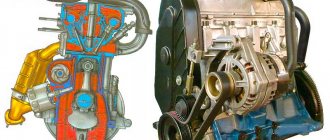
Toyota Corolla engine , or rather the engines that are installed on Russian versions of the Toyota Corolla sedan are very interesting. Firstly, they are all gasoline and are of the same design. These are in-line 4-cylinder, 16-valve units with an aluminum cylinder block and timing chain ! In addition, the design uses a double variable valve timing system VVT-i. Which makes the performance of Corolla engines quite good. The main advantage is, of course, real efficiency with good dynamics. In addition to the chain drive in the timing belt of the 11th generation Corolla engines, there are also hydraulic compensators in the cylinder head, which deprives you of the “pleasure” of adjusting the valves manually. Among the shortcomings, we can note the poor maintainability of these power units. The manufacturer simply forgot about the repair dimensions. In fact, full-scale production of power units has been established in China at the FAW plant. The power units get under the hood in Turkey, and from there the finished cars are transported to the Russian market.
Below are detailed technical characteristics of each Corolla engine.
Engine tuning options
The naturally aspirated 4S FE engine most often has underrated performance on cars for export to Europe.
Mechanical tuning to get 200 hp. With. costs much more:
- you will have to buy an intercooler to cool the air to increase the compression ratio;
- instead of the standard exhaust manifold, a direct-flow exhaust and a “spider” are mounted;
- The intake tract channels are polished and a zero resistance filter is used.
Tuning 4S-FE
Supercharged tuning will cost even more, and the service life of the ShPG and cylinders, valves and crankshaft will sharply decrease. In addition to installing the turbine, you must perform the following steps:
- porting of the cylinder head (grinding irregularities to reduce aerodynamic losses);
- changing the exhaust shape and installing high-performance injectors;
- turbo kit and replacement of camshafts with wide-phase modifications;
- setting up systems, changing the program control controller.
Thus, the 4S-FE motor initially has a high service life. Designed to assemble C, D and D+ class sedans for the Japanese and European markets.
Which motor is better
As can be seen from the history of the model, only three types of engines were installed on the car of this series. And the manufacturer at one point refused to use the four-liter one - this fact should raise alarm bells. If you suddenly come across a car with such an engine, then you shouldn’t buy it - there won’t be any big problems with it if it was operated in careful hands. But only now it is very difficult to find any spare parts for it due to its not very widespread distribution.
It has a huge resource, but if the mileage is already several hundred thousand, it’s worth thinking about whether you need to buy such a car. This engine, by the way, was installed on the Toyota Soarer and Crown Majesta.
The 2JZ-GTE engine with two turbines is the most worthy of the entire line. But when buying, you should not forget that more than 15 years have passed since the last car was released, and turbines tend to break down. Repairing them is a very expensive business. The same exact motor can be found on those produced in the period 1993-2002. Toyota Supra.
The “simple” six-boiler 2JZ-GE has a very high reliability indicator. Owners of cars with this engine noted its reliability and simplicity - no problems with turbines, and they often carried out repairs and maintenance themselves. This engine was installed on the Crown, Cresta and Altezza models.
Read: Review of Toyota Corolla 2010-2012
4S FE Engine Performance
Technical characteristics of the Toyota Land Cruiser Prado Toyota Land Cruiser Prado 2.7 AT 163 hp
4WD Toyota engines have a good service life before repairs. The mileage declared by the manufacturers before major repairs is 300 thousand km. With proper care and timely maintenance, the resource of the unit can be increased to 500 thousand km.
The engine design allows for a major overhaul with boring the block and replacing the cylinder-piston group to the next repair size.
For the SFE engine, the instructions provide the following repair sizes of pistons:
- Nominal – 82.457-82.467 mm;
- First repair (0.5) – 82.937-82.967 mm;
- Second repair (0.75) – 83.187-83.217 mm.
The need for repairs can be determined after comparing the actual and maximum clearance of the cylinder-piston group:
- Actual – 0.053-0.073 mm;
- Maximum – 0.120 mm.
In many ways, the service life of the engine depends on high-quality and timely execution of in-line repairs.
Subtleties of repair and purchase of a contract motor
Also, during the operation of 5A-FE motors, minor shortcomings are revealed:
- the engine is prone to high wear of camshaft beds,
- fixed piston pins,
- Difficulties sometimes arise with adjusting the clearances in the intake valves.
However, a major overhaul of the 5A-FE is quite rare.
If you need to replace the entire motor, on the Russian market today you can easily find a contract 5A-FE engine in very good condition and at an affordable price. It is worth clarifying that engines that have not been used in Russia are usually called contract engines. Speaking about Japanese contract engines, it should be noted that most of them have low mileage and all manufacturer requirements regarding maintenance are met. Japan has long been considered a world leader in the speed of updating its car lineup. Thus, a lot of cars end up at car wreckers there, the engines of which have a fair amount of service life.
Specifications 4S FE
Gasoline engine Gazelle Next 2.7 l. timing device, technical specifications Evotech 2.7
Initially, the plant management used smaller volumes of combustion chambers in the engine than in the previous 1.8 liter engine instead of 2.0 liters. A simplified in-line petrol engine with 16 valves and two camshafts according to the DOHC scheme was used.
4S FE camshafts
4S FE cylinder head
The drive of one timing camshaft in these engines is belt driven. Attachments are arranged mainly on the passenger side, in the front. It is possible to overhaul it yourself and modernize the engine to increase power.
