burnout, valve deformation, defective cam, wear of oil seals. If the compression level has dropped in one cylinder, there is a high probability that major engine repairs will not be required. To eliminate the problem, sometimes simply cleaning the combustion chamber from the deposits that have formed is enough. Another situation is when compression is below normal in all cylinders. In this case, repairing the “heart” of the car must be approached comprehensively. This is a more severe case, because it will require adjusting the timing gaps and restoring the tightness of the combustion chamber, which will ultimately require a major overhaul.
In diesel engines, in addition to problems with liners, wear of the cylinder bore can also be detected. With this disease, blue smoke appears from the exhaust pipe, which is formed due to incomplete combustion of diesel fuel. This happens because the gap between the components increases, which causes the formation of low pressure in the combustion chamber.
What is the compression of diesel engines?
The compression ratio in diesel engines is significantly higher than in gasoline engines, since the ignition of the fuel mixture in diesel units occurs not from a spark, but from compression under high pressure. The fuel is heated to its ignition temperature at a pressure of about 35 kg/cm2. Naturally, the final pressure, which is sufficient to ignite diesel fuel, also depends on certain conditions such as the condition of the motor itself or the ambient temperature. However, we can conclude that as compression decreases as a result of piston wear, a diesel car becomes increasingly difficult to start.
Experts have determined the compression value of a diesel engine sufficient to start it under conditions of different external temperatures:
- 40 - the power unit starts at temperatures down to -35 degrees.
- 36 - the vehicle will start at temperatures down to -30 degrees.
- 32 - starts after a long period of parking at temperatures down to -25 degrees.
- 28 - the fuel will ignite after a long stay at -15 degrees.
- 25 - the engine starts without problems after a long stay in a warm environment at -15 degrees.
- 22-23 - a power unit that has not cooled down starts immediately; long-term parking is possible only in a garage at positive temperatures.
- less than 18 - even a warm engine will not start under any conditions.
Normal compression table for diesel cars
The values given below will be reliable when starting serviceable engines, in vehicles where all systems are working. If there are malfunctions, these indicators may not correspond to reality.
Compression values for diesel engines of some car models:
- Kamaz EURO-0 - compression 29-35 kg/cm2.
- Kamaz EURO-1 - compression 29-35 kg/cm2.
- Kamaz EURO-2 - compression 29-35 kg/cm2.
- Kamaz EURO-3 - compression 32-37 kg/cm2.
- Kamaz EURO-4 - compression 32-39 kg/cm2.
- YaMZ 236 - compression 33-38 kg/cm2.
- YaMZ 236 Turbo - compression 33-38 kg/cm2.
- YaMZ 238 - compression 33-38 kg/cm2.
- YaMZ 238 Turbo - compression 33-38 kg/cm2.
- YaMZ 240 - compression 33-38 kg/cm2.
- YaMZ 240 Turbo - compression 33-38 kg/cm2.
- D240-245 (MTZ80-82) - compression 24-32 kg/cm2.
- MAN F90/2000 - compression 30-38 kg/cm2.