Why do my fingers knock in the engine when accelerating? Let's understand the problem
Drivers often wonder why their fingers knock in the engine when accelerating.
It seems that the engine is working normally, but at the same time the knocking noise still appears. Motorists are divided into those who do not react to this phenomenon; other people panic when such a sign appears and immediately rush to the nearest service center. In fact, both behavior options are not entirely correct. Such knocking can lead to serious problems, so you need to look for the cause and eliminate it. At the same time, most of the reasons that cause this behavior of the power unit can be easily eliminated even by an inexperienced motorist. Why do my fingers knock in the engine when accelerating? To answer this question, you need to understand why this phenomenon occurs. In normal conditions, ignition of the combustible mixture occurs evenly. Explosive combustion of fuel begins near the spark plug and simultaneously spreads in different directions. The explosion propagation speed is about 20-30 m/sec. In the event of detonation, the over-enriched mixture begins to explode immediately after entering the combustion chamber. The blast wave moves chaotically, colliding with the walls of the cylinder, the remainder of the mixture explodes. The wave speed can reach 1000 m/sec.
Consequences
.
As we have already found out, detonation is essentially uncontrolled combustion of fuel. At the same time, the cylinder walls heat up unevenly; in places where the blast wave hits, the temperature rises significantly. This can lead to deformation of the cylinder block. The piston may also overheat and become deformed. A blast wave under certain conditions can damage the valves. It can also damage the connecting rods. In any case, systematic and severe detonation will lead to the need for major engine repairs
.
Negative consequences of detonation
Detonation, by its nature, is destructive in nature, can lead to breakdown of various parts and assemblies, and can also become a fundamental reason for engine overhaul. Therefore, modern internal combustion engines operating at high speeds can fail in a short time, precisely because of detonation processes.
There is a very common misconception among car owners that an increase in pressure due to an increase in speed has a positive effect on increasing engine power. But the situation is exactly the opposite. The duration of the blast wave is very short (0.0001 s).
The same time is allocated to increase the pressure on the pistons. Consequently, they will not be able to affect the engine power in such a tiny amount of time. And it is quite likely to cause significant damage to various components and parts.
When the blast wave hits the cylinder walls with enormous force, it significantly destroys the oil film. This film protects the CPG parts not only from “dry” friction, but also from corrosion, so its destruction will inevitably lead to partial mechanical wear and damage to the parts.
In addition, when a shock wave is formed in a sharp form, the thermal output from the burnt gas begins to increase towards the cylinder walls, which causes overheating of the internal combustion engine. This, in turn, will affect the condition and performance characteristics of gaskets, seals, spark plugs, pistons, etc.
Causes and solutions
This phenomenon can be caused by a large number of factors. They have varying degrees of danger. Sometimes, a small detonation is quite acceptable. All possible options for the occurrence of this phenomenon will be discussed below.
The most harmless is detonation, which occurs with a sharp increase in speed. If at 1000 rpm
sharply depress the gas pedal, accelerating the work to
4000-5000 rpm
, then you can hear a short-term detonation. This is quite a common occurrence. There is no need to be afraid of this; in this case, detonation will not lead to dire consequences. The reason is a sharp increase in the fuel supplied to the engine; the amount of air initially remains at the same level, this causes premature oxidation of the fuel, which is accompanied by explosions. The only way to combat this phenomenon is to avoid a sharp increase in speed.
How to avoid?
It would be useful for every car enthusiast to know how to avoid problems with detonation. There are certain countermeasures that can reduce the risk of this type of knocking occurring. All techniques are usually aimed at preventing premature ignition of the fuel mixture. The easiest way is to increase engine speed. This can be achieved in several ways. When driving, try to increase the speed smoothly. If you want to start sharply, then first slowly spin the engine to the required speed, and only then start moving.
You can also reduce detonation by selecting the heat value. In this situation, select “hot” candles. They will allow the mixture to be burned more efficiently and without residue. In this case, no turbulence will arise here.
Conclusion
. Such a phenomenon as detonation always appears unexpectedly and can frighten car enthusiasts. In this case, they begin to wonder why the fingers in the engine are knocking during acceleration. In fact, there may be several reasons for this phenomenon. Moreover, not all of them can indicate a breakdown; sometimes these are design features.
Why do my fingers knock in the engine when accelerating? Let's understand the problem"
Why do my fingers knock in the engine when accelerating? Let's understand the problem
Why do my fingers knock in the engine when accelerating?
To answer this question, you need to understand why this phenomenon occurs. In normal conditions, ignition of the combustible mixture occurs evenly. Explosive combustion of fuel begins near the spark plug and simultaneously spreads in different directions. The explosion propagation speed is about 20-30 m/sec. In the event of detonation, the over-enriched mixture begins to explode immediately after entering the combustion chamber. The blast wave moves chaotically, colliding with the walls of the cylinder, the remainder of the mixture explodes. The wave speed can reach 1000 m/sec.
Consequences
. As we have already found out, detonation is essentially uncontrolled combustion of fuel. At the same time, the cylinder walls heat up unevenly; in places where the blast wave hits, the temperature rises significantly. This can lead to deformation of the cylinder block. The piston may also overheat and become deformed. A blast wave under certain conditions can damage the valves. It can also damage the connecting rods. In any case, systematic and severe detonation will lead to the need for major engine repairs.
