Planetary reductor
,
differential gearbox
(from Latin differentia – difference, difference) is one of the classes of mechanical gearboxes. The gearbox is called planetary because of the planetary gear located in the gearbox that transmits and converts torque. A planetary gearbox may have one or more planetary gears.
Planetary gear in action. The driver is stopped.
Content
- 1 Design and principle of operation of a planetary gearbox
- 2 Application of planetary gearboxes 2.1 Universal planetary gearboxes
- 2.2 Planetary gearboxes in cargo winches
- 2.3 Planetary gearboxes in power tools
- 2.4 Planetary gearbox in drive axles and wheels
- 2.5 Planetary gearboxes in the gearbox
- 2.6 “Geared starter” of automobile engines
Design and principle of operation of a planetary gearbox
Planetary gearbox design.
- The sun gear
is in the center of the gearbox. - The ring gear (epicycle)
is on the periphery of the gearbox. - Satellites
are three small gears between the sun and crown gears. - Carrier
- not shown (mechanically connects all satellites); satellites rotate on carrier axes.
Depending on the kinematic diagram of the drive, rotation can be applied to any element of the gearbox and removed from any other. In this case, the third element must be inhibited. By changing the scheme for supplying and removing torque within the same planetary gear, you can obtain different gear ratios and directions of rotation. This feature is used in planetary gearboxes.
Stepped
Such gearboxes are usually made with gears. The number of pairs of gears can range from four or more. The greater the number of gear ratios of the box, the more efficiently the engine power is used. It is not customary to set it higher than eighth gear - drivers begin to get confused.
Stepped manual transmission.
As the weight of the car increases, the need for better distribution of engine power on different sections of the road and driving modes also increases. Sometimes even an 8-speed gearbox is not enough. To do this, an additional one is installed on the main gearbox - it is called a multiplier. Their overall work has a positive effect on the fuel and speed characteristics of the car. The box is switched using a special lever.
Step transmissions include all boxes with pairs of gears. For example, a manual transmission.
Strictly speaking, most transmissions are manual (manual). A manual transmission is more correctly called a manual gearbox. It just so happens that the name “mechanical” is already an established name.
A manual transmission has several shafts:
- leading, receiving torque from the clutch;
- the slave to whom this moment must be transferred;
- intermediate, with the help of which this moment is transmitted.
The structure of the box is similar to that of a conventional gearbox. There may be three or more shafts.
Diagram of a car gearbox.
On all shafts, gearbox gears are secured with keys, which mesh with gears on adjacent shafts. So, from the gear on one shaft, through the gearing, the moment passes from the drive shaft to the driven shaft. Additionally, a shaft with a reverse gear is installed inside the gearbox. It is often taken out separately.
Since the gearing cannot be connected at different gear speeds, their rotation must first be synchronized. For this purpose, box synchronizers were invented. The synchronizers are moved by a lever to the desired pair, come into contact with the rubbing surfaces, begin to rotate and transmit torque from the drive gear to the driven gear until the speeds are synchronized and are brought into engagement.
In addition to the classic design with fixed shafts, which is the most common, a stepped gearbox can have driven shafts rotating around the drive shaft. This type of gearbox is called planetary and is installed on some models of super-heavy trucks or forklifts.
Diagram of a classic gearbox design.
Application of planetary gearboxes
Universal planetary gearboxes
Industry around the world produces many standard series of planetary gearboxes and geared motors for use in drives of various general industrial mechanisms, for example, domestic 3MP [1]. One standard size provides various gear ratios from units to tens and hundreds. Advantages over conventional helical gearboxes are compactness, over worm gearboxes - greater durability and efficiency, depending on specific designs - ease of manufacture, up to certain gear ratios - lack of self-braking.
Planetary gearboxes in cargo winches
The use of a planetary gearbox in winches has additional advantages: the engine, compact gearbox and drum lie on the same geometric axis; you can build in a simple release mechanism to unwind the cable in a section with a small moment; good efficiency, lower lubrication requirements and predictable self-braking compared to worm gear. It is widely used in mounted automobile electric winches, hoists, and small stationary lifting mechanisms. At the same time, other types of gearboxes have their own advantages for winches: for worm ones, this is guaranteed self-braking and a small number of elements; for cylindrical ones - the absence of a massive rotating carrier, which simplifies the manufacture of mechanisms of very high power.
Planetary gearboxes in power tools
Screwdriver in disassembled form.
On the right you can see the satellites and the ring gear of the first stage of the gearbox. Common hand-held power tools with a low rotational speed of the working part (screwdrivers, impact wrenches, electric screwdrivers) are usually built using a multi-stage planetary gearbox. In addition to compactness with a large transmitted moment, small requirements for the strength and accuracy of the body of the tool itself, such a gearbox allows you to easily switch gear ratios (“speeds”) by mutually fixing the elements and limiting the torque on the working body — by fixing one of the ring gears with an adjustable ratchet.
In high-speed powerful tools (corded drills, chain saws, etc.), lubrication of the satellite axes with grease compounds added during assembly would be difficult; at the same time, the gearbox housing, subject to large dynamic loads, is initially made more durable. Therefore, instead of planetary gearboxes, they usually use conventional one- or two-stage helical gearboxes.
Planetary gearbox in drive axles and wheels
Trolleybus, planetary gearbox of the rear drive axle. The hole for filling transmission oil is indicated (closed with a screw plug).
Wheel reducer of the MAZ-7310 military vehicle.
