Checking the solenoid valve of the carburetor 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex
The presence or absence of idle speed on the engines of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars with carburetors 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex often depends on the serviceability of the carburetor solenoid valve.
If any problems arise with the engine idle speed, first check the solenoid valve. 1. Turn on the ignition, but do not start the engine.
2. Remove the wire tip from the solenoid valve terminal.
This way we de-energize it. Its shut-off needle is in a forward position and closes the hole for supplying the fuel mixture to the idle system of the idle system fuel nozzle.
3. We put the tip of the wire on the terminal of the solenoid valve.
That is, we apply voltage to it. A click should be heard. This shut-off needle retracted into the valve body and opened the fuel supply hole into the idle system. This means the valve is OK.
If there is no click, we check whether the solenoid valve itself or its electrical circuit (EPHH system) is faulty.
4. We connect a piece of wire between the plus of the battery and the terminal of the solenoid valve.
A click appears - the electrical circuit is faulty. Let's check it further. There is no click - we change the valve.
In addition, we check the idle speed system fuel nozzle inserted into the tip of the solenoid valve. To do this, unscrew the valve from the carburetor. We take out the jet with pliers and visually inspect it. The jet should not be deformed; we wash its holes and clear them of contamination.
We check the integrity and presence of the sealing ring on the valve. Worn out, it can be a source of “suction” of foreign air and a leaner fuel mixture and, as a result, engine tripping.
Notes and additions
— If the electrical circuit of the solenoid valve of the carburetor 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex is faulty, you can apply current from the terminal plus the ignition coil to its terminal by extending the wire directly. Thus, it is possible to restore the idle speed of the car engine, which was lost due to the fault of the carburetor EPH system. It is not worth driving in this way for a long time, since the valve will be constantly energized, which discharges the battery, and it is also possible to short circuit this electrical circuit not protected by a fuse.
— An indicator of the correct operation of the Solex carburetor solenoid valve is the following check. With the engine idling, remove the wire tip from the terminal on the valve. The engine should stall. That is, in this case the valve is de-energized, and its needle has blocked the access of the fuel mixture to the idle system.
— It’s better to check a new valve ready for installation in the carburetor first. We connect its terminal with a piece of wire to the positive of the battery and touch the valve body to the negative of the battery. The needle should retract. If this does not happen, the valve is faulty, or its needle gets stuck when moving, which is also not good.
Five more articles on the site on carburetors 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex
Why do you need a guide bushing?
The guide bushing can quite rightly be considered the main element on which the resource and proper operation of the “seat - valve plate” tandem depends. The material from which the part is made and its design itself are primarily aimed at working under conditions of high speeds of the valve stem fixed in it, constant high-temperature loads and the almost complete absence of lubrication in the valve-bushing pair.
Causes and consequences of deformation
The described conditions lead to the fact that during engine operation, the valve guide bushing also wears out, which is why, over time, its alignment with the valve stem may be disrupted. Subsequently, the part breaks even more and the valve begins to “walk” and does not fit tightly to its seat, and this, in turn, leads to the chamfer of the seat breaking over time. As a consequence, you can get a burnout of the valve and have to replace the seat.
Appearance of bronze guide bushings for VAZ 2108–2109 models
Also, due to the “walking” of the valve in a broken guide, the oil seals can quickly become unusable. They simply will not be able to hold oil with increased angular displacement of the valve stem. The result will be oil getting into the engine, and if you also take into account that more oil will pass through the broken bushing than usual, then the situation will not be pleasant. Carbon deposits on valves and other parts around the combustion chamber will increase, the level of harmful exhaust emissions will increase, and you may end up with a prematurely failed catalytic converter. And simply replacing the valve stem seals is not enough, as the problem will soon return again.