This phenomenon can be caused by a large number of factors. They have varying degrees of danger. Sometimes, a small detonation is quite acceptable. All possible options for the occurrence of this phenomenon will be discussed below.
The most harmless is detonation, which occurs with a sharp increase in speed. If you sharply press the gas pedal at 1000 rpm, accelerating the operation of the power unit to 4000-5000 rpm, you can hear a short-term detonation. This is quite a common occurrence. There is no need to be afraid of this; in this case, detonation will not lead to dire consequences. The reason is a sharp increase in the fuel supplied to the engine; the amount of air initially remains at the same level, this causes premature oxidation of the fuel, which is accompanied by explosions. The only way to combat this phenomenon is to avoid a sharp increase in speed.
But sometimes detonation can appear during normal operation of the power unit. In such cases, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the malfunction as quickly as possible. Otherwise, it will lead to engine repair. So, detonation may have the following reasons:
What is engine knocking?
The appearance of engine knocking in most cases indicates that in the area of mating of certain parts there has been a critical increase in the gaps between the elements. If the engine lubrication and cooling systems are functioning normally, then noise and knocking begin to appear at clearances that, on average, are double or more times the permissible parameters. The strength of the knock directly depends on how much the gap has increased. It turns out that knocking in the engine is the impact of parts against each other, the load at the point of contact increases significantly. In this case, wear of parts occurs much faster.
The rate at which further wear increases will depend on the size of the gap, materials of manufacture, load, lubrication efficiency and a number of other factors. For this reason, some components can go through tens of thousands of kilometers with a knock without serious consequences (the timing belt), while others (CVM and CPG) can fail after just a few kilometers. In some cases, the engine may knock even if the clearances are normal and there is no serious wear on the parts. This knocking noise can be caused by:
- detonation and heavy loads on the internal combustion engine;
- distortions of parts inside the engine;
- jamming of individual elements;
- loss of protective and other properties by motor oil;
Fingers knocking in the engine: reasons
The piston pin is an integral element of the crank mechanism. This part represents the axis of movement of the connecting rod in the place where the connection with the piston is made. In other words, piston pins make it possible to create a movable, hinge-type connection in relation to the connection between the connecting rod head and the piston.
The loads that the piston experiences as a result of the combustion of the charge of the fuel-air mixture in the cylinders of the internal combustion engine are also transferred to the piston pins. At the same time, the finger is subjected to an inertial force, a bending force. In this article we will look at the reasons why fingers knock in the engine during acceleration, why fingers knock under load, etc.
Read in this article
Piston pins knock: why does this happen?
Let's start with the fact that the knocking of piston pins in an engine can be caused by several reasons. Conventionally, these reasons can be divided into two groups:
In the first case, knocking of the piston pins occurs due to wear of the loaded elements. It is also possible that mistakes were made during the repair of the internal combustion engine and installation of new piston pins. If otherwise, the fingers may not be the right size for the seat, or defects may have arisen during their installation. The result is that play occurs at the junction of the piston and the pin and a knock appears. These knocking noises can be easily heard when the engine is cold, and can also knock after warming up. The tapping sound is most clearly heard when the piston is at TDC and BDC.
In the second case, the driver can hear a distinct knocking sound of the piston pins, which occurs only under certain conditions. This phenomenon is called engine detonation and does not mean that there are any mechanical problems in the pin-piston-connecting rod connection. It turns out that your fingers are knocking on an internal combustion engine with a working timing gear. Let's figure it out.
If we imagine that during the upward stroke of the piston the mixture explodes rather than burns, then the speed of flame propagation increases greatly. The expanding gases press with enormous force on the bottom of the piston, preventing it from rising to TDC. As a result, the piston literally “staggers” in the liner, and the load on the crankshaft, including the piston pins, increases significantly. The driver hears a distinct metallic knock in the engine precisely at such moments, as the gas pressure in the cylinder increases greatly. At the same time, the engine power decreases, the engine begins to smoke and vibrate, and the temperature of the power unit rises. Note that detonation can occur in both gasoline and diesel engines.
Such an abnormal combustion process of the mixture destroys the internal combustion engine, leads to burnout of the pistons, breaks piston rings, etc. The consequences of detonation can be very serious, as engine parts experience a significant increase in load and are destroyed. Defects occur both at the bottom of the piston and at its head. The shock wave from the explosion of the fuel charge knocks down the oil film on the cylinder walls, resulting in wear of both the rings and the cylinder walls themselves. Vibrations from detonation combustion cause destruction of connecting rod bearings (liners); defects arise in the area of the partitions that are present between the piston rings. In a word, detonation can significantly reduce the life of any internal combustion engine.
Due to detonation, the fingers briefly knock during acceleration. This especially often manifests itself when the driver tries to accelerate while driving, for example, uphill, while remaining in a higher gear. This type of detonation is called finger knocking when driving under tension. In order not to overload the engine, it is necessary to promptly switch to the gear that corresponds to the driving conditions. All this depends only on the driver. In parallel with this, there are several other reasons why fingers begin to tap.
