Every car owner may experience one very interesting, incomprehensible headache in the form of smoke from the exhaust pipe, and especially owners of cars with a diesel unit. It seems that the car will drive and work, but the fact that it smokes will not leave its owner any peace.
The situation is interesting because the smoke can be of different colors: black, white, gray or smoke blue smoke, blue smoke is the most common. And for a certain reason, there will be smoke of a certain color.
The cause of black smoke may be fuel that has not burned completely. Smoke of this color occurs when there is an excessive supply of fuel or the fuel is of poor quality. A lack of oxygen will have the same effect. The same reasons are involved in the appearance of gray smoke. The smoke is gray in color only because the defects are not as serious as those that cause a black trail behind the car.
A diesel engine emits bluish smoke and there may be different reasons for this. If blue smoke is emitted while the car is running on a cold engine or an already warm one, then you should think about problems in the diesel unit. This effect can be caused by two problems:
- The fuel does not burn out.
- Engine oil enters the engine.
To understand why a diesel engine smokes, you need to diagnose it without resorting to the help of special devices. You can identify the problem by the degree of smokiness and the smell it carries.
Unburned fuel
This guess will be confirmed by the presence of a pungent and pungent odor from the exhaust system. This will mean that the unburned fuel comes out along with the smoke in a vapor state.
Fuel may not burn out for various reasons. It is possible that the fuel is supplied too late or that some cylinder does not cope with its task and cannot burn diesel fuel.
As a rule, every effect has causes. The consequence, in this case, is unburned fuel and, as a result, the diesel smokes blue. So what are the reasons and malfunctions in diesel components that can lead to this?
Injection pump faulty
If the cause of blue smoke is a delayed injection, then you should pay attention to the wear of the high pressure fuel pump (HPF). It is easy to guess that the fuel will not have time to burn out if it is supplied late.
So, we have decided on one of the possible culprits. But why does this happen? The design and operation of the injection pump is quite complicated. To explain in simple words, the operation of this unit is based on the movement of special mechanisms for supplying fuel, which constantly rub and contact each other.
The fuel itself serves as a lubricant for the parts. Quite a tricky solution, because diesel fuel has a greasy structure. But with the arrival of winter, a transition to winter fuel is made.
It is called winter because its viscosity is reduced, namely, those same lubricating fractions are missing or their quantity is not enough to lubricate the “hardware” in the pump. This is what causes the fuel injection pump to wear out. And the wear of this part of the unit, in turn, along with the profile of the wave washer, causes a delay in fuel injection.
The mechanism is as follows: the fuel does not have time to heat up because it is supplied late, and the cylinder begins to work poorly with surges. As a result, the fuel that does not have time to burn is released outside in the form of blue smoke.
If you warm up the engine after driving a few kilometers, the bluish trail behind the car will disappear or decrease so much that it cannot be traced. But pump problems will not be corrected by this. When the engine is warm, even fuel supplied late has time to burn almost completely due to the high temperature background.
Poor engine compression
There are times when strong blue smoke comes out when starting the engine. And then after proper warming up the smoke disappears. This picture is quite common in the courtyards of our country, when there are columns of smoke, and the driver is running, clutching his head, and cannot understand what is happening.
The reason for this is low engine compression. Due to this defect, the temperature during compression does not reach the required value, so the fuel does not burn out completely. Even if the engine has one cylinder with low compression, the operation of such an engine is possible. But it will smoke until the overall temperature rises and the faulty cylinder begins to cope with the incoming fuel and ignite it.
Blue smoke can be caused by untimely injection or low compression. By the way, most modern diesel engines are equipped with a device on the fuel pump that performs early injection when the engine is still cold.
With this function, the engine runs harder, but the fuel has time to burn completely. The engine heats up, and the device returns fuel injection to its initial state, the engine begins to “purr” and becomes pleasant and soft to the ear.
Blue smoke on cold diesel - Treatment of joints
Every car owner may experience one very interesting, incomprehensible headache in the form of smoke from the exhaust pipe, and especially owners of cars with a diesel unit. It seems that the car will drive and work, but the fact that it smokes will not leave its owner any peace.
The situation is interesting because the smoke can be of different colors: black, white, gray or smoke blue smoke, blue smoke is the most common. And for a certain reason, there will be smoke of a certain color.
