↑ Wheel alignment angles after maintenance
After the first maintenance (after 1500–2000 km) and during further operation of the vehicle, the wheel alignment angles should be:
- camber — 0°30'±20' (0° 5'±20')*;
- longitudinal angle of inclination of the turning axis - 4°±30' (3°30'±30')*;
- toe - 2-4 mm (3-5 mm)*.
The difference in the longitudinal angles of inclination of the turning axes of the right and left wheels should not exceed 0°30'.
Before adjusting wheel alignment, check:
- tire air pressure;
- axial clearance in the front wheel hub bearings;
- serviceability of shock absorbers (no rod jamming);
- radial and axial runout of tires;
- clearance in the upper ball joints of the suspension;
- free movement of the steering wheel.
Eliminate any detected faults and make the necessary adjustments.
The importance of regular wheel alignment
Wheel alignment - what is it? How often should a wheel alignment be done? Why do you need to do a wheel alignment? Let's try to answer without delving too deeply into the technical rationale.
The main mistake car owners make with regard to the procedure for adjusting wheel alignment angles (the same as wheel alignment or wheel alignment) is an underestimation of the importance of this procedure. As a rule, wheel alignment is performed in two cases - exclusively after replacing suspension and steering parts, less often during seasonal replacement of tires - and this is wrong!
In the service documentation of most modern cars, checking (if necessary adjusting) wheel alignment angles is a standard item of each “major” scheduled maintenance (usually TO-2, less often TO-3) - since all moving and elastic suspension elements are subject to natural deformation and wear during use.
After all, not only ball joints, shock absorber strut supports, steering rod joints and steering rack/integral steering gear mechanisms take impacts from road unevenness, but also, for example, silent blocks of levers and springs, which clearly affects the parameters of the factory installation, such as and sagging of elastic suspension elements, such as springs, springs and torsion bars, also entails a change in wheel alignment angles!
Incorrect or untimely adjusted wheel alignment angles affect not only intensive tire wear, but, what is much more important, the car’s handling and its behavior on the road as a whole, and this is not only your safety, but also the safety of other road users.
Believe me, daily parking on one side on the curb over 10,000 km between service intervals can seriously change the installation angles - as a result, the car will pull to the side when driving in a straight line, and, naturally, tread wear.
The shock load on the front suspension when overcoming artificial obstacles at high speed, for example, speed bumps, especially on cars with MacPherson strut suspension, can bring the parameters of the steering wheel tilt axis (caster) to zero or even a negative value, and this will inevitably affect handling .
Short and simple
If the camber angles on the right and left are different, then the car begins to pull to the side and constant steering is required. Impaired alignment leads to so-called yaw on the road. A car with caster below the factory value refuses to independently return the steering wheel to the zero position, which is especially noticeable when exiting corners.
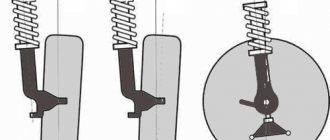
↑ Control and adjustment of wheel alignment angles
Monitoring and adjustment of wheel alignment angles can be carried out both on a loaded vehicle and on an unloaded one, however, monitoring the angles on a loaded vehicle gives more accurate results. Therefore, in critical cases, it is recommended to control and set angles on a car under a static load of 3136 N (320 kgf), which corresponds to approximately the weight of four people and a load of 40 kg in the trunk.
The car is loaded either with special weights suspended from the bottom of the body, or with ballast (280 kg) placed on the seat cushions and in the trunk (40 kg). The front seats should be in the middle position of their longitudinal travel. The cargo in the trunk is evenly distributed. The lack of fuel is compensated by the cargo located on the right side of the trunk area.
After installing the car on the stand, immediately before checking the angles, “press” the car’s suspension, applying a force of 392–490 N (40–50 kgf) 2–3 times, directed from top to bottom, first on the rear bumper, and then on the front. In this case, the wheels of the car must be parallel to the longitudinal axis of the car.
What are the alignment angles of car wheels, the procedure for checking and adjusting them
The movement of a car on the road can have a different character. The behavior of a vehicle is influenced by many factors, but first of all it depends on the design of the suspension (shock absorption system), tire size and type, and in addition, on the wheel alignment angles. UUC seriously affect the vehicle's driving behavior, as well as the service life of suspension parts and tire wear.
In order for the front wheels of a vehicle to experience the least resistance when rolling, their rotation must be parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. To increase the stability of the car on the road and improve handling, it is necessary that they are installed at certain angles in relation to each other and the body part.
During the operation of the vehicle, a gradual change in the values of these angles occurs. At first, this does not in any way affect the quality of handling and ride, but when they reach a critical value, it becomes noticeable that the car cannot maintain a straight trajectory without constant steering. In addition, tires begin to wear unevenly. Periodic (every 20-30 thousand km) checking the wheel alignment angles will help to avoid this. If it is determined that the UUC values do not correspond to the factory parameters, they must be adjusted. An unscheduled check and, if necessary, adjustment is carried out if the chassis has experienced a strong impact while driving - this most often happens when a car moving at high speed “flies” into a large pothole.
What angles of the front car wheels are there?
When adjusting the installation of the front wheels, you need to take into account the values of three angles: castor, toe and camber.
Castor
Castor is the angle of longitudinal inclination relative to the vertical of the rotary axis. It can have a positive or negative meaning. Correctly set caster ensures that the front wheels independently return to their original position after cornering and affects the camber of the vehicle wheels when the steering wheel is turned.
When the steering wheel is turned in one direction or another, the wheels also tilt in the same direction, which ensures a stable position of the car moving in an arc. For cars with a driven rear axle, the castor value should be about 10-12°; for front-wheel drive cars, this figure is set within 5-8°.
