How does Multi Point Injection correspond to modern times?
A number of automakers in Europe and Asia believe that this type has no future, since the rapid development of technology will quickly leave behind the “new product”. This is partly true. Only the Volkswagen concern and its structural divisions, including Škoda, actively develop and support MPI. Business card: engines with volumes of 1.3, 1.4 and 1.6 liters.
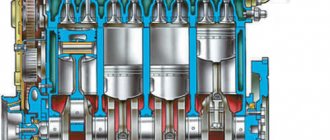
The main feature of the power unit is the absence of any turbocharged supercharger. The design is simple and intuitive:
- a gasoline pump that supplies the combustible mixture to the intake manifold under high pressure. Operating indicator three atmospheres;
- Through the injector inlet valve, fuel enters the cylinder, where ignition occurs and exhaust gases are removed.
Multi Point Injection is equipped with a water cooling circuit for the combustible mixture. It sounds unusual, it’s hard to imagine, but the system works successfully. The presence of a non-standard design is explained by the fact that there is an increased temperature above the cylinder head, and the fuel is supplied under low pressure. The consequences are negative, the risk of boiling, the formation of a gas-air plug. Without a third-party cooler, the operation of the power unit is impossible.
Advantages of MPI
- simplicity of design. Obviously, such engines are simpler than power units equipped with TSI with turbochargers, but not of the carburetor type. Owners carry out a number of repairs on their own, without resorting to the help of service station specialists. Clear savings on monthly maintenance;
- loyal attitude of the system to fuel quality. In relation to the CIS countries, where fuel is not always “good”, this option is acceptable. The power unit runs quite comfortably on AI-92 gasoline;
- The average service life before major overhaul is 300,000 km. These figures are provided by the manufacturer. In practice, the resource is 50,000 km less. Few people take into account the factor of timely replacement of engine oil, cleaning elements, and refueling with high-quality fuel;
- minimal risks associated with overheating;
- possibility of mechanical adjustment of the ignition timing;
- the design provides for the presence of rubber supports above the engine. This allows you to dampen vibrations during operation.
Disadvantages of MPI
- increased fuel consumption. The factor is quite controversial; it can be interpreted in different ways. In comparison, it is increased by 7%. This scares and repels many potential buyers;
- low torque, and as a consequence average power factor. The fuel mixture is mixed directly in the intake ports, not in the cylinders. This is atypical for most designs and causes confusion among TSI designers.
Cars with pre-installed MPI are not considered frisky, fast, or active. Rather an average level for connoisseurs of leisurely drive and family vacations.
Sales statistics for the CIS and the Russian Federation, among other things, show that for owners the priority indicator remains power rather than practicality.
Characteristic symptoms of MPI malfunction
- reduction in power while driving;
- increased fuel consumption;
- the indicator on the central instrument panel indicates that there is a “Check Engine” malfunction;
- the exhaust pipe comes out in blue, white or black. At the same time, this indicates a faulty injector and fuel equipment;
- unstable operation at idle speed;
- difficult cold start;
- increased operating sound, vibration.
Frequent causes of breakdowns
- violation or disregard of technical inspection deadlines;
- third-party technical (mechanical) damage, accidents, collisions, impacts;
- installation of non-original parts, components, consumables;
- refueling with low-quality fuel with a high content of chemical impurities;
- violation of the rules for using a machine or power unit;
- inconsistency of temperature conditions, oil viscosity indices;
- systematic loads above normal.
Advantages
The MPI engine is distinguished by its unpretentiousness in fuel quality and can operate on 92-octane gasoline.
By its design, this engine is very durable, and its shortest mileage without any repair work, as the manufacturer informs, is 300 thousand km, of course, if the oils and filters are changed on time.
Thanks to its not very complex design, the MPI engine can be easily and inexpensively repaired in the event of a breakdown, and in general this is noticeably reflected in its price. The conventional design sets it apart from the TSI, which has a high-pressure pump and a turbocharger device. The MPI engine is also less likely to overheat.
Another advantage of the motor is the presence of rubber supports located directly under the engine. This significantly reduces noise and vibration while moving.
