Automatic transmission, what is it?
The hydromechanical transmission has a lot of advantages, the main one being comfort when dosing torque to the drive wheels. However, it also has a number of disadvantages: the complexity of the design, low efficiency and high cost. Also, the automatic transmission cannot boast of long service life and reliability. But the popularity of automatic machines is growing and the number of cars even in the budget segment looks convincing.
The automatic transmission, the operating principle of which we will consider today, appeared on production cars in the late 50s of the last century. The first automatic transmission had only three stages, and its design is in many ways similar to modern hydromechanical units. Today they produce automatic transmissions with 7-9 shift ranges, but many do not fully understand that any automatic transmission consists of three main devices:
- Hydraulic clutch or torque converter.
- Manual transmission.
- Automatic transmission control system.
All this equipment is usually called hydromechanical automatic transmission. Before using an automatic transmission, it would be useful to at least briefly learn how it works.
Automatic transmission design
A standard automatic transmission consists of the following main elements:
- torque converter;
- planetary reductor;
- clutches (friction and overrunning);
- drums;
- shafts.
Design and principle of operation of the torque converter
The torque converter is installed between the gearbox and the engine. The purpose of this element is to transmit torque when starting the car. At high speeds, this device is usually blocked by clutches located inside. Thanks to this, less fuel is consumed and slippage disappears.
Recommended article: Robotic gearbox (manual transmission) and its operation
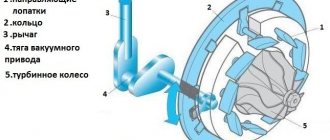
The design of the torque converter is as follows: three wheels: turbopump, stator, turbine. Usually the stator is stationary and connected to the automatic transmission housing. In some designs, the stator may not be attached, and its immobility will be ensured by special couplings. This braking allows for a wide range of speeds.
It is thanks to the use of a torque converter that there is no kinetic energy and, accordingly, the car moves smoothly and there is no load on the car’s transmission. The only downside is slippage, which generates additional heat and increases fuel consumption.
The operating principle of a torque converter is different from a fluid coupling. Its torques on the turbine and pump wheels are different. To save fuel, a rigid mount between the turbine and the pump was introduced into the device. This braking occurs when a higher speed is reached. When controlling an automatic transmission using a computer, the moment when blocking is necessary is selected by the control program.
This lock also allows you to have the same fuel consumption as a manual transmission. With its help, you can implement engine braking and also economical fuel consumption. In this mode, fuel injection stops, but only when the torque converter elements are blocked.
Planetary gearbox and its operation
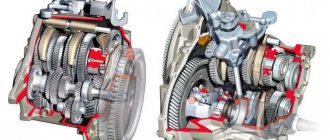
The automatic transmission includes a mechanical transmission. It is necessary for the vehicle to move in reverse, which is carried out using a stepwise change in torque. The planetary gearbox used in the design of the automatic transmission has compact dimensions and coaxial operation. Usually there are several of them in automatic transmissions. They are connected in series to each other. Thus, their joint work is realized.
Thanks to this design, the mechanical component of the automatic transmission is provided with the required number of stages. Modern car models have from 6 to 8 stages, and there are also 9-speed ones. The planetary gearbox in the box is called a planetary gearset.
Recommended article: The braking system in a car is a must
How does a torque converter work?
The torque converter is similar in function to the clutch in manual transmissions. Its main task is to transmit and change torque from the engine crankshaft to the input shaft of the manual transmission. It also serves to dampen torsional vibrations. The torque converter is a completely autonomous unit. It is placed in its own crankcase and consists of pump, turbine and reactor wheels. It also requires a lock-up clutch and a freewheel to operate.
The engine crankshaft flange is rigidly connected to the pump turbine, and the turbine wheel is rigidly connected to the input shaft of the mechanical part. A reactor wheel is located motionless between them. Each of the wheels has specially shaped blades to interact with the working fluid, transmission oil. The lock-up clutch locks the torque converter wheels in optimal operating conditions, and the freewheel makes the reactor wheel move in the opposite direction under certain conditions.
