The task set by the designers for ABS is to prevent wheel locking during sudden, emergency braking. The main result of the system is to keep the car on a given trajectory and maintain its controllability. Sharply pressing the brakes on a car without ABS in most cases results in the car drifting into oncoming traffic or into a ditch.
Even without such catastrophic consequences, the car still starts to skid - at least it gets to its fellow travelers in the lane. The situation becomes even more aggravated on slippery and wet road surfaces. In addition to increasing the braking distance, such conditions simply guarantee that the car will be thrown out of its trajectory. During emergency braking, ABC prevents such troubles, making it possible to avoid a sudden obstacle or brake without loss for yourself and others.
Content
- Alarm lamp
- Sensor check
- ECU
Does ABS work on dry roads? Well, in such an emergency situation the system must also react. By the way, with its help, the braking distance is reduced, and significantly - up to 20%. So you can say that your ABS is capricious only if it is constantly activated, and at low speeds. And this time, a third of the complainants eventually withdraw their complaints: their driving style is to blame. Either they constantly tear the pedal, and the system perceives the situation as an emergency, or they repeatedly press the brake, confusing the ABS electronics.
Bleeding the brake system with ABS, taking into account the features of the system
Bleeding ABS brakes requires some technical skill. In addition, you need to read the instructions for the design and operation of the vehicle's braking system.
Bleeding brakes with ABS, its features: - if in a car the hydraulic valve block, pump and hydraulic accumulator are located in one unit, then replacing the brake pads with your own hands, with replacing the technical fluid and bleeding the brake system is done in the same way as bleeding the brakes on a car without ABS (turn off (remove) the fuse, thereby turning off the system). By pressing the brake pedal and unscrewing the RTC bleeder fitting, we bleed the circuits. Then turn on the ignition - the pump will expel air from the circuit. Now tighten the fitting and release the brake pedal. If the “ABS fault” light goes out, it means you did everything right. — if the hydraulic module with valves and the hydraulic accumulator are in different units, it means that the brake system is bled using a diagnostic scanner, which takes data from the ABS ECU. However, you most likely don't have it. Thus, brakes with ABS are pumped only at AutoServiceTim service stations. — The brake system with ABS and electronic activation system (SBC or ESP) is pumped only at a car service center.
How to bleed a brake system with ABS
Attention! We should not forget that the pressure in the brake system can reach 180 atmospheres. Therefore, before disconnecting the brake lines on any brakes with ABS, the pressure accumulator must be discharged. To do this, turn on the ignition and press the brake about 20 times. All this is done in order to prevent the release of technical fluid.
Alarm lamp
But when the light responsible for ABS does not go out after 2-3 seconds after turning on the ignition, the system does not activate when turning, when the pedal is soft, at low speed, when the road surface is dry, and the incident is accompanied by suspicious sounds, it’s time to be wary .
The verification will include several stages. Ringing of the entire chain. The wires may be damaged, the terminals may come loose or oxidize, and the corresponding fuses responsible for the sensors on the wheels may blow out.
The main vulnerable component in the ABS, according to users and experts, is sensors. By themselves they are quite reliable. But they are located in such a place that they constantly experience too much stress. Dust, leaking oil and other delights of road life greatly affect the performance of devices. Often it is enough to simply clean the socket and the sensor itself so that it again starts sending the required signals to the on-board computer.
Failures often occur after repairs to any other components located near the sensor. In this case, rest assured: he simply left his nest and does not correctly perceive the incoming information. When you reinstall it to the proper depth, it becomes operational again.
Common breakdowns
A slight cracking sound when pressing on the brake pedal is quite normal. This sound occurs due to the functioning of modulators. If the ABS is faulty, its indicator lights up and does not go out even when the engine is running. There are several most common malfunctions of the anti-lock braking system:
- Deactivation based on self-diagnosis results. This may be caused by a malfunction of the control unit or damage to the ABS touch sensor wiring.
- After activation, ABS self-diagnoses, but then turns off. This problem can be caused by broken wires, broken contacts or their oxidation, where the supply of power and signals is disrupted.
- An error appears, but the ABC sensor works. This is a consequence of a break in the touch sensor. It can also be caused by differences in tire pressure or even different tread patterns.
- Complete loss of system functionality. There can be a lot of reasons for this, ranging from sensor breakdowns to wear of the wheel bearings.
This is interesting: Review of the five-door crossover Audi Q3
To identify a malfunction, you need to check the pressure and play in the tires, the performance of the comb and rotor. If the elements have chips, then it is better to completely replace them. If the problem remains unresolved, then the reason most likely lies in the electronic component. In this case, you need to get a diagnostic code.
Sensor check
However, everything wears out over time, and the speed sensor itself can be damaged. Replacing it is a serious matter, although the solution is not too expensive. Before you go for a new one, check how viable the old one is. For this:
- The front end is raised with a jack or lift so that the suspicious slope is suspended;
- A voltmeter is connected to the sensor. Already during docking he must give evidence. Typically the voltage output is about 0.7 V. If it is there, that’s good, but it’s not enough;
- The wheel is turned by hand. The data on the device should change, even if only slightly;
- An arrow that remains motionless (or numbers on the display that have not changed) indicates a failure of the DS.
Read the article
“How to check the speed sensor” for more details.