Intake manifold
The given technical characteristics of the 4S FE from the bottom table will help the owner to rationally use the available capabilities:
| Manufacturer | Kamigo Plant Toyota |
| Engine brand | 4S FE |
| Years of production | 1990 – 1999 |
| Volume | 1838 cm3 (1.8 l) |
| Power | 92 kW (125 hp) |
| Torque moment | 162 Nm (at 4200 rpm) |
| Weight | 160 kg |
| Compression ratio | 9,5 |
| Nutrition | injector |
| Motor type | in-line petrol |
| Ignition | DIS-2 |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Location of the first cylinder | TVE |
| Number of valves on each cylinder | 4 |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum alloy |
| Intake manifold | cast duralumin |
| An exhaust manifold | cast iron |
| Camshaft | cast, 2 pcs. |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder diameter | 82.5 mm |
| Pistons | original with counterbores |
| Crankshaft | crankpins 48 mm |
| Piston stroke | 86 mm |
| Fuel | AI-95 |
| Environmental standards | Euro 4 |
| Fuel consumption | highway – 5.2 l/100 km combined cycle 6.7 l/100 km city – 8.2 l/100 km |
| Oil consumption | 0.6 – 1.0 l/1000 km |
| What kind of oil to pour into the engine by viscosity | 5W30, 10W40, 10W30 |
| Which engine oil is best by manufacturer | ZIC A, ZIC X5, Dragon SN SAE, Shell HX7, GT Turbo Coat |
| Oil for 4S FE by composition | synthetics, semi-synthetics |
| Engine oil volume | 3.3 l on Mark II, Cresta, Chaser, 3.9 l on all other Toyota cars |
| Operating temperature | 95° |
| ICE resource | declared 300,000 km actual 350,000 km |
| Adjustment of valves | washers |
| Cooling system | forced, antifreeze |
| Coolant volume | 5.9 l |
| water pump | Just Drive JD |
| Spark plugs for 4S FE | BKR6EYA from NGK, K16R-U11, K20R-U11, BC5EY11, Q16R-U11 |
| Spark plug gap | 1.1 mm |
| Timing belt | 13503-63011 |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Air filter | SA-161 Shinko, 17801-74020 Toyota |
| Oil filter | Sakura C1139, VIC C-110 |
| Flywheel | 8-bolt fastening, body lightened with 6 round holes |
| Flywheel mounting bolts | M12x1.25 mm, length 26 mm |
| Valve stem seals | manufacturer Goetze, inlet light, exhaust dark |
| Compression | from 13 bar, difference in adjacent cylinders maximum 1 bar |
| XX speed | 750 – 800 min-1 |
| Tightening force of threaded connections | spark plug – 35 Nm connecting rods – 25 Nm + 90° crankshaft pulley - 108 Nm valve cover – 44 Nm cylinder head – two stages 49 Nm + 90° |
Engine 5S FE: characteristics, maintenance, malfunctions, repairs
The 5S FE engine is a power unit manufactured by Toyota. This motor has high technical characteristics and quite a lot of varieties and modifications. The applicability of the power unit is wide.
Specifications
The 5S FE engine is one of the largest power units produced by Toyota. The cylinder block is based on the predecessors 3S and 4S, but with a larger piston diameter.
Toyota Camry 5S FE.
Structurally, it turns out that the engine has a huge advantage - if the timing belt breaks, it does not bend the valves.
Main technical characteristics of the 5S engine:
| Name | Index |
| Manufacturer | Kamigo Plant Toyota Motor Manufacturing Kentucky |
| Model | 5S FE |
| Volume | 2.2 liter (2164 cm3) |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 16 |
| Fuel | Petrol |
| Injection system | Injector |
| Power | 132-138 hp |
| Fuel consumption | 9.0 l/100 km |
| Cylinder diameter | 87.1 mm |
| Recommended oils | 5W-30 10W-30 |
| Engine life | 300,000 km |
| Motor applicability | Toyota Camry Toyota Celica Toyota Mark II Wagon Qualis Toyota Harrier Toyota Scepter Toyota MR2 |
Motor modifications
The 5S engine has quite a few modifications that are used in various Toyota vehicles.
5S FE engine under the hood of a Mark 2.
- 5S-FE Gen 1 is the main engine. Shafts phase 220 with lift 7.25 mm, compression ratio 9.5, power 130 hp. Years of production: from 1990 to 1992, Installed on Toyota Celica V ST184 and Toyota MR2 SW21.
- S-FE Gen 2 is the second version of the engine, different camshafts are used with a phase of 218 and a lift of 8 mm, power is 135 hp. The engine was installed from 1993 to 2001, on the Toyota Camry XV10 and Celica ST204.
- 5S-FE Gen 3 - third generation of engine, power 133 hp. Installed from 1997 to 1999 on Toyota Camry XV20.
- 5S-FE Gen 4 - the latest version of the engine, power increased to 136 hp. Installed on Toyota Camry XV20 from 2000 to 2001.
Service
Maintenance of the 5S engine is carried out at intervals of 15,000 km. Recommended maintenance must be performed every 10,000 km. During maintenance, oils and filters are changed, and engine performance is also diagnosed.
Repair of 5S FE cylinder head.
Conclusion
The 5S motor has fairly high technical characteristics. Fairly easy to maintain and repair. As for tuning, a complete overhaul of the engine. Chip tuning of the power plant is especially popular.
avtodvigateli.com
Pros and cons of the 4s fe engine
Toyota Land Cruiser 100 technical specifications and fuel consumption
Due to its design features and high technical characteristics, the motor has a number of advantages:
- High build quality. High-quality materials and high-tech equipment were used in production;
- Large motor resource. Thanks to the build quality and technical solutions used by the designers during development, the engine has a long service life. The manufacturer claims a lifespan of the power unit of 300,000 km. With normal maintenance, this figure can reach 1,000,000 km;
- Simplicity of design. The unit can be serviced and repaired by a person with minimal technical knowledge. Repairing the most common faults does not require the use of specialized equipment;
- Design of the gas distribution mechanism of the 4sfe motor. In the open position, the valves do not contact the pistons at top dead center.
- This design allows you to maintain the integrity of the valves in the event of a break in the gas distribution mechanism belt;
- Engine cooling system 4s fe. Thanks to the liquid cooling system, the engine operates well under high loads, regardless of ambient temperature.
4s fe engine review
The engine is a four-cylinder engine. The cylinder block is made of cast iron. Inside the block, the motor is equipped with non-removable sleeves. The cylinder head material is aluminum. This design avoids overheating of the cylinder head.
