Why do you need a differential for transfer cases or axles?
Let's consider the mechanics of car movement in a turn. A wheel moving along the outer arc of a turn travels a greater distance than one that rolls on the inner side. For example, when turning right, the left disc rotates faster than the right one because it has to travel a greater distance.
The differential box is designed to solve this problem. When driving at high speeds, good handling is the key to the safety of the driver and passengers. If you do not ensure that the wheel on the inside of the turn rotates at a lower speed, the tire will slip. This factor not only accelerates tire wear, but also makes driving difficult.
Differential torque distribution when driving straight
Advantages and disadvantages of self-locking gearboxes on the VAZ 2107
First, let's list the advantages that locking on the VAZ 2107 provides:
- increased traction of the driving wheels in any conditions;
- good cross-country ability in sand, mud and snow;
- improved acceleration dynamics;
- good cornering.
But the locking differential comes at a price:
- handling deteriorates in rear-wheel drive vehicles, which include the VAZ 2107;
- it becomes more difficult to hold the car when accelerating;
- the tendency of the “seven” to skid when cornering increases;
- high friction links appear, which lead to an increase in wear rate and fuel consumption.
Differential box device
The axle shafts (5) (3) facing each other at their ends . The same gears (4) , but of smaller diameter (satellites), are installed between them in the differential box. When braking forces begin to act on one wheel, its rotation slows down. The second disk continues to rotate at the same speed. If the wheelset were rigidly connected, large torsional forces would be exerted on the axle.
This is where satellites come into play. They simply scroll, allowing one axle shaft to rotate relative to the other. The mechanism operates the same way, regardless of whether the differential is in the transfer case , axle housing or gearbox. That is, one wheel can remain stationary and even rotate in the other direction.
- Drive gear
- driven gear
- Axle gear
- Differential satellites
- Wheel axles
Conventional gearboxes are ineffective for driving in difficult road conditions. On jeeps, differentials are installed in transfer cases and have forced or automatic locking. This is necessary so that when one wheel hits a surface with poor grip, all the torque is not transferred to it.
For example, the differential of the Niva transfer case of the Lada family is locked mechanically. This unit distributes force between the front and rear axles. Center differentials do not have locking. That is, one axle does not slip relative to the other, but the wheels always rotate independently.
On Chevrolet Niva cars, all three differentials are locked : in the transfer case and between the axle shafts on each axle. In addition, on Niva Chevrolet you can disable one axle. For example, if the rear wheels are slipping, you can switch the car to front-wheel drive mode. In this case, all the torque from the engine is transmitted to the front axle, which will pull the car.
Installing a limited slip differential
It is not difficult to install a self-locking differential on a VAZ 2107 with your own hands. It is enough to remove the factory gearbox and put a new one in its place.
If you plan to use a differential with forced locking, you will have to make additional contacts to operate the gearbox itself.
And there are also those differential models that support automatic shutdown when reaching a certain speed range.
It is worth noting that installation on VAZ 2106, 2108, 2109 is carried out identically. On newer models, released starting from the “ten”, installation is complicated only by the fact that it is performed on the front drive axle. By the way, if you use a disk system, it requires periodic maintenance (usually 2 times a year). Installation here is performed using the pressing method. You'll have to cook it a little. It is precisely because of the quality of the seam that the gearbox most often becomes unusable. The average permissible operating period is 15 thousand kilometers. On a VAZ 2114, where the load is less - up to 25 thousand kilometers.
Differential box malfunctions
Like any transmission element, the differential box operates under constant mechanical loads. Over time, minor malfunctions occur in this unit. If they are not fixed in time, a major breakdown will occur.
Most often, the main pair, satellites, axle gears and various bearings fail in this transmission unit. As a rule, repairing a differential box involves replacing these elements. Sometimes you have to change the entire assembly.
Minor defects on the surface of the satellites, gear teeth of the axle shafts and the main pair can be removed with sandpaper or a grinding tool. In the same way, you can correct minor damage to the differential gear box. If you do not have skills in this area, it is better to contact a car service. The masters will do everything faster and more competently.
