Where it all began, where it came from.
Let me make a small lyrical digression for those who do not know, or know but not fully, about this system.
In ancient times, the first cars running on internal combustion engines naturally did not comply with any environmental standards. And they didn’t exist then. They smoked, roared, blinded and smelled bad. Over time, there were more and more cars, and it was necessary to limit them in terms of noise, smell, smoke, etc. The units were improved (they came up with a muffler, for example)
Already during the conscious dawn of the auto industry, people came up with nonsense like global warming, environmentalists and other things. In addition to everything, they came up with EURO standards - 1, 2, 3, then 4 and 5. Euro standards obligated automakers to install systems on cars that would increase the environmental friendliness of cars. The main ones are the EGR system (afterburning of unburnt fuel) and the exhaust gas treatment system, i.e. their catalyses. This happens through a special device, if you can call it that - a catalyst.
I will write a separate detailed article about the EGR system later, because you can’t get rid of it with just one paragraph.
What are Catalysts and how does this system work?
I’ll try to explain “On my fingers”:
This whole system consists of:
— Oxygen sensors (Lambda probe they are also called)
After the mixture enters the cylinder, is compressed and burns, exhaust gases (combustion products) leave the combustion chamber through the exhaust manifold. On the path to freedom, the first gift from ecologists awaits them - the first group of oxygen sensors. Gases are controlled by the first oxygen sensor (or group on V-shaped engines). The sensor records various parameters, such as temperature, the content of various substances, etc. Then the gases enter the catalyst.
Catalyst, also known as Catalytic converter-neutralizer, or Catalytic converter. It looks like a big barrel in the exhaust system. The barrel is metal (sometimes similar to a muffler). Inside there are ceramic honeycombs. The honeycombs are specially coated with precious metals (Platinum, for example. Hence the very high cost of catalysts). The honeycombs have some resistance so that the flow slows down a little. Catalysts, depending on Euro standards, are of two types - First and second (initial and final, etc.). The first group of catalysts is usually located after the first oxygen sensors and is often part of the exhaust manifolds, the second is already directly in the exhaust tract (only Euro 4 and 5).
Getting into the catalyst, the gases are inhibited in the ceramic honeycombs, and entering into a chemical reaction (catalysis) with a coating of precious metals, they burn out. This whole thing is accompanied by a high combustion temperature. Further, having burned out, the gases pass into the exhaust pipe and (Euro 4 and 5) enter the second group of catalysts. After them comes the second group of oxygen sensors.
So, the Brains of the machine are monitoring this whole thing, precisely through the Oxygen sensors. There is a certain norm, written in the brains of the machine, that at the input (first group) it should be like this, at the output (second group) like this. Or the difference between input and output is written down. They say that if there is a cow at the entrance, then the output should be beef, and not half a cow or sawdust
Based on data from oxygen sensors, the brains control the formation of the mixture. They deplete it or enrich it with components - Air or Fuel. All this is needed for better afterburning
Well, to put it simply, the gases leaving the engine burn out at a high temperature, reducing harmful impurities and other bad contents, the absence of which our green friends fight so hard for.
The higher the euro standard, the stricter the standards, and the more gadgets there are to ruin the whole thing.
For example, before Euro 3 there were only front catalysts and oxygen sensors. With the advent of Euro-4, rear ones also appeared. The most severe of the existing standards is Euro 5.
As a result, instead of 100% of harmful emissions, only half, or even less, little smoke, little noise, everything is good. But not everything is as rosy as it seems.
Problems, and very big problems.
Over time, like any component, the catalyst is destroyed. There are many reasons for this:
- Shaking. Since the honeycombs are ceramic, over time they also break due to shaking and vibration.
— Aggressive temperature environment (for the rear wheels it’s water from the road, since they are under the belly, for the front wheels it’s temperature changes associated with cooling) From strong changes, the honeycombs crack and break.
— Poor quality of fuel. Unburnt fuel from the mixture, or a mixture with bad and heavy impurities getting into the catalysts, leaves deposits, particles on them, or even destroys them dynamically. This is especially true in Russia and the CIS.
— Products of the engine. As a rule - Oil and coke. But this is rather a case of exception, since they only get there if there is an engine malfunction. Like a leaking valve cover, or sagging rings.
- Time. There are no eternal mechanisms.
— Increased combustion temperatures in catalysts. As a rule, this is when there are a lot of foreign things in them and the whole thing burns even more intensely. The honeycombs simply begin to melt.
All this leads to the fact that the honeycombs are destroyed, split into large and small pieces, melt, in every possible way blocking the exit of exhaust gases. The consequences of all this are very sad:
— Reduced gas removal. From here the engine begins to “choke”. When everything is really bad and the catalysts are heavily clogged, the exhaust gases accumulate, create pressure in the exhaust system and remain in the combustion chamber. From here the engine begins to “choke” or even stall.
Causes and consequences of the malfunction
Causes
The main and most likely reasons may be:
- It may be clogged due to poor quality fuel. Due to the low quality of the fuel, the catalyst becomes clogged with its various components. During the operation of the car, these components gradually accumulate in the filter. If the filter is clogged, it becomes difficult for exhaust gases to escape and the engine begins to choke. This negatively affects engine thrust and dynamics;
- Engine malfunction. The oil scraper rings may partially fail, causing unburnt oil residues to enter the filter and clog it. People call this “oil burn due to a clogged catalyst”;
- The exhaust system is not working properly - another reason that the catalyst is clogged;
- Mechanical damage to the catalyst itself. Frequent driving on uneven terrain leads to destruction of the catalyst. Its smallest particles scatter and clog the filter honeycombs. Then the motor begins to malfunction.
Important! It happens that on new cars, despite low mileage, it is discovered that the catalyst is clogged. The reason for this may be the frequent use of low-quality gasoline.
The basic principle of operation, composition and symptoms of a clogged catalyst are now clear to us. This means that we have solved half of the problem. As they say, forewarned is forearmed
For a general idea, pay attention to the clogged catalyst in the photo. This is a rather terrible sight. The mesh is black and dirty, clogged with soot, and the exit of exhaust gases will be difficult
This is the result of driving more than 100 thousand kilometers or frequent use of poor quality fuel:
Consequences
A malfunction or blockage of this device can create serious problems, including the breakdown of the entire engine. The consequences depend on the degree of damage. If the catalytic converter is clogged, the car may not start the first time or stall while driving.
The car may consume more fuel than it should. Because the catalyst is clogged, exhaust gases can return to the cylinder, which can cause the entire cylinder-piston system to fail. The engine will wear out and eventually break down.
As you can see, important parts of the car can break because of one device. It costs a lot of money to install new parts, especially for the engine. To install it, you will have to sacrifice 50-100 thousand rubles. And without an engine, a car cannot operate.
What to do if you find that the catalyst is clogged? In this case, each car owner will act in his own way. Some will take their car to be repaired, others will decide to replace the catalytic converter themselves. All options are good. Let's discuss each of the possible options:
- Replacement with a new one. The purchase and installation of a new catalyst will take from 8.5 to 20 thousand rubles. If you count separately, a new device costs 7.5–15 thousand. And installation will cost 1.5–2 thousand. The cost of a product depends on its originality (there are original and non-original), brand and other less significant indicators. Plus there are additional services provided by the master.
- Self-cleaning is carried out if it can still be cleaned. But this is a device that cannot be repaired, so experienced people advise recycling the catalyst. The catalytic can be removed, but it may cost the exhaust system. But if you don’t care about the cleanliness of the world around you and you have a strong immune system, then you can safely get rid of it so as not to return to this problem in the future.
- Installation of a sports catalyst. It costs more than a regular one: 10 thousand rubles, excluding installation by a master. If installed, add an additional 5 - 10% hp. to the car's power. At the same time, comply with the EURO 4-5 standard. This catalyst does not require additional settings or other changes. The sports version looks like this:
P0420 - time to change the catalyst?
The most correct and reasonable way is to replace the catalyst.
For most cars older than 10 years (and this error is unlikely to occur on “new” cars), the cost of the catalyst is not that high. On analysis sites and online sites, the price of a used catalyst starts from 3-5 thousand rubles. Moreover, owners of Japanese cars can often afford to buy a contract catalyst without mileage in the Russian Federation for relatively little money. Many craftsmen simply remove the catalyst and install a flame arrester (or an empty pipe altogether). Doing this is categorically undesirable for many reasons. Let's look at why it is better to replace the catalyst with another one:
For which cars is this relevant?
It is impossible to say that error P0420 is typical for a specific make or model of car. This is a common mistake.
