The technical condition of the rear axle is checked in various driving modes: when starting from a standstill, free rolling, sharp acceleration and deceleration, engine braking, cornering and high speeds. Four tests are carried out.
I test. Move at a speed of 20 km/h so that the noise is clearly audible. Then gradually increase the speed to 90 km/h, noticing when the noise comes and goes. Next, monitor the appearance and disappearance of noise by braking the engine. Typically, noise is detected at the same speeds both during acceleration and deceleration.
II test. At a speed of 90 km/h, turn off the speed to listen to the noise when rolling freely until it stops. If the noise is the same as in the first case, then it is not caused by the gearbox, since noise does not occur in the gearbox without load. If the noise disappears during the second test, then there is reason to assume that the noise is caused by the gearbox or bearing.
III test. Listen to noises by increasing the crankshaft speed of the engine of a stationary car. If noise occurs, as in the first test, it is not caused by the gearbox, but, for example, by the air filter, muffler, engine or car body.
IV test. A noise noticed during the first test and not appearing during subsequent tests is greater. partly caused by the gearbox. To verify this, raise the rear axle, start the engine and engage direct transmission. This way you can be sure that the noise is caused by the gearbox and not by the suspension or body of the car.
Continuous noise in the rear axle is caused by:
deformation of the rear axle beam;
wear of the splines of axle shafts and gears;
Improper adjustment, wear or damage to bearings and gears.
If the noise occurs when the car accelerates, then:
differential bearings are incorrectly adjusted or worn;
the gear engagement is incorrectly adjusted when replacing gears or main gear bearings;
wheel bearing is damaged.
If the noise occurs when the car slows down, then:
the gear engagement of the main gear is incorrectly adjusted;
.too large clearance in the main gear drive gear bearings.
If noise occurs both when accelerating and when decelerating the vehicle, then:
the main gear drive gear bearings are worn or damaged;
there is no clearance in the meshing of the main gears.
If the noise appears when the car is moving around a turn, then:
the gearing of the differential gears is incorrectly adjusted;
the axle gears are jammed in the differential box;
satellites turn tightly;
There is a burr on the satellite axis.
If knocking noises occur when starting the car, then:
there is a large gap in the spline connection of the drive shaft and its flange;
there is a large gap in the meshing of the main gears;
The socket for the pinion axle in the differential box is excessively worn.
If noise is heard from the rear wheel, then the wheel bearing is worn or damaged.
To remove the axle shaft, remove the wheel and brake drum. A drum seized to the axle shaft flange cannot be knocked down with a hammer, as the brake disc may bend or even break the drum. In this case, proceed as follows. Unscrew the screws securing the drum to the axle flange and lift the rear axle. Start the engine, engage second gear and increase the speed to a speed of 30 km/h. When braking hard, the drum will be removed. However, this method is not entirely safe, since a slipped drum can injure people or damage the wheel arch. In this case, the differential may also suffer. Therefore, in a safer method, first the seating belt of the axle shaft is generously moistened with brake fluid. After some time, from the side of the brake flap (the car is on a ditch or overpass), through a wooden spacer, strikes with a hammer on the edge of the drum until it is removed from the axle shaft flange. When installing the drum, it is necessary to lubricate the contact surfaces of the flange and the drum with graphite powder, heat-resistant grease 1-13, or at least Litol-24. In this case, the drum will be easier to remove.
The axle shaft is knocked out together with the puller (196). If necessary, remove the axle shaft seal. Check the runout of the axle shaft. For a semi-axis installed at the centers, the runout of the worked surfaces should not exceed 0.07 mm, and the runout of the flange should not exceed 0.12 mm.
The wheel bearing is replaced if its radial clearance is more than 0.12 mm and its axial clearance is more than 0.70 mm. The bearing locking sleeve is pressed onto the axle shaft with such an interference fit that it
you have to remove it under a press or a special device. Since the bushing cannot be reused, it can be machined, milled or sawed to reduce the interference.
The bearing installed on the axle shaft is fixed with a new locking sleeve, which is heated to a temperature of 300 °C before installation. The temperature can be determined by the blue-violet color of the tarnish. The heated bushing is installed on the axle shaft so that its outer large chamfer faces towards the splined end of the axle shaft. Press the bushing onto the bearing using a pipe. After cooling, the bushing should not move under a force of 20 kN (2 tf). When pressing in new axle seals for a Moskvich-2140 vehicle, a mandrel (197) is used.