The cause of black smoke may be fuel that has not burned completely. Smoke of this color occurs when there is an excessive supply of fuel or the fuel is of poor quality. A lack of oxygen will have the same effect. The same reasons are involved in the appearance of gray smoke. The smoke is gray in color only because the defects are not as serious as those that cause a black trail behind the car.
A diesel engine emits bluish smoke and there may be different reasons for this. If blue smoke is emitted while the car is running on a cold engine or an already warm one, then you should think about problems in the diesel unit. This effect can be caused by two problems:
- The fuel does not burn out.
- Engine oil enters the engine.
To understand why a diesel engine smokes, you need to diagnose it without resorting to the help of special devices. You can identify the problem by the degree of smokiness and the smell it carries.
The content of the article:
Unburned fuel
This guess will be confirmed by the presence of a pungent and pungent odor from the exhaust system. This will mean that the unburned fuel comes out along with the smoke in a vapor state.
Fuel may not burn out for various reasons. It is possible that the fuel is supplied too late or that some cylinder does not cope with its task and cannot burn diesel fuel.
As a rule, every effect has causes. The consequence, in this case, is unburned fuel and, as a result, the diesel smokes blue. So what are the reasons and malfunctions in diesel components that can lead to this?
Injection pump faulty
If the cause of blue smoke is a delayed injection, then you should pay attention to the wear of the high pressure fuel pump (HPF). It is easy to guess that the fuel will not have time to burn out if it is supplied late.
So, we have decided on one of the possible culprits. But why does this happen? The design and operation of the injection pump is quite complicated. To explain in simple words, the operation of this unit is based on the movement of special mechanisms for supplying fuel, which constantly rub and contact each other.
The fuel itself serves as a lubricant for the parts. Quite a tricky solution, because diesel fuel has a greasy structure. But with the arrival of winter, a transition to winter fuel is made.
It is called winter because its viscosity is reduced, namely, those same lubricating fractions are missing or their quantity is not enough to lubricate the “hardware” in the pump. This is what causes the fuel injection pump to wear out. And the wear of this part of the unit, in turn, along with the profile of the wave washer, causes a delay in fuel injection.
The mechanism is as follows: the fuel does not have time to heat up because it is supplied late, and the cylinder begins to work poorly with surges. As a result, the fuel that does not have time to burn is released outside in the form of blue smoke.
If you warm up the engine after driving a few kilometers, the bluish trail behind the car will disappear or decrease so much that it cannot be traced. But pump problems will not be corrected by this. When the engine is warm, even fuel supplied late has time to burn almost completely due to the high temperature background.
Poor engine compression
There are times when strong blue smoke comes out when starting the engine. And then after proper warming up the smoke disappears. This picture is quite common in the courtyards of our country, when there are columns of smoke, and the driver is running, clutching his head, and cannot understand what is happening.
The reason for this is low engine compression. Due to this defect, the temperature during compression does not reach the required value, so the fuel does not burn out completely. Even if the engine has one cylinder with low compression, the operation of such an engine is possible. But it will smoke until the overall temperature rises and the faulty cylinder begins to cope with the incoming fuel and ignite it.
Blue smoke can be caused by untimely injection or low compression. By the way, most modern diesel engines are equipped with a device on the fuel pump that performs early injection when the engine is still cold.
With this function, the engine runs harder, but the fuel has time to burn completely. The engine heats up, and the device returns fuel injection to its initial state, the engine begins to “purr” and becomes pleasant and soft to the ear.
It's all about oil
With this diagnosis, the “cloud” from the exhaust pipe will smoke from light to dark shades. It will depend on the concentration of oil that flows into the combustion chambers, engine operating conditions and warm-up temperature. At the same time, you will feel the burnt smell characteristic of the oil.
The appearance of such gas will be indicated by increased oil consumption. To solve this problem, you need to decide on suppliers of “unnecessary” fluid.
Wear of the cylinder-piston group
Very often, a diesel engine produces bluish smoke due to wear of the cylinder-piston group and timing components (gas distribution mechanism). Oil can get into the cylinder for several reasons.
- The piston ring clearances have been increased.
- The gaps between the valve stems and guide bushings have been increased.
- There is damage on the cylinder liner.
- The rings are destroyed.
- There are violations of the piston grooves and many other reasons.