Basically, error P0420 appears on cars whose mileage is more than 100 thousand kilometers.
In this case, the first error P0420 may appear closer to 100 thousand km. or it may appear when the engine has worked for over 300 thousand km.
Diagnostics of the control unit and error code P0420
If you look at the statistics of calls from motorists to service stations with such a problem as error P0420, you can identify several brands and models of cars that are susceptible to this problem. This may include:
- Ford Focus 2.
- Toyota Corolla.
- Kia Rio.
- Nissan Qashqai.
- Renault Logan
- Hyundai Solaris.
- UAZ Patriot.
- Opel Antara.
- Mazda 3.
- Suzuki Grand Vitara.
- Kia Ceed.
- Skoda Fabia
- Honda Accord, etc.
The ECU compares the values of oxygen sensors on vehicles that meet the Euro-3 environmental standard and higher. Therefore, this error cannot appear on older cars.
It is important to take into account that error P0420 can equally affect both an expensive foreign car and an inexpensive domestic car.
Troubleshooting the catalyst and oxygen sensor
This is mainly a problem with budget models or cars that have traveled a significant number of kilometers. For them, error P0420 appears a little more often.
The lower the quality of the fuel used, the faster the ECU will encounter an error indicating low efficiency of the catalyst.
This is another reason to give preference to good quality fuel, use the services of trusted gas stations, and perform timely maintenance.
Advantages of replacing the catalyst:
- The planet will thank you. Those around you too.
- No need to bother with ECU (electronic control unit) firmware
- The problem will be solved once and for a long time. There is no interference with the vital components of the vehicle (ECU).
Disadvantages of replacing the catalyst:
- relatively expensive (but what is 5 - 10 thousand for your favorite car?)
- very expensive for some car models
- There may be difficulties with passing the annual technical inspection and also with selling the car
This is interesting: How to adjust headlights with your own hands - a detailed explanation of popular adjustment methods.
Changing the catalyst and removing it is up to you. Let's take a closer look at the pros and cons of removing the catalyst in order to be more objective.
Replacing the catalyst with a flame arrester: pros and cons
How to remove a catalyst
Obviously, when installing a flame arrester instead of a catalyst, one cannot talk about a complete replacement of one unit with another. First of all, installing flame arresting equipment instead of catalysts will affect the amount of emissions.
Installing a flame arrester will help stabilize the exhaust system and reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases, but will not solve the problem. On the other hand, flame arresters are cheaper than new catalysts, and from a budget-saving point of view, this is an almost ideal way to debug the exhaust system.
One of the compromise solutions will be to find and install a universal catalyst. The cost of such elements is several times cheaper than the original ones, but will also ensure normal operation of the engine, in compliance with environmental standards. You will probably still have to adapt the firmware to the new exhaust and test the operation of the entire exhaust. Car owners who have installed such a device on their engine can safely undergo technical inspection and be confident in the environmental friendliness of their vehicle.
If you remove the catalyst, how will this affect fuel consumption?
it all depends on the emission control standards 1) if we have Euro-2, then the car has 1 lambda probe and it is located BEFORE the catalyst. accordingly, the ECU will not know in any way about the absence of a catalyst, and the dynamics of the car when the contents of the catalyst are eliminated will increase slightly due to the increase in the permeability of the exhaust tract - similar to a chimney in a house - the fewer obstacles, the higher the thrust... in a car this means better cleaning of the cylinders during the purge stroke - less exhaust enters the fuel-air mixture at the inlet. in this case, Lambda plays the role of a control element - according to its readings, the ECU controls the quality of the mixture (feedback) 2) if we have Euro-3, then the car has 2 lambdas - the first sensor is the same as in Euro-2 and performs the same function. the second sensor is located just BEHIND the catalyst and performs the CONTROL function of the exhaust quality - it worries about the environment... in this case, the content of unburnt mixture residues after the catalyst should be LOWER than BEFORE it - the readings of the control sensor should be less than the readings of the first. according to the “bypass program”, which still remains OBLIGED to provide the required quality of exhaust - in this case, the ECU forcibly “cuts” the mixture so much that the car becomes noticeably dull. the driver tries to compensate for the “dullness” by increasing the accelerator pedaling - and here you have increased consumption. . in modern garages and careless service stations they recommend simply knocking out the catalyst and driving on - this works on Euro-2, but Euro-3 has to be re-chipped in order to turn off the second lambda and bring the car into Euro-2 mode... I call such repair advisors - COLLECTIVE FARMERS! ! ! Let me explain: on my 210993i it’s Euro-3 with a BOSCH MP-7.0 ECU. I removed the catalyst... and in his hands he spun... I advise you to just crawl under the car and estimate its size - the diameter of the catalyst is several times larger than the diameter of the exhaust pipe connected to it!! ! The throughput of the catalyst is many times greater than the throughput of the rest of the part - the resonator and muffler! If you have the opportunity, look at them in cross-section - it’s useful to count the number of small holes-bypass channels in them - that’s the loss of power in the exhaust!! ! if the catalyst is clogged and the GORE_MASTER recommends that you knock it out, it is better to figure out WHAT, and most importantly WHY it is clogged - when you examine it, you will find both oil and bad gasoline...; -) this is an indicator of the level of car maintenance. If you need to do exhaust tuning, install a direct-flow resonator and a direct-flow exhaust... and you will get an increase in power due to the exhaust (I have it all - all the parts are calculated, and not just bought at the market because they are shiny)... the exhaust system operates at the same sound level as the standard exhaust system - it does not roar like a tractor, but MUTES the exhaust sound... VAZ 210993i, euro-3, bosh mp7.0, 620 thousand without boring/capitalization of internal combustion engine, 8 years
accordingly, the ECU will not know in any way about the absence of a catalyst, and the dynamics of the car when the contents of the catalyst are eliminated will increase slightly due to the increase in the permeability of the exhaust tract - similar to a chimney in a house - the fewer obstacles, the higher the thrust... in a car this means better cleaning of the cylinders during the purge stroke - less exhaust enters the fuel-air mixture at the inlet. in this case, Lambda plays the role of a control element - according to its readings, the ECU controls the quality of the mixture (feedback) 2) if we have Euro-3, then the car has 2 lambdas - the first sensor is the same as in Euro-2 and performs the same function. the second sensor is located just BEHIND the catalyst and performs the CONTROL function of the exhaust quality - it worries about the environment... in this case, the content of unburnt mixture residues after the catalyst should be LOWER than BEFORE it - the readings of the control sensor should be less than the readings of the first. according to the “bypass program”, which still remains OBLIGED to provide the required quality of exhaust - in this case, the ECU forcibly “cuts” the mixture so much that the car becomes noticeably dull. the driver tries to compensate for the “dullness” by increasing the accelerator pedaling - and here you have increased consumption. . in modern garages and careless service stations they recommend simply knocking out the catalyst and driving on - this works on Euro-2, but Euro-3 has to be re-chipped in order to turn off the second lambda and bring the car into Euro-2 mode... I call such repair advisors - COLLECTIVE FARMERS! ! ! Let me explain: on my 210993i it’s Euro-3 with a BOSCH MP-7.0 ECU. I removed the catalyst... and in his hands he spun... I advise you to just crawl under the car and estimate its size - the diameter of the catalyst is several times larger than the diameter of the exhaust pipe connected to it!! ! The throughput of the catalyst is many times greater than the throughput of the rest of the part - the resonator and muffler! If you have the opportunity, look at them in cross-section - it’s useful to count the number of small holes-bypass channels in them - that’s the loss of power in the exhaust!! ! if the catalyst is clogged and the GORE_MASTER recommends that you knock it out, it is better to figure out WHAT, and most importantly WHY it is clogged - when you examine it, you will find both oil and bad gasoline...; -) this is an indicator of the level of car maintenance. If you need to do exhaust tuning, install a direct-flow resonator and a direct-flow exhaust... and you will get an increase in power due to the exhaust (I have it all - all the parts are calculated, and not just bought at the market because they are shiny)... the exhaust system operates at the same sound level as the standard exhaust system - it does not roar like a tractor, but MUTES the exhaust sound... VAZ 210993i, euro-3, bosh mp7.0, 620 thousand without boring/capitalization of internal combustion engine, 8 years
may break the resonator...
will rise! you need to “deceive” the lambda
put a fake
I had the catalyst amputated on 21124, it ate like a horse... 13 liters
On a modern car, the *engine control* lamp may come on, consumption will increase!