If differential box is functioning normally, it's still worth thinking about preventive maintenance. By taking simple steps, you can avoid many problems, save time and money. When you change or add transmission fluid, add the “Reducer” compound from Suprotec to it.
Once in the transmission, the product forms a protective layer on metal surfaces. Damage is partially restored, minor nicks and dents are covered. This optimizes the performance of friction pairs. The domestic development does not change the composition of the lubricant and does not damage rubber or plastic parts. The composition is approved for use in differentials of any type.
How to identify a malfunction
Any breakdown is easier to prevent than to fix later. Every driver and car mechanic knows this. Early detection of a fault in the differential box is the key to reducing the cost of repairs. Every driver should know how to diagnose deviations in the operation of this unit.
When only the first signs appear: extraneous noise, you need to perform a simple operation to understand where the problem is. It is required to jack up the axle that is “under suspicion.” The gearbox is placed in neutral position. Rotate the wheel with your hands. Are there any extraneous sounds? Wonderful.
Now have a helper hold the opposite wheel. The disk on your side is spinning, but on the opposite side it is stationary? Great. This means that your car does not need to repair the differential box The source of extraneous noise is another node.
Don’t forget about preventive maintenance so that the transfer case or axle differential lasts for many thousands of kilometers. An excellent option: the “Reducer” composition from the domestic developer Suprotec. Follow all instructions in order to achieve maximum protective effect. During the break-in period, try to avoid high loads on the transmission.
Damage to differential, gearbox - claims and reasons
Complaints and causes of damage to the differential / gearbox (5.03-506.1)
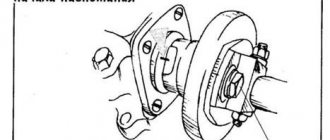
After dismantling the differential, damage (cut) was found to the clamping sleeve (spacer pin) securing the transverse shaft (differential pinion pinion axis), but no traces of jamming/wedging were found in the area where the pinion pinions are located ( Fig. 161a
).
The cause of the defect in this case may be improper installation of the clamping sleeve. Due to the cutting of the pin, the satellite axis is pushed out for a few seconds and therefore jamming/sticking does not occur. The solution to the problem is repair or, in case of severe damage, replacement of the crankcase with an X-part. Reassemble the damaged gearbox, including the intact differential axle, for analysis. To make a complaint, send a request for technical assistance, in which you describe the defect in detail and attach photographs of the satellite axis and differential satellites.
Differential detail 2
Rice. 1. Car bevel differential
1 - driven gear; 2.7 — differential box; 3, 6 — semi-axial gears; 4 — satellites; 5 — crosspiece (axis) of satellites.
Rice. 2. Cylindrical differential
1 - driven gear; 2.7 — differential box; 3, 6 — semi-axial gears; 4 — satellites; 5 — crosspiece (axis) of satellites. The drive wheels travel different distances when cornering or on uneven roads. If both wheels are rotated by the engine at the same speed, then one of them will certainly slip under such conditions. A differential installed between the wheels allows them to make different numbers of revolutions. It can have either bevel gears, like most cars, or spur gears. Both work the same. When turning, the inner wheel and the differential gear 3 connected to it through the axle shaft travel a shorter distance and rotate more slowly. In turn, the satellites 4 roll along the gear 3, which has slowed down, and rotate around their axes. At the same time, they impart additional rotation speed to the other differential gear 6 and the outer wheel. The operation of a differential is characterized by two properties that determine its advantages and disadvantages. The first property is that the sum of the revolutions of the differential gears (and the axle shafts associated with them) is equal to twice the number of revolutions of the differential box (or, in other words, the driven gear of the final drive). This means that when one wheel is stationary, the other begins to spin twice as fast. And if you stop the car with a transmission brake, that is, tell the differential box a zero speed, the axle shafts (and therefore the wheels) will rotate at the same speed in different directions. This property is used by experienced car drivers to turn the car on the spot without using the steering wheel. The second property is the distribution between the differential gears (half shafts) of the torque supplied to them in a given ratio. In most designs it is distributed equally, and such differentials are called symmetrical. The ratio is also made different - proportional to the load of the wheel. In this case, the differential is called asymmetrical. Let's look at the symmetrical drive axle differential, which is well known to all motorists. Due to the second property, when one of the wheels of the car slips and, due to the lack of traction with the ground, does not transmit torque, the mechanism inexorably imparts to the other wheel the same, that is, zero torque. In this case, the slipping wheel free of load quickly picks up speed, and the wheel located on solid ground, in accordance with the first property of the mechanism, reduces its rotation speed and eventually stops. As we see, the second property of the differential causes a big drawback that limits the vehicle's cross-country ability. To eliminate it, the differential action is blocked at the moment the wheel begins to slip.
