Differences in tread pattern
One of the first important factors is the tire tread. A properly selected tread will maximize the contact patch with the road and help remove water and slush, preventing rubbing. Wheels can be either directional or non-directional or asymmetrical. They differ in their technical characteristics, production costs and recommended conditions of use.
Asymmetrical
One of the types of tires is rubber with an asymmetric pattern. Such tires, in fact, are two “assembled” wheels, made of two parts with different patterns, where one is intended for dry asphalt, and the second for wet pavement. Such products can be recognized by the “outside” marking on the outer part of the wheels .
The fact is that the external side experiences large overloads when performing maneuvers. Accordingly, the sides have different degrees of rigidity to ensure maximum traction between the wheels and the road surface. Due to their versatility and technological complexity of the process, such products cost 15-20% more.
Directed
You can often find rubber with a directional pattern. This type can be recognized by the “Rotation” mark on the side surface. The tire pattern allows you to effectively drain water from the wheels and ensure good contact with the road in bad weather conditions.
The main disadvantage of this type of car tires is the inability to quickly replace them without removing them from the rim. Therefore, it is recommended to carry with you a spare tire with a universal non-directional pattern, so that installation on the right front or left rear seat will not cause problems away from the service center.
Non-directional
The most affordable and common tires are sets with a non-directional tread pattern. This is a rubber of a universal design with a standard purpose. The characteristics of such tires are average, but their cost is low due to the simple technological process. Often cars come off the assembly line with just such wheels - concerns have taken this convenient rule as a basis.
Structure of a wheel and a car tire
A very important part of the car are the wheels, which, in fact, guarantee the movement of the car. In addition, the role of the wheels is to smooth out shocks when moving and coming into contact with uneven surfaces.
Basic Concepts
A car wheel consists of a disk with a tire rim. The rim is welded to a disk, which is attached to the wheel hub or to the axle axle using tapered bolts or nuts. On passenger cars, the rim with the disc is one piece, therefore it is simply called a disc.
A car tire can be tube-type, in which the rubber tube is filled with air, or tubeless.
A tire that does not have a tube is called a tire. It consists of a frame and tread, sidewalls and sides. The basis of the tire is a frame, which is made of cord. For the manufacture of cord, nylon, cotton, nylon, viscose, fiberglass, and metal wire are used. On the outside of the tire there is a tread that touches the road surface and consists of a dense layer of rubber with a specific pattern.
Tires are, so to speak, shoes for your car. As we select shoes for each season, we naturally focus on the model and style. In the same way, you should choose the image on the protector based on the conditions and time of use. A winter tire, for example, has an oriented tread pattern and rotates according to an indicator printed on its side. A tubeless tire does not have an air rubber inner tube. Therefore, between the tire and the rim there is a cavity that is filled with air and sealed. Therefore, the rim of a tubeless tire is equipped with sealing beads on the rim. It should be noted that tubeless tires are more practical as they can withstand multiple punctures and damage at the same time thanks to the sealing layer.
Depending on the carcass, the cords in the tire can be diagonal or radial. With a diagonal arrangement, the threads go crosswise and connect the tires diagonally, and with a radial arrangement, they run at right angles to the sides. Radial tires are more practical.
Possible problems
Note that if the car suspension is faulty, you can sometimes hear noises and knocks - this is nothing more than a consequence of weak bolts, wear of the hinges, breakage of the spring and shock absorber. To fix this, you need to check and tighten the fastenings of the suspension parts, and replace broken spare parts with new ones. It must be said that tires wear out more quickly and unevenly, especially if the angle of the front wheels is broken and there is wear on the suspension ball joints, unbalanced wheels, as well as an unacceptable driving style.
If the car pulls away from straight travel, you need to check the air pressure in the tires, the stiffness of the springs, the front suspension arms, the upper support of one of the telescopic struts, or the car's anti-roll bar.
In order to eliminate high vibration of a car when driving, it is necessary to replace damaged tires or wheel rims, balance the wheels, and replace ball joints.
autoremka.ru
Differences in tire design
The wheels also differ in the structure of the frame and breaker.