Scheme of operation of a hydromechanical transmission
In order for the torque converter to deliver pure torque to the mechanical part, that is, to be blocked, it is necessary that the angular velocities of the first and last wheels equalize, then the central, reactor wheel begins to rotate in the opposite direction. The torque converter is locked under the influence of the kinetic energy of the working fluid, which acts on the blades of all three wheels. The torque converter locks up in each gear.
All modern automatic transmissions include a slipper torque converter lock-up clutch. This makes shifting gears on the go and starting off smooth and comfortable. The slipper clutch engages at a certain load or at a certain speed, which contributes not only to comfort, but also to fuel economy.
A car with an automatic transmission: advantages and disadvantages
Let's start with the positives. Installing an automatic transmission allows the driver not to use the gear lever while driving, and the foot is also not used to constantly depress the clutch when changing to a higher or lower gear.
In other words, the speed change occurs automatically, that is, the box itself takes into account the load on the internal combustion engine, the speed of the vehicle, the position of the gas pedal, the driver’s desire to accelerate sharply or move smoothly, etc.
As a result, the comfort of driving a car with automatic transmission increases significantly, gears are switched automatically, softly and smoothly, the engine, transmission elements and chassis are protected from heavy loads. Moreover, many automatic transmissions provide the possibility of not only automatic, but also manual gear shifting.
As for the disadvantages, they also exist. First of all, structurally, an automatic transmission is a complex and expensive unit, characterized by reduced maintainability and service life compared to mechanical (manual) transmissions. A car with this type of gearbox consumes more fuel; an automatic transmission delivers less torque to the wheels, since the efficiency of the automatic transmission is slightly reduced.
Also, the presence of an automatic transmission in a car imposes certain restrictions on the driver. For example, an automatic transmission needs to be warmed up before driving; it is advisable to avoid constant sudden starts and too intense braking.
A car with an automatic transmission must not slip; it is not allowed to tow a car with an automatic transmission at high speed over long distances without hanging the drive wheels, etc. Let us also add that such a box is more difficult and expensive to maintain.
Planetary gearboxes
The mechanical part of the automatic transmission consists of two or three planetary gearboxes for rigidly changing the gear ratio and inverting torque. All gearboxes that operate in the box are connected to each other in series and the more of them, the more stages the box can have.
The principle of operation of a planetary gearbox is similar to the operation of a conventional manual gearbox, only the change in torque values does not occur due to the engagement of one gear with another, as is the case in a manual transmission, but by blocking one of the elements of the planetary gearbox, as shown in the figure.
Either the ring gear is blocked, then the gearbox works to increase the speed, or the carrier, then the gear will be reduced. If you fix the ring gear in relation to the carrier, the transmission will become direct. The clutch packs, which move under the action of the working fluid, are responsible for blocking the planetary gear elements. It is also distributed using the automatic transmission control system.
This is the design of the most common automatic transmission. However, they also include robotic gearboxes with two clutches. Robots work exactly on the same principle as manual transmissions, only the gears are switched using actuators. Such units have virtually nothing to do with hydromechanical automatic transmissions.
Study the operation of the machine, and it will reward you with reliability and ease of use. Good luck to everyone on the roads and comfortable switching!
CVT automatic transmission.
The main elements of the CVT gearbox are: • CVT transmission; • mechanism for reversing movement; • mechanism for switching to neutral position; • control system.
The variator transmission consists of 2 pulleys connected by a belt. Each of the pulleys consists of 2 conical disks, which, at the command of the control system under the influence of a special drive, can move or move apart. In this case, the diameter of the pulleys changes.
At low engine speeds, the drive pulley has a small diameter (conical disks are spread apart). The driven pulley at this moment has its maximum diameter (the disks are compressed). As the speed increases, the diameter of the driven pulley decreases, and the diameter of the driving pulley increases. This changes the gear ratio.
When driving, the variator maintains engine speed at which maximum power is realized. An increase or decrease in speed occurs by smoothly changing the diameters of the pulleys and gear ratios.
The main difference between an automatic transmission and a variator is the method of transmission of rotation. The hydromechanical and belt methods have little in common, but in both cases the driver only operates the gas pedal.
Operating principle of a variable speed transmission
In addition, a characteristic feature of the variator is smooth, stepless gear shifting. This provides the most complete implementation of the engine’s capabilities and, as a result, high efficiency.