The lambda is located BEFORE the catalyst, and in no way knows about its existence... When you knock out all this ceramic crap from the inside with a rod, the throughput of the jammer increases, and noticeably. And the CO content in the exhaust. Power increases by several percent. And nothing will burn out, don’t be afraid. Yes, you can save money at the same time, it’s not a cheap thing... :-)))
On a VAZ 12, a friend was pleased and it became noisy in the cabin! but the consumption has not changed.
https://www.zamenakata.com/#!vigodaotcatalika/btz8z
the absence of a catalytic converter will affect the lambda, because there will be no exhaust gas pressure, everything will fly out into the pipe, and the consumption will increase. The catalytic converter also has a temperature sensor, which also affects the flow rate. So you shouldn't knock out the catalytic converter. I checked it myself by installing a whole catalytic converter, traction appeared at the bottom, and the vibration disappeared. And Glushak without catalytic converter will burn out faster and rot
I haven’t changed... a guttural sound has appeared
touch.otvet.mail.ru
Checking the catalyst
Deiners Blog Kia Rio-3, Catalyst -, Extinguish the flames. catalyst removal
So, the question arose, “How to check the catalyst?” The most effective and simple method is to dismantle the catalyst and inspect it.
Inspect the catalyst for clearance and clogging
The main signs and methods of checking the catalyst to see if it is clogged
We remove the catalyst and look at the condition of the honeycombs as a whole - if the honeycombs are clogged, you can check them through the light, and for this a light source will be useful. But not everything is as simple as it seems, sometimes, during long-term use, the catalyst fastening sticks so strongly that removing the catalyst can turn into a long and exciting task (personally, I unscrewed the two rear fastening nuts for 3 hours, in the end I couldn’t unscrew them - I had to cut it in half!). The work is extremely inconvenient because you need to work from underneath the car.
There are several other ways to check the catalyst: you can measure the exhaust for the content of harmful substances (with a faulty catalyst, the content of harmful substances increases significantly compared to a working catalyst), you can also check the back pressure at the outlet (a sign of a clogged catalyst is increased resistance and, as a result, pressure).
To objectively assess the condition, you need to combine both of these methods.
Tips to resolve the problem
Before running to a car service center, try to find out the reason yourself. To do this, you need to carry out a few simple checks. First, try to remember which gas station you last refueled at and whether you filled it with the correct fuel. If previously you always filled with A98 gasoline, and last time you decided to test A92, then it is quite logical that the system showed error P0420. In this case, just roll the remaining A92 and fill it with A98 this time. For many car owners, after changing gasoline, the error disappears.
Next, check the rear oxygen sensor connector. If he moved away a little, then this could very well cause an error. If everything is fine with this, then you will have to connect a computer to remove errors and data from the control unit.
Sources
- https://FixErro.com/46-%D0%BE%D1%88%D0%B8%D0%B1%D0%BA%D0%B0-p0420/
- https://DriverTip.ru/repair/chto-oznachaet-oshibka-p0420.html
- https://autotime.net.ua/oshibka-p0420-ford-effektivnost-katalizatora-nizhe-dopustimogo-urovnya/
- https://autotime.net.ua/oshibka-p0422-slishkom-nizkaya-proizvoditelnost-osnovnogo-katalizatora-bank-1/
- https://FB.ru/article/327217/oshibka-r-chto-s-etim-delat
- https://okeydrive.ru/oshibka-p0420-effektivnost-sistemy-kataliticheskogo-nejtralizatora-nizhe-urovnya-poroga/
[collapse]
The essence of the breakdown
How to check the gearbox oil yourself
The catalyst looks like a thick section of the exhaust system. A catalytic element coated with a special layer of platinum group metals is installed inside the housing. The element is made in the shape of a cylinder and has a honeycomb structure. A large number of honeycombs allows you to maximize the contact area of the exhaust gases with a special coating, thereby increasing the degree of exhaust oxidation.
It is the small diameter of the honeycombs that leads to them becoming clogged with deposits of low-quality gasoline and oil, reducing the flow area for exhaust gases. This is why it becomes more difficult for the car to “breathe”, since exhaust gases back up during the exhaust stroke. This, in turn, leads to poor purging of the chamber and incomplete combustion of the subsequent portion of fuel, which negatively affects consumption. In some cases, the honeycomb may melt, which leads to similar consequences.
We found out that there are only two options for catalyst failure:
- clogged catalyst when the honeycomb becomes clogged;
- wear of a special coating that reacts with exhaust gases.
Causes
The catalyst is capable of faithfully serving up to 150-200 thousand km. But in practice, it happens that many drivers have to find out about the breakdown of this system much earlier. The following reasons lead to accelerated failure:
- poor fuel quality;
- zhor oil, the combustion products of which will settle inside the honeycomb. Increased oil consumption may occur due to a faulty turbine;
- improper operation of the engine associated with adjustment of the ignition system, power supply and valve timing;
- mechanical damage to the element or sudden temperature changes. For example, a wave of ice water entering under the car when the catalyst is significantly heated by exhaust gases.
Consequences
Many drivers ignore the signs of a clogged catalyst, considering this element only a “fighter” for the preservation of the environmental environment. There is no need to do the same under any circumstances. After all, the catalytic converter is a standard “diagnostician” of engine operation. Therefore, errors that appear on the catalyst can signal not only the failure of the element itself, but also a malfunction of the ignition system.
Let's consider the main consequences:
- fuel consumption increases. Since the resistance of the exhaust gases has increased, to overcome this force the driver has to press the gas pedal harder, increasing the fuel supply;
- the temperature of the exhaust system increases. Hot gases linger longer in the area preceding the catalyst. This especially affects turbocharged engines, where the temperature difference between the “cold” and “hot” parts increases significantly.
The principle of operation of the catalyst and its functions
The main function of the neutralizer is to completely burn the exhaust so that it enters the atmosphere as purified as possible from such types of harmful greenhouse gases as:
- carbon monoxide;
- nitrogen oxides;
- hydrocarbons.
While the engine is running, the inside of the converter heats up to a temperature of over 700 degrees. Under such conditions, afterburning of gases occurs. And the above listed harmful chemicals are neutralized through reactions with an active catalyst. Two oxygen sensors, Lambda probes, are installed at the entrance and exit of the device, which analyze the composition of the exhaust. And if the content of toxic gases meets the standards, the sensors do not give any signals.
Lambda probe and fuel consumption. Again about fuel economy - DRIVE2
A very interesting thing, there was never a reason to be interested in it until I exchanged the Moskvich for another car. I heard something somewhere about the lambda probe, it seems like it sometimes breaks, but I was never interested in what it does. Now I'm interested. Two pieces of information. What did you find about the lambda probe?
Sometimes there is one per car, sometimes there are two or more. More often than not, one is installed in the exhaust manifold and a second one is installed immediately at the outlet of the catalyst. Catalytic converter for "unburnt exhaust gases". Systems for afterburning unburned mixture.
The lambda probe (oxygen sensor) detects the lack of oxygen in the exhaust gases. If the mixture is rich (air/gasoline ratio) above the optimal 14.7, there is practically no oxygen in the exhaust gases, the sensor reacts immediately. A voltage appears from the sensor of 0.9-1.0 volts (with a normal mixture it is always lower)
(with a ratio of about 14.5, the voltage from the sensor is approximately 0.5 volts) The mixture is rich - oxygen is oxidized and is not in the exhaust gases. The sensor gives three pulses per second. The command goes to the car’s on-board computer.
Does it really affect fuel consumption? Yes, it does. Specific situation.
There was a problem on one car. First came the savings (significant from 17-18 to 13). Then obviously surrogate gasoline was poured in and after that the person started having problems. The consumption began to increase, went back to 17 and higher, to 19, and they could not understand the reason. There were no errors on the on-board computer, a trip to the technical department for diagnostics. The center also did not help to identify the cause. Diagnostics “on the computer” showed that everything was fine, there were no errors. Only a check at another dealer (full check of all systems and sensors on the go) helped to find the cause. As it turned out, there was a constant overflow of gasoline (due to incorrect operation of the lambda probe) and therefore there was an overconsumption. There might have been an opinion that “ToplivoDar doesn’t work.” The lambda probe has failed. Precisely from surrogate fuel. Those. Even if the “Check Engine” light is not on and the car was checked at the stand, this does not mean that the lambda probe is working. This turned out to be the case and this was confirmed by Master No. 2. After replacing the lambda probe (three weeks to find the causes), the consumption is again 13 liters per 100 km. Instead of 17-18 tee. With FuelDar. And again only AI 92 gasoline
And about cars too. There is already a second such car, the Mazda CX7 “on the add-on”. But as always, the owners often don’t say anything. Perhaps the second owner already has a problem with the lambda probe. To the question “what is the consumption”, they have not yet started using the FuelDar additive - he did not answer in detail.