Difference between TSI and MPI
(double supercharging with stratified injection) - this is the abbreviation TSI. This interpretation was given by Volkswagen engineers at the initial stage. Afterwards, it was renamed Turbo Stratified Injection. Now many concerns use the abbreviation, only with the addition of a few letters to distinguish it.
Differences between the two types:
- TSI has a standard inflation system. The engine can have two superchargers at the same time: a turbocharged compressor and a mechanical type;
- MPI does not have superchargers; they are not provided for by the design. When it comes to MPI, we mean naturally aspirated power units;
- TSI puts forward a number of requirements for engine oil, viscosity coefficient, replacement frequency;
- In TSI, fuel is injected directly into the cylinder cavity. For this purpose, a specially shaped head, pistons, and fuel injectors are made;
- In MPI, fuel initially enters the intake manifold, and then into the cylinder when the valves open. For this design, the presence of a gasoline pump is not at all necessary, since the standard pressure is sufficient to supply fuel.
If breakdowns occur, repairing MPI will cost several times less than TSI. This factor has significant power; for many potential owners it is fundamental.
MPI engine means a fuel injection engine that uses a multi-point fuel injection system. She gave the name to this power unit - Multi Point Injection. In other words, each has its own injector (nozzle). This scheme was developed and implemented by the Volkswagen concern. Historically, for the Wolfsburg automakers, the MPI system was the first fuel injection system. Now this type of unit no longer meets modern economic and environmental requirements for automobile engines. Until recently, it could be said that this type of engine was discontinued and the last car model of the concern where it was used was the second series. But suddenly there was a revival of the MPI engine, and it became in demand again! Let's keep the intrigue and tell you about it at the end of the article. Now let’s say that the most prominent representatives of this family of engines in recent years have been the 1.4 (80 hp) and 1.6 liter (105 hp) power units.
Feature of the MPI engine in a multipoint injection system
New naturally aspirated 1.6 MPI as an alternative to TSI: test drive and disassembly
We have good news for those who want to buy a new Octavia, Yeti or Golf, but are afraid of TSI engines. This year, a new 1.6 CWVA naturally aspirated petrol engine came out of the VAG forge. You can buy Skoda Octavia and Volkswagen Golf in Belarus with it today. By the way, at a very reasonable price. But what is the new 1.6 MPI and how does it drive? Yuri Gladchuk understood this.
The letter designation of the new product is CWVA. Installed (and will be installed) on some VAG models for all markets except European countries. Belarusians now have access to Octavia and Golf with this engine. Next year there will also be a Skoda Yeti.
The new engine should not be confused with Polosedan’s 1.6 MPI (CFNA). The statement that it is based on BSE, which was once famous for its reliability, is also incorrect. These are completely different power units.
EA211 instead of EA111
First, let's look at the VAG engine lines.
New motors of the EA211 series (which includes CWVA) replaced the EA111. The latter have been produced since 2005, the series includes both naturally aspirated and turbocharged engines. In our country, the most widespread of them are 1.2 and 1.4 TSI. We recently wrote about them - provided they are properly maintained, there is no need to be afraid of these engines. The main attention should be paid to the timing chain drive. What about the new engines?
In 2013, the EA111 was replaced by a new Volkswagen series of gasoline compact cars, the EA211. The range of VAG engines includes larger 1.8 and 2.0 TSI engines - they have also been updated and are representatives of the third generation of the EA888 series. The EA211 line includes TSI engines (turbocharged gasoline engines with direct fuel injection), TGI (turbocharged engines with direct injection for running on both gasoline and gas fuels) and MPI (atmospheric gasoline engines with intake manifold injection). The working volume of power units is 1.0, 1.2, 1.4 and 1.6 liters, power is from 60 to 150 hp.
MPI engine in detail
We have already mentioned the first and main distinguishing feature of these power units - multi-point fuel supply. But those who are more familiar with car engines can say that, for example, TSI engines also have multipoint injection. Therefore, we move on to the second difference - the lack of supercharging. That is, there are no turbochargers for pumping the fuel mixture into the cylinders. Conventional, which supplies fuel at a trivial pressure of 3 atmospheres to a special intake manifold, where it is then mixed with air and sucked through the intake valve into the cylinder. As you can see, at this moment it is very similar to the operation of a carburetor engine. There is no trace of direct fuel injection into the cylinder, as in TSI or GDi schemes.