Why you shouldn't neglect checking
When repairing an engine, it is better to pay special attention to its head. Often it is this part of the engine that is to blame for the fact that the level of compression in the cylinders is far from the desired level. When repairing cylinder heads, motorists sometimes limit themselves to only grinding the valves to their seats, believing that there is nothing particularly wearable in all-metal bushings. At the same time, checking how large the gap between the part and its valve is will be completely worthwhile. When the obtained clearance figures go beyond those recommended by the car manufacturer, then no amount of grinding in the valves or replacing the valve stem seals will protect against problems in the future.
Materials used to make bushings
For the manufacture of bushings, materials with good wear resistance and thermal conductivity are used. Among these you can find:
- special cast iron alloys;
- bronze;
- brass;
- metal ceramics.
In terms of thermal conductivity and cost, brass, along with bronze, are among the leaders, so the vast majority of bushings are made from alloys of these metals.
Nuances to consider
Most bushings have a special support collar on the outside, designed to ensure proper fixation of the part vertically in the cylinder head. If the part is smooth, then installation is carried out using a special mandrel.
For intake valves, the guide bushings should not protrude so as not to increase the aerodynamic drag of the intake channel. Exhaust valve bushings are designed to “hide” the valve stem as much as possible to protect the latter from high temperatures and better heat dissipation.
Appearance and location of the valve guide in the cylinder head
The manufacturing precision of the bushings is very high. This is necessary to obtain the most accurate alignment and the best fit of the valve plate and seat during engine operation. The outside of the body of the part that is to be pressed into the cylinder head must be processed as cleanly as possible; there should be no scratches or marks on it. This ensures optimal heat removal from this accessory to the block head.
Video: review of valve guides for VAZ 2108–2109
Solenoid solenoid valve: where it is used + types and principle of operation
In addition to the usual manual valves, you can also see an automatic solenoid valve in the store. It allows you not only to control the flow of liquids and gases in pipelines at a distance, but also to automate this process.
Such devices differ in internal design and purpose. However, the principle of operation for all of them is the same - the closing/opening of the tap occurs due to the operation of an electromagnet.
In this article we will look at why such a valve is needed and how it works. We will also talk about the main types of solenoid valves.
What is it needed for?
A check valve is required for the pressure maintenance system in the water supply to work correctly. That is, the water will not go back into the well after the pump pumps up pressure, otherwise it will work constantly.
Why is a solenoid valve needed?
Solenoid valves are a category of modern shut-off valves for pipelines for a wide variety of purposes. In everyday life, such electric valves are used in cars, special equipment, water supply systems and automatic watering and heating systems.
They are also widely used in industry to regulate current and control the transport of a variety of liquids and gases.
The solenoid valve for water or gas does not have any sensors inside. With its help, you can only regulate or completely block the flow of the working environment. If automation of these processes is required, then you will have to additionally install external measuring instruments, tying the operation of the electrovalve to them.
For example, use an additional controller and a water leakage sensor in combination, so that when a leak is detected, the solenoid valve receives the appropriate command from the controller and shuts off the pipeline.
The advantages of using solenoid valves include:
- quick adjustment of the working medium current through the pipeline;
- versatility and reliability of the device;
- long service life;
- small size and light weight;
- variety of instrument types.
The valve operates literally within a split second after the signal is given. It is designed to work with liquids under different pressures, from 0 to 25 bar, and with varying temperatures, from -20 to +120 ° C. At the same time, in a de-energized state, such an electric valve can remain either in a closed or open position - it all depends on the modification of the device.
In water supply systems, it allows you to automatically shut off the water supply if the pipes burst. And in heating systems, such a valve is used as a device for regulating the flow of coolant.
Types and groups of gas valves
EGCs differ in design features, which determines their classification:
- by type of execution - normally closed or normally open;
- by type of working medium - for water, gas, air, steam, fuel;
- according to operating features - conventional and explosion-proof;
- according to the principle of action - direct, indirect, combined.
Depending on the number of strokes of the saddle, the devices are:
- single-stage or one-pass.
The valve can be in the open or closed position. Having received an electrical signal, it opens completely and ensures the passage of the required amount of fuel; - two-stage or two-pass.