Knock - piston pin
| Diagram of the K-69 M NIIAT device. |
The knocking of the piston pins is sharply metallic, disappearing when the ignition is turned off. The presence of a knock indicates an increased gap in the interface between the pin and the bushing of the upper head of the connecting rod or the pin and piston bosses.
The knock of the piston pins is double, metallic and sharp.
The knock of the piston pin is rhythmic, high-pitched with a sharp metallic tint and is heard in zone 2 of the cylinder arrangement in all engine operating modes. It intensifies with increasing load. This knocking noise may disappear completely when the spark plug of the faulty cylinder is disconnected. If the knocking of the piston pins is heard in several cylinders, then to specifically determine them it is necessary to disconnect the high-voltage wire from the spark plug. Typically, knocking can occur for two reasons: due to too early ignition or a large increase in the gap between the bushings and piston pins.
| Places to listen to engine mechanisms. |
The knock of the piston pins is heard as weak, clear metallic blows. It can be heard well when the engine speed changes. A knocking noise can occur as a result of wear on the piston pins and holes in the piston bosses, or wear on the pins and holes in the bushings of the connecting rod heads.
The knock of the piston pins is sharp and metallic. Sometimes it is confused with knocking caused by detonation in the engine cylinders, but their nature is different. The knock of the piston pins, unlike detonation, is better heard at idle. As a result of intense wear of the connecting rod pin or head, the gaps increase, which causes knocking.
Usually the knock of the piston pins is double metallic and sharp; caused by excessive clearance and is best heard when the engine is idling.
To prevent knocking of the piston pins, which absorb large dynamic loads during operation, they are selected to the pistons and connecting rods with the minimum clearances necessary to ensure normal lubrication. Therefore, the diameter of the holes for the piston pin in the piston is made somewhat smaller than the diameter of the pin itself. Therefore, at normal room temperature, the finger sits in the piston not with a gap, but with a slight interference, which, when the piston heats up (in working condition), disappears and a gap appears instead.
| Tightening torques for bearings in KIM. |
Knocks that require immediate engine shutdown for repair include knocking of the crankshaft peaks and knocking of the piston pins. At the same time, detonation knocks (a high-pitched ringing blow) should not be mistaken for the knocking of fingers.
A sign of piston pin wear can be sharp, distinct, high-pitched knocks when the engine is running, significantly different from piston knocks. Piston pin knocking is caused by wear of the bronze bushing in the upper end of the connecting rod, an increase in the diameter of the hole in the piston bosses and wear of the pin.
During detonation, a loud knocking sound is heard in the cylinders, especially strong when the engine is running at full load. Detonation is usually mistakenly identified as piston pin knocking.
During hot running without load, check the oil pressure in the line, measure and, if necessary, adjust the minimum stable and maximum idle speed of the crankshaft. Using a stethoscope, listen to the engine in areas of possible knocking of piston pins, pistons, connecting rod and main bearings.
To prevent the appearance of residual deformations in the piston and damage to the seating surfaces under the pin, dismantling and installation of the piston pin should be carried out after preheating the entire set (during dismantling) or only the piston (during installation) in hot water to 70 C. Disassemble the pistons with piston pins selected for them at the factory are not possible, since this will disrupt their fit, which ensures normal operation of the joint: with a tighter fit than provided by the factory assembly, knocking of the pistons is possible on a cold engine, and with a less tight fit, knocking of the piston pins on a warm engine is possible .
Knock of piston pins: fuel, ignition and internal combustion engine temperature
As already mentioned, the piston is attached to the connecting rod using a piston pin, and it is necessary to realize the possibility of movement of the piston in relation to the connecting rod. The occurrence of increased loads leads to the fact that the fingers knock in the seats. If everything is in order with the crankshaft on the engine, then the main culprit is detonation.
Fuel in the cylinders may begin to detonate:
- as a result of general or local overheating of the motor;
- if there are problems with the composition of the mixture;
- refueling with gasoline with an octane rating that is inappropriate for a given internal combustion engine leads to detonation;
- if the ignition timing (IAF) is too early, then detonation also occurs;
- malfunctions of the ECM sensors (DPKV, coolant temperature sensor, knock sensor) can lead to explosive combustion of the mixture in the cylinders;
It should be borne in mind that engine detonation may well occur even on a new engine. If the temperature of the unit is normal and there are no problems with the operation of the cooling system, then the possibility of refueling with unsuitable fuel should be ruled out. Next, you need to start checking the ignition, mixture quality and electronic sensors of the internal combustion engine control system (on units with an injector).
Engine or valve clanging
Go to another dealer, otherwise you will “get through” to repair the engine.
The most important feature is that now the octane rating is the responsibility of the “respectable seller”
It’s great when the car is new, the engine runs quietly and you can’t hear it when accelerating with the pedal to the floor. But time moves inexorably forward and a moment comes when you notice that the former silence has simply disappeared, and under the open hood you see a bubbling monster, which previously emitted a pleasant singing, now offends your ears with something completely absurd.
Read more: How to properly connect running lights yourself
Noisy operation of a car engine is often associated with problems in the gas distribution mechanism: increased gaps and knocking always appear, like an uninvited pair of inseparable guests. The very first thing that might come to mind is to adjust the clearances in the valve drive.