The third distinctive feature is the presence of a water cooling system for the fuel mixture. This is explained by the fact that rather high temperatures develop in the area of the cylinder head, and the fuel enters under relatively low pressure. Therefore, it can simply boil and form gas-air plugs.
Operating principle of the MPI power plant
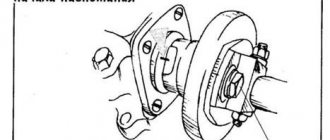
First, it is necessary to explain to ignorant readers that the abbreviation MPI stands for an internal combustion engine, each cylinder of which has a separate injector. The name MPI DOHC is much more common. Here the second part of the name indicates two camshafts with four valves.
The operating principle of the basic mechanisms that make the MPI engine function is quite simple. However, it deserves separate consideration.
Fuel is supplied simultaneously from several points. As mentioned earlier, each cylinder has a separate injector, and a special exhaust port is designed to supply fuel. Multi-point fuel supply is also typical for the TSI engine, however, it is distinguished by the presence of supercharging, which is absent in the engine in question.
A special intake manifold is an intermediate link, where fuel is supplied under a pressure of three atmospheres by a special pump. A mixture of gasoline and air is formed in it, after which it enters the cylinders through the intake valve. The entire process is carried out at elevated pressure.
Briefly, the operation of the engine can be described in three stages:
- First, fuel from the gas tank is delivered to the injector by a pump;
- After receiving a certain signal from the electronic control unit, the injector directs fuel into a special channel;
- In this direction, the fuel mixture is delivered to the combustion chamber.
Some similarity of the operating principle with a carburetor unit is offset by the presence of a liquid cooling system. This need is explained by excessive overheating of the space near the cylinder head.
A strong increase in temperature can cause the fuel, which is under low pressure, to boil. The gases released during this process can form unwanted gas-air plugs.
Another distinctive feature of the MPI engine is the presence of a specific hydraulic drive control mechanism, consisting of a clutch equipped with a grease nipple and a special system that sets certain limits for trim.
It is usually represented by rubber supports, the distinctive feature of which is the ability to independently adapt to the operating mode of the power unit. Their main purpose is to reduce noise and vibration during engine operation.
The design of the engine with the MPI index also includes eight valves, located in pairs on each of the four cylinders. An important part of such an engine is the camshaft, which is considered an essential part of the system.
Advantages and disadvantages of MPI engines
Advantages
First, about the advantages, and they are so significant that even now many people enjoy using cars with such engines. Especially in our country, where the requirements for environmental friendliness are not as stringent as in Europe (a vivid example of which is the presence of mercilessly burning “kopecks” and other domestic and foreign antique movables). And the cost of fuel is still not as high as for Europeans.
- Simplicity of design. Of course, this is not a carburetor, but neither is it a TSI with its high-pressure pump and turbocharger. And the simplicity of the design automatically means that the unit itself and its possible repairs are affordable.
- Lower requirements for . The MPI engine performs quite well on 92 gasoline. Try pouring it, for example, into a modern Volkswagen Passat. This kind of omnivorousness, by the way, somewhat neutralizes one of the disadvantages of such engines (more about them below) - lower efficiency.
- Less prone to overheating.
MPI engines have no special requirements for fuel quality
Another advantage, although not directly related to
The scheme of the injection power unit under consideration is the presence of rubber supports under the engine. This significantly reduces noise and vibration when driving.
Flaws
- Less economical. It's nothing you can do. Multipoint injection is, of course, good, but supercharging together with direct injection of fuel into the cylinder (like TSI systems) is better.
- Weak torque and lack of power. Still, the capabilities of the circuit, which provides for the connection of air with gasoline in the manifold, and not in the cylinder, are somewhat limited. So for fans of drive and racing at traffic lights, the MPI engine is not suitable. Too sluggish.
And yet, if we sum up the advantages and disadvantages, the final result makes these power units quite competitive, especially for our domestic realities. It is no coincidence that the Russian Germans abandoned the turbocharged 1.2-liter TSI engine, preferring the proven and unpretentious 1.6-liter MPI horse.