EGC may be in an intermediate position. This is necessary for a smooth start of the burner. The valve, which is partially opened, opens completely after a certain time and ensures the operation of the equipment in the maximum permissible mode. Partial opening results in a stable flame on the burner; - three-stage or three-way.
This type of solenoid valve is equipped with devices with 2 power levels. In this design, the first stroke starts the unit, the second repeats the functions of the first stage of two-stage devices, and the third ensures that the equipment operates at full power; - modulating.
In this case, the device is equipped with modulating gas valves in which the seat opens to a user-specified position.
According to the type of control, valves are:
- with manual control.
These are simple designs whose shutter is activated by turning a control wheel or lever. Such devices are highly reliable and low cost; - automatic.
The design of such models is equipped with an electric drive, which allows you to control the device from a distance. Most often used in industrial facilities: gas pipelines, heating networks, production lines.
Based on their functional purpose, the following types of gas valves for boilers and other devices are distinguished:
- back.
Protects the pipeline from gas circulation in the opposite direction. A check valve mechanism allows current to flow in only one direction; - safety.
It is a protective device that prevents emergency situations due to a sharp pressure drop in the gas pipeline.
How does a solenoid valve work?
The solenoid valve consists of:
- steel, cast iron, brass or polymer housings;
- induction coil with core (solenoid);
- working locking element;
- seal;
- damping spring.
The copper induction coil inside the shut-off device is located in a sealed housing, where access to water is closed. The blocking or opening of the working medium current channel occurs due to the rod and membrane extending under the action of the solenoid.
In a de-energized state, under the influence of a spring, the valve completely shuts off the current channel or leaves it completely open. Further, after applying voltage to the coil, the core and the rod are displaced, as a result of which the cross-section of this duct increases/decreases.
The general principle of operation of the electromagnetic valve under consideration is simple - the movement of the rod occurs in it due to electromagnetic induction. When electric current flows through the coil, the core located in its center is affected by an electromagnetic field, the strength and direction of which depend on the applied voltage in volts.
As a result, the shut-off element is displaced and the flow area of the valve changes.
Electrovalves with low control voltage are designed to operate in small diameter pipelines and with low pressure of the working medium. The scope of their application is quite limited.
But such valves are easier to integrate into a control system on low-voltage semiconductor devices and connect to various microcontrollers. They are usually used in water supply systems and heating circuits of private houses.
Check valves for submersible pumps: installation rules
Before starting installation, you need to correctly select the place where the part will be installed. The location is dictated by the type of submersible pump. You can select any element; it will interact with the device, regardless of its type, brand and model. This is due to the fact that the operating principle of the equipment is the same. It is quite possible to replace check valves for submersible pumps yourself; to do this, you will need to carefully study the proposed material.
Pump connection diagram
Most pumps are already equipped with the required part from the factory. There is such a device at both the inlet and outlet. Such devices do not require additional devices.
If you purchased a vacuum pump, then the check valve must be installed in front of the accumulator, but after the unit itself. Ball or spool type devices work best with this type. If the pump is surface-mounted, it may have several such elements at once. One of them is installed in the hose through which water flows. The part must be placed at the end of the hose lowered into the water. The second element is mounted in front of the hydraulic accumulator. Any type of product is suitable for this device. Some models are an exception; The manufacturer indicates in the instructions for the device which ones are required.
Composition of the water pumping system
In order to install the return element, you will need to cut it into the pipe. To do this you need to purchase fittings and couplings. Before starting work, you need to turn off the water or stop the system so that the water flow does not interfere. Then the required element is cut into the right place.
Helpful information! You can make the fixation more durable using fum tape. Make sure that the element is facing the right way, otherwise it will not work. If it is lifting, check that the axle is vertical.
Elements for pumping stations are installed after the ratchet. They are located on the main suction pipe. It is possible to install it directly in front of the station, but this option is inferior in quality to the first one, since in this case the amount of water can be significantly reduced.