Often this helps, but sometimes it may seem that the knocking has only gotten worse, because one or even several valves continue to knock. And at first glance it is not clear why this is so? The clearances have been adjusted and the camshaft looks quite good.
And the thought immediately comes to mind that the problem is not on the surface, but is hidden somewhere inside, but where? It’s about to be sorted out, but my hands still don’t get around to it, and the knocking gets louder and louder!
And sometimes there are completely unobvious problems, as a result of which it is not possible to limit yourself to just replacing the damaged part. In any case, before you start repairing or changing something, find the cause of a specific malfunction. Very useful.
Otherwise, very soon and quite unexpectedly, a recently installed mechanism may find itself in a similar situation. And to avoid this, it is better to be aware of the conditions under which it works.
The main reason influencing the appearance of knocking is the increasing gap between the camshaft cams and the levers. If the gap between these parts increases, the cam will knock on the rocker, resulting in extraneous sounds, like a metallic clatter.
The larger the gap becomes, the more wear and damage will increase, which will ultimately lead to complete failure of the entire internal combustion engine.
The gap between these parts is set by manufacturers depending on the make of the car, but is the same size for certain models.
A reduced gap is also bad, because in this case the valve becomes clamped, and after a certain time it will stop closing completely.
If you continue to drive with the valves not tightly closed or clamped, then you cannot avoid engine overheating, as well as a decrease in compression. The possibility of complete failure of one or even several cylinders cannot be ruled out.
In addition to improperly adjusted valves, knocking in the engine can also be caused by detonation of the power unit. Engine detonation is similar in nature to a micro-explosion, during which a fiery wave hits the cylinder walls and other elements of the piston group.
As a result of such impacts, valve knocking can occur. Remember also that sometimes a metallic clatter is not necessarily associated with damage to the valves.
The main signs characterizing the occurrence of detonation are: increased vibration, black smoke from the exhaust pipe or another unusual color of smoke, decreased power and overheating of the power unit.
1. Check not only the engine intake valve, but also the exhaust valve. First of all, ensure normal oil pressure and check all its basic characteristics.
2. If valve knocking occurs “when cold,” then this is the first sign that the pusher has worn out. If the tappets are dirty or leaking, they can cause insufficient oil flow to the valves. That is why during overheating a characteristic metallic knock can be heard.
If the oil pressure is normal, check the clearances; it is quite possible that valve adjustment will be required. The gaps are adjusted using special feeler gauges. They are installed in the gap between the rod and the rocker arm or the pusher and the cam, it all depends on the location of the camshaft. If everything you do is unsuccessful, then you should seek help from qualified specialists, otherwise you will ruin your power unit.
If the engine knocks on the way, it is unlikely that it will be possible to deal with it locally. You can check the oil level, because insufficient lubrication is associated with damage to parts, which causes knocking. Usually, after the oil is added to the nominal level, the knocking noise in the engine should stop.
Next, find out two things: whether the knocking noise increases under load and how quickly it increases as speed increases. If the answers are positive, then the crankshaft bearings are most likely damaged.
Continuing further movement with such a defect is very dangerous, because the engine will soon fail with the prospect of further repairs.
There was a knocking noise in the car’s power unit after it was filled with low-quality fuel at a dubious gas station. If the knocking is of a fading nature, then, as a rule, it is not dangerous.
Some of them can appear in the engine without visible changes for tens of thousands of kilometers. Therefore, to move further or not will depend on the increase in the intensity of the knocking.
If you notice this, then you should immediately stop driving and turn off the engine.
Cars typically may have two or more valves per cylinder. One of them launches the combustible mixture, the other releases exhaust gases. Accordingly, the valves acquired their names: intake and exhaust.
And the mechanism that drives these valves is called gas distribution or simply valve. Once the engine reaches high temperatures, the parts begin to expand.
Therefore (remember seventh grade physics) the engine in a cooled state must have gaps strictly defined by the manufacturer.
If the valves are adjusted incorrectly, this will lead to a decrease in engine efficiency and rapid wear of its parts. For example, if the clearance is too small, the valves along with their seats will burn. With large gaps the situation is different: the valves will not open completely, as a result of which the engine power will drop significantly, and you will hear a metallic clicking sound.
On average, every 25 thousand kilometers there is a need to adjust the valves. The level of knocking in the engine compartment often depends on the number of valves in the engine a particular car model has. Therefore, the more of them, the stronger the knocking when they wear out. In order to prevent this unpleasant noise, hydraulic tappets are used to maintain the valve clearances in a certain constant position.
— remove the valve cover;
- lift one wheel with a jack;
— install a device for pressing the valves;
— count where the intake and exhaust valves are;
— turn the wheel until the shaft elbow is at the top, and measure the gap at the first valve;
What's the result?
So, if your fingers are knocking during acceleration, your fingers are knocking under load, etc., then first you should:
- fill with high-quality fuel;
- check and adjust the ignition timing;
- eliminate problems with fuel supply that lead to a lean mixture;
- check the power system for possible air leaks;
- diagnose the operation of the engine cooling system;
- carry out diagnostics of the internal combustion engine and decarbonize the engine (if necessary) to remove carbon deposits from the combustion chamber;
Why does the fuel-air mixture detonate in the combustion chamber? Reasons causing detonation. Consequences of detonation combustion of fuel in internal combustion engine cylinders.