Rice. 3. Center differential locking mechanism
1 - driven shaft connected to the differential driven gear; 2 - movable gear coupling; 3 — differential box; 4 — gear ring of the driven shaft. Manual locking is carried out by a cam or gear clutch 2, which connects the differential box 3 and one of the differential gears and the associated axle shaft 1. However, whatever the drive of the locking device (mechanical, pneumatic, electric), the moment it is turned on is determined by experience and qualifications the driver, who must sense the onset of slipping in a timely manner. Sometimes, after overcoming a difficult section, he forgets or is late to turn off the lock. This results in increased tire wear, fuel consumption, and additional loads on transmission parts.
Replacing the differential bearing
1. Without worrying too much about their integrity, compress this damaged part.
2. If you have a special puller, remove the outer rings from the gearbox and clutch housings. If there is no special device, first remove the axle shaft seals. Then remove the bearing rings from the outside of the crankcase. But, be prepared: in this case, the seals deteriorate and must be replaced.
3. If there is an adjusting ring under the gearbox housing ring, then before installing new rings in the crankcase, you need to select the adjusting ring again.
4. A damaged speedometer drive gear can be replaced in such a way that the bearing remains intact. To do this, take two screwdrivers and press on the inner ring of the bearing, pressing the part itself. In this case, the drive gear will be destroyed, but this does not matter - it must be replaced.
5. This is how the VAZ 2110 differential is disassembled, broken parts are replaced and minor defects are corrected. Now you can assemble this mechanism in the reverse order of disassembly. During the process, do not forget to treat the parts with transmission oil, and fasten the driven gear with the tooth markings facing outwards (see photo above).
Replacing bearings for VAZ 2110
Well, we’ve come to the differential, which should also be removed from the box. Next we do the following:
- remove the side gears from the differential by turning the satellites 90 degrees;
Differential VAZ 2110
- we take a special puller and remove the retaining ring, which sits in the axis of the satellites (in rare cases, you can use pliers with thin teeth);
- after removing the retaining ring, the satellite axis and, along with it, the satellites themselves will easily come out;
- take a head of the required size and an extension;
- We begin to unscrew the bolts that secure the driven gear to the differential housing;
- after this, the driven gear is removed from the housing (a hammer can be used to remove it).
At this stage, you need to stop and start carefully inspecting the working surfaces of the removed parts. The satellites, side gears, spherical surfaces of the differential housing, etc. are subject to inspection. If small irregularities are found, they should be eliminated with small sandpaper. If the parts have significant irregularities, then they need to be replaced.
Now you should take a good look at the differential bearing seats. If significant deterioration of these places is noticed, then the housing must be replaced, and if there is pitting (sinks) on the raceways and rolling elements, as well as traces of indentation and damage to the cages, the bearings are replaced. Let's continue:
- take a special puller;
- press the bearings from the differential;
- then we also press out the outer rings from the gearbox housing.
VAZ 2110 bearing replacement
The outer rings are also pressed out with a puller, but with a different one. If it is missing, then first press out the cuffs of the axle shafts, which are subsequently replaced with new ones. After this, the outer rings are removed using a bit.