The pipe can be filled not only with water, but also with air, which is sucked in by the pump. Air entering the system will make it noisy. If the station uses a vibration pump, it is best to place the valve in front of the receiver. You can choose any place in the discharge pipe for this, but it is advisable to place it in a place accessible for maintenance.
Part fixed to the station pipeline
The item is most often mounted in front of the station. When installed on a running system, it must be located between the pump and the station. The same is done if the system has a receiver. The pipeline is divided into two parts, on one of which a valve is placed. Then the pipes are connected again using a squeeze.
You can familiarize yourself with the installation process on different types of equipment below:
Types of solenoid solenoid valves
There are several varieties of the device in question. Such devices are classified according to the material of the body, design and de-energized position of the lock inside, type of seal and method of connection to the pipes.
Each of these options is designed to work with a specific medium in terms of composition, temperature and pressure. The solenoid valve must be selected carefully. If you take a device that does not meet the requirements, it will not last long.
According to the method of connection, solenoid electrovalves are divided into:
And in size they can be from 6 to 150 DN (from 1/8 to 6 inches). There is an option for any pipeline.
The body of the electrovalves in question is made of:
- plastic (reinforced PPA, PVC, nylon);
- of stainless steel;
- brass;
- cast iron
Each of these options has its own characteristics for pressure and temperature of the working environment. These numbers should be carefully studied in the device passport so as not to make a mistake with your choice. At the same time, any of the above variations is suitable for plumbing or heating in a private house.
Classification #1 - by internal structure
Based on the design of the control element, valves are divided into three groups:
Household solenoid valves are usually made with a membrane. This is a cheap and reliable option that can easily cope with regulating the flow of water in domestic heating and water supply systems.
The main separation of solenoid valves is carried out according to the position of the locking mechanism when the electromagnet is de-energized.
According to this parameter, solenoid electrovalves are divided into:
- normally closed, valve closed (NC);
- normally open, valve open (NO);
- bistable.
In the first case, until voltage is applied to the solenoid, the core is lowered down due to spring pressure and there is no water flow. In the second case, when the device is de-energized, the channel, on the contrary, is completely open, and it closes only after power is applied.
The third option is that the position can be either open or closed.
Classification #2 - based on operating principle
Functionally, solenoid electrovalves for water at 220 V and other voltages are:
The first ones have only one connection pipe to the pipeline. These are safety devices designed to release steam or water when the pressure in the pipes is too high.
Three-way devices come with three pipe connections for connection to pipes. Such options are designed to redirect flow from one pipeline to another.
Three-way valves are most widely used in heating systems. Such devices make it easy to transfer coolant from one circuit to another to mix the working environment.
As a result, the temperature of the water in the system changes, but the source of thermal energy continues to operate without changing the mode.
Also, solenoid valves are:
- direct action;
- indirect action.
In the first, the core moves solely under the influence of an electromagnet. Secondly, its movement is also affected by the pressure of the working environment.
Classification #3 - based on the material of the seal and membrane
Inside the body of the solenoid valve there is a membrane that blocks the flow of water. Plus, there is a seal between the coil and the main one with the pipes. Both of these elements are made of elastic polymer materials.
The seal in solenoid valves can be made of:
- FPM (FKM, VITON) – fluoroelastomer;
- EPDM – ethylene-propylene elastomer;
- NBR – nitrile butadiene rubber.
The first option is characterized by a high maximum operating temperature and resistance to oils and gasoline. The second is cheap and resistant to salts, alkalis and acids dissolved in water. The third one calmly tolerates contact with petroleum products and is usually used in industry and automobiles.
This material does not greatly affect the price of the solenoid valve. Its parts are too small in size. The type of seal and membrane should be selected based solely on the characteristics of the working environment.
The thermal properties of the seals are presented in the following table:
Device
The technical design of such a product is simple, because has only three main elements:
- Round or rectangular/square body made of galvanized sheet metal or stainless steel. Installed in openings of building structures - floors, walls, partitions, incl. fire protection, attached to them on one or both sides.