The most common causes of engine knocking are: piston knock, connecting rod knock, crankshaft knock. What to do if the engine suddenly starts knocking while driving.
The appearance of knocking noises in different diesel operating modes. Fault diagnosis. The nature of the knocks of the crank mechanism, timing gear, and fuel equipment.
What can knock, whistle, rustle and make other extraneous sounds under the hood after starting the engine. Diagnostics and determination of faults.
The design and purpose of the piston pin in the design of the crank mechanism of the internal combustion engine. Types, features of manufacturing and installation of piston pins.
Purpose of the piston in the design of the internal combustion engine. Features and design of the piston, oil scraper and compression rings.
Where does the knocking in the engine come from: how to find out
Specialists diagnose problem nodes by the nature of the knock, its tone and area of localization. A stethoscope is widely used for diagnosis. You can also make your own device for listening to engine knocks. To solve the problem, you will need a steel rod to which you need to solder a metal can. The bottom of such a container will effectively act as a membrane. To determine the cause of the knocking, the end of the rod is applied to various parts of the diagnosed internal combustion engine, while the can is pressed tightly against the ear.
The tone of the sound is an indirect sign, since on different engines the knock may appear louder or muffled. For example, the conventional knock of the crankshaft main bearings on a 1.4-liter Korean car may well be louder and easier to hear compared to the knock of connecting rods on a 3.0-liter German car. Often, the individual design features of each engine can cause a knock that has a different sound color, but the breakdown may be the same.
If we talk about diagnostics based on the nature of engine knocking, then it is worth highlighting a constant knocking, periodic knocking with one frequency or another, as well as occasional knocking. In the latter case, it is worth understanding the impacts that occur unevenly.
Engine knocking is usually associated with engine speed, that is, with the frequency at which the crankshaft rotates. The faster the engine spins, the higher the knocking frequency. The indicated frequency may or may not coincide with the crankshaft speed. It is also worth noting that the sound can become more or less intense (differ in strength) depending on the operating mode of the internal combustion engine.
For example, with an increase in the speed and load on the engine, there is a natural increase in the loads on the moving parts of the crank mechanism and the timing belt. In this case, the worn elements will knock more strongly than when the engine is idling. At this stage, when diagnosing, it is important to determine whether the knocking increases with increasing speed. This often requires experience, since it is necessary to listen for knocking against the background of the general increasing noise of the operating unit.
In parallel with this, it is necessary to separately take into account the fact that the oil pressure in the engine lubrication system also increases with increasing speed. In some cases, the engine oil itself acts as a “damper”, and the knocking itself may become less intense even with increased load on the engine. For this reason, an important parameter is the temperature of the internal combustion engine. The engine may knock heavily when hot because the oil is diluted. At the same time, the knocking may hardly appear when cold. The opposite situation also happens when the engine knocks distinctly when cold, but after reaching operating temperature the noise disappears or is minimized.
Engine fingers knock when accelerating
Any extraneous noise in a car engine should alert the driver. Even if the malfunction does not in any way affect the driving characteristics of the car, its very appearance should make the car owner think about diagnostics.
One problem that is often ignored by drivers is engine knocking. It appears when the car picks up speed, and if you do not pay attention to it, over time serious problems may arise in the operation of the motor. In this case, most often the driver can determine the reason why the engine fingers knock during acceleration, as well as correct the situation, without contacting a service center.
How to determine which hydraulic compensator is knocking - DIY car repair
The very definition of “knock of fingers” does not entirely correctly describe the situation that occurs in the engine when the problem in question occurs. There are no “fingers” knocking in the engine, and the sound itself comes from the impact of the blast wave on the cylinder walls.
During normal engine operation, the air-fuel mixture enters the combustion chamber, and its explosion occurs evenly, starting from the spark plug. In such a situation, the speed with which the blast wave propagates is about 20-30 m/s. If the engine has problems with detonation, that is, an excessively enriched mixture enters it, then it detonates immediately after entering the combustion chamber. The blast wave begins to spread chaotically and collide with the walls of the cylinder at enormous speed, up to 800-900 m/s.
The operation of an internal combustion engine is necessarily associated with the release of heat. As you know from a physics course, when heat interacts with a metal, it expands. Motor designers take this fact into account when designing them and provide thermal clearances. When calculating thermal clearances, special attention is paid to the valve mechanism of the car, where an error can lead to valve burnout or knocking in the engine.
So that car workshops and drivers can control the clearance, the engine valve mechanism has the ability to adjust it. It must be performed as the machine operates, since worn parts lead to a change in the gap.
Initially, adjusting the gap was done using washers and levers, which was extremely inconvenient and also too difficult for the end driver. Over time, designers proposed a more modern solution - the use of hydraulic compensators. These mechanisms independently select the required gap and do not require additional settings. But problems can also arise with them, and the most well-known of them is the appearance of a knock during engine operation.