The Russian version of Skoda Yeti has an MPI engine
Now, we think it will be clear what an MPI engine is. If you have any questions about this article, please ask. We will definitely answer.
The MPI distributed (multipoint) fuel injection system is used only on gasoline engines and is the most popular in the world. In this system, each cylinder is equipped with an individual injector that injects fuel directly in front of the intake valve. Multipoint injection ideally meets high environmental standards, as well as the requirements for mixture formation in modern engines.
Pros and benefits of MPI
Compatriots who have already been lucky enough to get to know MPI engines better, before switching to a car with a different engine, will probably think carefully about whether they can get a set of those advantages thanks to which power plants with multipoint injection have won worldwide recognition:
- Simple device
. It cannot be said that it is simpler than that of carburetor models, but in comparison with TSI engines equipped with injection pumps and turbochargers, the superiority is obvious, which is expressed in the cost of the car, not so significant operating costs and the ability to carry out many types of repairs yourself. - Moderate demands on the quality of fuels and lubricants.
This is especially important for Russia, since it is impossible to guarantee the availability of high-quality gasoline and oils always and everywhere. MPI engines are quite unpretentious and perform well when using low-octane gasoline no lower than 92. - Reliability.
According to the developers, the minimum mileage without breakdowns for a car with MPI is at least 300 thousand km, but only on the condition that the oil and filters are replaced on time. - Low chance of overheating.
- Adjusting the ignition timing.
- Availability of engine support system.
It is based on the use of rubber supports. And although this is not directly related to the design of the engine, it still affects its “health” and the comfort of the owner, since the supports effectively dampen noise and vibrations that occur during movement. An interesting fact is that the adjustment of the supports to the operation of the motor is carried out automatically.
The basic operating principle of the MPI system
The designation MPI stands for Multi-point injection, which means “multipoint injection”. This marking is most often found on European cars.
Multipoint injection system design
It consists of the following elements:
- throttle valve;
- distribution line or fuel rail;
- (injectors);
- mass air flow sensor or air pressure and temperature sensor;
- fuel pressure control.
Distributed injection scheme
In such a power system, air from the atmosphere passes through the air filter, and then enters the intake manifold through the throttle valve. It is then distributed through the cylinder channels.
In turn, fuel is supplied by a pump through a ramp to the injectors. The latter are located near the intake valves of the cylinders, which reduces fuel losses and the likelihood of fuel settling in the intake manifold. The operation of the injectors is controlled by the engine ECU. The control unit calculates the amount of fuel that should flow through the injectors based on information about the modes, load and engine speed, as well as on information about the amount of air entering the system received from a whole set of sensors (temperature, pressure). In accordance with the calculations, the ECU sends pulse signals to the electromagnetic injectors, causing them to operate.
In addition to controlling the operating modes of the injectors, the control unit regularly diagnoses the state of the injection system and, if faults are detected, issues a corresponding error signal on the dashboard (“Check Engine”).
MPI operating modes
Depending on the operating mode of the injectors, several types of systems are distinguished:
- Simultaneous injection. In such a system, all injectors open simultaneously, supplying fuel to each cylinder. This scheme is an improved mono-injection, since the ECU controls the process of opening and closing all injectors as if it were opening one. On the other hand, the amount of fuel supplied to each individual cylinder may be different.
- Pair injection. The opening of the electromagnetic injectors occurs in pairs, but one operates on the intake stroke, and the second at the moment. Currently, this scheme is used only at the stage of starting the engine or in emergency mode.
- Individual injection. This is the most commonly used design, in which each injector is fired individually on the intake stroke. To ensure their operation, the system is equipped with a valve timing sensor. It is installed on the camshaft and determines the firing time of each injector depending on the position of the shaft. Fuel is injected into each cylinder once per engine operating cycle. The classic sequence of injectors is: 1-3-4-2.
MPI messages
MPI messages consist of two main parts: the data sent/received, and accompanying information (envelope entries) that help send the data along a specific route. Typically there are three callable parameters in MPI message passing calls that describe the data and three other parameters that specify the route:
Message = data (3 parameters) + shell (3 parameters)
| start buffer, number, data type | target, tag, communicator |
| DATA | SHELL |
Each parameter in the data and envelope will be discussed in more detail below, including information about when these parameters should be coordinated between sender and recipient.