If necessary, we also replace the gear responsible for driving the speedometer (see How to properly repair a speedometer). In this case, the bearing can be compressed so as not to destroy it. To do this, take two screwdrivers and apply simultaneous force to the inner ring.
Differential and its installation
The differential, after the bearings are replaced, is reassembled. To make the replacement process go smoothly, it is recommended to use video reviews and instructions, which are abundant on the Internet today. It would not be amiss to look at photos and pictures of suitable ones, because do-it-yourself replacement likes more visual examples.
Tampilkan kontrol pemutar
- Dipublikasikan tanggal 15 Sep 2017
- Adjustment of Differential Bearings is carried out when replacing gearbox housings, differentials and bearings.
How does a differential work?
The design of any passenger car includes a differential. This mechanism is specifically designed to allow the drive axle wheels to rotate at different speeds. This way it is possible to avoid wheel slipping and improve the vehicle's maneuverability.
When a car moves on an uneven road or takes a turn, the wheels of the drive axle travel different lengths of the path. To prevent tires from slipping on the road surface, the rotation speed of the wheels must be different. For this purpose, every car includes a differential.
Comparison of differential locks on Lada 4×4 (VAZ 2121)
The first video review compares the cross-country ability of SUVs in deep snow. The following participants took part in the test: Lada 4×4 with DAK, with DAN and without differential lock. To ensure the accuracy of the tests, all three cars had the same wheels with Bear tires.
Based on the results of the races, you can notice an obvious difference between the competitors:
- Lada 4×4 with DAK coped with the task.
- Lada 4×4 without a self-locking brake was not only unable to drive through deep snow, but also stalled, trying to overcome the snowdrifts along the previously left track.
- Lada 4×4 with DAN passed the test best of all.
Another comparison of self-locking differentials was carried out by another group of VAZ 2121 car enthusiasts. This time the tests took place in the summer, on sand and mud.
SUVs with different “blockages” tried to climb the mountain, as a result:
- With DAK - I managed to climb the slope on the 3rd attempt.
- WITH DAN - I managed to climb the hill only on the 5th try.
Despite this, the expedition participants noticed that on the way to the test site, the Lada 4×4 with DAN confidently drove under its own power, unlike many other SUVs.
During the break, they said that much still depends on the manufacturer and the gap in the design of the device. The minimum gap allows you to work more accurately; torque is transferred to the second wheel after a slight shift of the first. It also plays an important role which lock will be installed on the front wheels and which on the rear wheels.
Where can I buy?
Differential locks and other accessories are available at low prices in our online store.
What kind of differential lock do you recommend for the VAZ 2121? Maybe because of the high price (about 10 thousand rubles) there is no point in using it at all? Let us remind you that other important factors also influence the cross-country ability of an SUV.
Keywords: 4x4 front suspension | rear suspension 4x4 | Niva front suspension | Niva rear suspension
6
3
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter..
- When the updated Lada Largus FL will be released, new details
- Test drive Lada XRAY (1.8l, 122 hp, AMT) from Stillavin and Vakhidov
- Review of Lada Vesta Exclusive with photos and videos (new sedan equipment)
- Comparison of costs of maintaining LADA and foreign cars
What is a differential?
The differential is a mechanism that allows the wheels of the drive axle to rotate at different speeds, as well as with the same or different torque supplied to the wheels.
The differential is one of the main structural elements of the transmission. It can be located in the following places:
— in the gearbox in a front-wheel drive car; — in the rear axle housing to drive the drive wheels (in rear-wheel drive cars); — in the housing of the rear and front axles for driving the drive wheels (in all-wheel drive vehicles); - in the transfer case for driving the drive axles, if the car is all-wheel drive.
In the transmission of cars that have one drive axle, the differential is installed between the wheel drives, therefore it is called inter-axle. A center differential is found in all-wheel drive vehicles between the drive axles.
DIY differential repair
What can you do on your own to fix this part? Several consistent recommendations will help you solve the problem.