- A movable damper, of which there can be from one to several, connected into one working structure that tightly covers the entire internal section of the product body.
- Drive - a mechanism of various types, principles, modes of action that brings the damper to the open position, because Most products intended for installation on protected objects are manufactured in the so-called normally closed design.
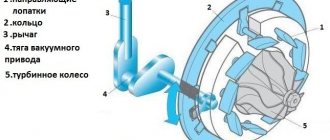
Operating principle of the carburetor solenoid valve
The carburetor solenoid valve is used to regulate the supply of the fuel mixture bypassing the throttle valve, which is controlled by the accelerator pedal. At idle, fuel enters the ICE inlet manifold through a separate channel. This is why the solenoid valve is also called the vehicle idle air control valve. The main purpose of the valve is to stop the fuel supply in inertial modes, which, for example, allows engine braking and coasting.
Installation
For the most part, plastic sewers are installed in private houses and apartments. Air valves are also selected from the same material - PVC or polypropylene. Like any sewerage products, they have a socket with a rubber seal at the end. The whole installation consists of putting the device on the prepared pipe. All.
For reliability, you can first coat the joint with plumbing sealant, but even without this measure the connection is airtight (as long as the pipe and device are of normal quality).
Signs of a malfunctioning carburetor solenoid valve
A malfunction of the carburetor solenoid valve can be determined by several characteristic signs:
- the engine regularly stalls at idle;
- the engine stalls when coasting;
- Fuel detonation occurs after the ignition is turned off.
The instability of the solenoid valve can also be determined by a drop in engine speed when an additional load is turned on (car radio, headlights, etc.). Thus, the main sign of a valve malfunction is unstable engine operation in idle mode.
Where to buy EGC?
If you are interested in high-quality solenoid valves, please contact. Our catalog includes a wide range of industrial drive equipment from European manufacturers. We offer a large selection of sensors, automation systems, recorders and power supplies for various purposes.
You can make a purchase from our company without much difficulty. The prices for gas appliances will pleasantly surprise you, and registration will require a minimum amount of time.
For additional information about gas valve models and their characteristics, please contact our managers by calling +375 (17) 513-99-92.
Valve check
Checking the solenoid valve for correct operation can be done in three different modes:
- when the engine is idling;
- when braking the engine;
- after turning off the ignition.
The general serviceability of the valve can be checked after turning on the ignition. To do this, you need to increase the engine idle speed to 2100 RPM. After crossing this mark, a characteristic click should be heard, which means that the valve has closed. After this, you can lower the speed, as soon as its number reaches 1900 RPM, a click should be heard again, meaning that the valve has opened.
When braking with the engine while the gear remains engaged, the valve should not open, even if the engine speed has dropped below 1900 RPM. If a click is heard at this moment, the valve is not working properly.
If detonation and vibration occur after the engine ignition is turned off, this means that the valve does not close the idle jet and the fuel mixture enters the engine, which also indicates a malfunction of the solenoid valve.
You can also simply check the valve by disconnecting the power cable with the engine running. The motor should stop immediately after disconnecting.
You can check the valve by completely disconnecting the device from the carburetor. After dismantling the valve, you can connect it to the battery, after which you should hear a click and the valve needle should retract into the device. After turning off the power, you should hear a click again and the needle should move out.
The problem with the solenoid valve may lie not only in its malfunction, but also in the electronic control unit and in the wires. You can check the functionality of the wire using a multimeter (12 V ± 10%).
Checking the functionality of the control unit will require connecting the valve to the battery using an additional wire. A standard voltage control light is also required. First you need to disconnect the supply wire from the valve and connect it to the positive terminal of the battery. An additional wire is also connected to the battery positive. After this, you need to start the engine, at the cut-off of 900 RPM the warning lamp should light up, after reaching 2100 RPM it should go out. When it drops to 1900 RPM, it lights up again. If these indicators are met, but the engine stalls at idle, then the fault is probably in the valve control unit.