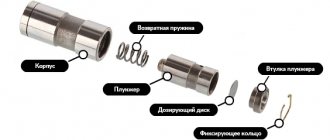
An automobile hydraulic compensator is a piston, with the bottom of which the camshaft cam interacts. The piston contains a ball valve, the task of which is to open the valve to allow oil to enter the piston cavity. The plunger is responsible for transmitting force from the camshaft cam to the valve stem.
During operation, oil enters the piston. It fills the free space, after which it begins to press on the plunger. This causes it to move upward along with the piston until the mechanism rests against the camshaft cam.
Thus, it is possible to achieve automatic selection of the optimal gap due to the hydraulic compensator mechanism.
When the camshaft cam presses on the hydraulic compensator piston, some of the oil pours out of it, after which the ball valve blocks the path of the oil, the piston moves down and a gap is created.
The hydraulic compensator, unlike washers and levers, does not require additional adjustment when engine parts wear out. In any case, the gap is adjusted due to the flow of more oil into the hydraulic compensator.
Read more: Why the scooter does not start, the starter does not turn and does not work: repairing the mechanism on a moped
A faulty hydraulic compensator is easy to determine. If there are problems with this element, it begins to knock during operation. The consequence of knocking of the hydraulic compensator is incorrect or untimely adjustment of the valve clearance, which can lead to problems with the engine.
The reasons why the engine hydraulic compensator knocks can be classified according to the conditions under which they occur. Depending on whether the hydraulic lifters are knocking on a cold or warm engine, the faults that can cause the problem differ.
Problems with the operation of hydraulic compensators can arise in two cases: if the mechanism itself malfunctions or due to problems in the oil supply system. On a cold engine, the following are the main reasons why hydraulic compensators knock:
- Element contamination. If the hydraulic compensator is dirty, the plunger of the mechanism may jam in the seat. There is also an increased risk of the ball valve sticking in the open position;
- Oil contamination. Dirty operating fluid, contaminated with friction products, will cause the hydraulic compensator to knock on a cold engine. Because of it, the oil supply channel may become clogged, but this problem will disappear when the engine warms up, due to the washing out of the “garbage” with the flowing heated operating fluid;
- Mechanical wear of the hydraulic compensator. If damage occurs on the plunger or its seat, the oil will not be retained in the sub-plunger space, maintaining the required pressure, and accordingly, the mechanism will not be able to work properly, providing the required clearance;
- High oil viscosity. When a car uses high-viscosity oil, before the engine is completely warmed up, it does not have time to reach the hydraulic compensators, which is why knocking occurs in them;
- Severely dirty oil filter. If obstacles arise through the oil filter, cold oil will not be able to fully flow into the cylinder head.
Important: It is necessary to distinguish between the knocking of hydraulic compensators on a cold engine and when the engine starts. Many drivers are mistaken in believing that if a characteristic sound is heard when starting the engine, there are problems with the hydraulic compensators. The knocking noise may occur and subside quickly because some of the valves remain open (due to the location of the camshaft) after the engine is stopped.
The reasons for the knocking of hydraulic compensators on a hot engine partially repeat the malfunctions that cause this problem to occur on a cold engine. Here are some problems that are typical only for a hot engine:
- The seating area of the hydraulic compensator has increased, and as the engine warms up, it becomes even more spacious due to the expansion of the warm metal;
- Problems with the oil pump. Most often, the malfunction is due to the fact that the oil pump does not produce the required pressure;
- Little or too much oil in the system. Because of this, the oil may become enriched with air, which critically affects the operation of the hydraulic compensator. A high air content in the oil leads to its compression during operation of the hydraulic compensator, and it begins to knock. This problem occurs only on a hot engine, since only as the engine warms up does the oil become enriched with air.
The situation when hydraulic compensators knock only on a hot engine rarely occurs. Most often, the problem occurs both on a cold and warm engine, and it is associated with bad oil, a dirty oil filter, or damage to the hydraulic compensator.
Since there are several hydraulic compensators installed in the engine, it is necessary to determine which of them is knocking during operation before replacing or performing detailed diagnostics. In service centers, the search for a faulty mechanism is carried out using a special device for measuring noise levels. Acoustic diagnostics is an effective method for finding a problematic hydraulic compensator.
You can also diagnose the hydraulic compensator on a disassembled engine. To check them, you will need to remove the valve cover, and then make an effort to push through each element individually. Hydraulic compensators, which can be easily recessed under external influence, have insufficient oil pressure, which indicates their malfunction. A jammed hydraulic compensator cannot be drowned using human power.
Important: Pay attention that during the diagnostic process the hydraulic compensators are not pressed by the camshaft cam.
Problems with hydraulic compensators do not have a strong impact on the wear of other engine components, but the solution to the problem should not be delayed. Troubleshooting of the hydraulic compensator should be carried out, since problems that arise may indicate a malfunction of the lubrication system.
Faulty hydraulic compensators themselves will lead to a decrease in engine power, deterioration in vehicle acceleration dynamics and an increase in gasoline consumption.
In most cases, knocking of hydraulic compensators is associated with problems in the lubrication system, which are caused by poor oil. Therefore, if extraneous sounds appear from the hydraulic compensators on a cold or hot engine, the first step is to change the oil and oil filter.