To remove the gearbox, the axle shafts are pulled out of the gears. The gearbox bearings are pressed out using pullers and mandrels. After washing, the parts are carefully checked. The meshing spot of the gear teeth should be in the middle of the tooth, the working surface of the teeth should be intact, without chipping. Since the main gears are produced for spare parts at the factory in selected sets, if there is a defect on one gear, both gears are replaced. Check the holes of the satellites, their axle, the journals of the axle gears, the holes in the gears and the support washers. Shallow marks are sanded with fine-grained sandpaper. Defective parts must be replaced. At the slightest suspicion of insufficient performance, the bearings are replaced.
When assembling the differential box under the axle gears
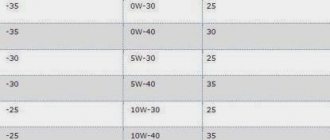
install support washers of suitable thickness so that the axial clearance of the gears is 0..D35 mm for ZAZ-968A cars, up to 0.2 mm for Moskvich, 0..10 mm for VAZ and up to 0.45 for GAZ-24 mm.
In order for the gearbox to operate silently and for a long time, the main gear bearings are installed with interference and the engagement of their gears is adjusted both in terms of clearance and the contact patch in the mesh.
The gearbox of the Moskvich-2140 car is assembled and adjusted as follows.
To ensure proper meshing of the gears, the distance from the end of the drive gear to the axis of the driven gear should theoretically be 53.4 mm. When gears are assembled at the factory, the correct contact patch and silent engagement are obtained by moving the drive gear along its axis. The height of the drive gear head can also vary within tolerance. The amount of these corrections is marked on the ends of the gears. If the amendment has a “+” sign, then it is subtracted from the size of 53.4 mm, and if there is a “—” sign, the amendment is added. The resulting size is the actual size when assembling a given pair of gears. Deviations within + 0.05 are allowed. -0.02 mm.
The clearance in the mesh is needed to compensate for temperature changes and deviations during the manufacture of parts, as well as to achieve the correct contact patch.
The engagement gap should be within 0.10. 0.22 mm, however, for a single pair of gears the difference between the largest and smallest clearance should not exceed 0.08 mm.
11.3 Repair of main gear and differential
Malfunctions of the main gear and differential have the following symptoms: increased noise when driving, knocking in the main gear, increased heating of the main gear housing (rear axle housing in cars with a classic layout) and oil leakage.
Increased noise while driving is a consequence of incorrect adjustment of the final drive gear pair, its damage, incorrect adjustment, wear or destruction of the bearings, as well as a decrease in the oil level below the minimum. The increased noise level is eliminated by adjusting the engagement of the gear pair of the main gear by selecting shims or replacing the worn gear pair and (or) bearings, as well as adding oil to the required level.
The cause of increased noise when turning a car can also be jamming of the satellites on the axle due to damage to the working surfaces in the places where the satellites fit on the axle. To ensure normal rotation of the satellites, it is necessary to disassemble the differential, remove minor damage to the working surfaces with fine sandpaper, or replace damaged parts.
The main gear and differential, as well as the gearbox, are among the most reliable elements of a car’s transmission, and the need for their repair usually arises after prolonged use of the car or in case of violation of recommendations for the use of oil or operating rules. A knock in the main gear occurs when there is a sudden change in driving mode due to wear of the supporting surfaces of the gearbox and differential gears. In this case, replacement of worn parts is required.
How does the differential on a car work when it fails?
Differentials are generally reliable little machines, but they also have to withstand all sorts of serious stress over the years. Differential failure symptoms will vary in type and severity depending on the vehicle, but most will display a standard set of warnings. Regular scheduled maintenance and inspection can prevent surge problems from occurring.
Broken or chipped teeth
Broken or severely chipped gear teeth usually cause some sort of "jump" in power transmission, which usually manifests itself as vibration that increases with speed. A broken tooth on your pinion and outer ring gears, which are always carrying power, will always cause jumping or vibration. A broken tooth on a gear is a “spider” – the gear will vibrate when turned in any direction; Broken teeth on axle gears will cause vibration when turning in one direction, but not necessarily in the other.