Performance characteristics
Table No. 1
| Name of parameters | Meaning |
| Control method | semi-automatic or manual |
| Rated supply voltage, V | 12 |
| Current consumption, A | 130… 160 |
| Maximum vacuum, kgf/cm2, not less | 0,8 |
| Fire pump water filling time, s, no more: – from a height of 3.5 m – from a height of 7.5 m | 2040 |
| Continuous operation time, s, no more | 60 |
| Type of vacuum unit overload protection device | Automatic, electronic |
| Average oil consumption (motor oil according to GOST 10541) per operating cycle, ml | 5 |
| Overall dimensions of the vacuum unit, mm, no more: | 400 x 220 x 220 |
| Overall dimensions of the control unit, mm, no more: | 150 x 140 x 75 |
| Product weight (total), kg, no more | 25 |
ECU
The on-board computer can fail much less often than sensors. However, software glitches also occur in it. If the test shows the integrity of the electrical circuit and the functionality of the sensor, but errors are displayed constantly, changing and difficult to recognize, you may have a problem with the ECU. In order to refute or confirm suspicions, you should do the following:
- Manually disable the sensors on all wheels at once;
- Start up and make a circle around the neighborhood, braking at different speeds and with different sharpness;
- Since no information is sent to the ECU, it should not react in any way to your experiments.
If, nevertheless, the ABS somehow responds, it’s time to take the “brains” for diagnostics. You shouldn’t start moping right away: often simply reprogramming and resetting errors returns the system to normal. In any case, you already know why ABS works on a dry road, and what you have to fight with.
Principle of operation
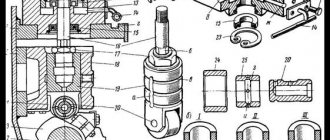
The ABS sensor and the development of a modernized braking system for motor vehicles have made it possible to increase the safety of equipment operation. Car manufacturers began adding ABS to their products around the 70s. The ABS sensor consists of the following elements:
- speed sensors;
- mechanisms mounted on wheels;
- hydraulic block;
- control block.
The main component of the equipment is the control unit. This part is responsible for receiving and analyzing signals coming from sensors. The information received is carefully studied by electronics, after which it draws conclusions about the level of slip of car wheels. The control is carried out by hydraulic valves.
The pressure supplied by the main brake center (main brake center) creates pressure on the brake calipers. This allows the brake pads to be pressed against the discs. Regardless of the driver’s effort when pressing the pedal and the situation, the pressure inside the brake system will still be normal. The advantage of ABS is that each wheel is analyzed, preventing blocking.
This is precisely the principle of operation of the ABS system. On vehicles equipped with all-wheel drive or rear-wheel drive, there is only one auto sensor located in the rear axle structure. Information about the risk of locking is received from the nearest wheel, and a special pressure command is sent to all wheels, regardless of how the ABS sensor is designed.
This is interesting: What does the “Give Way” sign look like and how to read it in different situations?
Reducing or increasing pressure is carried out in a stepwise manner thanks to special modes. If there are any problems, the ABS is switched off and the brakes function independently. Equipment malfunctions can be identified by a special indicator on the dashboard.
Transportation and storage
Transportation and long-term storage of the components of the vacuum pump are carried out in standard packaging. Before packing the vacuum unit, drain the oil from the oil tank.
The control unit and all documents must be packed in moisture-proof bags.
When transporting a vacuum pump, the safety of its components must be ensured from mechanical damage and precipitation. Long-term storage of products must be carried out in heated warehouses at a temperature not exceeding 40 °C.
We invite you to watch a thematic video on the topic Vacuum systems
Purpose of indicators
| "Nutrition" | control unit power is on; |
| "Vacuuming" | the electric drive is turned on, the vane pump rotates; |
| "Pump is full" | the fire pump is completely filled with water, the fill sensor has triggered; |
| "Not the norm" | one of the system malfunctions was recorded: 1) the time of continuous operation of the electric motor exceeded 50... 55 seconds. Short flashes of the indicator alternate with longer ones; 2) the contacts of the traction relay are burnt, the engine does not start. The indicator flashes evenly; 3) the electric motor is overloaded (the vane pump is blocked by frozen water or foreign objects). The indicator blinks evenly. |
Maintenance
The ABC-01E vacuum pump is highly reliable, subject to the operating rules outlined in this manual.
To avoid product failure, it is necessary to take into account the following requirements when installing, operating and maintaining a vacuum pump:
When installing the product, exclude the possibility of foreign objects (particles) getting into the cavity of the vane pump.
Monitor the condition of the vane pump lubrication system: replenish the oil tank in a timely manner and eliminate possible blockages in the oil line and other malfunctions.
Use the vacuum pump only for its intended purpose.
Do not allow the unit to operate in overload mode, in particular:
- – according to the time of continuous operation;
- – when a large amount of water gets into the cavity of the vane pump.
To ensure constant technical readiness of the product, the following types of maintenance are provided: daily maintenance (ETO) and maintenance TO-1. The list of works and technical requirements for carrying out these types of maintenance are given below.
| Contents of work | Technical requirements (methodology) |
| 1. Daily maintenance | |
| 1.1. Checking the presence of oil in the oil tank | Maintain the oil level in the tank at least 1/3 of the volume |
| 12. Checking the functionality of the vacuum pump and the functioning of the vane pump lubrication system | Carry out the check in the fire pump test mode for “dry vacuum” in accordance with clause 6.2. When turning on the vacuum pump, the oil supply tube must be completely filled with oil up to jet 2 (Fig. 2) |
| 2. maintenance TO-1 | |
| 2.1. Checking the tightness of fasteners | Check the tightness of the fasteners of the vacuum pump components and electrical connectors |
| 2.2. Checking oil consumption | Average oil consumption per operating cycle of 30 seconds. must be at least 2 ml. In case of non-compliance - see clause 7.5 |
| 2.3. Cleaning the working surfaces of the fill sensor | Remove sensor pos. 6 (see Fig. 1), clean the electrode and surface “A” of the housing (see Fig. 3) to the base metal. |