The engine is distinguished by its simplicity of design and unpretentiousness to operating conditions and the quality of fuel consumed. The gas distribution mechanism is belt driven. This reduces the noise level when the internal combustion engine is operating.
Due to the simplicity of its design, the 4s engine is repairable and easy to maintain. For normal operation of the power plant, it is necessary to regularly change the lubricant, filter elements and gas distribution mechanism belt.
Review of faults and methods for repairing them
Due to the presence of counterbores in the pistons, the 5S FE engine does not bend the valve, but has some characteristic malfunctions:
| Vibrations and hum at medium speeds | 1) pulley misalignment 2) wear of the pillows 3) nozzle clogged 4) production of a candle | 1) adjusting the timing belt and attachments 2) replacing pillows 3) replacing injectors 4) replacing spark plugs |
| Floating speed XX | 1) fuel pump failure 2) air filter clogged 3) coked intake manifold 4) damper clogged | 1) cleaning the fuel pump 2) filter replacement 3) washing the collector with a special detergent 4) cleaning the throttle |
| Reduced motor power | EGR valve failure | replacing the USR valve |
Repair 5S-FE
Maintenance schedule 5S FE 2.2 l
In order for the 5S FE engine to last more than 300,000 km, the manufacturer recommends adhering to the maintenance schedule:
- the drive belt of the attachment and camshaft must be replaced after 50,000 km;
- It is recommended to adjust valve clearances after 30,000 miles;
- cleaning of the ventilation is provided by the crankcase manufacturer every 2 years;
- the manufacturer recommends filling in new engine oil and replacing the oil filter after 7,500 km;
- The fuel filter should be replaced after 40,000 miles;
- the air filter is updated annually according to the manufacturer's instructions;
- the additives inside the antifreeze from the factory have a resource of about 40,000 km;
- replacement of spark plugs in the DIS-2 engine system is carried out after 20,000 mileage;
- The intake manifold begins to burn out after 60,000 km.
The 5S-FE power drive is considered not particularly popular, but quite reliable in maintenance and operation.
Is it possible to tune the 4s fe engine
In order to improve technical characteristics, car owners perform tuning of the power plant. For this:
- Flashing the electronic control unit.
- Reprogramming the electronic control unit allows you to change the moment at which the fuel mixture is supplied and ignited. Programming is carried out on specialized equipment;
- Install high performance nozzles;
- Timing camshafts are replaced with products with a different phase;
- Eliminate irregularities in the intake and exhaust tracts. This allows you to freely sell the air mass into the combustion chamber and remove exhaust gases;
- By installing an intercooler, the air mass entering the combustion chamber is cooled.
List of internal combustion engine modifications
During the existence of the internal combustion engine, the engine characteristics were adjusted several times, so the 4S-FE engine has two modifications:
- Gen 1 – years of production 1991 – 1999, power 115 hp. With. especially for Toyota Corona;
- Gen 2 – produced 1995 – 1999, power 125 hp. pp., compression ratio 9.5, modified intake manifold.
Motor 4S-FE Gen2
The 4S-Fi engine cannot be considered a modification of the 4S-FE, even conditionally. It is rather a predecessor of a power drive with distributed injection, in which a mono-drive was installed according to a completely different scheme. The two Gen versions listed use the same attachments as the base version.
Toyota 3S-FE
3S-FE in class “D/D+”
The honor of opening the list falls to the Toyta 3S-FE engine - a representative of the well-deserved S series, which is considered one of its most reliable and unpretentious units. A two-liter volume, four cylinders and sixteen valves are typical figures for mass-produced engines of the 90s. Camshaft drive by belt, simple distributed injection. The engine was produced from 1986 to 2000.
Power ranged from 128 to 140 hp. More powerful versions of this engine, 3S-GE and turbocharged 3S-GTE, inherited a successful design and a good service life. The 3S-FE engine was installed on a number of Toyota models: Toyota Camry (1987-1991), Toyota Celica T200, Toyota Carina (1987-1998), Toyota Corona T170 / T190, Toyota Avensis (1997-2000), Toyota RAV4 (1994- 2000), Toyota Picnic (1996-2002), Toyota MR2, and the turbocharged 3S-GTE also on Toyota Caldina, Toyota Altezza.
Disadvantages of the 4A engine
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Engine idle speed fluctuates or increases.
- The engine does not start, stalls with floating speed;
- The engine stalls;
- Increased oil consumption;
- The engine is knocking.
Disadvantages of the 4A motor in detail...
The reason for increased fuel consumption may be:
- Lambda probe malfunction. The defect is eliminated by replacing it. In addition, if there is soot on the spark plugs, and there is black smoke from the exhaust and the engine vibrates at idle, check the absolute pressure sensor.
- Dirty injectors, if so, then they need to be washed and blown out.
The cause may be a malfunction of the idle air valve and carbon deposits on the throttle valve, or a malfunction of the throttle position sensor. Just in case, clean the throttle valve, wash the idle air valve, check the spark plugs - the presence of carbon deposits also contributes to the problem with engine idle speed. It would not be superfluous to check the injectors and the operation of the crankcase ventilation valve.
This problem indicates a malfunction of the engine temperature sensor.
In this case, this may be due to a clogged fuel filter. In addition to searching for the cause of the malfunction, check the operation of the fuel pump and the condition of the distributor.
The manufacturer allows normal oil consumption of up to 1 liter per 1000 km; if it is more, it means there is a problem with the piston. Alternatively, replacing the piston rings and oil seals may help.
Engine knocking is a signal of wear on the piston pins and a violation of the timing valve clearance in the engine head. In accordance with the operating manual, the valves are adjusted after 100,000 km.
As a rule, all shortcomings and weak points are not manufacturing or design defects, but are a consequence of failure to comply with proper operation. After all, if you don’t service your equipment in a timely manner, it will eventually ask you to do it. You must understand that basically all breakdowns and problems begin after a certain resource has been exhausted (300,000 km), this is the first cause of all malfunctions and shortcomings in the operation of the 4A motor.