Please note: The first start of the engine after changing the oil will again be accompanied by knocking noises from the hydraulic compensators. This is due to the fact that after draining the old oil, the hydraulic compensators become “empty”.
If changing the oil did not help fix the problem, you need to determine which hydraulic compensator is knocking during operation. Having identified a faulty element, you can remove it from the engine and try to wash it in gasoline or kerosene, and then put it in place. This will help if the cause of the knocking lies in contamination of the hydraulic compensator.
Important: After washing, hydraulic compensators must be installed in the position where they were before removal.
(393 votes, 4.53 out of 5)
What does knocking fingers mean when accelerating a car?
The very definition of “knock of fingers” does not entirely correctly describe the situation that occurs in the engine when the problem in question occurs. There are no “fingers” knocking in the engine, and the sound itself comes from the impact of the blast wave on the cylinder walls.
During normal engine operation, the air-fuel mixture enters the combustion chamber, and its explosion occurs evenly, starting from the spark plug. In such a situation, the speed with which the blast wave propagates is about 20-30 m/s. If the engine has problems with detonation, that is, an excessively enriched mixture enters it, then it detonates immediately after entering the combustion chamber. The blast wave begins to spread chaotically and collide with the walls of the cylinder at enormous speed, up to 800-900 m/s.
Possible consequences
Underestimating the knock of engine piston pins leads to extremely unpleasant and sometimes very expensive consequences.
Detonation is actually an explosion. This is a destructive phenomenon that can cause damage to elements and components of the power unit. The most severe consequence of spontaneous combustion in the engine is the need to overhaul the internal combustion engine.
Modern engines, which constantly operate at high speeds, can fail in a short time precisely because of detonation.
When a blast wave hits the inner walls of the cylinder, the integrity of the oil film is disrupted. The purpose of the oil film is to protect the elements of the cylinder-piston group from friction, corrosion and wear. If the film disappears, even for a short time, active mechanical wear occurs. Parts are erased and the correctness of their operation is disrupted.
At the same time, detonation leads to an increase in engine temperature. And the temperature, which is uncharacteristic for internal combustion engines, provokes changes in performance indicators, destroys pistons, spark plugs, and deforms gaskets and seals.
Why is knocking fingers in the engine dangerous?
Fuel combustion elements moving chaotically in the cylinder increase the temperature of the cylinder walls. If the engine operates in this mode, then additional loads will be placed on all its elements. When the driver does not pay attention to the problem, it leads to the following malfunctions:
- Curvature of the cylinder block;
- Damage to the valve or connecting rods;
- Piston deformation.
The longer the knocking of fingers continues while the engine is running, the sooner the need for a major engine overhaul will arise.
Detonation and knocking of fingers in the engine: causes and solutions
Many motorists are concerned about the question, why do the fingers knock in the engine when accelerating the car? It is worth saying that the formulation of this question is initially incorrect.
Although the phrase “knock fingers” itself is very common, it is still incorrect. Piston pins cannot knock, but in fact we hear the sound of a shock wave of exploding fuel.
Fuel combustion in a working engine occurs sequentially. Starting near the spark plug, the flame gradually occupies the entire combustion chamber.
However, there is another type of combustion called detonation. During this phenomenon, the entire fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber explodes sharply, while the pressure and temperature in the engine cylinder increases significantly. Such an explosion is called detonation. And the knock from this explosion is the answer to the question of why the fingers knock in the engine.
There is also the concept of engine vibration, which is often confused with detonation. If detonation is associated with fuel combustion, then vibration is the process of vibration of the power unit caused by a malfunction of its installation.
Possible causes of engine knocking
It is worth noting that knocking may not progress at the same rate, that is, it may quickly or slowly intensify during operation. The list of main elements of the CPG, timing gear and crankshaft that can knock includes:
- knocking of the piston in the cylinder;
- piston pins knock;
- the camshaft knocks in the cylinder head;
- knocking of the crankshaft in the cylinder block;
- rocker arm and valve mechanism axis;
- valve and valve guide;
- valve and cylinder head;
If two timing parts, which are made of hard material, wear out, the engine may knock equally for a long period of time. If soft elements that work in tandem with parts made of harder material (main, connecting rod bearings, camshaft bearings) have worn out, then the extraneous sound will quickly intensify. Next we will look at the most dangerous engine knocks.
Currently reading
Installation and repair of the muffler resonator
How often to change the timing belt on a car: what you need...
The pistons are knocking
The sound of a knocking piston in the cylinders is localized in the cylinder block, has a dull tone (reminiscent of the sound of knocking on pottery), and may also be accompanied by clicks. It most often appears when it is cold, as well as at low speeds and when the gas is suddenly released while driving. After warming up, the knocking sound of the pistons on a cold engine disappears, as the piston undergoes thermal expansion. Usually the piston knocks when a gap of about 0.3 - 0.4 mm appears.
Piston pin knock
The piston pins knock loudly and high in tone, the knock is clearly metallic. It is clearly audible when changing the gas, as well as at the moment of releasing the gas or pressing the accelerator to accelerate. The localization zone is the cylinder block. Usually appear when there is a gap of about 0.1 mm.