3.1 Data
The buffer
in MPI calls is the location in computer memory from which messages are to be sent or where they are stored. In this sense, a buffer is simply memory that the compiler has allocated to a variable (often an array) in your program. The following three MPI call parameters are required to define the buffer:
Start buffer
The address where the data begins. For example, the beginning of an array in your program.
number
The number of data elements (points) in the message. Note that these are elements, not bytes. This is done to make the code portable because there is no need to worry about different data type representations on different computers. The MPI software implementation determines the number of bytes automatically. The number specified upon receipt must be greater than or equal to the number specified upon sending. If more data is sent than is available in the receiving buffer storage, an error will occur.
Data type
The type of data that will be transmitted is floating point, for example. This data type must be the same for send and receive calls. The exception to this rule is the MPI_PACKED data type, which is one way to handle mixed data type messages (the preferred method is the derived data type method). Type checking is not needed in this case. The data types already defined for you are called "basic data types" and are listed below
basic MPI data types for C
MPI data types C data types MPI_CHAR signed char MPI_SHORT signed short int MPI_INT signed int MPI_LONG signed long int MPI_UNSIGNED_CHAR unsigned char MPI_UNSIGNED_SHORT unsigned short int MPI_UNSIGNED unsigned int MPI_UNSIGNED_LONG unsigned long int MPI_FLOAT float MPI_DOUBLE double MPI_LONG_DOUBLE long double MPI_BYTE MPI_PACKED
Derived data types
Additional data types can also be defined, called derived data types.
. You can define a data type for non-contiguous data or for a sequence of mixed underlying data types. This can make programming easier and often results in faster code execution. Derived data types are beyond the scope of this introduction, but are covered in the Derived Data Types module.
Some derived data types:
- Contiguous
- Vector
- Hvector
- Indexed
- Hindexed
- Struct
3.2 Shell (envelope)
Recall that a message consists of data and a message envelope (envelope). The shell provides information about how shipments are related to receipts. Three parameters are used to define the envelope of the message:
Destination or source
This argument is set to the rank in the communicator (see below). The rank ranges from 0 to (size-1), where size is the number of processes in the communicator. The destination is determined by the dispatch and is used to determine the route of the message to the appropriate process. The source is determined by the receipt. Only messages coming from this source can be accepted when calling receive, but receive can set the source to MPI_ANY_SOURCE to indicate that any source is acceptable.
Tag
Tag (shortcut, label) is an arbitrary number that helps distinguish messages. The tags specified by the sender and the recipient must match, but the recipient may define it as MPI_ANY_TAG to indicate that either tag is acceptable.
Communicator
The communicator specified on send must equal the communicator specified on receive. Communicators will be discussed in more depth later in this module. For now it will be sufficient to know that a communicator defines a communication "universe" and that processes can belong to more than one communicator. In this module we will only deal with the predefined communicator MPI_COMM_WORLD, which includes all application processes.
Analogy
To more easily understand the parameters of the message environment, consider an analogy with an agency issuing claims (payment requests - receipts) for several needs. When sending a claim, the agency must indicate:
- The person receiving the claim (more specifically, its identification number). This is the purpose.
- What month does this claim cover? Since a person will receive twelve claims a year, he needs to know for which month this claim is coming. This is a tag (label, label).
- For what need is the claim issued? The person needs to know whether the lawsuit is for electricity or for telephone. This is a communicator.
MPI System Differences
Many people confuse MPI with distributed injection in general, which also includes a direct injection system (FSI, DISI, TSI), in which fuel is supplied directly to each cylinder. This is an important difference, since Multi-point injection involves the formation of an air-fuel mixture in the intake manifold channels in front of the intake valves.
In addition, engines with multipoint distributed injection are naturally aspirated, without the use of supercharging. This means that such engines have less stringent requirements for fuel quality.
Advantages and disadvantages of multi-point injection
Fuel rail of the distributed injection system
The main advantages of the distributed (multipoint) injection system are more economical fuel consumption and compliance with environmental standards in comparison with single injection or carburetor. On the other hand, the MPI engine is less powerful than engines with direct fuel supply to the engine cylinders. At the same time, in comparison with systems with direct injection, it is less expensive to maintain.