Cars with Lean Burn version engines will be very expensive; they run on a lean mixture and as a result their power is much lower, they are more capricious, and consumables are expensive.
All the described weaknesses and shortcomings are also relevant for engines 5A and 7A.
Possible breakdowns and methods of repairing them
The most common breakdowns are minor malfunctions that can be eliminated without the use of specialized equipment.
- The 4s fe engine troits. The engine may stall due to incorrect operation of one of the ignition coils. For repairs, it is necessary to check the performance of the coils and replace the failed part with a known working one;
- The 4s engine starts but won't start. The reason for incorrect starting of the power plant may be a failure of the fuel pump. The engine may not start due to the failure of one of the ignition coils. The coil needs to be replaced;
- Incorrect operation of the unit at idle. 4s engine, idle speed adjustment, which is possible after replacing the air filter element, may not idle correctly due to severe contamination of the throttle valve. Contaminants must be removed.
From the above it follows that the 4sfe engine is a reliable power plant. It is unpretentious to the quality of fuel and conditions of use. The motor works well at any ambient temperature. To improve technical performance, you can modernize the power unit.
4s fe engine
In the section Choosing a car, motorcycle, to the question What does engine 4s, 5a, etc. mean? asked by the author Alexander Zhakov, the best answer is DECODING LETTER CODES FOR TOYOTA PETROL ENGINES: G = twin cam (with a wide camber angle, 45 degrees or more with intake and exhaust valves) F = so-called. “economical” twin cam (small camber angle, about 22 degrees) T = with turbine Z = with supercharger E = fuel injection I = single-point fuel injection L = transverse engine (obsolete) B = two-carburetor (used only on non-Twincam engines, obsolete. )R = air supercharger (?)S = intake valves with swirl flow (small series in the mid-80'x)S = direct fuel injection and swirl combustion chamber (from 97/98)U = catalytic converterLPG = used as fuel. liquefied petroleum gas (rare) T - available for all turbocharged engines. Examples: 1G-GTE, 2L-TE. S - engine with direct fuel injection (mostly the most modern engines, developed after 1996). Examples: 4A-FSE, 1JZ-FSE. X is an engine designed to run on hybrid fuel or used in cars with hybrid power plants of the ICE-electric motor type. Examples: 1NZ-FXE, 1AZ-FXE. P - engine designed to run on liquefied gas. Example: 3Y-PE. H - special fuel injection system (brand designation: EFI-D). Example: 5E-FHE. The third after the dash (or the first - second, if the engine has two valves per cylinder and (or) does not belong to the category of engines with after the dash of the letter T, S, X, P, H) there is a letter carrying information about the method of creating the working mixture: E - engine with multi-point electronic injection (EFI); for diesel engines this means that they are equipped with an electronically controlled high-pressure fuel pump (HPF). Examples: 5A-FE (petrol), 2JZ-FSE (petrol), 2L-TE (diesel). i - engine with single-point (central) electronic injection (Ci - Central injector). TOYOTA only produced two of these engines: the 1S-Fi and its successor, the 4S-Fi. V - only the above-mentioned 1KD-FTV engine has what it means - it is still unknown. If there are no letters E, i, V after the dash, then this is either a carburetor gasoline engine (that is, not with electronic injection), or a diesel engine with conventional ( mechanical) injection pump. Examples: 4A-F (carburetor); 3C-T (diesel). Quite old TOYOTA gasoline engines (developed before 1988) may have the letters U or L after the dash, which is difficult to say what they mean. Examples: 1G-EU, 1S-U, 2E-L. Examples of engine names TOYOTA: 5A-FE - gasoline engine with 4 valves per cylinder and a “narrow” cylinder head, standard power range, with multi-point electronic fuel injection. 2C-T - diesel with 2 valves per cylinder, turbocharging and conventional (mechanically controlled) fuel injection pump. 2JZ-GTE is a gasoline engine with 4 valves per cylinder, a “wide” cylinder head, turbocharging and multi-point electronic fuel injection.
Toyota car engines (brief characteristics)
Material from Toyota Carina E
Jump to: navigation, search
Toyota engines
Since the beginning of the mass import of Japanese cars into Russia, several conventional generations of Toyota engines have already changed: - 1st wave (1970s - early 1980s) - now safely forgotten engines of old series (R, V, M, T, early A and S). - 2nd wave (second half of the 1980s - late 1990s) - Toyota classics (late A and S, JZ, etc.), the basis of the company’s entire reputation. - 3rd wave (from the late 1990s) - “revolutionary” series (ZZ, AZ, NZ). Characteristic features are light-alloy (“disposable”) cylinder blocks, variable valve timing, timing chain drive, and the introduction of ETCS. - 4th wave (from the second half of the 2000s) - evolutionary development of the previous generation (ZR, GR, AR series). Characteristic features: DVVT, versions with Valvematic, hydraulic compensators.
"A" (R4, belt)
In terms of prevalence and reliability, the A series engines share the primacy with the S series. As for the mechanical part, it is difficult to find more successfully designed motors.
At the same time, they have good maintainability and do not create problems with spare parts. Installed on cars of classes “C” and “D” (Corolla/Sprinter, Corona/Carina/Caldina families). 4A-FE
- the most common engine in the series, has been produced without significant changes since 1988, has no pronounced design defects
5A-FE
- a version with a reduced displacement, still produced in Chinese factories for Toyota of the Asian market and joint models
7A-FE
- late modification with increased displacement. In the optimal production version, 4A-FE and 7A-FE went to the Corolla family.