Video about the first
www.drive2.ru
Design and general principle of operation of the part
The device is a filter designed to clean exhaust gases from harmful toxic substances released from the car into the atmosphere. Otherwise, without it, harmful substances such as CO, CH and NO would enter our lungs.
In another way, the catalyst is usually called a catalytic converter or simply “catalyst”. Like any other car part, this filter is not immune to the loss of its ability to function properly. While performing its functions properly, after the car has driven for a long time, the catalyst may become clogged. This problem entails others that affect the operation of the engine and the machine itself as a whole.
Before you figure out why and how the catalyst can be clogged, you should consider what it looks like and what it consists of. Inside there are filters made of noble metals (iridium) and reminiscent of a honeycomb. It is these filters that trap toxic substances from exhaust gases. When exhaust gases enter the catalytic converter, the filter becomes very hot. Harmful gases CO, NO, CH remain there, then burn out and oxidize. Gases that are practically harmless to the environment: CO2, H2O and N2 enter the atmosphere. There is an exhaust gas sensor that shows the level of contamination of the exhaust gases in the catalyst
To imagine what the device itself looks like, as well as how the cleaning process occurs, pay attention to the explanatory drawing:
If you notice such phenomena as an increase in fuel consumption, the engine does not start well, problems with dynamics, or unstable acceleration of the car, then these are clear signs of a clogged catalyst. What can lead to the clogging of the catalytic converter with rubbish will be discussed below.
Do-it-yourself catalyst removal
Motorists often ask the question: is it necessary to remove the catalyst? Some drivers believe that making a hole in the KN ceramics adds power to the engine and improves the dynamics of the car. These arguments are incorrect - only the faulty catalyst needs to be removed, if the CO level is normal, it is better not to touch the KN.
You can remove the catalyst yourself, but to complete the work you will need welding equipment and a grinder.
On many modern cars, the main catalyst is welded to the exhaust manifold and is an integral part of it. To remove ceramics from such a CN, you must:
- disconnect the exhaust pipe of the muffler;
- remove the exhaust manifold;
- use a grinder to cut the neutralizer body;
- remove all the insides from the jar;
- weld the housing, install the manifold in place.
It should be taken into account that this measure is temporary; for normal engine operation it is necessary to install a flame arrester, or even better, a new catalyst.
The content of the article:
There are many benefits to removing the catalyst—or kata, as it's also called. Although it cleans harmful components from exhaust gases and helps reduce the impact on the environment, without it drivers will notice an increase in engine power. But often such a “surgical” intervention leads to the appearance of a smell after removing the catalyst, smoke, or, which is very unpleasant for the person driving, the catalyst is removed, the “Check Engine” is lit (warning on the dashboard).
Checking the catalyst for back pressure
The following describes a method for checking the condition of the catalyst against the back pressure created.
To do this, in front of the catalyst you need to weld in sampling fittings for sampling exhaust gases. It is advisable to weld fittings with threads and a channel shape; these fittings are similar to brake pipe fittings. After completing the measurements, plugs are screwed into these fittings.
It is advisable to make the plugs from brass - this will ensure that they can be easily unscrewed during operation. For measurements, you need to screw a brake pipe 400-500 mm long into the fitting, the purpose of which is to dissipate excess heat. We put a rubber hose on the free end of the tube, attach a pressure gauge to the hose, its measurement range should be up to 1 kg/cm3.
Back pressure can be measured while the vehicle is accelerating with the throttle fully open. The pressure is determined using a pressure gauge during acceleration, and as the speed increases, all values are recorded. If the back pressure values when operating with the damper fully open in any speed range exceed 0.35 kg/cm3, this means that the exhaust system needs modification.
This method of checking the catalyst is desirable, however, in real life, welding fittings is quite a murky business, so I did this: I unscrewed the lambda, which is located in front of the catalyst, and inserted a pressure gauge through the adapter. (It is advisable to use a pressure gauge more accurately up to 1 kg/cm3). As an adapter, I used a rubber hose, which I adjusted to size with a knife (do not forget that tightness is important).
This is what a professional service tool looks like
Diagnostics of the catalytic converter for back pressure
I measured it myself using a hose.
- We start the engine and take the pressure gauge readings (this is the back pressure at the outlet).
- We put the assistant behind the wheel, he raises the speed to 3000, we take readings.
- The assistant again raises the speed, but this time to 5000, we take readings.
There is no need to overclock the engine! 5-7 seconds is enough. There is no need to use a pressure gauge measuring up to 3 kg/cm3, as it may not even feel the pressure. The maximum pressure gauge is 2 kg/cm3, preferably 0.5 (otherwise the error may be commensurate with the measurement value). I used a pressure gauge that was not quite suitable, but the maximum was 0.5 kg/cm3, the maximum during an instant increase in revolutions from XX to 5000 (the pressure gauge jerked and fell to “0”). So, this doesn't count.
In your mind, these two methods can be combined like this:
1) unscrew the lambda located in front of the catalyst;
2) instead of this lambda, screw in a fitting;
3) screw a piece of brake pipe to the fitting (available with cap bolts);
4) put a hose on the end of the tube and push it into the cabin;
5) well, then, as in the first case;
On the other hand, we connect it to a pressure gauge, the measuring range of which is up to 1 kg/cm3. It is necessary to ensure that the hose does not come into contact with parts of the exhaust system.
The pressure is determined using a pressure gauge during acceleration, and as the speed increases, all values are recorded. If the back pressure values when operating with the damper fully open in any speed range exceed 0.35 kg/cm3, this means that the exhaust system needs modification.
6) due to a non-functioning (unscrewed) lambda, the check will start to light up; after the lambda is put in place, the check will go out;
7) the limit of 0.35 kg/cm3 is used for tuned cars, and for normal cars, in my opinion, the tolerance can be expanded to 0.5 kg/cm3.
If the diagnostics of the catalyst shows increased resistance to the passage of exhaust gases, then it is necessary to wash the catalyst; if washing is not possible, then the catalyst will have to be replaced. And if replacement is not economically feasible, then we remove the catalyst.
Every year, environmental standards are becoming stricter around the world. At the moment, in the countries of the European Union they use cars with emissions no lower than Euro-4. In Russia, they are less demanding regarding the environmental friendliness of exhaust gases. However, even modern Lada and GAZ vehicles are equipped with such a device as a catalyst. What is this element? How does he work? How to check the serviceability of the catalyst? All this and more will be discussed further in our article.
Question about catalyst and fuel consumption
v_i_t_a_r_a wrote:
If replacing the original parts of the exhaust system is expensive/unavailable for some other reason, there are always options to choose an analogue (for example, Walker, Bosal)
Unoriginals, they are... strange.
The original catalyst rotted and was removed almost a year ago. Now the time has come for Glushak. He, in principle, “suffered and suffered a lot,” and now there is nothing to cook there - it siphons from all the cracks. Some time ago, a decision was made to replace it with a new one. I was too lazy to buy the original (400+ bucks) and ordered the cheapest non-original (Tesh, number 260776). This has arrived: https://www.ingortech.ru/car/Photo/Details/Glushak/index.html
The execution is horse-like. In terms of sound, it works _significantly_ louder than the leaky original one (and I’m not one of those who likes to fart with a muffler...) I consoled myself: “Well, at least it’s new.”
Along with replacing the flasher, the timing belt was changed. After all this was done and I got into the car, I immediately discovered that it stopped driving. It goes after the engine spins up more than 2000 rpm, and before that it felt like I had a UAZ tied to my tail... In high-speed and all-wheel drive, uphill , generally barely drives and tries to stall.
I made a mistake, obviously, on the timing belt because... a “standard” jamb was discovered with a discrepancy between the marks on the gear and what was described in the document. I looked for a document for a long time, checked and looked at the ignition, idle and the like (which I wrote about here). No jambs were found.
Yesterday, in the process of regular scheduled renovations, as a personal initiative, the master installed the plugs. Those. I installed the old whistling one instead of the new one. He called me and said that after this transfer the car started driving like before again! I'll pick up the car today and have a look. But there is no point in particularly distrusting him because... He himself can clearly see the drop in power, fortunately, “precision instruments” are not needed for this :/
So, now, apparently, I will either install the new ORIGINAL, or look for a contract one in decent condition. This “replacement” is just crap that is not intended for this machine :/
suzuki-club.ru
Pros and cons of the alternative
When replacing a Toyota Corolla catalyst with a direct-flow damper, it is worth finding out what is more important to you and whether the advantages of installing it can cover the disadvantages, which, by the way, also exist. So, the advantages of replacing these parts:
- Once installed, this part will never burn out or clog;
- Engine power increases to 7 horsepower;
- Does not harm the turbine or engine;
- The flame arrester is much cheaper than the catalyst on the Toyota Corolla.