The disadvantages of distributed injection include the complexity of manufacturing, and, as a result, high cost. This also applies to repairs of the electronic system and injectors. Maintenance and diagnostics require specialized equipment and highly qualified specialists.
For domestic conditions, multipoint distributed injection systems are considered the most optimal in terms of cost and ease of maintenance, as well as in terms of the level of power received and operating comfort.
Few car owners know what an MPI engine is. This abbreviation stands for Multi-Point-Injection, and the engine itself is a design with a multi-point fuel injection system. To summarize the data, the peculiarity of such a motor is that each cylinder of the power plant receives its own injector nozzle. This technology was invented and implemented
Summarizing
The departure of engines from the world market with the MPI system is significantly influenced by all of the above indicators. Nowadays, many car enthusiasts prefer more powerful modern cars, the pace of which is steadily increasing.
The need to equip vehicles with more powerful units significantly underestimates the demand factor for Multi Point Injection engines. Compared to them, this motor is rather weak. But it’s still too early to completely write off the MPI engine, since the Skoda Yeti developers are trying to use it to its fullest on Russian roads.
MPI engines are gradually becoming a thing of the past, so it is increasingly rare to meet a car enthusiast who understands what they are talking about when they call this abbreviation. Those who have changed many cars or are interested in cars in general know about it.
Having replaced carburetor engines, becoming the next step in the development of the automotive industry, this type of engine is now giving way to advanced developments. Today, many people think in advance which engine should be installed in a personal car: TSI, FSI or MPI. Although many experts still consider the latter to be the most practical, reliable and trouble-free in the family of injection engines.
FSI is considered a more modern development, the next step after MPI. The BSE engine appeared in 2005 and is famous for its ability to withstand low quality domestic fuel.
Did you know?
The abbreviation MPI comes from the term Multi Point Injection, which means multi-point fuel injection.
The motor was actively used by the Volkswagen concern. It was gradually introduced at the Skoda subsidiary. The engines were installed there for the last time - on the Yeti and Octavia models. It should also be explained what MPI and TSI are. If the first term implies an internal combustion engine in which each cylinder has its own injector, then TSI has different interpretations.
So, initially the abbreviation meant double supercharging and stratified injection: Twincharged Stratified Injection. But recently, the abbreviation TFSI has become increasingly used, in which the additional letter F stands for Fuel.
You can often find another abbreviated name for the engine - MPI DOHC, what this means is easy to understand if you know that the term DOHC refers to engines that have 2 camshafts and 4 valves in the cylinder head.
Where is it implemented?
Now you understand a little about what an MPI engine is. For the first time, such technology was successfully introduced into the Polo model. Later, the Golf and Jetta also received such engines.
Note that such engines are outdated from the engine range. However, they are practical and trouble-free. Many experts argue that today such power plants do not meet modern standards of efficiency and ecology. In addition, quite recently one could say that the manufacturer stopped producing such motors. The last car to receive an MPI engine is the Skoda Octavia of the second series.
However, the technology has recently been revived and has become in demand. In the fall of 2020, the concern launched a production line for these engines at the Kaluga plant, where they began producing motors of the EA211 series.
Peculiarities
What features they have have already been written above. These are engines with a multi-point gasoline supply system. However, those in the know can tell you that TSI engines also use a multi-point fuel delivery system. Therefore, in this case it is appropriate to talk about other distinctive features - there is no supercharging in the MPI engines of Skoda and Volkswagen. This means that there are no turbochargers that would pump the fuel mixture into the engine cylinders. It uses the most ordinary gasoline pump, which pumps gasoline from the tank to the start manifold, creating a pressure of only 3 atmospheres. In the manifold, fuel is mixed with air and drawn into the combustion chamber through the intake valve. Actually, the system is very similar to the principle of operation of a carburetor, and there is no direct injection of fuel into the cylinders (as in FSI, TSI and GDi engines).
Now you have a better idea of what MPI engines are. It is appropriate to answer the second feature - the presence of a water cooling system. Thanks to it, the fuel is cooled. This is necessary due to the increased temperature conditions near the cylinder head. Since the temperature is high there and the fuel is supplied under low pressure, there is a possibility that the fuel mixture may boil, which will lead to the formation of gas air locks.