However, being installed on cars of the Corona/Carina/Caldina line, they eventually received a LeanBurn type power system, designed for the combustion of lean mixtures and helping to save Japanese fuel during quiet driving and in traffic jams. With this, the Japanese have pretty much spoiled our average consumer - many owners of these engines are faced with the so-called “LB problem”, which manifests itself in the form of characteristic failures at medium speeds, the cause of which cannot be properly identified and cured - either the low quality of local gasoline is to blame, or Whether there are problems in the power supply and ignition systems (these engines are especially sensitive to the condition of spark plugs and high-voltage wires), or all together - but sometimes the lean mixture simply does not ignite. Small additional disadvantages are the tendency to increased wear of the camshaft beds and formal difficulties with adjusting the clearances in the intake valves, although in general it is very convenient to work with these engines. “The 7A-FE LeanBurn engine is low-speed
, and it is even more torquey than the 3S-FE due to the maximum torque at 2800 rpm.” The outstanding torque at low speeds of the 7A-FE engine in the LeanBurn version is one of the common misconceptions.
All civilian engines of the A series have a “double-humped” torque curve - with the first peak at 2500-3000 and the second at 4500-4800 rpm. The height of these peaks is almost the same (the difference is almost 5 Nm), but for STD engines the second peak is slightly higher, and for LB engines the first one is slightly higher. Moreover, the absolute maximum torque of STD still turns out to be greater (157 versus 155). Now let's compare with 3S-FE. The maximum torques of 7A-FE LB and 3S-FE type'96 are 155/2800 and 186/4400 Nm, respectively. But if we take the characteristic as a whole, then the 3S-FE, at those same 2800 rpm, produces a torque of 168-170 Nm, and produces 155 Nm already in the region of 1700-1900 rpm. 4A-GE 20V
- a forced monster for small “sporty” models, replaced in 1991 the previous base engine of the entire A series (4A-GE 16V). To provide a power of 160 hp, the Japanese used a cylinder head with 5 valves per cylinder, a VVT system (the first use of variable valve timing on a Toyota), and a tachometer redline at 8 thousand. The downside is that such an engine will inevitably be more worn out than the average production 4A-FE of the same year, since it was not originally purchased in Japan for economical and gentle driving. The requirements for gasoline (high compression ratio) and oils (VVT drive) are more serious, so it is intended primarily for those who know and understand its features. With the exception of 4A-GE, the engines are successfully powered by gasoline with an octane number of 92 (including LB, for which the octane requirements are even softer). The ignition system is with a distributor (“distributor”) for serial versions and DIS-2 (Direct Ignition System, one ignition coil for each pair of cylinders) for later LBs.
"E" (R4, belt)
The main “subcompact” series of engines.
Used on models of classes “B”, “C” and, in rare cases, “D” (4E-FE - Starlet, Tercel, Corolla, 5E-FE - Tercel/Raum, Corolla, Caldina). 4E-FE
- the base engine of the series
5E-FE
- a version with an increased displacement
5E-FHE
- an early version, with a high redline and a system for changing the geometry of the intake manifold (to increase maximum power)
4E-FTE
- it is worth highlighting the turbo version of the base engine, which turned the Starlet GT into a “crazy stool” and “king of traffic light racing”. It is impossible to identify critical weak points in this series, but it is characterized by very weak crankshaft oil seals and a shorter service life of the cylinder-piston group, relative to the A series, which, moreover, is not formally subject to overhaul. Although you should always remember that the engine power must correspond to the class of the car - therefore, quite suitable for Tercel, 4E-FE is already weak for Corolla, and 5E-FE for Caldina. Working at maximum capacity, they therefore have a shorter lifespan and greater wear compared to larger volume engines on the same models. The minimum gasoline requirements for conventional modifications are 92. The ignition system is distributor, on the latest versions (since 1997) - DIS-2.
“G” (R6, belt)
1G-FE
is one of the best Toyota engines and a former leader in the informal reliability rating. Installed on rear-wheel drive models of the “E” and “E+” classes (Mark II, Crown). It should be noted that under the same name there are two actually different engines. In its optimal form - proven, reliable and without technical frills - the engine was produced in 1990-98 (1G-FE type '90). The disadvantages are that the oil pump is driven by a timing belt, which clearly does not benefit the latter (during a cold start with very thickened oil, the belt can jump or teeth can be cut; there is no need for extra oil seals leaking inside the timing case), and a traditionally weak oil pressure sensor. Overall an excellent unit, but you shouldn’t demand racing car dynamics from a car with this engine. In 1998, the engine was radically changed - by increasing the compression ratio and maximum speed, the power increased by 20 hp, but this was achieved at a high price. The engine features VVT, Variable Intake Manifold System (ACIS), distributorless ignition and Electronically Controlled Throttle Valve (ETCS). The most serious changes affected the mechanical part - only the general layout and some of the dimensions were retained. The design and filling of the cylinder head have completely changed, a hydraulic belt tensioner has appeared, the cylinder block and the entire cylinder-piston group have been updated, and the crankshaft has changed. It should be noted that for the most part 1G-FE spare parts type'90 and type'98 are not interchangeable. In addition, the valves now begin to bend when the timing belt breaks. The reliability and service life of the new engine have certainly decreased, but the main thing is that all that remains of its legendary indestructibility, ease of maintenance and unpretentiousness is its name.
"S" (R4, belt)
The most successful and proven series of engines, and taking into account their widespread use, generally the best Toyota engines.
Installed on cars of classes “D”, “D+”, “E”, (3S-FE - Corona, Camry-Vista, 4S-FE - Corona, Camry-Vista, Mark II, 5S-FE - Camry-Scepter, Camry- Gracia). 3S-FE
is the base engine of the series - powerful, reliable and unpretentious.
Without characteristic disadvantages, with the exception of some noise, “slow flow of oil to the camshafts at startup” and oil consumption due to waste in older (with a mileage of 200 thousand km) engines. Design disadvantages for maintenance - the timing belt, which also drives the pump and oil pump, is overloaded, the engine is inconveniently located under the hood (piled up to the engine shield). The best modifications of the engine were produced in 1990-96, but the updated version that appeared in 1996 could no longer boast of the same problem-free performance. Serious defects include the rare, but sometimes occurring, especially on type '96, breaks of connecting rod bolts with the subsequent appearance of a “fist of friendship”. 4S-FE
is a variant with a reduced displacement; its design and operation are completely similar to the 3S-FE.