Several broken teeth
While you may hear some wheezing or banging noises associated with one missing tooth, you will almost certainly hear it when you have more than one. Teeth tend to break in sets of two or three in sequence. Each tooth that breaks increases the length of the skip and the intensity of the engagement, resulting in even more noise and vibration. This noise may alternatively be described as crackling, banging, or snapping, depending on the differences and the observer.
Special Features of the Mechanism
Broken teeth on one gear may not completely disengage the differential, but broken teeth on a ring or gear will do. On a gear, broken teeth will result in a complete loss of power transmission when turning one way or the other. Eventually, the gaps between the teeth will become so large that the gear will not engage at all, and the differential will officially fail.
Restricted Slip Symptoms
Limited slip differentials tend to lose their slip-limiting qualities as they wear. A traditional clutch type differential will lose the ability to transfer power to the slower spinning wheel, essentially turning it back into a standard "open" differential. Viscous clutch differentials, favored by some manufacturers, use a viscous, compression-sensitive fluid to transfer power. Once the fluid wears out, the differential will gradually be unable to transmit power while driving or turning.
Related articles:
- Will it hurt if you use a friction modifier on a sliding axle without restriction?
- Limited Slip Differential vs. Locking
- Differences between positioning and limited slip
- What are the differences between limited slip axles and limited slip axles?
- What is Posi Track?
- How to Identify a Limited Slip Differential
Disassembling the final drive and differential
To disassemble the single final drive of a GAZ-51, you must:
- unscrew the nuts of the studs securing the flanges of the axle shafts and remove the axle shafts 11;
- unscrew the bolts securing the two halves of the crankcase, separate them and remove the differential assembly;
- unscrew the bolts securing the cover 28 and seat 4 of the bearings of the main gear drive gear and remove the drive gear from the crankcase along with flange 1 and seat with bearings 5;
- Unscrew and unscrew the nut 30 securing the flange, remove the flange, oil seal 3, bearing cover 28, thrust ring, seat with bearing and shims 27;
- remove the tapered roller bearing from the drive gear shaft 2, remove the retaining ring and the cylindrical roller bearing 7 from the end of the drive gear;
- Unscrew and unscrew the bolts connecting the two halves of the differential cup 14, separate the cup, remove the crosspiece with support washers 24 of the pinion gears 8 and the semi-axial gears 19 also with support bronze washers 22.
To disassemble the double final drive of a ZIS-150 vehicle, you must:
- unscrew the bolts of the axle shaft flanges and remove the axle shafts 1;
- Unscrew the rear crankcase cover;
- unscrew the locking plates of the adjusting nuts 2 and b and unscrew the nuts;
Car suspension differential repair
| Removing and installing the differential | from 1600 rub. |
| Fixing differential leaks | from 800 rub. |
| Differential repair | from 6000 rub. |
| Replacing the differential | individually |
*** The prices presented on the website are not a public offer; you can check the cost of work with the car service manager by phone or at the technical center at Ekaterinburg, st. Artinskaya 17A.
| Submit a request for differential repair, our service center specialists will contact you as soon as possible and answer all your questions. | Order service |
The TransMax auto repair shop is a certified auto service center specializing in the repair of differentials.
Advantages of repairing and diagnosing differentials at the TransMax car service center.
PROFESSIONAL EQUIPMENT
The TransMax repair area is equipped with the latest technological innovations. For diagnostics, we use modern stands, as well as original scanners. Only high-quality equipment - machines, power tools, special kits, pullers.
CRATIFIED SPECIALISTS
TransMax employs only professionals. Each mechanic, electrician, diagnostician and car mechanic is highly qualified, has the appropriate rank and has extensive experience in car repair. Your car will be in good hands.
WORK WARRANTY 12 MONTH.
Thanks to the high professionalism of our employees and the use of high-quality spare parts and modern equipment, we guarantee proper operation of the vehicle after repair, subject to the rules of its operation.
Mechanics at the TransMax auto repair shop professionally repair differentials in Yekaterinburg. The work is carried out using exclusively high-quality parts from original production or trusted manufacturers. If signs of a unit breakdown appear, you should immediately contact the service: timely diagnostics and repairs will prevent damage to adjacent units, as well as large financial costs.