Under the rubber layer there is a frame responsible for the rigidity of the product. A large number of threads made of metal or nylon form a durable structure that determines the technical parameters of the wheel. In particular, the index of the maximum permissible load (kg) on one wheel depends on this. This parameter is indicated near the tire size. The larger the parameter, the more weight the wheel can carry. For example, the number 91, which corresponds to a certain maximum load of 615 kg. Sometimes the marking contains an additional Reinforced parameter, which indicates an increased number of cord threads, which increases the load index by three units.
Based on the type of weave, tires are divided into diagonal and radial.
Diagonal tires
Sometimes you can find bias-ply tires on cars. According to the classification, they are suitable for standard use at low speeds. A nylon or nylon thread is used as a base, which is covered with its own layers. The number of layers can be 2 or more.
Bias wheels do not have their own designation in the tire markings. If radial tires can be identified by the letter in the product size: tire size “P”, tire category, then the diagonal product has the sign “/”, which means just such a design. Due to the simpler production method, bias-ply tires are less expensive, but their performance is significantly worse than that of a competitor.
Radial tires
The most common are tires with radial cords. Metal threads form rings that do not intersect with each other, and the belt is equipped with an additional reinforced cord. Such tires are more preferable for a car, although they are more expensive.
- radial tires are tubeless - there is no tube inside, which is indicated by the letters TL (“Tube Less”);
- the reinforced design has a sidewall that is not so afraid of cuts and loads;
- the weight of such a kit is less, which has a positive effect on fuel consumption;
- have better thermal conductivity, which allows you to move longer at high speed on a flat road;
- under higher pressure it works better and is able to withstand 15-20% more load.
What is a car wheel made of?
If you want to know when the first wheel was invented, then you will not be able to find out the exact answer to this simple question, because this date is still unknown. In books and the Internet you can only find various assumptions on this matter. However, it is known for certain that in the fourth millennium BC a primitive wheel already existed.
The purpose of a modern automobile wheel is to convert the torque transmitted from the engine through the transmission into the forward motion of the vehicle, in this case, a car. Wheels can be driven, steered or supporting. In addition, if we take into account front-wheel drive cars, the steered wheels are also driving wheels. Since the wheel has some elasticity, it partially absorbs minor unevenness in the road surface.
If the first wheels were made of wood or stone, then the modern car wheel has a very complex structure that every car enthusiast should know. The wheel of a passenger car in the version in which we are accustomed to seeing it consists of the following elements:
- rubber tire (tire);
- thin rubber chamber;
- air valve;
- wheel rim.
Today, most passenger car wheels are not equipped with outdated tubes, and air is pumped directly into the space between the tire and the rim. much more practical, durable and reliable than the chamber version.
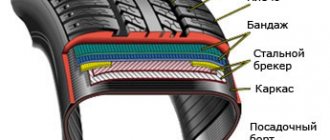
Structure of a car tire
The tire of a modern wheel in the process of evolution has turned into a product with a rather complex internal structure. A standard tire consists of the following parts:
- tire tread;
- frame (cord);
- side part;
- board.
The basis of any tire is a strong frame or, as it is also called, . Many people mistakenly believe that cord is the steel wire in the tire beads. This is partly the correct opinion, however, the cord is located over the entire area of the tire and is attached to the steel wire in the beads. The frame can also be made of wire or nylon, nylon and similar materials.
Modern car tires according to the type of frame are divided into. It is very easy to distinguish a radial tire by the presence of the letter “R” in the marking, for example 185/60R14. In addition, on such a tire you can see the inscription “Radial”. Diagonal tires are very rarely found on the market, because in many respects they are inferior to modern radial tires.
As for the internal structure, the carcass threads in a bias-ply tire are arranged diagonally, and each subsequent layer intersects with the previous one. In a radial tire, the carcass threads are simply stretched from one bead to the other without crossing.
A tire with a radial carcass is more resistant to wear, which accordingly indicates a longer service life before the tread wears out. In addition, radial tires have minimal rolling resistance, which has a very positive effect on fuel consumption.
- This is the upper part of the tire that is in contact with the road surface and provides reliable traction. The tread of any tire is a layer of rubber of a certain thickness with various pattern configurations. Actually, the pattern means a very complex relief, consisting of grooves, furrows and protrusions.