Its characteristics are sufficient for most models, but it is completely unsuitable for the Mark II family. 3S-GE
is a souped-up engine with a “Yamaha-designed block head”, produced in a variety of variants with varying degrees of boost and varying design complexity for sporty models based on the D-class.
Its versions were among the first Toyota engines with VVT, and the first with DVVT (Dual VVT - variable valve timing system on the intake and exhaust camshafts). 3S-GTE
- turbocharged version.
It is worth remembering the disadvantages of supercharged engines: cost of operation (better oil and minimum frequency of its replacement), difficulty in maintenance and repair, relatively low service life, high probability of rapid turbine failure. All other things being equal, it should be remembered: the Japanese buyer did not buy the turbo engine for driving “to the bakery”, so the question of the residual life of the engine and the car as a whole will always be open; this is three times critical for a car with mileage in the Russian Federation. 3S-FSE
- version with direct injection (D4), the worst gasoline engine in the range.
An example of how easy it is to turn an excellent engine into a nightmare with an insatiable thirst for improvement. It is definitely not recommended to buy cars with this engine. Or, if this seems inevitable, you should really imagine what the owner will face, how and how much it will cost to periodically restore it, and most importantly, why he needs these problems. A detailed description of it requires a separate book (for a somewhat more complete description, see this material). The main problem is the wear of the injection pump, as a result of which a significant amount of gasoline enters the engine crankcase, which leads to catastrophic wear of the crankshaft and all other “rubbing” elements. Due to the operation of the EGR system, a large amount of carbon deposits accumulates in the intake manifold, affecting the ability to start. A “fist of friendship” due to broken connecting rods is a standard career ending for many 3S-FSEs. However, there are plenty of problems with other engine systems, which have little in common with normal S-series engines. 5S-FE
is a version with an increased displacement. Disadvantage - as on most gasoline engines with a volume of more than 2 liters, the Japanese used a gear-driven balancing mechanism here (non-disconnectable and difficult to adjust), which could not but affect the overall level of reliability and level of oil requirements. The ignition system is distributor-type on early engines, since mid-1996 DIS-2 or DIS-4. Gasoline - 92 for civilian versions and, preferably, 95 for forced ones.
“FZ” (R6, chain + gears)
Replacement of the old F series, good quality classic engine with large displacement.
Installed on heavy jeeps (Land Cruiser 80..100). “JZ” (R6, belt)
Massive top series of the 1990s, in different versions installed on all passenger rear-wheel drive Toyota models.
1JZ-GE
- the base engine for the Mark II and Crown families. (1 jz is not better for a man :-D)
2JZ-GE
- a variant with an increased displacement.
1JZ-GTE, 2JZ-GTE
- high-power turbocharged versions (without limiter 300-320 hp).
1JZ-FSE, 2JZ-FSE
- options with direct injection. They had no significant drawbacks and were very reliable with proper operation and proper care. The downside is that all attachments are driven by one long belt with a hydraulic tensioner, which is not durable. It is worth noting that JZ engines are sensitive to moisture, especially in the DIS-3 version, so washing them is highly not recommended. After modernization in 1995-96. The engines received a VVT system and distributorless ignition, and became a little more economical and high-torque. It would seem that this is one of those rare cases when the updated Toyota engine has not lost too much in reliability. However, more than once I had to not only hear about the problems of fresh JZs with the connecting rod and piston group, but also see the consequences of the pistons sticking with their subsequent destruction and bending of the connecting rods.)
"MZ" (V6, belt)
One of the first heralds of the “third wave” were V-shaped sixes for initially front-wheel drive cars of the “E” class (Camry), as well as SUVs and vans based on them (Harrier/RX300, Kluger/Highlander, Estima/Alphard).
1MZ-FE, 2MZ-FE
- improved replacement for the VZ series.
The light-alloy liner cylinder block does not imply the possibility of a major overhaul with boring to the repair size; there is a tendency to coking of the oil and increased carbon formation due to intense thermal conditions and cooling features. Cases of mechanical destruction of such motors are also associated with this, as well as with not very competent operation. On the 2MZ-FE and later versions of the 1MZ-FE, a variable valve timing mechanism was used. 3MZ-FE
- version with increased displacement, intended mainly for the foreign (American) market
"RZ" (R4, chain)
Basic longitudinal gasoline engines for medium-sized jeeps and minibuses.
The 3RZ-FE
is the largest in-line four in the Toyota range, and is generally characterized positively; you can only pay attention to the overcomplicated timing drive and balancer mechanism. The ignition system in early versions is distributor, in later versions it is DIS-4 (separate ignition coil for each cylinder). The engine was often installed on models of the Gorky and Ulyanovsk automobile plants. As for consumer properties, the main thing is not to count on high thrust-to-weight ratio of fairly heavy models equipped with this rather modest engine.
"TZ" (R4, chain)
Horizontal engine designed specifically for placement under the body floor (Estima/Previa 10..20).
This arrangement made the drive of attached units (carried out by a cardan transmission) and the lubrication system (something like a “dry sump”) much more complicated. This also arose great difficulties when carrying out any work on the engine, a tendency to overheat, and sensitivity to the condition of the oil. Like almost everything related to the first generation Estima, this is an example of creating problems from scratch. 2TZ-FE
is the base engine of the series.
2TZ-FZE
- a less common forced version with a mechanical supercharger.
"UZ" (V8, belt)
For almost two decades, it has been the top series of Toyota engines, designed for large business-class rear-wheel drive vehicles (Crown, Celsior) and heavy SUVs (LC 100..200, Tundra/Sequoia). Very successful motors with a good margin of safety. In the 2000s, variable valve timing was introduced.
"VZ" (V6, belt)
Overall an unsuccessful series of engines that quickly and almost completely disappeared from the scene.