The main advantages are probably over, now it’s worth considering the disadvantages:
- The fuel burns out in the exhaust system, so the entire exhaust system begins to collapse faster. However, if you digest it, there will be no problems;
- The exhaust sound increases and changes. Depending on the power, the sound becomes stronger. The problem can be solved with good sound insulation of the body;
- The sensitive electronic system of modern cars, when installing a flame arrester, needs to be re-flashed. This is due to the fact that a sensor is installed in the catalyst, and if the computer notices its malfunction, the errors will haunt you;
- A high level of exhaust toxicity, but if you do not care about this problem, then it cannot be called a minus.
It is worth noting that the damper is most often an element of the direct-flow exhaust system, which is installed on sports cars. In the case of the Toyota Corolla, installing such a part is quite possible, and one might even say desirable, if you are not bothered by the disadvantages listed above. Buying it is not so difficult, but disassembling the exhaust system and digesting the cans is even easier. The only thing you have to do is turn to a good computer engineer to rewire your brain. In any case, installing this part on a Toyota Corolla instead of a catalyst will cost much less.
Diagnosis and elimination of errors
Although it is a faulty catalyst that most often leads to the appearance of error P0420, you should not rush to conclusions. The catalytic converter is not a cheap part, so sometimes a motorist in a hurry can waste a considerable amount of money.
First you need to do some diagnostics. In many ways, it allows us to confirm or refute the theory that the catalyst’s service life has come to an end.
The current task is to fix the problem that caused error P0420 to appear. To begin with, it is recommended to rule out simpler causes.
- Low quality fuel. If you have visited questionable gas stations or filled up with fuel that was not intended for your engine, it is better to drain the remainder and fill with normal gasoline. Then drive it, burn out the remaining fuel in the line and see how the car behaves with good fuel.
- Ignition. Or rather the lead angle. Check if the torque is set correctly. If not, the exhaust temperature may be higher than permissible, which will lead to a corresponding error.
- Oxygen sensor. In this case, the second or lower lambda probe is checked. To check, swap the two sensors, as they are identical and interchangeable. If this corrects the situation, replace the old sensor. However, if the second sensor breaks down, another error usually appears. This is P0134.
This is interesting: Generator malfunctions - signs and symptoms: how to check the diode bridge with your own hands
If the measures taken did not confirm your guesses and the reason is still in the catalyst, it will also need to be checked.
Diagnostics of the catalyst involves the use of a special stand and equipment. Therefore, such procedures are unlikely to be carried out in a garage environment.
The test generates a graph of the output voltage between a pair of oxygen sensors. Additionally, data on decreasing and increasing fuel supply is checked.
When checking the output voltage, make sure that the readings vary depending on the air-fuel mixture used.
If the mixture is lean, the voltage should be 100 mV or higher. If the mixture is enriched, then up to 900 mV.
If there are deviations from the norm, you can solve the problem with the catalyst in several ways:
- Replace the old catalyst with a new original one. Very expensive, but right. Prices for parts for foreign cars can be about 40-50 thousand rubles or more.
- Replace with an analogue one. These are Chinese and other catalysts. Here you will have to spend 5-15 thousand rubles. But keep in mind that metal, and not original ceramic, catalysts last literally 50 thousand km.
- Install the decoy. This is what they call the ECU firmware so that the unit does not react to the absence of a catalyst. An emulator is installed to ensure stable operation of the internal combustion engine and exhaust system.
If you remove the catalyst, the car will not meet the stated environmental standards.
Whether this is a serious reason to still spend money on a full replacement, decide for yourself.
If the catalyst is simply clogged, causing its performance to decrease, cleaning it can help. There are DIY methods for cleaning. Plus, many car services are ready to do this for money.
Common diagnostic mistakes
The most common error when diagnosing P0422 is due to failure to follow the diagnostic protocol. Failure to follow the protocol may result in unnecessary catalyst replacement that will not correct the problem.
Oxygen sensors are also often mistakenly replaced. Oxygen sensors should be checked before replacement and should not be considered the only problem causing P0422.
Diagnostic methods
Let's move on to specific methods that will help determine the malfunction. The easiest ways to find out about clogged cells:
- it is necessary to start and spin the engine to maximum speed; In the low, medium and high speed modes, sharply press the accelerator pedal to the floor. The engine should not “fail”, but rather respond sharply to the driver’s commands. If there is a weak, delayed response, or the engine does not spin up at all (at 4-5 thousand rpm), then we can safely talk about the need for repairs;
- place your hand on the exhaust pipe. The movement of exhaust gases is of a pulsed nature. You can feel each cylinder pushing out exhaust gases in turn. If you feel a constant smooth flow of exhaust at idle, this is a direct sign of a clogged catalytic converter. You can also ask an assistant to press on the gas, spinning up the internal combustion engine, and then immediately turn off the engine (you need to do everything quickly). After stopping the engine, there may be a slow release of gases that have accumulated due to deposits in the honeycombs. You can bring a fire source (match, lighter) to the exhaust pipe;
- visual inspection method. To do this, it is necessary to remove part of the exhaust with the catalytic element. Shine a flashlight through it to identify clogged honeycombs. Please note that if it was not fuel consumption or a drop in power that forced you to check the catalyst, but Check Engine, then this testing method is not very good. The element may visually look clean, but the special layer will no longer perform its functions. Therefore, the corresponding indicator lights up on the panel.
Counterpressure
You can check the system using a pressure gauge. The essence of the method is to screw in a regular air pressure gauge instead of a lambda probe (before the catalyst). This must be done using a special adapter. You will also need a hose connecting the pressure gauge and the adapter.
To check the catalyst, start the engine. In any of the operating modes, pressure readings should not significantly exceed the range of 2-3 kPa (0.2-0.3 Atm.). If you do not want to do the diagnostics yourself, contact a diagnostic center. Instead of a spark plug, specialists screw in a special sensor that measures the counter pressure. Reliable information is obtained by analyzing oscillograms of engine operation. Testing the efficiency of the exhaust system in this way at home is an impossible task. The device itself and diagnostic software cost a lot of money.
Now you know how to check the catalyst or particulate filter yourself, if we mean a diesel car.