The tread pattern of each line of tires is developed individually to ensure maximum grip on the road surface, depending on operating conditions.
At the moment, there are car tires with road, universal off-road and other tread patterns. However, regardless of the pattern configuration, all tires are divided into summer, winter and so-called all-season. The tread of winter tires has a deeper and more embossed pattern than summer tires. In addition, the top layer of a winter tire is made of softer rubber. All-season tires are a kind of marketing ploy and in terms of road grip quality they are comparable to summer tires.
Wheel rim
The connecting link between the tire and the hub is the wheel rim on which the tire itself is mounted. A disk with a tire on is a wheel assembly, which is secured to the hub using bolts or nuts. Currently, the most common and cheapest are stamped metal discs. However, to improve the appearance of the car and to reduce the weight of the wheel, wheels cast from aluminum alloys and so-called forged models are used.
Dimension (marking) of tires and wheels
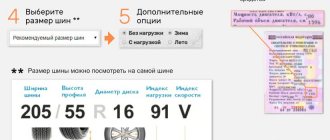
The operating instructions for each vehicle contain information about the size of tires and wheels. Each car tire certainly has a marking that can be seen on its side. The marking contains information about the width and height of the profile, seat diameter and type of tire.
For example, the marking 180/60R14 is deciphered as follows:
- 180 – profile width, measured in millimeters;
- 60 – percentage ratio of the height and width of the profile, in this case the height of the profile is equal to 60% of its width;
- R – radial tire;
- 14 – tire diameter, measured in inches (one inch equals 2.54 centimeters).
It is worth noting that the profile width is not a strictly regulated size. For example, in winter it is advisable to use tires with a narrow profile, and in summer - with a wider one. However, you should not deviate too much from the recommended values, because contrary to expectations, a tire that is too wide on a standard rim can impair handling.
Wheel rims also have size markings. For example, consider the following marking: 5.5J*14 ET49 PCD4*100 D56.6 in which
- 5.5J – disk width, measured in inches;
- 14 – diameter of the tire seat, also measured in inches;
- ET49 – disc offset, measured in millimeters and indicates the distance from the longitudinal axis of the disc to the plane of the hub. The higher the value, the deeper the wheel is recessed into the arch;
- PCD4*100 – the disk has four holes for fastening to the hub, the distance between the axes of the holes is 100 mm;
- D56.6 – diameter of the central centering hole in millimeters. This parameter must correspond to or exceed that specified in the operating instructions (centering rings will be required).
A little about the operation of tires and wheels
It should be remembered that proper operation can greatly extend the life of both tires and rims. Before each trip, regardless of the distance, the condition of the vehicle's wheels should be checked by visual inspection.
Under no circumstances should tires have visible damage or bumps. If you notice a cut or an unnatural bulge on the side of the tire, then you should replace the wheel with a spare tire and visit a tire shop for troubleshooting and possible repair of the damaged wheel.
Driving on damaged tires is unacceptable, because such a tire is likely to simply explode at high speed. And an instant loss of pressure is fraught with undesirable consequences. In addition, you should constantly monitor the tire pressure, which must strictly correspond to the recommended one. Both high and low pressure have a very negative effect on tire life and vehicle handling.
v-mireauto.ru
Seasonality of tires
Driving safety is affected by what tires the driver uses in a given season. According to the classification of car tires, rubber is divided into three categories:
- summer;
- winter;
- all-season.
Summer tires
The basis for the manufacture of any type of summer tires are hard grades of rubber compounds. Due to this, the tires feel great at very high speeds, providing effective traction. Products can be recognized by a smooth profile with a maximum contact patch, a developed cooling system and the absence of additional markings.
However, such tires are poorly suited for driving at negative temperatures. Even at air temperatures below 7, any summer tire is already “tanning” and simply does not cling to the asphalt. In such conditions, such tires will have an increased braking distance and incorrect reactions to maneuvers. So summer tires are not suitable for winter driving.
Winter tires
In winter, the car must be shod with special tires based on soft rubber. Such sets are indicated by a snowflake pictogram or the letter W-winter on the end of the product.