Installed on front-wheel drive business-class cars (Camry-Windom and Camry-Scepter of the first generation, Camry-Prominent) and medium-sized jeeps (HiLux Surf, including the early version 3VZ-E). They showed themselves to be unreliable and capricious: a fair love for gasoline, a little less for eating oil, a tendency to overheat (which usually leads to warping and cracks of the cylinder head), increased wear of the crankshaft journals. And what about the sophisticated hydraulic fan drive? And on top of that, the relative rarity and high cost of spare parts. 5VZ-FE
- used since 1995 on HiLux Surf / LC Prado 185/90..210/120 models and large vans of the HiAce family. This engine turned out to be the best in the series and less whimsical.
"AZ" (R4, chain)
Replacement of S series engines, installed on models of classes “C”, “D” and “E” (Corolla Blade, Matrix, Premio family, Camry), vans based on them (Ipsum, Noah, Estima), SUVs (RAV4, Harrier, Highlander). The most serious and widespread defect is spontaneous destruction of the threads for the cylinder head mounting bolts, leading to a violation of the tightness of the gas joint, damage to the gasket and all the ensuing consequences.
"NZ" (R4, chain)
Replacement of series E and A, installed on models of classes “B”, “C”, “D” (Vitz, Corolla, Premio families).
Despite the fact that the NZ series engines are structurally similar to the ZZ, are quite boosted and sometimes work even on not the lightest “D” class models, nevertheless, of all the engines of the 3rd wave they can be considered the most problem-free. “SZ” (R4, chain)
The SZ series owes its origin to the Daihatsu division and is an independent and rather interesting “hybrid” of engines of the 2nd and 3rd waves. Installed on class “B” models (Vitz family, related Daihatsu models). For more details about the design, see “SZ Series. Transitional option." The disadvantages include the occasional timing chain jump, which inevitably leads to damage to the valves.
"ZZ" (R4, chain)
A new generation of engines replaced the good old A series after 1998.
Moreover, it cannot be said that the Japanese made another breakthrough in terms of power indicators - more attention was paid to efficiency, environmental friendliness, and modernization prospects. And manufacturability, which, unfortunately, still prevailed in the fight against durability. Installed on models of classes “C” and “D” (Corolla, Premio families), SUVs (RAV4) and minivans. Pros. Some may believe that the timing chain drive is more reliable, the VVT system has improved traction characteristics at the bottom, specific power and torque have increased, and engine weight has decreased. Minuses. There is a reason to talk more substantively here. — The VVT mechanism (including a pulley, valve and filter) is still poorly mastered in repair, and in operation it requires exclusively high-quality and clean oil, moreover, of low viscosity and therefore prone to burning. — A chain with a hydraulic tensioner also places special demands on the oil, and concessions in favor of reducing noise inevitably turn into a disadvantage in durability. And most importantly, replacing a belt with rollers after 80-100 thousand km is cheaper than replacing a chain with tensioners, dampers and sprockets after 150-180 km. - The compression ratio has noticeably increased (10-10.5 or more) - therefore, you should no longer rely on traditional Toyota gasoline omnivory, although the Japanese have worked in this direction on power supply and ignition. — A standard disease of the ZZ series has become the problem of increased oil consumption due to waste, caused by design features - wear and sticking of the piston rings, often accompanied by liner wear. — And finally, maintainability. Adopting global traditions, Toyota was also able to make a literally “disposable” engine - its aluminum design does not provide for such a thing as a “repair size”, there are no original repair pistons, nor the possibility of boring. 1ZZ-FE
is the basic and most common engine of the series.
For more information about the design, features and disadvantages, see “1ZZ-FE. No room for error." 2ZZ-GE
is an uprated engine with VVTL (VVT plus first-generation variable valve lift system), which has little in common with the base engine.
Unfortunately, this is the most “delicate” and short-lived of the charged Toyota engines. For more details about the design, see “2ZZ-GE. Apotheosis". 3ZZ-FE, 4ZZ-FE
- versions for models of the European market. The main drawback is that the lack of a Japanese analogue does not allow you to purchase a budget contract motor.
"AR" (R4, chain)
A new mid-size series of transverse engines with DVVT, complementing and replacing the 2AZ-FE. Installed on class “D” models (Camry family) and SUVs (RAV4, Highlander, RX), mainly on the North American market.
"GR" (V6, chain)
A replacement for the MZ series, which appeared in the mid-2000s and features light-alloy blocks with an open cooling jacket, timing chain drive, VVT or DVVT. Longitudinal or transverse arrangement, installed on many models of different classes - Corolla (Blade), Camry, modern rear-wheel drive (Mark X, Crown, IS, GS), top versions of SUVs (RAV4, RX), medium and heavy jeeps (LC 120.. 150, LC 200).
"KR" (R3, chain)
A three-cylinder replacement for the youngest engine of the SZ series, made according to the general canon of the 3rd wave - with a light-alloy lined cylinder block and a conventional single-row chain.
"NR" (R4, chain)
A new small-displacement engine with DVVT, which will eventually replace the 2NZ-FE and 2SZ-FE. Installed on models of classes “B” and “C” of the foreign market (Corolla, Yaris).
"TR" (R4, chain)
A modified version of the RZ series engines with a new cylinder head, VVT system and hydraulic compensators in the timing drive.
"UR" (V8, chain)
Replacement of the UZ series - engines for top rear-wheel drive vehicles (Crown, GS, LS) and heavy jeeps (LC 200, Sequoia), made in the modern tradition with an alloy block, DVVT and with the D-4 version.
"ZR" (R4, chain)
Replacement of the ZZ series and two-liter AZ. Characteristic features of the new generation are DVVT, Valvematic (on the -FAE versions - a system for smoothly changing the valve lift height), hydraulic compensators, crankshaft deaxling. Installed on models of classes “C” and “D” (Corolla, Premio families) and minivans based on them (Noah).
A few words about diesels
1N, 1N-T
— like all small-displacement diesel engines, they worked under extremely stressful conditions, and therefore had a short resource.
Very sensitive to oil viscosity, prone to crankshaft damage during cold winter starts. There is practically no technical documentation of any kind (therefore, for example, it is impossible to correctly adjust the fuel injection pump), and spare parts are extremely rare. 2C
is a generally reliable and unpretentious naturally aspirated diesel engine, but low-power for the models it was installed on.