For example, severe gap defects in the area of the piston grooves allow the combustion chamber to “suck” oil. This is possible even if the oil scraper rings are in good condition. With a long period of operation, the cylinders can change their shape, for example, become elliptical. Due to changes in shape, compaction deteriorates.
Wear of this group of parts also causes a decrease in compression. When measuring compression, it is worth taking into account the ability of the oil to seal gaps. It turns out that if the cylinder is faulty, then the compression should be too high. To carry out diagnostics of the CPG (cylinder-piston group), take measurements and obtain an accurate assessment, certain requirements must be met.
If the mechanisms do not have a very large deterioration in quality, then the notorious smoke can be seen when the engine warms up. After warming up, the level of the symptom decreases or disappears completely. This is explained by the fact that at high temperatures the parts expand and the gaps become sealed.
An increase in oil consumption occurs when the bridges between the piston grooves break down. Also, high oil consumption is caused by broken rings as a result of wear or overheating of the engine. If you use low quality oil and do not change it on time, the piston rings seem to “stick” and lose their mobility.
Deterioration of the piston rings and cylinder seals will cause increased fuel consumption.
The fact of oil ingress can be detected by the characteristic noise in engine operation and knocking, accompanied by changes in speed and load on the engine.
Timing belt faulty and other reasons
Oil smoke can be caused by the following:
- Burnt or damaged valves.
- Worn valve stems and guides.
- Malfunctions in valve stem seals.
Why blue smoke is emitted on a warm engine can be explained by relying on the fact that the oil dilutes with increasing temperature of the internal combustion engine. The following example can be given. This can always be observed when tractors are operating.
It often happens that when the engine is idling, oil accumulates on parts, forming films, thereby accumulating in the exhaust system. Then when the tractor driver presses the gas pedal, the exhaust pipe splashes out thick blue smoke.
The fuel supply system may be faulty or the valves may not be tight. All this can cause a diesel unit to smoke blue. A burnt-out valve gives the exhaust gases a white-bluish tint. This valve defect can be traced to the low compression of the faulty cylinder. Plugs are also susceptible to carbon deposits and deposits, which will indicate this deficiency.
Turbine malfunctions are possible. They may resemble the symptoms of unhealthy valve stem seals. To make sure of this, you can probe the turbocharger pipes for the presence of oils. Turbocharger seal problems are more difficult to identify because the oil that enters the exhaust system burns completely.
Also, the causes of blue smoke may be malfunctions of the crankcase ventilation or problems with ignition in the cylinder. Very often, blue smoke is accompanied by a decrease in thrust, and atmospheric and turbo diesel engines may have seal leaks, etc.
It is worth noting that the reasons for this behavior of the car may be poor fuel quality. Therefore, you should only refuel from those companies that provide good quality fluids. Beware of gas stations that offer diesel fuel at a low price.
Source: AvtoDvigateli.com
By
It's all about oil
With this diagnosis, the “cloud” from the exhaust pipe will smoke from light to dark shades. It will depend on the concentration of oil that flows into the combustion chambers, engine operating conditions and warm-up temperature. At the same time, you will feel the burnt smell characteristic of the oil.
The appearance of such gas will be indicated by increased oil consumption. To solve this problem, you need to decide on suppliers of “unnecessary” fluid.
Wear of the cylinder-piston group
Very often, a diesel engine produces bluish smoke due to wear of the cylinder-piston group and timing components (gas distribution mechanism). Oil can get into the cylinder for several reasons.
- The piston ring clearances have been increased.
- The gaps between the valve stems and guide bushings have been increased.
- There is damage on the cylinder liner.
- The rings are destroyed.
- There are violations of the piston grooves and many other reasons.
For example, severe gap defects in the area of the piston grooves allow the combustion chamber to “suck” oil. This is possible even if the oil scraper rings are in good condition. With a long period of operation, the cylinders can change their shape, for example, become elliptical. Due to changes in shape, compaction deteriorates.
Wear of this group of parts also causes a decrease in compression. When measuring compression, it is worth taking into account the ability of the oil to seal gaps. It turns out that if the cylinder is faulty, then the compression should be too high. To carry out diagnostics of the CPG (cylinder-piston group), take measurements and obtain an accurate assessment, certain requirements must be met.