There are studded and non-studded tires. The first ones are equipped with special metal spikes and are excellent for driving on icy surfaces. However, such wheels spoil the road and quickly wear out when driving on asphalt, so their use is justified only if you must often drive on ice in winter.
Modern expensive winter Velcro can provide excellent handling 90% of the time. Winter tires are divided into Scandinavian and European types. The first has a developed pattern that allows it to cling to loose snow and is suitable for harsh snowy winters. The second is aimed at mild climates and feels great on cold, wet asphalt or slushy snow.
All-season tires
The classification of tires and wheels puts all-season tires into a separate class. Tires are designated by the letters M+S, AS or 4S (Mud+Snow, All Season, 4Season). All-season tires are a compromise solution for the driver, however, they are not a panacea for all ills.
Such kits are most effective when the thermometer is near zero. If the air temperature is below -10, then such rubber also becomes tanned, and at high temperatures it “floats”. In winter, snow chains can come to the rescue, but it is still better to have two sets of profile tires. Tires without rims should be stored in their place in a vertical stack and in a dry place.
Differences in seasonal patterns
Everyone wants to buy a set of tires of excellent quality, but at minimal cost. To understand in general terms what to pay attention to, first let’s look at the differences between winter and summer models.
Tires designed for hot weather are made from harder rubber than winter models. This nuance is due to high speed and temperature conditions. Soft rubber used in winter tires deteriorates significantly faster in summer. In turn, summer tires in the cold will also not be able to provide high-quality grip, since they will literally “stiffen”.
In addition to the composition of the rubber mixture, the tires in question differ in tread depth and pattern. Also, almost all winter models are laminated, and many of them even have studs, which provide improved traction on ice and compacted snow. But such tires with spikes do not behave well on dry asphalt, where their performance drops noticeably, and the spikes often fly out.
All-season tires are a kind of compromise between summer and winter tires. At first glance, it is a universal tire that demonstrates decent performance all year round, and therefore does not require replacement in the off-season. However, practice shows that such tires are noticeably inferior to both summer and winter models in the corresponding periods, demonstrating very average results. Therefore, all-season tires deserve the attention of those motorists who live in regions with mild climates, such as the Mediterranean, where annual temperature changes have a small range.
Types of profiles
Another important technical characteristic of the tire is the type of profile.
This determines the conditions under which the tires can be used. The tire profile is indicated in the wheel size. There are two types of classification - European and American. European marking, for example, 195*45*R17. For passenger cars, 195 is the tire width, 45 and 17 are the profile width and bore diameter. American - 32*11*R17 - says what the outer diameter of the wheel is, then the tread width, and then the diameter of the rim.
Low profile tires
Low profile tires are more suitable for dynamic driving. Thanks to the small ratio of the profile height to its width, the maximum contact patch is ensured. This allows you to realize the potential of the engine, improve handling and reduce braking distance. True, such wheels, due to their design, are less comfortable.
Wide profile tires
Wide-profile tires have a more developed pattern, feel better on wet asphalt and are less prone to aqualpanation. These tires are softer and will better protect the disc when it gets into a hole. The degree of wear of the pattern is indicated by TWI symbols. This indicator is located in various places and will allow you to determine the time for timely replacement.
Main characteristics
When choosing summer tires for your car, be sure to pay attention to the characteristics that car enthusiasts consider the most important, and on the basis of which manufacturers present their products on the market. The first thing that catches your eye is the price. It is formed based on the marketing positioning of the product, the quality and composition of materials, tread pattern, novelty of the model and, of course, the brand.
The following are the characteristics:
- Clutch efficiency (dynamics of braking and acceleration).
- Exchange rate stability.
- Noise comfort and smooth ride.
- Wear resistance.
- Controllability.
- Resistant to slashplaning and aquaplaning.
- Maximum permissible loads and speed.
- Stability in corners.
- Tire weight.
Currently, not a single manufacturer has yet created a tire that could become a standard, demonstrating all the listed characteristics at the highest level. The reason for this is the mutual exclusion of some of these parameters. Based on this statement, only one conclusion can be drawn - for each driver and car, the best option will be the tire that is selected in accordance with the requirements of the car manufacturer, the driving style of its owner and the objective road conditions of the area where you have to drive most often. Having correctly assessed the real capabilities of the vehicle and your preferences in driving style, you will certainly buy summer tires that will be ideal for you.