Convergence
Toe, like castor, can also have a positive or negative meaning. The closer to zero this indicator is, the less resistance the car’s wheels encounter when rolling.
Negative toe occurs when the intersection point of the longitudinal lines of the front wheels is at the rear of the car. This should not be allowed, since in this case the controllability of the vehicle is reduced, it responds less well to steering wheel movements, which causes “yaw” and can lead to an uncontrolled skid.
If the toe angle of the front wheels is positive (their longitudinal lines intersect in front of the vehicle), the car responds better to steering movements and turns into turns without difficulty. When adjusting the rear axle, a positive toe value is also set. This allows the vehicle to gain additional stability when driving in a straight line.
If the toe-in indicator deviates greatly from normal, the tire tread quickly wears out in a sawtooth pattern. If the deviation is negative, accelerated wear of the internal part occurs, if positive - the external part.
Camber
The angle with this name is located between the vertical rotation and the plane of the vehicle wheel. When the wheel is tilted outward, the camber will have a positive value, and toward the center of the car, it will have a negative value. If the camber indicator deviates from the norm, this will result in accelerated tread wear. In addition, when driving, the car will drive in the direction where the camber is greater.
How to properly regulate the Criminal Code?
If you arrive at the wheel alignment stand and see that the technician has taken up the adjustment without prior preparation, we advise you to refuse his work, since nothing good will come of it. When starting a procedure such as adjusting wheel alignment angles, you first need to assess the technical condition of the machine. This checks:
- The presence of play in the hub bearings and in the steering wheel.
- Serviceability of the components of the depreciation system.
- Presence of wheel rim runout.
- Tire air pressure indicator.
It should be remembered that the UUK should be checked and adjusted when the vehicle is completely unloaded. This means that you must first remove everything unnecessary from the interior and trunk, and the technician must ask the car owner about this before starting work. If he did not do this, it is unlikely that his professionalism is at a high level.
At the last stage of preliminary preparation, the steering rack must be set to the middle position. It is calculated by turning the steering wheel all the way from one side to the other and counting the total number of revolutions. The resulting number is divided in half. This value will exactly correspond to the middle. If this step is missed, the result may be different turning radii on the left and right sides. This will not have the best effect on driving comfort.
After completing the preparation, you can begin to directly work with the corners. They are regulated in a strictly defined sequence:
- Castor.
- Collapse.
- Convergence.
Castor, like camber, can be installed in different ways, the choice of which depends on the type of suspension. The design of many models, even such well-known ones as BMW, does not provide for adjustment of these angles at all. To adjust toe on any car, change the length of the steering rods.
Conclusion
Often, motorists experiment with settings of the control unit for various purposes, especially when it comes to sports cars. But if you are not the owner of a racing car or a regular participant in various rallies, it is better to adjust the angles of your car wheels according to the factory settings - this will have a beneficial effect on handling and will extend the life of the tires and suspension.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Article Rating
Tags: featured, UUK adjustment, wheel alignment angles
- Related Posts
- The procedure and features of tire studding
- What to do in case of car theft?
- How to avoid extra costs when installing additional equipment on a car?
Subscribe
0 Comment
Inline Feedbacks
View all comments
↑ Angle of longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation. What to do if it does not meet the norm?
↑ Front suspension:
- front wheel hub bearings;
- hub cap;
- adjusting nut;
- washer;
- steering knuckle axle;
- wheel hub;
- stuffing box;
- brake disk;
- ball pin of the upper support;
- rounded fist;
- ball pin protective cover;
- upper support bearing;
- upper suspension arm;
- upper support bearing housing;
- compression progress buffer;
- compression stroke buffer bracket;
- shock absorber support cup;
- shock absorber mounting pads;
- cushion washer;
- suspension spring insulating gasket;
- suspension spring upper support cup;
- upper suspension arm axis;
- inner bushing of the hinge;
- outer bushing of the hinge;
- rubber bushing of the hinge;
- support washer;
- adjusting washer;
- spacer washer;
- bracket for fastening the cross member to the body side member;
- front suspension cross member;
- stabilizer bar mounts;
- stabilizer bar cushion;
- stabilizer bar;
- body spar;
- lower arm axis;
- lower suspension arm;
- lower arm axle mounting bolts;
- suspension spring;
- stabilizer bar mounting clip;
- shock absorber;
- shock absorber mounting bolt;
- nut securing the shock absorber bracket to the suspension arm;
- bracket for attaching the shock absorber to the lower suspension arm;
- suspension spring lower support cup;
- lower support liner clip;
- lower support bearing housing;
- ball pin race insert;
- lower support bearing;
- ball pin;
- front wheel rotation limiter.
If, when checking, the angle value does not correspond to the data given above, change the number of adjusting washers 27 installed between the axis of the lower arm and the cross member.
↑ How to adjust or adjust the camber angle of the front wheels
If the camber angle differs from the norm, adjust it by changing the number of adjusting washers 27 installed between the lever axis and the cross member, following the table:
↑ What to do if the camber angle and longitudinal inclination of the wheel rotation axis changes when the number of washers in the packages changes?
To increase the camber angle, remove the same number of washers from both bolts, and to decrease it, add more.
↑ What to do if the toe-in of the front wheels is different?
If the toe-in value differs from the norm, loosen the side tie-rod clamps and use wrench 67.7813.9504 to turn both couplings the same amount in opposite directions; In this way, the couplings are screwed in or out and change the length of the side rods.
After making the adjustment, install the tie clamps with the slot horizontally with an upward or downward deviation of no more than 60° and tighten them in this position. When the nuts are tightened, the edges of the slots in the tie clamps should not touch.