The carrier with satellites has been removed. The drive axles of MAZ trucks, Ikarus buses, LiAZ of previous years, ZiU-9 trolleybuses, T-150K, K-700 tractors, heavy wheeled military and earth-moving vehicles use planetary gearboxes that transmit torque from the axle shaft to the wheel hub. . The use of a planetary gearbox in the final drive (spaced gear) allows you to reduce the diameter of the main gear and, therefore, increase ground clearance, or use a single-stage final drive instead of a two-stage one. At the same time, the axle shafts and differential are lighter, transmitting less torque.
At the same time, the use of planetary wheel gearboxes increases the unsprung masses and spreads them away from the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, introduces additional parts that require high manufacturing precision (at least 8 “extra” highly loaded gears in each axle and their bearings), and adds service points. In the case of spur gearboxes, the noise of a moving vehicle increases significantly, amplified by the resonances of an elastic and relatively thin wheel rim. The consequence of all this is a tendency to abandon such a design on modern mass-produced machines. Also, the abandonment of such structures leads to simplification in car repair and maintenance.[2]
Due to the convenience of their layout (axial symmetry, unloading of parallel-running gears, large gear ratios, compactness), planetary gearboxes have found application in electric and hydraulic wheel motors of transport vehicles and the chassis of special equipment. The gearbox makes it possible to pair a structurally optimal built-in motor with a large, slowly rotating wheel of a low-speed unit. Two-stage gearboxes are found in the wheel motors of mining dump trucks.
An electric bicycle with a low-power front wheel motor.
With the advent of relatively inexpensive and mass-produced electric bicycles, the requirement to reduce the cost of the motor-wheel design led to the use of a built-in planetary gearbox instead of installing rotor magnets directly on the hub. This solution increases static traction with less wheel weight, but causes additional noise and high-frequency vibrations transmitted to the frame. At the moment (2015), the majority of bicycle wheel motors up to 500 W are geared [3]. At higher power, the diameter of the motor in the hub and the rated current are large, and as a result, the available torque is already sufficient for a light device. In addition, creating a cheap gearbox for such power is already becoming problematic, and as the speed of a powerful bicycle increases (100 km/h and above [4]), vibrations from a high-speed large-diameter electric motor can exceed the permissible limits.
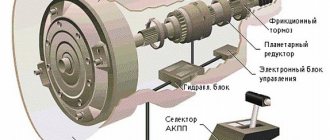
Planetary gearboxes in the gearbox
Cutaway view of an automatic transmission.
In automatic gearboxes, torque is transmitted from the shaft with the sun gear to the shaft connected to the carrier. If the ring gear is braked, then the satellites will roll around the sun and ring gears, causing the carrier to rotate. The gear ratio will be equal to the ratio of the number of teeth on the sun gear to the number of teeth on the crown gear. If the ring gear is released (released), then the torque will be transmitted directly, the ratio is 1:1. In modern designs of automatic gearboxes, the Lapelletier planetary mechanism is most often found [5].
Ford T manual planetary gearbox parts.
Occasionally, there are also mechanical planetary gearboxes, characterized by compactness and shock-free operation, but at the same time complexity and high cost. An early version of such a unit is the Ford-T box. Later, planetary gearboxes were used on tanks, for example, the Soviet T-64 of the 60s. Planetary gear shifters are much more widespread on bicycles. “Planetary bushings” can have up to 14 speeds (usually three), a built-in brake, with careful use they are durable and reliable, do not require maintenance, but are generally more expensive and heavier than traditional chain shifters.
"Geared starter" of automobile engines
In those who received in recent years [ when?
] distribution of “geared” starters also uses a planetary gearbox.
The engine of such a starter operates with less mechanical loads, has less weight, and is electrically more optimal. In general, a “gear” starter has better efficiency and puts slightly less load on the battery. Due to the short-term operation, the gearbox can be made with greater tolerances and thus significantly reduced in cost without compromising reliability, which is important for a relatively inexpensive spare part. At the same time, there are specimens with a plastic ring gear, which, although the least loaded of all, if performed poorly, sharply reduces the reliability of the entire starter. [ source not specified 964 days
]
A little bit of history
The first analogues of automatic transmissions appeared in the early 30s of the last century. Ford-T cars use a planetary manual transmission, the first “semi-automatic” ones appear in cars of the Reo and General Motors corporations. The appearance of the first full-fledged automatic transmissions occurred on General Motors cars in the 40s. Automatic transmission options appeared in Oldsmobile, Cadillac and Pontiac cars.
In the USSR, automatic transmission was installed at Chaika, then at GAZ. We used automatic transmissions in city LiAZs and special vehicles. In the 70-90s, there was almost no use of automatic transmissions; they returned to them already in the 2000s, when consumers began to choose foreign cars offering both “automatic” and “manual”.
Ball bearing
Ball bearing, animation.
A ball bearing is an example of a planetary gearbox in which the cage is the carrier, the inner ring performs the functions of the sun gear, the outer ring performs the functions of the ring gear, and the satellites are balls.
In the animation above, note that the rotation speed of the inner ring is noticeably higher than the rotation speed of the ball cage. If you release the outer ring, the rotation speeds will be equal (direct transmission will be engaged)
. If you brake the carrier, the outer ring will rotate.
Low-power gearboxes (for scientific or measuring instruments) can be constructed using ordinary ball bearings. For example, ball-bearing planetary gearboxes are used in the design of a vernier, which is used to finely tune a radio station to the desired receive/transmit frequency.