Signs of a broken differential
Since the differential is responsible for distributing the rotation speed between the axle shafts, damage to its parts will affect the controllability and maneuverability of the car. The following are noted:
- noise and hum in the transmission;
- grease leaks on the device body;
- shocks, blows and knocks during maneuvering; overheating of the device (case temperature > 60 C);
- bridge jamming.
If the car is equipped with a self-locking differential, then a sign of its malfunction will also be the wheels slipping on the axle. A broken forced locking differential will not respond to disconnection, which means there will be no rigid connection between the housing and the axle shaft.
Causes of differential failure
If the vehicle is used correctly, differential failure occurs due to natural wear and tear. The parts do not fulfill the declared service life for several reasons:
- damage to the differential housing;
- erasing the teeth of gears and satellites;
- wear of friction packs;
- cracking of seals or gaskets;
- loose or missing drive gear nut;
- backlash of the hypoid gear or drive gear;
- violation of roller bearing adjustment;
- The wheel alignment angle is not adjusted;
- wheel bearings are damaged.
As a rule, such consequences are caused by improper operation of the car: sudden starts with the wheels turned out, hitting the bottom against obstacles, or refusal of scheduled maintenance of the unit - replacing or maintaining the lubricant level.
For differentials equipped with an electric drive, the cause of the breakdown may be damage to the electrical wiring, a voltage drop in the network, a blown fuse, or a malfunction of the locking sensor.
Differential repair
TransMax mechanics identify faulty differential elements first on a lift, and then dismantle the unit and then disassemble it. Each element undergoes cleaning and troubleshooting. Lubricant leaks are eliminated by replacing sealing elements and adjusting fasteners and connections. Worn differential parts are replaced with new ones, since none of them can be restored, including the housing. It is worth noting that the driven and driving gears are replaced in pairs, regardless of which of them is worn out and which is not.
The cam (clutch) clutch in differentials with forced locking is restored only if the cause of the malfunction is wear on the cams, when they spontaneously disengage when the load increases. The surface of these parts is restored by grinding or milling. In other cases, the coupling is replaced as an assembly.
The electrics of the differential with automatic locking are repaired: the wiring, fuses or locking sensor are replaced. An experienced TransMax electrician will easily identify the fault and promptly carry out repairs.
By contacting the TransMax auto repair shop, our clients receive:
- competent specialist consultation;
- prompt and high-quality repair of differentials of any design;
- installation of only high-quality spare parts;
- repair warranty – 12 months regardless of the complexity of the work;
- the most reasonable prices for differential repair in Yekaterinburg.
Disassembling the final drive and differential
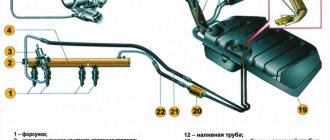
Rice. Main gear and differential of the GAZ-51 car: 1 - drive gear flange; 2 — drive gear shaft; 3 - oil seal; 4 — bearing seat; 5 — tapered roller bearings; 6 — rear axle housing; 7 — roller bearing; 8 — satellite; 9 — breather; 10 - oil seal; 11 — axle shaft; 12 — axle housing; 13 — brake pipeline; 14 — differential cup; 15 - drain plug; 16 - gasket; 17 — driven gear; 18 — differential cup; 19 — axle gear; 20 — differential bearing; 21 — oil deflector; 22 — bronze washer of the axle gear; 23 — differential cross; 24 — satellite support washer; 25 — support plate; 26 — gaskets for adjusting the drive gear bearings; 27 — gaskets for adjusting the engagement of the main gear gears; 28 — bearing cover; 29 — mud deflector; 30 - flange nut.
To disassemble the single final drive of a GAZ-51, you must:
- unscrew the nuts of the studs securing the flanges of the axle shafts and remove the axle shafts 11;
- unscrew the bolts securing the two halves of the crankcase, separate them and remove the differential assembly;
- unscrew the bolts securing the cover 28 and seat 4 of the bearings of the main gear drive gear and remove the drive gear from the crankcase along with flange 1 and seat with bearings 5;
- Unscrew and unscrew the nut 30 securing the flange, remove the flange, oil seal 3, bearing cover 28, thrust ring, seat with bearing and shims 27;
- remove the tapered roller bearing from the drive gear shaft 2, remove the retaining ring and the cylindrical roller bearing 7 from the end of the drive gear;
- Unscrew and unscrew the bolts connecting the two halves of the differential cup 14, separate the cup, remove the crosspiece with support washers 24 of the pinion gears 8 and the semi-axial gears 19 also with support bronze washers 22.