Catalyst emulator "P0420-OFF"
Cities of Ukraine where you can get our products: Avdeevka, Alexandria, Aleksandrovsk, Almaznaya, Alupka, Alushta, Alchevsk, Amvrosievka, Ananyev, Andrushevka, Anthracite, Apostolovo, Armyansk, Artemovo, Artemovsk, Artemovsk, Artsyz, Akhtyrka, Balakleya, Balta, Bar , Baranovka, Barvenkovo, Bakhmach, Bakhchisarai, Bashtanka, White Church, Belgorod-Dnestrovsky, Belz, Belitskoye, Belogorsk, Belozerskoye, Belopole, Belyaevka, Berdichev, Berdyansk, Beregovo, Berezhany, Berezan, Berezovka, Berestechko, Berislav, Bershad, Bobrinets, Bobrka, Bobrovitsa, Bogodukhov, Boguslav, Bolgrad, Bolekhov, Borzna, Borislav, Boryspil, Borshchev, Boyarka, Brovary, Brody, Broshniv-siege, Bryanka, Buzukov, Burshtyn, Buryn, Busk, Buchach, Valki, Vasylivka, Vasilkov, Vatutino, Vakhrushevo, Vashkovtsy, Velikiye Mosty, Verkhnedneprovsk, Verkhovtsevo, Vizhnitsa, Vilkovo, Vinniki, Vinnitsa, Vinogradov, Vishnevoe, Vladimir-Volynsky, Voznesensk, Volnovakha, Volochisk, Volchansk, Volnogorsk, Volnyansk, Vorozhba, Vysoky, Vyshgorod, Gadyach, Gayvoron, Gaysin , Galich, Genichesk, Hertsa, Glinany, Globino, Glukhov, Gnivan, Gnidyn, Golaya Pristan, Gorlovka, Gornyak, Gorodenka, Gorodishche, Gorodnya, Gorodok, Gorodok, Gorokhov, Gorskoye, Grebenka, Gulyaypole, Debaltsevo, Derazhnya, Dergachi, Dzhankoy, Dzerzhinsk, Dimitrov, Dneprodzerzhinsk, Dnepropetrovsk, Dneprorudnoye, Dobromil, Dobropolye, Dokuchaevsk, Dolyna, Dolinskaya, Donetsk, Drohobych, Druzhba, Druzhkovka, Dublyany, Dubno, Dubrovitsa, Dunaevtsy, Evpatoria, Enakievo, Zhashkov, Zhdanovka, Zhovti Vody, Zhidachiv, Zhitomir , Zhmerinka, Zhovkva, Zalishchiki, Zaporozhye, Zastavna, Zbarazh, Zborov, Zvenigorodka, Zdolbunov, Zelenodolsk, Zenkov, Zimogorye, Zmiev, Znamenka, Zolotoye, Zolotonosha, Zolochev, Zolochiv, Zorinsk, Zugres, Ivano-Frankivsk, Izmail, Izyum, Izyaslav , Ilovaisk, Ilintsy, Ilyichevsk, Ingulets, Inkerman, Irpen, Irshava, Ichnya, Kagarlyk, Kozatin, Kalinovka, Kalush, Kamenets-Podolsky, Kamenka, Kamenka-Bugskaya, Kamenka-Dneprovskaya, Kamen-Kashirsky, Kanev, Karlovka, Kakhovka, Kerch , Kivertsy, Kiev, Kiliya, Kirovograd, Kirovsk, Kirovskoe, Kitsman, Kobelyaki, Kovel, Kovsharovka, Kodyma, Kozyatin, Kolomyia, Komarno, Komsomolsk, Komsomolskoe, Komsomolskoe, Konotop, Konstantinovka, Kopychintsy, Korets, Korosten, Korostyshev, Korsun-Shevchenkovsky , Koryukovka, Kosiv, Kostopol, Kotovsk, Kramatorsk, Krasilov, Krasnoarmeysk, Krasnogorovka, Krasnograd, Krasnodon, Krasnoperekopsk, Krasny Liman, Krasny Luch, Kremenets, Kremennaya, Kremenchug, Krivoy Rog, Krolevets, Kuznetsovsk, Kupyansk, Kurakhovo, Ladyzhin, Lanovtsy, Lebedin, Lisichansk, Lozovaya, Lokhvitsa, Lubny, Luhansk, Lutugino, Lutsk, Lviv, Lyuboml, Lyubotin, Makeevka, Malaya Viska, Malin, Manganets, Mariupol, Marinka, Melitopol, Mena, Merefa, Mirgorod, Mironovka, Miusinsk, Mogilev-Podolsky . Novograd-Volynsky, Novogrodovka, Novodnistrovsk, Novodruzhesk, Novomirgorod, Novomoskovsk, Novoselitsa, Novoukrainka, Novoyavorovsk, New Bug, Novy Rozdol, Nosovka, Obukhov, Ovruch, Odessa, Ordzhonikidze, Orekhov, Oster, Ostrog, Ochakov, Pavlograd, Pervomaisk, Pervomaisk, Pervomaisk, Pervomaisky, Perevalsk, Peremyshlyany, Pereyaslav-Khmelnitsky, Pershotravensk, Pershotravensk, Pesochin, Petrovskoye, Pivdenny, Pyryatyn, Pogrebische, Podgaitsy, Podgorodnoe, Pokotilovka, Pologi, Polnoe, Poltava, Pomoshna, Popasna, Pochaev, Privolye, Priluki, Primorsk, Pustomyty, Putivl, Pyatikhatki, Rava-Russkaya, Radekhov, Radomyshl, Radyvyliv, Razdelnaya, Rakhiv, Reni, Rzhishchev, Rovenki, Rivne, Rohatyn, Rodinskoye, Rozishche, Romny, Rubizhne, Rudki, Saki, Sambir, Sarny, Svalyava, Svatovo, Sverdlovsk, Svetlovodsk, Svetlodarsk, Svyatogorsk, Sevastopol, Severodonetsk, Seversk, Selidovo, Semenovka, Seredina-Buda, Simeiz, Simferopol, Sinelnikovo, Skadovsk, Skalat, Skvira, Skole, Slavuta, Slavutich, Slavyansk, Smela, Snezhnoye, Snigirevka, Snyatin, Sokal, Sokiryany, Soledar, Solonitsevka, Sosnovka, Starobelsk, Starokonstantinov, Old Crimea, Old Sambir, Stakhanov, Stebnik, Storozhinets, Stryi, Sudak, Ship Cherry, Sumy, Sukhodolsk, Happiness, Tavriysk, Talnoye, Tarashcha, Tatarbunary, Teplik, Teplogorsk , Teplodar, Terebovlya, Ternovka, Ternopil, Tetiev, Tismennitsa, Tlumach, Tokmak, Torez, Trostyanets, Truskavets, Tulchin, Turka, Tyachev, Uglegorsk, Ugledar, Ugnev, Uzhgorod, Uzin, Ukrainka, Ukrainsk, Ulyanovka, Uman, Ustilug, Fastov , Feodosia, Khartsyzsk, Kharkov, Kherson, Khirev, Khmelnik, Khmelnitsky, Khodorov, Khorol, Khorostkov, Khotyn, Khristinovka, Khust, Tsyurupinsk, Chasov Yar, Chervonograd, Chervonozavodskoye, Chervonopartizansk, Cherkasy, Chernigov, Chernivtsi, Chigirin, Chop, Chortkiv, Chuguev, Shargorod, Shakhtersk, Shepetovka, Shostka, Shpola, Shchelkino, Shchors, Energodar, Yuzhnoukrainsk, Yuzhny, Yunokommunarovsk, Yavorov, Yagotin, Yalta, Yampol, Yaremcha, YasinovatayaIndirect signs
You can often determine a malfunction of the exhaust gas cleaning system by how the car behaves. A breakdown will cause the following symptoms:
- Acceleration dynamics and throttle response deteriorate. A clogged catalyst will lead to a drop in power; engines sometimes cannot even spin up to high speeds. If you press the gas sharply, there will be no immediate reaction;
- fuel consumption increases;
- There is a pungent smell of exhaust gases when it is cold.
The car will start without any problems.
You can foresee accelerated wear of the converter if you do not eliminate increased consumption or outright oil consumption for a long time, ignore problems with the power and ignition system, and do not pay attention to the choice of gas station and fuel quality
Check Engine
This is a universal engine fault indicator. Therefore, you definitely need to know the error code. The decoding of the codes can be found in the repair and operating instructions.
Please note that the Check Engine lights up only on those cars that have two lambda probes in the exhaust system. The first is installed before the catalyst and is used to regulate fuel supply and ignition timing (affects consumption). The second sensor is designed to monitor the health of the catalytic converter. This is the one that will throw the error. The cause of the icon on the panel may be a simple break in one of the wires or destruction of the heating element.
Fuel and oil consumption after removing the catalyst » News Online
Fuel and oil consumption after removing the catalyst - how much will it increase, the consequences of knocking out the exhaust gas converter and aspects of correct tuning.
Even in old cars, when the resistance of the exhaust system changed, or when the breather was released from the air filter into the atmosphere, problems began with the mixture, oil was thrown out, and so on.
A modern motor is generally a perfectly calibrated and calculated mechanism. Its power supply system and exhaust tract are initially designed for the resistance of the exhaust system that the catalyst creates.
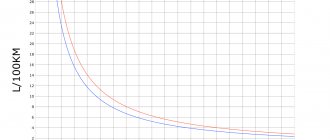
Using the example of a Kia Rio with a 1.6 engine:
| With catalyst | Without catalyst | |
| Fuel consumption, l/100km | 7.8 | 11-12 |
| Oil consumption, l/1000 km | Up to 0.5 as normal | From 1 to 3 |
Hence the increased oil and gasoline consumption, which can be seen in the table, and this is still a fairly loyal option.
Why has oil consumption increased?
When the catalyst is removed, the engine begins to become unbalanced, the cylinder head of which was designed to work with resistance. When a person releases the gas while descending from a mountain, or simply before a traffic light, braking with the engine, a vacuum forms in the exhaust tract. Because of this, oil begins to rush through the valve seals. Especially if they are worn out.
Which cars start to burn oil?
For Kia, Hyundai, Toyota (especially with MZ engines), Volno and others. Considering that a car service often offers to cut out the catalyst, its “masters” often trick people into replacing valve stem seals, or even overhauling the engine, citing the fact that dust from the catalyst got into the combustion chamber and killed the piston. After repair, of course, the engine continues to consume oil.
What to do. The best way out is to install the catalyst back. Or, if it is very expensive, install something similar.