If the mechanisms do not have a very large deterioration in quality, then the notorious smoke can be seen when the engine warms up. After warming up, the level of the symptom decreases or disappears completely. This is explained by the fact that at high temperatures the parts expand and the gaps become sealed.
Causes of black smoke from a diesel engine muffler
The higher the engine speed, the thicker the cloud of black smoke - this sign indicates incomplete combustion of fuel in the engine.
Finally, check the coolant level and make sure it is dropping. If there is enough loss of coolant that the engine sprays in the morning, it means you have a serious problem. If it's losing coolant, whatever you do, don't add coolant or drive the car. Diluting the fuel or oil can kill the engine in a hurry if too much coolant gets into one of these systems.
There are also less likely causes, such as a methanol in the water system that is leaking into the engine, or a bad grid heater, but these few ideas should get you started. Jeff Kittin Redding, California. The jury is still out on how well this type of setup will work. The arrangement of these turbochargers typically consists of two naturally aspirated turbochargers feeding an interstage compressor, which then feeds the high pressure turbine, which then feeds the engine. In short, four turbines in three stages.
This most often happens for two reasons:
- Too much fuel is supplied to the combustion chamber;
- Diesel fuel is of too poor quality.
For what reasons can too much fuel be supplied to the engine? Here are the most important of them:
- Wear of the injectors, as a result of which fuel, which should be supplied under high pressure and evenly distributed throughout the combustion chamber, simply flows due to low injection pressure;
- Incorrect fuel supply setting in the high pressure fuel pump (HPF);
- Excessive wear on the speed controller in the fuel pump;
However, it should be added that black smoke can also appear as a result of a lack of air in the combustion chamber. This could be caused by a clogged air filter or a faulty EGR valve.
Diagnosis of the cause of white smoke
Why would anyone run so many turbochargers?
Even the nastiest single turbos we typically know of a grenade, if you try to push them around 100 psi, that's too much pressure even for a billet ball bearing design. However, the seal allows for much higher pressure ratios, often in excess of 250 psi. The downside to using a lot of turbochargers is that each turbine wheel has a certain amount of power to spin, so unless it actually requires that much boost pressure, running more of a simple set of compound turbos will just take away power and add complexity.
Remember that gray smoke indicates the same problems as black smoke, only in this case they are not as obvious.
Causes and methods of eliminating black smoke from the exhaust pipe of a diesel engine
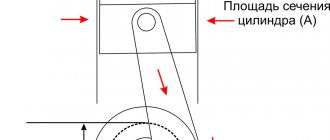
The appearance of smoke in engines running on diesel fuel occurs much more often than in gasoline power units. It's all about the principle of fuel ignition. To carry out this process, the air in the diesel engine is heated to 750-800 degrees and pressure is created. In a gasoline engine, ignition occurs from the spark plug. Plus, diesel fuel requires a higher temperature to ignite than light fractions of fuel. Compared to a gasoline engine, in a diesel engine the mixture is formed in a very short time, which leads to its heterogeneity.
Do not forget: in order to burn 1 liter of fuel, up to 15 liters of air are required. Smoke indicates a malfunction of one or more systems at once. There are several reasons for this.
Air filter dirty
This element of the fuel system belongs to the category of consumables. Therefore, it must be changed on time in accordance with the instructions for the machine. However, if it is constantly used in difficult conditions, for example, with heavy dust, then the intervals between replacing the air filter should be reduced. It is especially important to prevent moisture from getting on it. If this does happen, the filter must be thoroughly dried or a new one installed.
Standard rectangular air filter
The frequency of replacing the air element is from 15 to 30 thousand km. It is recommended to change the filter along with the oil, i.e. after about 10 thousand km. The replacement process can be entrusted to specialists at a service station or you can do everything yourself: it is not difficult. Each machine attaches the filter differently: these can be bolts, screws, or plastic latches. But in most cases, the algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Place the car on a level surface, activate the handbrake, turn off the engine;
- open the hood, find the location of the filter and remove its cover;
- pull out the air element carefully so that accumulated dust and debris do not get inside the engine;
- plug the inlet pipe with a clean rag;
- using a compressor, or better yet, a vacuum cleaner, remove dust from the seat;
- remove the rags from the pipe and install a new filter;
- return the cover to its place and secure it.