Causes of phase regulator malfunction
Malfunctions are divided directly into the phase regulator and its control valve. So, the reasons for the malfunction of the phase regulator are:
- Wear of the turning mechanism (blade/vane) . Under normal conditions, this happens for natural reasons, and it is recommended to change the phase regulators every 100...200 thousand kilometers. Contaminated or low-quality oil can accelerate wear.
- Displacement or mismatch of the set values of the phase regulator rotation angles . This usually occurs due to the fact that the rotating mechanism of the phase regulator in its housing exceeds the permissible rotation angles due to metal wear.
But the reasons for VVT valve failure are different.
- Failure of the phase regulator valve seal . For Renault Megane 2 cars, the phase regulator valve is installed in a recess in the front of the engine, where there is a lot of dirt. Accordingly, if the oil seal loses its tightness, then dust and dirt from the outside mixes with the oil and enters the working cavity of the mechanism. The result is jamming of the valve and wear of the rotating mechanism of the regulator itself.
- Problems with the valve electrical circuit . This could be a break, contact damage, insulation damage, a short to the housing or to the power wire, a decrease or increase in resistance.
- Ingress of plastic shavings . On phase regulators, the blades are often made of plastic. As they wear out, they change their geometry and fall out of their seat. Together with the oil, they enter the valve, disintegrate and are crushed. This can lead to either incomplete valve stem travel or even complete jamming.
Also, the reasons for the failure of the phase regulator may lie in the malfunction of other related elements:
- Incorrect signals from DPKV and/or DPRV . This may be due to problems with these sensors, or to the fact that the phase regulator has worn out, which is why the camshaft or crankshaft is in a position beyond the permissible limits at a particular time. In this case, together with the phase regulator, you need to check the crankshaft position sensor and check the DPRV.
- Problems with the ECU . In rare cases, a software failure occurs in the electronic control unit and even with all the correct data, it begins to generate errors, including in relation to the phase regulator.
Installing the carburetor solenoid valve
When replacing a solenoid valve, it must be adjusted correctly so that the incoming fuel-air mixture meets the required parameters. The installation is carried out with the engine running, as this will allow you to accurately adjust the valve. In a carburetor, the valve is located under the air filter cover, so to remove a faulty solenoid valve, you must first remove the air filter cover.
First, you need to hand-screw the valve into the carburetor seat and put on the standard wire that connects the valve to the control unit. After this, you need to start the car’s engine, which will stall and possibly try to stall. If the engine still maintains speed, then further tightening of the valve into the carburetor is done using a wrench (13 or 14 depending on the type of valve). Further installation is carried out in the following way:
- the key is turned 1–2 cm clockwise, after which the wire is removed;
- if the car engine does not stall, then the wire is put on again and the procedure is repeated;
- As soon as the engine stalls after removing the wire, the valve is installed correctly in the carburetor.
Installation of the solenoid valve must be carried out carefully so as not to damage the fuel nozzle and seat in the carburetor. During the installation process, the size of the fuel mixture entering the engine is automatically adjusted, after which tripping and detonation stop. For precise adjustment, you can tighten the “quality” and “quantity” screws on the valve.
If, after tightening the valve several times and disconnecting the wire, the engine still does not stall, this means that fuel is entering the engine bypassing the solenoid valve and it is necessary to look for a malfunction in the fuel supply system.
Operating principle of the phase regulator
To understand why the phase regulator cracks or its valve jams, it makes sense to understand the principle of operation of the entire system. This will give a better understanding of breakdowns and further actions to repair them.
The engine does not perform the same at different speeds. Idle and low speeds are characterized by so-called “narrow phases”, in which the exhaust gas removal rate is low. Conversely, high speeds are characterized by “wide phases”, when the volume of gases released is large. If “wide phases” are used at low speeds, then the exhaust gases will mix with the newly incoming ones, which will lead to a decrease in engine power, and even stop it. And when “narrow phases” turn on at high speeds, it will lead to a decrease in engine power and its operating dynamics.