Advantages
MPI engines boast unpretentiousness to the fuel used and operate efficiently on 92-octane gasoline. Also, the design of such an engine is very durable, and its mileage without any intervention or repair averages 300 thousand kilometers. Of course, it is necessary to change filters and oil on time. The 1.6 MPI (and other car models) is characterized by a simple design, and in case of any breakdown it can be inexpensively repaired at a service station. In this case, the design feature of such engines compares favorably with more complex TSI engines with high-pressure pumps and turbochargers. MPI motors also overheat less.
The last more or less relevant plus is the rubber supports located under the engine. They help reduce noise and vibration while driving.
Interface operation
The basic mechanism of communication between MPI processes is the transmission and reception of messages. The message contains transmitted data and information that allows the receiving party to selectively receive them:
- sender — rank (number in group) of the message sender;
- recipient - recipient's rank;
- attribute - can be used to separate different types of messages;
- communicator - process group code.
Reception and transmission operations can be blocking or non-blocking. For non-blocking operations, functions are defined for checking readiness and waiting for the operation to complete.
Another method of communication is remote memory access (RMA), which allows the memory region of a remote process to be read and modified. A local process can transfer the memory area of a remote process (within a window specified by the processes) into its memory and back, and also combine data transferred to the remote process with data available in its memory (for example, by summing). All remote memory access operations are non-blocking; however, blocking synchronization functions must be called before and after their execution.
Minuses
If you believe the reviews, MPI engines are less dynamic, and there is an explanation for this. Due to the fact that gasoline is mixed with air in the exhaust ports (before it is supplied to the cylinders), these engines are limited. Also, the eight-valve system with a timing belt makes it clear that the engine lacks power. Therefore, such engines are not designed for quick start and acceleration.
The second disadvantage is that it is uneconomical. Multipoint injection is inferior in efficiency and economy to supercharging with direct fuel injection into the cylinders. As mentioned above, this technology is implemented in TSI engines.
MPI engine - a solution for Russian roads
In addition, cars with such engines are better suited for Russian operating conditions. The fact is that the quality of fuel sold at some gas stations leaves much to be desired. However, for MPI engines, even gasoline with a higher sulfur content is easily accepted, and the engine processes this type of fuel perfectly. And the robust design of the power plant itself provides additional reliability and protection from excessive mechanical loads that occur when driving on bad roads with potholes. So it’s fair to say that MPI engines are better suited for Russia. Perhaps because of this, a production line for the production of such engines was established at the Kaluga plant. Now we have finally figured out what an MPI engine is and what its features, advantages, and disadvantages are.
Principle of operation.
This type of engine (translated as multi-point injection) is a non-turbocharged engine that runs on gasoline and uses multi-point distributed injection of fuel passing through the injector during its operation. MPI does not have a fuel rail, like many other types of engine, and also does not have fuel injection into the cylinders themselves; only one injector is used for each cylinder separately.
This power unit has its own individual fuel injection structure. It can be roughly expressed as follows: there is one injector per individual cylinder, the fuel supply is carried out through a specially made exhaust channel.
MPI is also equipped with an ignition advance function, which ensures increased sensitivity of the gas pedal. The structure of this engine is unthinkable without cooling the fuel mixture (MerCruiser) with water, thereby achieving the required temperature of the fuel mixture. This helps to greatly increase the stability of the engine by getting rid of gas plugs (air).
This type of power unit is also equipped with a new system that independently controls the hydraulic drive. There is a clutch with a grease nipple, a system that allows you to limit trim and has memory (its basis is rubber supports that independently adjust to the operating mode of the engine, thereby significantly reducing vibration and noise during operation).
The engine has a system of eight valves (two valves per cylinder) and a camshaft. The most prominent representatives in this family of engines are considered to be the MPI 1.6 engine (105 hp) and the MPI 1.4 liter engine (80 hp).