If it is not possible to purchase a new product, you can clean the old one, but this is only a temporary measure: you will still have to buy a filter.
Summary
Let's briefly list:
- First of all. It is necessary to fill the tank with known high-quality fuel, and it is advisable to drain the remains of the previous one. After this, you can evaluate the quality and intensity of exhaust gases.
- It is worth checking or immediately changing the fuel filter
- The next step is to check or replace the engine air filter to avoid airborne contaminants.
- With some skills and knowledge of the design of modern cars. You can independently check the operation of the injection system and the operation of the injectors
- It is worth noting that in the case of a diesel unit, the most common cause is dirty injectors, so have them cleaned immediately
- To be on the safe side, you can measure the compression in each cylinder and compare it with the nominal pressure tolerances for your car.
Low compression in cylinders
This parameter of engine operation can be checked at the nearest service station or done independently if you have a compression meter or compressograph. The difference between these devices is in the method of outputting information for reading. In the first case, the compression level is shown by a dial gauge. In the second, everything is displayed on a computer monitor with the ability to print out the results.
To carry out measurements correctly, certain conditions must be met. The air filter should not be clogged, the crankshaft rotation speed should be 200-250 rpm. The required compression value is indicated in the documentation for the machine.
- Disconnect the corresponding valves from the high pressure pump (HP pump) to stop the fuel supply;
- turn off the injection pump dispenser;
- remove the glow plug;
- Connect the measuring device to the flange;
- crank the crankshaft with the starter and at the same time take readings from the compression meter or compressor;
- take readings when the pressure stops increasing;
- test each cylinder, recording the data obtained.
Engine compression is affected by the condition of the cylinder-piston group. If the pressure is significantly different from the norm, the reason most often lies in worn parts: piston rings, pistons themselves, cylinder walls. This is often due to low quality fuel and lubricants. The situation can be corrected by boring the block in a specialized workshop. If the discrepancy between the compression and the parameters specified in the documentation is insignificant, you can use special additives.
Another reason for decreased compression is the lack of tightness of the valves. This will require disassembling the mechanism and cleaning (replacing) parts.
Checking the functionality of the injectors
If one of them is clogged, the motor will “triple”: it’s not difficult to figure out the culprit. You need to start the engine and turn off each injector one by one. A change in the sound of a running motor indicates the normal condition of the part. If there is no response from the power unit, we can assume that the problematic spare part has been found. But if the injector overflows, then finding it will require a more complex procedure. Before testing, prepare a 20 ml disposable syringe and a transparent IV tube.
- remove the plunger from the syringe;
- start the engine and connect the syringe to the “return” of the nozzle, i.e. insert the tube into the neck of the medical instrument;
- hold the syringe for a couple of minutes until it fills with diesel fuel (if it does);
- repeat the operation for all injectors.
An empty syringe or 4-5 ml of diesel fuel in it indicates the serviceability of the part. The presence of 10-15 ml inside is a sign of its partial functionality (repair and cleaning are possible). A volume of 20 ml of fuel in the syringe indicates the need to replace the injector. The exact volume of diesel fuel that it must dump back must be indicated in the vehicle instructions.
How to check the injection pump
Incorrect operation of this device may be accompanied not only by black smoke, but associated symptoms include:
- increased fuel consumption;
- unstable idling;
- problems when starting a diesel engine;
- constant overheating;
- drop in power, sluggish acceleration;
- extraneous noise during operation of the power unit.
The best option for checking the performance of the fuel injection pump is to use a stand in an auto repair center. In a garage, you can only partially check the pump:
- To check the plunger pairs of the device, remove the timing belt and slowly rotate the pulley. If you feel variable force, there is no water in the parts. If it is present, the shaft will not rotate, and the pump may jam at startup.
- The pressure in the pump is checked using the RB-4802 tester or another similar device. It is screwed in instead of the fuel pump pipe. The correct readings are 300 kg/sq.m. see, if this is not the case, replace the plunger pair.
- In an electronically controlled motor, the speed sensor may break. In this case, diesel fuel does not enter the cylinders. The sensor is checked with an ohmmeter: infinite resistance indicates a break.
- Another reason for poor fuel injection pump performance is fuel leakage. To check the assumption, start the engine and shake the axis of the device lever. If you see diesel fuel leaking, replace the rubber seal in the problem area.