To avoid problems during replacement, you should screw in a pressure gauge instead of the oxygen sensor and measure the pressure that is created in the exhaust manifold in different modes. Then select a universal catalyst for these values.
Installing a flame arrester instead of a catalytic converter does not provide much resistance and the problem remains.
Is it dangerous? Of course, the engine wears out faster, carbon deposits can form on the valves followed by burnout, and some even have piston skirts that break off. You can’t drive like this for a long time, especially if the consumption is more than 1 liter per 200-500 kilometers.
Why has gasoline consumption increased?
After removing the neutralizer, gasoline consumption begins to increase due to an excess of oxygen in the exhaust system.
The lambda probe reads the indicators, and the computer in response to this gives a command to enrich the mixture. Driving with a rich mixture not only kills the spark plugs and promotes the formation of carbon deposits, but also prevents the engine from reaching operating temperature, running normally, and so on. The driver's speed fluctuates, he cannot start when hot, the engine is shaking, there is vibration.
What should you do? If there is only one lambda probe, then you can often get by with flashing the system. If there are two of them, then they put a decoy on the second one, and then again they do painstaking flashing.
It is difficult to achieve normal parameters with cut out catalysts, although this procedure has already been worked out on many brands. Problems with maintenance cannot be ruled out.
In principle, there are so many problems with removal that it is not worth doing it at all, especially in the hope of “tuning” that the car will “breathe” and drive. The increase in power was measured on a stand, there is a maximum of 2-3 horsepower. On older carburetor cars, where you can adjust the mixture manually and play with the needle profile, implementing such “tuning” is somewhat easier.
Many will say that after all the adjustments, consumption dropped and the car began to drive better, but, unfortunately, on a significant number of modern cars, it is unrealistic to achieve this by completely removing the catalyst.
Tags: catalysts
news-online.info
The essence of the breakdown
The catalyst looks like a thick section of the exhaust system. A catalytic element coated with a special layer of platinum group metals is installed inside the housing. The element is made in the shape of a cylinder and has a honeycomb structure. A large number of honeycombs allows you to maximize the contact area of the exhaust gases with a special coating, thereby increasing the degree of exhaust oxidation.
It is the small diameter of the honeycombs that leads to them becoming clogged with deposits of low-quality gasoline and oil, reducing the flow area for exhaust gases. This is why it becomes more difficult for the car to “breathe”, since exhaust gases back up during the exhaust stroke. This, in turn, leads to poor purging of the chamber and incomplete combustion of the subsequent portion of fuel, which negatively affects consumption. In some cases, the honeycomb may melt, which leads to similar consequences.
We found out that there are only two options for catalyst failure:
- clogged catalyst when the honeycomb becomes clogged;
- wear of a special coating that reacts with exhaust gases.
Causes
The catalyst is capable of faithfully serving up to 150-200 thousand km. But in practice, it happens that many drivers have to find out about the breakdown of this system much earlier. The following reasons lead to accelerated failure:
- poor fuel quality;
- zhor oil, the combustion products of which will settle inside the honeycomb. Increased oil consumption may occur due to a faulty turbine;
- improper operation of the engine associated with adjustment of the ignition system, power supply and valve timing;
- mechanical damage to the element or sudden temperature changes. For example, a wave of ice water entering under the car when the catalyst is significantly heated by exhaust gases.
A single case of using bad fuel, as well as a sharply increased oil consumption, cannot cause failure of the catalytic converter. Only a long period of operation under conditions harmful to the catalyst can lead to breakdown and the appearance of an error on the dashboard.
Consequences
Many drivers ignore the signs of a clogged catalyst, considering this element only a “fighter” for the preservation of the environmental environment. There is no need to do the same under any circumstances. After all, the catalytic converter is a standard “diagnostician” of engine operation. Therefore, errors that appear on the catalyst can signal not only the failure of the element itself, but also a malfunction of the ignition system.
Let's consider the main consequences:
- fuel consumption increases. Since the resistance of the exhaust gases has increased, to overcome this force the driver has to press the gas pedal harder, increasing the fuel supply;
- the temperature of the exhaust system increases. Hot gases linger longer in the area preceding the catalyst. This especially affects turbocharged engines, where the temperature difference between the “cold” and “hot” parts increases significantly.
Catalyst repair and replacement
Let's start with the fact that the catalyst cannot be repaired. The way out in this situation is either to replace the device or remove the catalyst. Taking into account the high cost of such a part (even cheaper universal analogues), the second option for removing the neutralizer is widely practiced in the CIS countries.
Simply put, the ceramic inserts are removed from the catalyst, after which the empty “blank” is put in place. At the same time, the standard firmware of the car's ECU is adjusted; it may also be necessary to install a lambda probe, etc. The main thing is that the engine operates normally without a catalyst.
Another option is to immediately cut out the catalyst and install a flame arrester (pipe with holes). This solution allows exhaust gases to be effectively removed, the engine runs smoother, throttle response improves, but the exhaust sound becomes louder, and the exhaust system itself suffers and its service life is reduced.
How severe is the catalyst efficiency error?
With this error, the driver does not experience problems driving a Ford . This code can be ignored. However, if you do not pay attention to this problem, serious damage can be caused to other parts of the car.
If the cause of the error is not corrected promptly, the catalytic converter may be seriously damaged. Since the catalytic converter is an expensive part, it is very important that the cause of the problem be repaired as soon as possible. If the catalyst is destroyed, its remains may enter the engine cylinders, which will result in a major overhaul of the Ford or replacement of the unit.
Catalyst malfunctions
There are basically 4 signs of a bad catalytic converter:
- Burning check (as mentioned above, error P0420 during diagnosis);
- Decreased cravings;
- Unpleasant exhaust smell;
- Rattling sound from under the bottom.
Now about all the signs and symptoms of a faulty car catalyst in more detail.
The error about a faulty catalytic converter lights up only when the car has two oxygen sensors, and if there is only one (the one before it), then the lambda will not know that something has happened to the catalytic converter.
Regarding the speed, when the catalyst fails, the car begins to what is called “stupid”. There is a deterioration in the dynamics of the car, the engine power drops, and it begins to pick up speed poorly. In some cases, the speed arrow on the instrument panel may jerk or float at idle.
When the honeycombs are destroyed and chemical processes are disrupted, the exhaust gases can acquire a poisonous and pungent odor of hydrogen sulfide (also known as the smell of rotten eggs), very often drivers can complain about such odors while sitting in the car or if they sniff the gases emanating from the exhaust. If you have special equipment, you can measure the level of CO and CH; it will probably be overestimated. At the initial stage, minor contamination of the catalyst honeycomb may not be noticed, because the exhaust from low-quality gasoline will be similar. But the driver will need to press the accelerator pedal a little harder to compensate for the loss of power.
If it is completely sad and the catalyst has collapsed, then you will hear rattling, the strumming of scattered ceramic honeycombs or the hum of an empty barrel.
The listed causes of catalyst malfunction can manifest themselves both comprehensively and individually. When such signs of a malfunction of the car’s catalyst appear, it is necessary to repair the catalyst (cut out and install a flame arrester, you will need to install an additional blende) or if the network is replaced, the money must be exchanged for a new one. Since in this case the exhaust system becomes unable to function effectively, and this becomes a serious danger to the engine. Therefore, if the first symptoms of a faulty catalyst arise, you need to take some action and not let the situation worsen.
Most often, catalyst failure occurs for the following reasons:
- the operating rules have been violated (as specified in the manual). As a result, the ceramic core melts or the honeycomb becomes clogged with soot;
- the service life has expired, natural destruction of the catalytic layer or ceramic occurs during long-term use of the car.
- due to mechanical impact, for example, after an accident.
Tell me, if the catalyst is clogged, gasoline consumption may increase? - Engine
Thanks for the answer.
I just want you to understand.
that inserting a shaitan scanner into the ob2 connector is not an off-level service. EPTA INSERT THE PRESSURE GAUGE INSTEAD OF THE FIRST LAMDA AND SEE THE INCREASE IN PRESSURE TO THE CATALYST. this already seems like a normal answer. In this case - CDU - a clogged catalyst that does not reduce the CO rate, but also does not create back pressure. which can damage the engine. You can check it with a tea scanner. about the paired graphics lambda 1 - lambda 2. = (equal to) Shit gasoline.
ASS is a clogged catalyst that creates back pressure in the exhaust.
and taking into account the cost of these offs. services - I really want them to learn to distinguish between an EAR and an ASS.