Advantages and disadvantages of MPI motors
First of all, it should be noted the undeniable advantages of the design of the unit in question, namely:
- The presence of an ignition advance function in the power plant device helps to increase the sensitivity of the throttle located on the gas pedal. This significantly expands the possibilities of driving;
- Water cooling of the gasoline-air mixture allows you to maintain an acceptable temperature in the engine, protecting against the formation of gas-air plugs;
- A progressive system that controls the hydraulic drive makes it possible to significantly reduce the noise and vibrations produced by a functioning motor.
Other advantages of power units labeled MPI include the following:
- Unpretentiousness to fuel quality. For domestic motorists, the opportunity to use inexpensive AI-92 gasoline is especially attractive, which results in significant savings at the gas station;
- Reliability and strength of the structure. The manufacturer declared a minimum service life of 300 thousand km. However, trouble-free engine operation is impossible without periodic replacement of lubricant and filters;
- The extreme simplicity of the power unit design is reflected in the cost and complexity of repairs.
One cannot do without a fly in the ointment, which somewhat detracts from the listed advantages of the MPI motor. In our case, a significant drawback of such engines is the loss of power that occurs due to the limitations of the intake system. However, although the units in question lose their dynamism due to the presence of eight valves in the timing mechanism, a measured, quiet ride is ensured with their help.
Flaws.
Due to the fact that the process of mixing fuel occurs in special exhaust channels (before it enters the cylinders), such engines have limited capacity in the intake system. And this, in turn, affects torque and power performance. Also, they cannot be called daring and “dynamic”. The presence of an 8-valve system with a timing belt also indicates significant losses in power. In general, they are designed for slow, leisurely driving.
Due to its structure, which is relatively old, MPI is slowly being taken out of mass production. The latest car models equipped with this power unit were the second generation Scoda Octavia. At the same time, the third generation has already been equipped with more advanced and modern engines.
MPI's place in the hierarchy of parallel programming tools
Creating a parallel program includes two main stages:
- the sequential algorithm is subject to decomposition (parallelization), i.e. splits into independently working branches; For interaction in the branch, two additional non-mathematical operations are introduced: receiving and transmitting data.
a parallelized algorithm is written as a program in which receive and transmit operations are written in terms of a specific communication system between branches.
The communication system, in turn, includes two components: software and hardware.
For the purposes of this document, we will take the hardware as a given, without analyzing how it will develop in the future, which type is better and which is worse, and why. From the point of view of a programmer, there are two basic working methods (or, as they say today, paradigms) - data can be transferred:
- through shared memory, synchronization of access of branches to such memory occurs through semaphores,
- in the form of messages.
The first method is basic for SMP machines, the second is for networks of all types. However, in principle one can be simulated through the other:
- shared memory on non-SMP complexes - by organizing a single virtual address space on physical RAM isolated from each other; such hardware
is often used on NUMA machines; - on an SMP machine, shared memory serves as a degenerate communication channel for transmitting messages.
Therefore, a single programmer interface can
be created, nevertheless, for a long time the creators of computers and operating systems followed different paths. For example, to work with semaphores and shared memory in Windows, in Unix 4.4BSD and SVR4 approximately the same actions are represented by different sets of system calls. In the world of local/global networks, a standard seems to have been developed - this is TCP/IP. However, to work with intramachine networks, where the composition of subscribers and traffic routing are strictly fixed, and the probability of packet delivery is 100%, the versatility and flexibility of TCP/IP negatively affect the speed, therefore, for MPP machines, programmer interfaces are created individually (or rather, they were created individually until MPI appeared).
Thus, we can consider the need for a programmer interface standard that would make the creation of parallel applications the same:
- mobile,
- effective,
- reliable,
... how C and Unix made programming in general. It was decided to make MPI the standard of choice for the main computer manufacturers. They formed the MPI Forum, and a specification was released that all specific developments must meet. The project's parent organization, Argonne National Laboratory, USA, distributes the MPICH
(MPI CHameleon), which has been ported to most platforms. Most MPI implementations created by other developers are based on MPICH. In theory, the resulting hierarchy of development tools should look something like this:
| Parallel application | ||
| Rapid Application Development (RAD) Tools Parallelizing Preprocessors | ||
| MPI | ||
| shared memory and semaphores | individual interfaces with message passing | TCP/IP |
| SMP machines | MPP machines | networks |