Problems with the turbocharger (turbine)
Its faults can be identified independently, without removing the unit from the machine. In addition to the appearance of black (gray) smoke from the exhaust pipe, problems with the turbocharger are indicated by:
- excessively noisy engine operation under load;
- constant overheating;
- reduction of power unit traction and dynamics;
- increase in fuel consumption.
You can check the turbine's performance by ear and visually. A normally functioning unit should not creak, hiss or whistle. Check the tightness of the pipe connections and the condition of the air filter. To make sure that there is no wear on the device, turn its rotor: it should not touch the body (play of no more than 0.05 mm is allowed).
There are also unexpected reasons when the engine smoke is increased. The “culprit” may be the ignition system control solenoid valve, which looks like a small bolt. Sometimes it is enough to hit it so that the engine stops smoking: the correct ignition angle is restored.
Diesel engines
Engines running on heavy fuel have recently become very, very popular. They are installed even in compact city cars, and for SUVs, minibuses and other large vehicles, the availability of a diesel engine version has become almost mandatory.
Article on the topic: Carburetor engine power supply system - looking for vulnerable spots!
In principle, in diesel engines, black smoke from the exhaust pipe is quite likely the norm. Especially in good old trucks like MAZ. But strict environmental requirements force manufacturers of modern heavy fuel engines to clean the exhaust, for which a so-called particulate filter is installed. Actually, black smoke from the exhaust on diesel cars is often just a clogged particulate filter. Accordingly, replacing it completely eliminates the problem.
Also, in such engines there is a problem of fuel overflow due to the fault of the fuel pump. Here it is a high pressure fuel pump. This is treated as in gasoline engines, by replacing it. By the way, this pleasure, for diesel engines of modern foreign cars, is not cheap at all.
Well, another reason that causes the appearance of black smoke is an incorrect ignition timing. Here you just need to set this parameter correctly.
If blue (grey) smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe
There are several reasons for this phenomenon: improper formation of the fuel torch, “uncomfortable” conditions for ignition of the fuel. The causes of blue smoke from a diesel exhaust pipe may be related to oil. When it gets into diesel fuel, the viscosity drops sharply. This results in the lubricant being unable to withstand friction. Identifying the problem of blue smoke is not difficult; to do this, you need to pull out the dipstick. If oil drips from it and you smell fuel, engine diagnostics and repairs are necessary. Oil can enter the combustion chamber in several ways:
- through worn oil scraper rings when they are stuck or worn out;
- through bad turbocharger bearing seals;
- from the air filter if the crankcase ventilation does not work (clogged).
Blue smoke from the exhaust pipe of a diesel engine can appear when the fuel stream is ineffective, when the diesel fuel does not burn completely and comes out of the muffler. It gives the smoke a bluish tint. But there is another danger here: the mixture begins to burn at the bottom of the piston, and not in the chamber; as a result, the part experiences enormous loads, which leads to scuffing on the cylinder walls. A diesel engine produces blue smoke even when the fuel is poorly ignited, which is associated with wear of the CPG elements, low compression, and faulty glow plugs. Except for the last case, there is only one way out - a major overhaul of the power plant.
Blue smoke from engine
Engines with injection
In injection engines, the fuel mixture is formed electronically, and this mixture is supplied to the combustion chamber through an injector. If the injector becomes clogged, a certain pressure must be reached in order for the fuel mixture to reach its destination. Moreover, the mixture is not injected evenly, resulting in excess fuel that does not burn as it should. This problem is solved by cleaning the injector, either mechanically or using special chemicals that are added to the fuel. The first option is more effective, and the second is simpler and more affordable. Such cleaning is carried out approximately every 60 - 70 thousand kilometers.
Article on the topic: The car stalls when you press the gas
Another reason for the incorrect formation of the fuel mixture in engines with direct fuel injection is the electronic component itself. The information necessary for the proportional formation of the fuel mixture is provided by various sensors. This includes a mass air flow sensor, a throttle position sensor and other devices of this type. Accordingly, if incorrect information is supplied, or if it is absent altogether, the correct proportions between fuel and air are violated, which leads to the appearance of unburned excess fuel and, accordingly, black smoke from the exhaust pipe. In fact, there are other symptoms characteristic of such situations. These include floating speed, excessive fuel consumption, jerking while driving, and other engine malfunctions.