Rice. Main gear and differential of the ZIS-150 car: 1 - axle shaft; 2 and 6 — differential bearing adjustment nuts; 3 — bearing cover; 4 — differential cup; 5 — driven cylindrical gear; 7 — intermediate shaft bearing covers; 8 — gaskets for intermediate shaft bearings and bevel gear engagements; 9 — gaskets for adjusting the engagement of bevel gears; 10 — drive gear cup; 11 — spacer sleeve; 12 — bearing cover gaskets; 13 — bearing cover; 14 - flange; 15—oil seals; 16 — adjusting washers for drive gear bearings; 17 - intermediate shaft.
To disassemble the double final drive of a ZIS-150 vehicle, you must:
- unscrew the bolts of the axle shaft flanges and remove the axle shafts 1;
- Unscrew the rear crankcase cover;
- unscrew the locking plates of the adjusting nuts 2 and 6 and unscrew the nuts;
- Having uncoiled and unscrewed the nuts, remove the bearing caps 3 of the differential cups 4 and remove the differential assembly;
- unscrew the glass 10 and remove it together with the drive gear;
- disconnect the main gear housing, unscrew the covers 7 bearings of the intermediate shaft 17 and remove it from the housing.
Signs of a broken differential
If the drive axle is in good condition, the truck operates almost silently. Continuous knocking sounds while driving indicate a breakdown of the MAZ center differential.
Signs of trouble:
- Increased oil temperature;
- Noise;
- Lubricant leak.
If extraneous sounds appear on turns, the differential of the MAZ middle axle is damaged. Knocks appear when gears and other parts wear out.
If there is not enough oil in the crankcase, an unpleasant noise appears.
Causes of lubricant leakage:
- The lids are loose;
- Oil level is higher than normal;
- Ventilation breathers or pipelines are clogged.
Subsequently, the lubricant enters the differential through holes in the housing.
Repair of differential cup
Defects of the differential cup are:
- wear of bearing seats;
- wear of the holes for the journals of the satellite crosspiece;
- wear of the holes for the journals of the axle gears.
Worn seating areas of the differential cup bearings are restored by chrome plating, followed by grinding to the required size, as well as metal surfacing by welding. Surfacing should be carried out with heating to avoid warping of the cup. If the differential cup is made of steel, then cold expansion of the bearing seats can also be used.
Defects and restoration of differential cups on MAZ drive axle
The differential box cups are made of malleable cast iron KCh 37-12.
Cups are restored:
- in case of scoring, risks or uneven wear of the end under the washer of the axle gear;
- wear of the holes for the crosspiece tenons;
- scuffs, risks or wear of the spherical surface under the satellite washers;
- wear of the holes for the axle gear pin;
- wear of the journals under the differential bearings and for the right cup when the journal under the driven gear is worn.
Cups are rejected if they are cracked or broken.
The left and right cups of the differential box are rejected when the distance from the axes of the holes for the spider pins to the supporting surface for the axle gear is more than 47.2 mm.
In case of scratches, scuffing or wear of the spherical surface under the satellite washers to a size of less than 134.36 mm, the spherical surface is bored to one of the repair dimensions given in table. 55, and surface roughness Rz 20. The left and right cups are rejected if the size is more than 134.36 mm.
The left and right cups are structurally different from one another. Therefore, their repairs based on distinctive defects and sizes will be considered separately.
Before surfacing, the holes in the left and right cups of the differential box are cleaned to a metallic shine and the holes are welded alternately to a diameter of 22 mm with an electrode with a diameter of 4 mm. Then install the left cup on the studs of the right one, simultaneously aligning the holes with the mounting pins, and screw the nuts onto the studs, tightening them to capacity. The assembled cups are fixed in the jig and holes are drilled to a diameter of 23 mm on a radial drilling machine, two holes are countersinked to a diameter of 24.8 mm in a line and two holes are reamed to a diameter of 25+0.023 mm in a line and a surface roughness of 2.5 microns .
After this, the cups are disassembled and the sharp edges of the holes for the crosspiece tenons are filed down with a chamfer of 0.5x45°. Before disassembling the cups, it is necessary to mark with paint their relative positions, which are observed during assembly. The differential box cups are then assembled.