Since it has already been said that the differential is located in the gearbox, therefore, for repairs this unit must be removed from it. To do this, read the article, which talks about how to remove the differential (step No. 30).
Differential diagram VAZ 2110
1. Take out the semi-axial gears, turning them around the axis of the satellites 90 degrees.
2. Before removing the satellites, you need to remove the retaining ring from their axis.
3. Now you can easily remove the axle and two satellites.
4. To release the driven gear, you need to unscrew the mounting bolts in the differential housing.
5. Remove the part from the body using a hammer and chisel.
6. Everything that has been disconnected: satellites, their axle, gear - carefully inspect for defects. If the surfaces of these parts, and the surface of the body itself, have irregularities or polyps, carefully remove them with fine-grained sandpaper.
Be prepared for the fact that some defects cannot be eliminated, which means you will have to buy a new part.
7. Pay special attention to the driven gear in the gearbox. It is possible that defects in this part interfere with the normal operation of the differential. If you find significant tooth wear, chipping or wear, the gear will have to be replaced.
Tip: Drive and driven gears are sold together (as a pair). Therefore, it is better to replace both at once. On the driven gear, the manufacturer must indicate the number of teeth of both the first and second gears. However, “trust, but verify,” says the proverb, and to check, it is better to count and check the number of teeth.
8. Check the suitability of the bearings. Their damage is indicated by pitting and indentation marks on the running tracks and rolling elements. Verdict: requires replacement.
The differential housing itself will have to be replaced if the bearing seats are significantly worn.
Attention! To successfully repair and replace this VAZ 2110 and 2112 unit, you must purchase instructions, a diagram and a set of additional tools. If you do not have these 2 components at your disposal, it is best to entrust the repair to professionals in a car service center.
For adjustment and repair you will need:
- Set of socket wrenches (heads),
- Universal round nose pliers,
- Special version of pliers for removing the retaining ring system,
- Thin chisel
- An ordinary hammer.
Stages of repair.
The stages of work on adjusting and replacing the differential on the VAZ 2110 and 2112 are as follows:
- First, dismantle the assembly itself directly from the gearbox.
- Turn the central axis of the satellites 90°, then use a socket wrench to remove the axial gear from the housing structure.
- Remove the retaining rings from the central axis of the satellites.
- Remove the axle itself and each of the two satellites from the metal case.
- Remove all secured bolts in the driven gear structure.
- Insert the chisel into the gap that appears between the inner race of the bearing and the end of the differential box. For convenience, you can press the driven gears from the metal body of the unit.
- Next, you need to inspect the working surface of the satellite set, the central axis, the semi-axial gear and the surfaces of the body itself in contact with them. Minor unevenness can be removed using fine-grained sandpaper. Parts on which you find significant defects must be replaced.
- It is imperative to check the gearbox driven gear.
If chips, breaks, minor chipping or significant wear of the teeth are detected, this gear must be replaced. Attention! At the factory, specialists select a set of gears for the main drive only in pairs according to the characteristics of the contact patch. That is why replacing the driven gear must be accompanied by replacing the drive gear. - If faults are detected in the bearings, they must be replaced by first pressing them into the metal differential structure using a puller.
- All that remains is to press the outer set of rings from the gearbox housing and clutch using a special puller. If you do not have a puller, you must first press in a set of axle shaft seals, and from the outside, use a punch to remove the bearing rings themselves.
- When replacing all defective elements, all that remains is to assemble the VAZ 2110 and 2112 differential in the reverse order. Be sure to pre-lubricate each part with any brand of gear oil before installing it in the gearbox. The driven gears must be installed with the outside of the tooth markings facing up.
At this point, the stages of replacing and repairing the differential end. All that remains is to adjust and check the operation while driving around the car.
Differential diagram, types of differentials
If we talk about the design of the differential, it is built on the basis of a gearbox. Depending on what type of gear transmission was used, bevel, cylindrical and worm differentials are structurally distinguished.