Not so often, but it still happens that the reason for the appearance of excessive portions of fuel in the combustion chamber is the fuel pump, which is usually located in the gas tank. If, for some reason, it supplies gasoline with a pressure higher than the calculated one, excess will inevitably arise.
As for eliminating the described breakdowns, it is most often impossible to determine which sensor is ruining your life without the help of a specialist and diagnostic equipment. Well, in the case of a pump, it almost always has to be changed. Although here, it is better to consult a professional.
Why does diesel smoke white?
Thick, light exhaust indicates the presence of water (coolant - antifreeze) in the combustion chamber.
She can get there in different ways:
- cylinder head gasket is torn;
- The throttle cooling pipe has failed.
To determine the cause of white smoke from the exhaust pipe of a diesel engine, look into the expansion tank. If the above versions are correct, you will see the oiliness of the liquid in the container, its low level and the smell of exhaust gases. When you remove the crankcase, instead of oil there will be an incomprehensible liquid there. To solve the problem, you will need to install a new gasket and/or replace the pipe. But don’t panic if the diesel engine smokes when cold and then stops: this is normal.
White smoke from engine
White steam from the exhaust pipe of a gasoline engine
This is not a typo. It's really not about smoke, but about steam. About water vapor. How can it be distinguished from other emissions from a car's exhaust system? First of all, it's white, like cigarette smoke. Secondly, if you bring a white napkin to the exhaust, the steam will not leave any traces on it except moisture. Thirdly, if there is no fog, rain or frost outside, then this is not steam, but smoke. We'll talk about it in the next section.
Where does this steam come from? In fact, there are several sources at once. The simplest is condensation accumulating in the exhaust pipe. It forms there when, after another trip, the system is still hot, and the temperature outside is always lower. All. The condensate droplets are ready. Then, when you start the engine, they will begin to evaporate and appear as white “smoke” from the exhaust pipe.
The second source of white vapor is condensation, which is formed as a result of a sharp change in temperature and humidity in the exhaust pipe and beyond. For example, if there is severe frost or damp weather outside, the car can hover constantly. Moreover, the clouds of steam will be so thick and dense, as if a vaper had settled in the exhaust pipe (who doesn’t know what kind of miracle this is, google it).
The next source of white “smoke” is moisture entering the engine cylinders. It can get there either with fuel or with air, which is used by the carburetor or injection system to prepare the air-fuel mixture. Under the influence of high temperatures in the combustion chambers, this moisture turns into steam, which has nowhere else to go except to escape from the exhaust pipe.
As you can understand, white steam from the exhaust pipe of a gasoline engine is not an indicator of any malfunction. Unless water gets into your fuel tank. Everything else is not scary, and with the onset of good weather or after the engine warms up, it goes away by itself.
It’s a completely different matter if white steam constantly pours out of the exhaust pipe, regardless of air humidity and temperature. Moreover, in specific dense clubs. Such smoke is also steam, but it may already indicate depressurization of the cooling system. Moreover, not about the external one, which can be seen visually by the smudges, but about the internal one. That is, the coolant penetrates the cylinders and evaporates very intensively.
The consequences of operating an engine with such a malfunction can end very sadly. Firstly, there is a high probability of leaving the engine without a sufficient volume of coolant, and it will seize from overheating. Secondly, antifreeze that gets into places where it is not needed will very effectively wash away the oil film there, as a result of which engine lubrication will significantly deteriorate. The result can be both overheating and accelerated wear of rubbing parts.
Consequences of ignoring the problem
The most unfortunate result is engine jamming and subsequent major repairs. A less complex, but also unpleasant consequence is a reduction in the service life of the power unit. Therefore, it is easier and cheaper to identify a faulty unit or part in a timely manner and repair or replace it. For example, when a particulate filter becomes clogged, dirt begins to get into the lubricant, causing the oil line to become clogged.
As a result, the motor parts begin to overheat and work under increased load, which leads to a reduction in the service life of the motor. In the worst case, valves and pistons burn out.
The appearance of smoke of any shade from the exhaust pipe does not mean that major repairs are immediately required. This is just a serious signal that cannot be ignored, so as not to “run into” an expensive restoration of the power unit at a car service center. It is recommended to stop using the car as soon as possible and to diagnose the engine condition at the initial stage.