When restoring the differential box cups, the following requirements for the relative position of the surfaces must be met:
- the axis of the surface of the holes for the studs of the differential crosspiece must be in the plane of the junction of the cups - the permissible deviation is no more than ±0.05 mm;
- the axes of the surfaces of the holes for the crosspiece tenons must be perpendicular to each other with a deviation of no more than ±0.05 mm;
- the displacement of the center of the axes of the surfaces of the holes for the studs of the differential crosspiece relative to the axis of the surfaces for the journals of the semi-axial gears should not exceed ±0.05 mm;
- non-concentricity of the mating surfaces of the cups and journal for the differential bearing is allowed no more than 0.03 mm;
- non-perpendicularity of the supporting surface under the semi-axial gear and the surface under the journal of the semi-axial gear is allowed no more than 0.05 mm;
- non-perpendicularity of the differential bearing stop surfaces, cup connector and bevel driven gear flange (for the right cup) relative to the mating surface of the cups is allowed no more than 0.05 mm;
- the non-concentricity of the spherical surface under the satellite washers, the surface under the axle gear journal and the journal surface under the driven bevel gear (for the right cup) relative to the mating surfaces should not exceed 0.05 mm;
- the center of the spherical surface must lie in the plane of the cups’ separation with a deviation of no more than 0.05 mm.
restoration of the differential of the MAZ drive axle
Repair of satellite crosspiece
During operation, the necks of the satellite crosspieces wear out heavily in the landing areas.
To restore the seats of the satellite gears, the holes of the latter are ground or reamed until the correct geometric shape is obtained, and the journals of the spider are increased by chrome plating and the holes of the satellites are ground to the same size.
If it is impossible to apply chrome plating, the crosspiece necks are ground or ground with a cutter (after annealing the necks), and then cemented steel bushings are pressed onto them and ground to the size of the satellite holes. A more complex way to restore the necks of the cross is to deposit metal on them by welding, followed by mechanical processing and carburization.
wet business
The six-speed DSG with wet clutches (DQ250) appeared much earlier than the “dry” gearbox. The main modernization of the DQ250 took place in 2009, and after that it causes a minimum of problems - this is what they think at dealerships and the Moscow representative office of the Volkswagen concern. Unofficials do not agree with this and claim that in the first years after the modernization there were problems with mechatronics, similar to those that arose with the DSG7, but later the situation improved.
In 2013, the manufacturer partially changed the box body so that it would not interfere with the removal of the suspension arm bolt, and also updated the internal and external filters. In addition, new software versions and modifications to the wet clutch are periodically released—the unit has been upgraded for the fourth time.
Rapid wear of the differential bearings of a 6-speed DSG robot is a typical consequence of chip tuning and inadequate operation. | Overheating of the satellite axle and the monstrous destruction of its seat in the differential housing of the DSG6 gearbox are the result of passion for chip tuning and driving with frequent and prolonged wheel slip. Overheating of the satellite axle and the monstrous destruction of its seat in the differential housing of the DSG6 gearbox are the result of passion for chip tuning and driving with frequent and prolonged wheel slip. | Such serious destruction of the gears of the DSG6 exclusively indicates inadequate operation. The notorious chip tuning and frequent starts “to the floor” at traffic lights lead to such a disastrous result. Such serious destruction of the gears of the DSG6 exclusively indicates inadequate operation. The notorious chip tuning and frequent starts “to the floor” at traffic lights lead to such a disastrous result. |
Wet clutch robots have many advantages over dry clutches. However, the DSG6 also has serious drawbacks. For example, the oil circuit combines the clutch, mechatronics and mechanical part of the box - and often repairing the DQ250 involves replacing a bunch of elements. It happens that the wear products of the clutch get into the mechatronics and it starts to play the fool, quickly finishing off the clutch and the elements of the mechanical part of the box. Sometimes the participants in the conspiracy change places in random order. Hence the requirement from the factory to change the oil in the gearbox every 60,000 km. But it’s better to play it safe and reduce this interval to 40,000 km.
The second drawback of the DQ250 is known from classic automatic machines. Cars with DSG6 are contraindicated for prolonged wheel slipping - overheating of the oil leads to disastrous consequences.