AND DID NOT PISS SUCH COMPLETE DILLETANTS LIKE ME WITH OUR PRICES AND OUR STUPIDITY
ALTHOUGH THERE IS A MORE CORRECT WAY TO CHECK THE CATALYST. IT SEEMES TO ME HERE IS THE ALGORITHM: 1) Disconnect the wire from one of the spark plugs (then it is best to insert any spare spark plug into it and put it away on ground, optimally - turn off the corresponding injector) 2) Start the engine on the remaining cylinders (on 3, usually 3) Look at the stability of operation at idle and when revving up 4) Unscrew the disconnected spark plug 5) Start the engine again on 3 cylinders 6) Again evaluate the stability of operation and the intensity of the revving up. 7) If in step 6 the engine works much better than in step 3 and there is a powerful exhaust coming from the spark plug hole, then the exhaust system is seriously clogged...
CYLINDER WITHOUT PLUG AND COIL. IT WILL SMOKE. ALL THE SMOKE AND ALL THE BACK PRESSURE MUST GO THROUGH THE CYLINDER HOLE INTO THE ATMOSPHERE. THROUGH THE OUTLET VALVES. through the hole of least resistance. Vot.
Post edited by LIfe_Line: 22 October 2012 - 22:27
www.celica-club.ru
Self-test methods
If you know that your car has a high mileage or you are worried that the fuel you use may someday make itself felt, then it is worth checking once again whether the catalyst is clogged. It is not necessary to visit a service station. Whether the catalyst is clogged or not, you can check it yourself at home. There are several verification methods:
- The simplest method is visual inspection. It will take some effort to get the catalyst out. Because over the period of operation, bolts and nuts can rust and stick to the pipes. Let's assume that we managed to remove it. Since filters take the brunt of cleaning exhaust gases, we check them. The filter should be transparent. If you look from one end of the catalyst, you should see the sky at the other end. But sometimes the other end may be aligned with the exhaust manifold and may not be easy to view. Then we take a flashlight and shine it into the collector. If the light does not pass through, then the catalyst is clogged. Or, after removal, small pieces of metal and other rubbish fall out from inside - this is a sign that the catalytic converter is clogged.
- Checking for catalyst back pressure is the most popular method. To do this, you need to unscrew the oxygen sensor, and in its place screw in a pressure gauge through a special adapter (you can use a tube from the brake system). Having screwed in the pressure gauge, you need to start the engine and check the pressure at different speeds. If at 2500 the device shows 0.3 kgf/cm3, then this is the norm. A maximum of 0.5 is allowed. If it is more, then this already indicates that the catalyst is clogged. This method has one drawback - unscrewing the oxygen sensor requires effort. Since the bolts become covered with rust during use, it will be difficult to unscrew them.
- Checking the temperature of the catalyst requires a special electronic pyrometer device. This is a thermometer that is designed for remote temperature measurement. So with the help of this device it is necessary to measure the temperature of the catalyst in its different parts. Before checking, you should start the engine and warm it up (driving for about 20 minutes). Using a pyrometer, we check the temperature at the weld and at the place after the “catalyst”. If the temperature in two places is the same, or the temperature at the place after the “catalyst” is less than at the weld, then this means a malfunction;
- The most effective way to determine a malfunction is to measure the pressure using a motor tester. To do this, you need to unscrew one spark plug and screw in a special pressure sensor instead. At various speeds, pressure is measured and the results are analyzed by a motor tester;
- There are other ways to check. You can check for smell without removing the catalyst. If you smell a pungent odor, that's bad.
Advice! You can check whether the catalytic converter is clogged or not by another method: checking the exhaust gases at idle. What is needed for this? Just start the engine and increase the speed. The second person closes the exhaust pipe with his hand. You need to wear a glove on your hand to avoid damaging it. We create resistance to gases coming out of the pipe. If you feel resistance from gases from the pipe, then everything is fine with the catalyst. And if not, then it's clogged.
Notice that the “CHECK ENGINE” sign lights up. This may serve as a signal that the catalyst is clogged
And finally, dear car owners, watch the video on how to check if the catalyst is clogged:
- How to determine that it is the valves that are knocking
- Valve knocking: causes and consequences
- Why do car headlights sweat from the inside?
- Checking the clutch for slipping and wear
Signs and symptoms of a clogged catalyst - GlushakoFF on DRIVE2
Determining the signs of a faulty catalyst
Exhaust system catalyst - explanation. This component of the muffler system plays a fairly important role, since it is not only a kind of exhaust gas filter and burns out harmful CO2 impurities, but is also directly responsible for fuel consumption and the dynamic characteristics of the engine. A fairly common question arises among car owners in connection with the serviceability of the catalytic converter and the time it takes to repair or replace it. Let's start with how to determine as accurately and correctly as possible whether the catalyst is clogged and what its symptoms are without the help of special diagnostic equipment.
Destroyed catalyst symptoms
1) The first sign of a clogged or melted or destroyed catalyst is the degree (pressure) of exhaust gases leaving the rear of the muffler. Here you can understand whether your catalyst is clogged or destroyed, since if the catalyst is destroyed, the smell of the exhaust will be acrid and bluish, and if it is clogged, the exhaust will barely come out of the pipe.
2) The second and more common symptom is an unjustified, sudden increase in fuel consumption (taking into account a working engine and high-quality fuel). This is all explained quite simply, a faulty catalyst does not maintain the optimal afterburning temperature of exhaust gases (the normal temperature of a EURO-4 catalyst is from 350 to 750 degrees Celsius) and the injection system, by monitoring the oxygen sensor (lambda probe), automatically increases the fuel supply for temperature increases, but gasoline flies into the pipe and the temperature does not increase.
3) The next, also common sign of a clogged catalyst is the appearance of a metallic sound in the exhaust system during acceleration or brisk throttling. This incredibly annoying ringing comes from either the manifold catalyst or the secondary one (depending on their presence in the car), and this rattling and ringing is facilitated by a half-destroyed catalyst, or a completely clogged catalyst block that has moved from its seat.
Clogged catalyst - symptoms
• We will not talk about a decrease in acceleration dynamics and a decrease in draft characteristics in the topic of a clogged catalyst, since there are many reasons influencing these factors, and they can be a typical chain reaction, for example, to an injector that has not been cleaned for a long time or faulty spark plugs and coils ignition We can definitely say that if the car has lost low-end thrust, then you shouldn’t immediately blame the catalyst, you just need to carry out diagnostics and figure out the reason.
• Now we will tell you how to determine whether the catalyst is clogged or destroyed using diagnostic equipment. Here everything is a little simpler (if you have naturally defined devices, a diagnostic OBD cord and a program) and more understandable. Using diagnostics, you can immediately determine the malfunction of the catalyst based on existing ERRORS
. Also, every car equipped with a self-diagnosis system has a so-called CHECK ENGINE, a warning lamp that signals any malfunctions by turning on and not going out when the engine is running.
Here are the main and typical signs of a faulty catalyst in the exhaust system, with which you can diagnose whether it is worth replacing the catalyst
to a new or universal one, or remove it completely and put a flame arrester in its place.
Thank you for your attention, good luck on the roads. _____________________________________________________
Contact us by phone. in St. Petersburg: 988-77-91
Read our
BLOG
Visit our website:
GlushakoFF
Join our VK group:
GlushakoFF
www.drive2.ru
How to solve the problem of a clogged catalyst without expensive repairs
First of all, you should try catalyst recovery. It is possible to restore catalysts only if they have an intact structure and are free of mechanical damage. If the engine is operated in normal mode, when the catalyst is not clogged critically, it can be completely saved by cleaning it with a special mixture.
It is necessary to purchase a special catalytic converter cleaner, carefully knock out sections of the catalyst (the housing will need to be cut with further restoration) and process the knocked-out element according to the instructions of the manufacturer of the chemical composition.
Perhaps knocking out the catalyst is suitable as a temporary “emergency” measure, but not as a solution to the problem. On most modern cars, those same “lambda probes” are connected to the electronic engine control unit, and their readings are taken into account when preparing the air-fuel mixture. At a minimum, in this case you will have to reconfigure the “brain” of your engine to operate without a catalyst.
Causes of P0420 Ford error code?
- Damaged muffler or muffler leak
- Damaged exhaust manifold or leak in the exhaust manifold
- Damaged exhaust pipe or leaky exhaust pipe
- Ford engine misfires
- Catalyst oil contamination
- Faulty catalytic converter ( most common )
- Faulty engine coolant temperature sensor
- Faulty upper or lower lambda probe
- Damage to the wiring or connectors of the Ford
- "Overflow" fuel injector
- High fuel pressure
- Using the wrong type of fuel (using leaded fuel instead of unleaded fuel)