Diagnosis and localization of the problem
In the first case, the exhaust is blue, pungent, and has a pungent odor. The reason is that only well-atomized diesel fuel burns in the cylinder. Drops of unburned diesel fuel fly out of the exhaust pipe in a vaporous state. The other part of the drops burns inside the cylinder, but on the piston itself. This causes severe overheating of the piston, which can lead to melting or burnout.
The culprit of the malfunction turns out to be the fuel equipment of the diesel engine. Often the problem lies in the injection pump and diesel injectors. Smoking from the bluish exhaust when the diesel engine is warming up indicates a malfunction of the glow plugs or a drop in compression in the cylinders.
In the second case, the exhaust takes on a color from whitish-blue to dark blue. The color of the exhaust directly depends on the amount of oil penetrating into the combustion chamber, the operating mode of the internal combustion engine and the degree of engine warming up. The smell of exhaust with a lot of oil is burnt, such smoke takes a long time to dissipate in the air.
The appearance of oil smoke is accompanied by an increase in engine oil consumption. During operation of the internal combustion engine in transient modes, the smoke with impurities of burnt oil is thicker. The catalyst (catalytic converter) of gasoline engines cleans the exhaust of oil even at high consumption. On diesel internal combustion engines, oil exhaust is more noticeable.
Smoke from the exhaust pipe after an oil change
This is quite a common case that leaves the car owner bewildered. It would seem that it is fresh oil, of high quality, maybe even very expensive... But the engine, which was working properly before replacement, suddenly begins to smoke furiously. How can new oil have such an effect on the engine?
The answer lies in the viscosity of the oil, as well as in the degree of wear of the piston group parts. As a rule, this kind of smoking appears only in cases where a less viscous oil is replaced by replacing a more viscous oil. For example, it was 10W40, but they filled it with 5W30. The problem is that less fluid oil penetrates less well where there is already wear and microscopic gaps. When a less viscous oil is poured in, it “leaks” into the combustion chambers more easily, and then you already know...
What are the consequences of such exploitation? Firstly, driving a car that behaved like this after an oil change is highly not recommended. There is obvious wear and tear that requires urgent repairs. Secondly, in some cases the situation can be corrected by decarbonizing the engine. Thirdly, the latter works only in 20% of cases, and in the rest, it is impossible to do without repairing the piston.
Blue smoke: wear of the cylinder-piston group
The most common reason that a diesel engine produces blue smoke is wear of the cylinder-piston group and timing parts. Oil entering the combustion chamber may occur due to increased piston ring gaps, gaps between valve stems and guide bushings. Damage may occur on the cylinder liner; rings, piston grooves, etc. may be destroyed.
The presence of strong gaps in the area of the piston grooves causes oil to be “sucked” into the combustion chamber. This happens even taking into account the normal condition of the oil scraper rings. Additionally, the shape of the cylinder can change, which significantly reduces the sealing by means of rings. The cylinders may take on the shape of an ellipse, resulting in gaps appearing. Wear of the CPG causes loss of compression, and crankcase gas pressure also increases. When measuring compression, it must be taken into account that the oil in the cylinders can seal the gaps. It turns out that the compression in the faulty cylinder will be too high. To obtain accurate results for assessing compression and the state of the CPG, a number of specific requirements must be met.
If the CPG is not worn out much, then blue smoke is clearly visible during the engine warm-up process. After reaching operating temperature, the smoke intensity decreases or the blue diesel smoke completely disappears. This is explained by the expansion of parts as a result of heating, which causes sealing of the gaps. An example is that diesel is bad, but a repeated hot start occurs without problems.
Oil consumption increases as a result of breakage of the bridges between the piston grooves. An increase in engine oil consumption results from broken rings as a result of wear or overheating of the diesel engine. Using low quality oil and not changing it on time leads to stuck piston rings. The rings “stick” in the piston grooves, and their mobility is completely lost.
Direct (excessive oil consumption) and indirect signs help identify oil getting into the cylinders due to CPG wear. The second group includes: the appearance of noise from the operation of the engine, various knocking sounds appear with changes in speed and load on the engine, the intensity of blue or gray smoke changes as the engine warms up, unstable operation of the diesel engine is noticeable when starting “cold”.