Additionally, the malfunction is diagnosed by unscrewing the spark plug. With the spark plugs removed, fuel combustion in the cylinder does not occur, which means there is no load on the piston.
Let us add that such a knock also occurs as a result of using fuel that is unsuitable for this type of engine (detonation), as well as with a significant load on the engine at low crankshaft speeds (driving uphill in high gear).
We also recommend reading the article about why the engine may have a metallic knock when cold. From this article you will learn about the peculiarities of the knocking of the power unit before reaching operating temperatures.
Knock of crankshaft main bearings (liners)
This knocking noise occurs as a result of wear that appears on the crankshaft liners. The sound is metallic, slightly muffled, and localized in the area of the engine crankcase. It can be clearly heard at low speeds of a warmed-up engine (low engine oil pressure), when the speed rises sharply and when the gas is released. The gaps increase between the neck and the liner, amounting to about 0.1-0.2 mm. When the lubricant pressure drops to critically low levels, the knocking will be loud in all modes.
It should be noted that the crankshaft can also suddenly start knocking due to the use of low-quality motor oil or a lubricant that does not meet the manufacturer’s tolerances for this type of internal combustion engine. In this case, the oil must be changed immediately, and the lubrication system must be flushed before replacement.
Connecting rod bearings are knocking
If the connecting rod bearings are knocking, then the sound is similar to a similar malfunction of the main bearings, but can be heard more clearly. The appearance of such a knocking noise with a sharply increasing intensity when the crankshaft speed changes indicates the need for urgent repairs. It is prohibited to operate the engine with such a knocking noise, since the engine, in simple terms, risks “caught a wedge”.
Causes of engine detonation
The octane number of fuel is an indicator characterizing the coefficient of resistance of the fuel to ignition during compression (in other words, the detonation resistance of the fuel). Accordingly, an engine with a high compression ratio must meet gasoline with a high octane number. All modern engines have a high compression ratio, and if low-octane fuel is used in them, the likelihood of detonation is very high. Although high-octane gasoline is more expensive than low-octane gasoline, it is not worth saving on it.
Glow ignition is the spontaneous combustion of fuel in the engine cylinders. The reasons for this phenomenon may be burning soot or high temperature of the combustion chamber. It is also very important to select a spark plug with a suitable heat rating (there are “cold”, “medium” and “warm” plugs) so that the overheated insulator of the central electrode of the plug does not cause a fire.
A lean fuel mixture and an increase in the amount of air in the mixture compared to gasoline can also cause detonation. If a lean mixture enters the engine cylinders, it is much more likely to cause detonation than a normal mixture.
Detonation can also occur due to high engine load. Why the fingers “knock” in the engine when accelerating a car is precisely because the engine is overloaded. If you try at all, for example, to start right away in third gear, then with a high probability you will not even hear a dull knock, but a loud clang.
What's Really Happening
Before naming the reasons why fingers knock in the engine, you need to understand the essence of this expression.
Old cars actually quite often emitted an extraneous sound, the provocateur of which was the piston pins. This was due to the fact that the cars of those times were equipped with metal parts with low strength and resistance to wear during active use.
The fingers were exposed to high temperatures and increased loads. All this led to gaps appearing on the piston pin seats. It was because of them that extraneous sounds were formed, which were rightly called the knocking of fingers.
It will be useful: The headlights on my car are dim, what should I do?
But if we talk about modern cars, then in their regard the question of why fingers knock in the engine during acceleration does not sound entirely correct and correct. This is more a matter of habit and an established phrase.
Current automakers use high quality steel and use special processing technologies for all components. All this has led to the fact that the likelihood of a defect and damage to the finger itself is almost completely eliminated. If a finger on a modern car becomes deformed, then you will no longer have to think about eliminating the knock, but about a major repair.
Despite all the changes, the term has not disappeared and continues to be actively used.
Nowadays, finger tapping actually refers to sound vibrations arising from the shock wave that is formed when the air-fuel mixture explodes inside the combustion chamber. In short, this is engine detonation.
In the case of new cars, knocking fingers refers to detonation in the engine.
Regardless of which concept is convenient for the motorist to use, the problem requires mandatory and urgent intervention. You need to figure out how to determine if a finger knock appears directly in the piston (detonation), and how to deal with the current situation.
Methods to combat detonation
The engine has a special detonation damping system, which includes a special part of the engine control program, sensors and an actuator unit. The sensor is designed to respond to detonation. When it occurs, a voltage will appear on the piezocrystal plate of the sensor, depending on the amplitude and frequency of oscillations of the sound wave of the explosion. The control unit receives a signal from the sensor and, when detonation is detected, optimizes the operation of the ignition system until it stops. However, this system is not omnipotent. If the fuel is low-octane gasoline, it will not be able to help.
The engine is experiencing detonation: what to do?
The first thing to do when there are characteristic sounds coming from under the hood is to try to reduce the load on the car’s engine. You should not accelerate sharply and demand the maximum from the engine - this will only wear it out and shorten its service life.
If you use low octane fuel, you should switch to high octane alternatives. There is no point in buying expensive gasoline; regular 95 will do just fine. Just in case, check the high-voltage wires and spark plugs: it is because of them that detonation often occurs.
If none of the above helps, you should contact a car service for help.