A bevel differential is typically used as a cross-axle differential, while a cylindrical differential is used between axles in all-wheel drive vehicles. A worm differential can be installed both between wheels and between axles.
The design of any differential includes a housing, satellites and side gears. The housing receives the torque from the main gear, after which it is transmitted to the gears and satellites. The driven gear of the main gear is fixed directly to the housing. Inside the housing there are axes on which the satellites rotate.
It is through the semi-axial gears that torque is transmitted through the axle shafts to the drive wheels. If the left and right gears have the same number of teeth, the differential is called symmetrical. For asymmetrical differentials, which are installed between the drive axles of the car, since they distribute torque between the wheels in a certain ratio, a different number of teeth is characteristic.
The traction force on a machine wheel is affected by the radius of the wheel, as well as the torque supplied to it. A certain traction force is produced on the dynamic radius of the wheel, which provides the torque that must be transmitted by the differential to the wheels.
If the car has poor grip on the road or one of the wheels is unloaded, then the traction force and torque on this wheel are practically absent. This means that the car will not be able to continue moving. A bevel differential, which is often found on domestic passenger cars, has a similar feature. Such a differential, usually used as a cross-axle differential, is called symmetrical, since it evenly distributes torque between the wheels.
Thus, when one of the wheels of the car has poor traction and there is practically no torque on it, the same thing happens to the second wheel, since the symmetrical differential transmits the same force to it. It turns out that if one of the wheels slips, the traction force on the second wheel will approach zero, which will negatively affect the vehicle’s cross-country ability.
Design features of RPA
In a free or simple differential, the right and left axle shafts are not rigidly connected to each other. A differential with increased internal friction will limit the independence of the axle shafts relative to each other. One of the main and most common rotation limiting schemes is the principle based on locking through discs (high friction differential).
RPA version
In addition to the main components of the free differential, the design of the RPA includes a set of friction and steel washers, which are located between the axle shaft and the housing. Friction discs are connected to the axle shaft, steel washers are connected to the unit body.
The side gear and friction discs always rotate together, while steel discs rotate only with the housing block. If the disk pack is compressed, the entire structure will begin to move as a single unit, and power will be transmitted directly to the axle, slowing down or stopping the rotation of the satellite.
A preload spring is installed in the space between the side gears, which exerts constant pressure on the clutch discs, compressing them slightly. In addition, the special design of the satellite gear and the play that exists between the axle shaft and the side gear increase the repulsive force, which will compress the disks on the axle whose wheel has the best grip. This will allow the power to be distributed evenly between the slipping wheel that is on ice and the one that is on level ground, and the slipping will stop.
Differential lock
In order to improve the vehicle's cross-country ability, differential locking is used, the degree of which is assessed using an indicator such as the locking coefficient. It is a number calculated as the ratio of the torque at the wheel that is lagging to the torque at the second wheel. For symmetrical differentials, this indicator is 1; for limited-slip differentials, which include a fully locking differential, a multi-disc differential, a viscous coupling, a torsen, a quay, the locking coefficient is in the range from 1 to 5.
Why is it brewed?
So, we come to the most popular question among novice street racers. A welded differential is made to make it easier for the car to skid just when turning. This phenomenon is called drift. A welded differential is most often done on older rear-wheel drive cars.
View gallery
This is especially true for the old domestic “classics”, where there is no blocking. What is a differential lock? This function allows you to change the torque transmission on the axle shaft. So, when the lock is turned on, the wheels rotate at the same angular speed. The system acts directly on the rear axle. "Niva Chevrolet" is also equipped with a lock. But this system is quite expensive and significantly affects the cost of the car. Therefore, not every machine has it. What to do in this case? There is only one way out - weld the differential. The procedure is quite simple, and you can do it yourself. The only thing you will need is a good welding machine and a mask to protect your eyesight when working with electrodes.
View gallery
After all, a bright electric arc greatly affects the human eye. Therefore, do not forget to wear a mask before work.