2C-E, 3C-E
- diesel engines with electronically controlled injection pump.
They create few technical problems, but in terms of maintainability - alas, there are very few people in the whole country who can deal with this very Japanese electronic fuel injection pump. 2C-T, 3C-T, 3C-TE
- turbocharged diesel engines.
Not very successful engines - high tendency to overheat (consequences - burnout of the gasket, cracks and warping of the cylinder head), short-lived turbines. This is more pronounced in minibuses and heavy vehicles with more strenuous working conditions. A typical example is Estima, where, being also unconventionally configured, the turbodiesel constantly receives damage to the head and gasket and often knocks out all the oil through the seals. 2L, 3L, 5L
are relatively successful naturally aspirated diesel engines, the best in the L series.
2L-T, 2L-TE
are perhaps the worst turbodiesels in the entire Toyota range today.
A total problem of overheating, aggravated, among other things, by a poorly thought-out cooling system, total failure of turbines... Moreover, the tendency to fatal overheating is observed not in critical modes, but also in absolutely ordinary operating conditions - for example, during more or less long driving on the highway . 1KZ-TE
- came to replace and gradually replaced 2L-TE.
The inherent defects were, if possible, eliminated, which was facilitated by the increased working volume - the ancestor was frankly weak for heavy machines. There were also some difficulties: a tricky gear-belt drive of the timing and balancing mechanism, turbocharging, electronic fuel injection pump, high cost of spare parts and their rarity. And with all this, standard turbodiesel problems regularly occur on it. In fact, the legend about the “outstanding reliability” of the 1KZ-TE was formed at a time when there were disproportionately fewer of these engines than the familiar and problematic 2L-T (by the same logic one can argue that the most reliable engine is the Toyota V12 - about their breakdowns generally unknown in the Russian Federation). 1KD-FTV
is the successor to 1KZ-TE, which received a common-rail fuel system.
Its problems are quite typical - sensitivity to the quality of Russian diesel fuel and completely inadequate, disproportionate repair costs
.
A common malfunction is a violation of the tightness of the cylinder head joint. 1HZ
- from the H series, only this Toyota diesel, the best in terms of reliability, is worth highlighting. Simple design, simple injection pump, naturally aspirated... One problem - it is quite rare, installed only on various types of Land Cruiser, commercial vehicles and domestic home-made ones.
Some general notes
1. Platinum spark plugs.
Spark plugs with platinum or iridium electrode coating are prescribed for installation on -GE type engines, some engines with DIS-2 and DIS-3 ignition (that is, where sparking occurs twice as often as usual), some LeanBurn engines, turbocharged engines, some engines with difficult access to spark plugs, and now to almost all engines of the latest generations.
Practice shows that normal operation is ensured by ordinary spark plugs, but platinum spark plugs in good conditions objectively demonstrate significant (per 100 thousand km) durability. But the additives in local gasoline will not allow them to withstand that much - resistance to them does not increase at all with the rising price of candles. It is also worth paying attention to the trend of changes in the standard size of spark plugs in new engines - versions with a thinner and longer threaded part and a 14 mm hexagon instead of the usual 16 are becoming widespread. 2. Octane number.
Most Toyota engines successfully consume 92-octane gasoline, with the exception of supercharged engines and forced engines with a high compression ratio.
As for the 95th, engines respect it only if it is of normal quality, which is not so common in our regions. The 98th is a case where the porridge can be spoiled with oil - it should only be used for those turbocharged engines that detonate on a regular 95th. For a confident winter start, naturally, 92-octane gasoline is best suited 3. Hydraulic compensators.
Most owners of cars with Toyota engines until recently had no problems with hydraulic compensators - since the mid-80s they have not been installed on new modifications of engines.
Among the rare exceptions are the lower motors of the ancient Y and K series, the production of which, however, continued until the end of the 2000s, some versions 1NZ-FE and 2SZ-FE. However, on engines of the 4th wave, hydraulic compensators and valve drive through rocker arms are already used en masse. 4. Timing drive.
On multi-valve Toyota engines, there were two traditional options for driving camshafts: in the -FE, one shaft was driven by a belt, the second - from the first using a gear drive, in -GE, both shafts were driven by a belt.
As for chain engines, regardless of the index, the chain goes to both camshafts. When a belt breaks on most mass-produced engines, the valves and pistons do not meet. Exceptions are the forced 4A-GE, 3S-GE, V-shaped sixes, D-4 engines and, of course, diesel engines. With the latter, due to the design features, the consequences are especially severe - valves bend, guide bushings break, and the camshaft often breaks. For gasoline engines, chance plays a certain role - and in a “non-bending” engine, the piston and valve covered with a thick layer of soot sometimes collide, but in a “bending” engine, on the contrary, the valves can successfully hang in the neutral position. 5. Power.
For cars on the Japanese market there are no generally accepted official documents on engine power; the importer, customs, and MREO all take part in assigning these numbers. In addition, it is customary for us to measure power according to the DIN 70020 (Deutsche Institute den Stadarten) or EEC standard, and for the Japanese - according to JIS D1001 (Japan Indusrial Standard), which, when converted to DIN, gives numbers several (3-5) percent lower declared by the manufacturer. And this is not to mention the American SAE... So all indicated power values are indicative and depend on the specific year of manufacture and the specific model. However, in most cases the error does not exceed ±5%.
5. Common characteristic problems.
Among the irritating problems, we highlight: frequent cracks in plastic radiator tanks (and Toyota has not escaped this problem), long-term burning of the oil pressure lamp after starting the engine (according to observations, it does not affect the operation of the engine, but is still abnormal and often untreatable), “ utt" - cold start in winter conditions is not the first time.
PS In conclusion, one cannot help but thank Toyota for the fact that it once created engines “for people”, with simple and reliable solutions, without the frills inherent in many other Japanese and Europeans. And even if the owners of cars from “advanced and advanced” manufacturers disparagingly called them junk cars - so much the better!
Source - ""