With adequate operation, burnt or worn synchronizer rings are a fairly rare malfunction for modern DSGs. Typically, the service life of the rings is not less than the service life of the box. Nowadays, ring wear is much more common in conventional manual transmissions. With adequate operation, burnt or worn synchronizer rings are a fairly rare malfunction for modern DSGs. Typically, the service life of the rings is not less than the service life of the box. Nowadays, ring wear is much more common in conventional manual transmissions. | Replacing the sixth and reverse gear fork bearings in DSG7 is a fairly common procedure. It’s not for nothing that the manufacturer produces a corresponding repair kit. Replacing bearings in an unofficial service will cost 40,000–45,000 rubles - provided that the remaining “consumables” of the box do not require updating. Replacing the sixth and reverse gear fork bearings in DSG7 is a fairly common procedure. It’s not for nothing that the manufacturer produces a corresponding repair kit. Replacing bearings in an unofficial service will cost 40,000–45,000 rubles - provided that the remaining “consumables” of the box do not require updating. |
Most often, problems with DSG6 are caused by inadequate operation - engine chip tuning and aggressive driving. As a result, the clutch life is reduced several times. But it’s much worse that in such conditions the mechanical part of the box suffers greatly. For example, the teeth of gears and the main pair grind down - and wear products quickly kill the unit.
At the same time, the DQ250 feels great in circuit racing without any software intervention. You only need to change the oil in the middle of the season. But the hobby of “flying” in the city with a ragged driving regime often results in serious expenses: a full-fledged repair of the DSG6 from unofficials costs about 120,000 rubles.
WITH RESERVEFor a long time, specialists at unofficial service stations have noticed that the factory volume (1.7 liters) of transmission oil in the mechanical part of the DSG7 is not enough to fully lubricate some components. High gear gears, upper shaft bearings and reverse forks suffer from oil starvation, which is clearly visible when troubleshooting a tired robot. When repairing boxes and replacing the mentioned elements, servicemen fill in approximately 2.1 liters of oil. Practice has shown that with such a volume of liquid these parts last much longer. Moreover, an increased oil level does not cause side effects and does not cause oil seal leaks. With the last update of the DSG7 in 2014, the manufacturer moved the crankcase ventilation to the top of the case - a breather appeared there. In addition, unofficials noticed that the factory oil level has become higher, and its volume is approximately 2.0 liters. Q.E.D. |
Repair of gears, shafts and axle shafts
Worn and chipped gear teeth are repaired using the methods indicated in the note “Gearbox Repair.” Worn end surfaces of semi-axial gears and satellites are machined or ground, followed by installation of new washers that absorb axial load. In this case, the gap between the ground end side of the semi-axial gears and the inner surface of the cup should be 0.5-0.8 mm.
The gap is checked with a feeler gauge through the windows of the differential cup. The difference in gaps when measured in all windows should not exceed 0.1 mm.
Worn bearing seats on the drive gear shaft and on the intermediate shaft of the main gear are restored by chrome plating or turning, followed by pressing on steel bushings. The crumpled splines of the axle shafts and the drive gear shaft (if there is no twisting) are repaired by welding the metal, then the splines are milled and heat treated.
If the thread is broken at the end of the drive gear shaft or at the end of the axle shaft (GAZ-MM and M-20 Pobeda cars), the thread is cut off by turning on a machine, then the metal is deposited, machined to the required size and a new thread of the nominal size is cut.
How does a differential work?
— Rapid wear of the tires on each of the drive wheels,
— Poor road handling when turning the car (the absence of this unit will especially affect speeds greater than 70 km/h).
It is precisely due to the bevel differential on the VAZ 2110 and 2112 that it is possible to give a pair of drive wheels different rotation speeds. When they work together with the main gear, it is possible to reduce the speed, after which information from the gearbox is sent to the drive wheels.
You can find out about problems in the operation of this node by 2 symptoms in its operation:
- There is a hum in the gearbox when driving at high speeds,
- The appearance of a knocking or crackling sound in the bridge during a turn, even at low speed.
The cause of differential failure is most often damage and gradual wear of the bearing set. Also, damage to the oil seal and crosspiece can lead to problems in the operation of this element. The damage itself occurs either when the oil level in the system is insufficient, or during prolonged use of the vehicle.