Wireless run-flat technology
Continuing the conversation about what types of car tires there are, it’s worth remembering puncture-free tires with an All Steel tread pattern and hard sidewalls.
Often European automakers equip their cars with such kits as standard. Due to their special design, such wheels can travel 80 km with no tire pressure at all. Moreover, after repair and installation of the wheel in its place, the tires will remain suitable for use. You can recognize such products by the RF (Run Flat) marking on the inner cover.
Radial tires
more elastic and therefore passengers feel more comfortable while the car is moving. Radial tires also have low rolling resistance and can last longer than diagonal tires.
But radial tires still have a drawback, and how can there be no drawbacks! The downside is the low strength of the sidewalls; tires fail upon contact with a curb stone, and such damage is usually caused by the so-called damage commonly known as “hernia.”
The tire must be chosen according to the driving style and its operation, so every car enthusiast must, before making a choice, decide on the answer to the question: “what tire should be on the wheel of my car?”
For SUVs and crossovers
There is also a classification of tires by purpose.
Various additional inscriptions may indicate this. For example, the letter P indicates that it belongs to passenger vehicles, T indicates tires for trucks. This classification allows you to find the best car or truck tires. And kits for SUVs or crossovers are identified by the letters AT (All Terrain). When choosing shoes, carefully look at the maximum speed index. The value in km/h is indicated by a Latin letter next to the maximum load index. A special table will help you understand the definition.
Dimensions
When choosing tires, you should be guided by the parameters recommended by the car manufacturer. On the sidewall of each tire there is a large amount of information that gives an understanding of the purpose of the tire and its geometric dimensions.
Decoding of the digital and letter values of the standard size : 205/55 R16 94V XL, where 205 is the width of the tire along the sidewalls (not the tread!) in millimeters, 55 is the profile , that is, the height of the tire as a percentage of the width, 16 is the diameter of the mounting hole in inches, internal diameter of the tire, 94 - load index (the maximum weight that the tire can withstand), V - speed index (in this case - 240 km/h), XL - reinforced tire carcass .
Driver tips
In conclusion, let us give you some advice.
- Search the Internet for reviews about the tire model you like, and also study the results of various tests in which it took part.
- Give preference to tires with reinforced sidewalls, which will withstand a powerful impact and avoid tire puncture.
- Take a closer look at car tires, which make it possible to save fuel, especially if the car is used constantly and for a long time.
- Buy tires, both summer and winter, produced by a well-known brand. The increased cost is a small price to pay for guaranteed quality, durability and safety.
Video on the topic:
Bushing Lubrication
You need to pay attention to the bushing immediately after the tires begin to rotate more tightly and (or) extraneous sounds appear while driving. Maintenance depends on what type of device is used (on industrial or bulk bearings).
Bulk bearings
The frequency of changing the lubricant is every 1-2 thousand kilometers. To lubricate the bushing, remove the wheel. The tire and tube should not be dismantled; they do not interfere with the lubrication process.
- Remove the eccentric, unscrew the nuts on the axle;
- After removing the axle, remove the bearings, preferably using tweezers;
- Wash the bearings thoroughly with gasoline or white spirit;
- Wipe the axle and bearing seat clean;
- Carefully inspect the bearings. If they are damaged, replace them with new ones. Check if the axle is bent. The “weak link” in this regard is the bushing axles;
- Using grease, lubricate the bearing seats, then install them in place. Lubricate the bearings themselves to ensure smooth rotation.
Now all that remains is to insert the axle and tighten the nuts of the structure. There is no need to be overzealous. The main thing is that the wheel does not dangle during installation.
Industrial bearings
To begin, knock out the axle from the drum side. As a rule, one bearing is knocked out along with the axle. Then knock out the second one, after inserting a screwdriver into the sleeve. Remove the drum and lubricate all seats. If the industrial bearing needs replacement, install a new one. The assembly is carried out according to an algorithm.