Changing the phases from “narrow” to “wide” allows you to increase engine power and increase its efficiency by closing and opening valves at different angles. This is the main task of the phase regulator.
There are several types of phase control systems. VVT (Variable Valve Timing), developed by Volkswagen, CVVT - used by Kia and Hyindai, VVT-i - used by Toyota and VTC - installed on Honda engines, VCP - Renault phase regulators, Vanos / Double Vanos - system used in BMW. Next, we will consider the principle of operation of the phase regulator using the example of a Renault Megane 2 car with a 16-valve K4M engine, since its failure is a “childhood disease” of this car and its owners most often encounter a non-working phase regulator.
Control occurs through a solenoid valve, the oil supply to which is regulated by electronic signals with a discrete frequency of 0 or 250 Hz. This entire process is controlled by an electronic control unit based on signals received from engine sensors. The phase regulator is switched on when the engine load increases (rpm value from 1500 to 4300 rpm) when the following conditions are met:
- serviceable crankshaft position sensors (DPKV) and camshaft position sensors (DPRV);
- there are no malfunctions in the fuel injection system;
- the phase injection threshold value is observed;
- the coolant temperature is within +10°…+120°С;
- increased engine oil temperature.
The phase regulator returns to its original position when the speed decreases under the same conditions, but with the difference that zero phase shift is calculated. In this case, the locking plunger blocks the mechanism. Thus, the “culprits” for a malfunction of the phase regulator can be not only the phase regulator itself, but also the solenoid valve, engine sensors, malfunctions in the motor, and malfunctions of the ECU.
Replacing and checking the solenoid valve on VAZ 2108, VAZ 2109, VAZ 21099
Welcome! From this article today you will learn for yourself how to correctly replace the solenoid valve on cars of the Samara family.
Summary:
Where is the solenoid valve located? It is wrapped in the carburetor body, and a block of wires is connected to its terminal. At first glance, after opening the hood it is very difficult to notice, and all this is because it is covered by the air filter housing. Therefore, to see this solenoid valve, you will have to bend down and thereby look under the air filter housing. For a more detailed location of this valve, see the photo below:
Note! For clarity, the air filter housing has been removed!
When should the solenoid valve be replaced? Most often, when the solenoid valve fails, the following problems begin to occur with the car engine:
- Firstly, the car’s idle speed becomes uneven, that is, the speed begins to fluctuate and in some cases the car simply stalls constantly.
Note! All this is due either to clogging of the idle jet which is installed on the valve, or to the failure of the solenoid valve itself, or to the lack of power to the same valve!
The meaning of the word Valve according to Efremova:
Valve - 1. A cover, disk covering the opening through which steam, gas, liquid, etc. passes. (in machines and mechanisms). 2. A part of a mechanism in musical wind instruments that serves to open and close a hole in the body and thereby change the pitch of the sound produced. // Harmonica key button. 3. A patch made from a piece of fabric that covers a pocket or seam on clothing. 4. Part of a hollow organ formed by the fold(s) of its inner membrane and covering something. passage, opening (in medicine).
How to replace the solenoid valve on a VAZ 2108-VAZ 21099?
Removal: 1) At the beginning of the operation, remove the air filter housing from the carburetor cover. (For how to remove the housing, read the article: “Replacing the air filter housing”)
2) Next, disconnect the wire block from the solenoid valve terminal.
3) Next, using a wrench, catching on the edges that are present on the solenoid valve, unscrew it completely. After unscrewing the solenoid valve, remove it from the car engine.
Note! Remove the valve carefully; when removing, do not lose the idle jet, rubber o-ring and cup that are present on this valve!
Installation: 1) Taking the new solenoid valve in your hands, install it in its place and then wrap it around the edges that are present on it.
2) After screwing, connect the wire block to it.
3) Finally, install the air filter housing onto the carburetor cover.
Turkish hookahs. Where's the valve, Karl?
Those who recently became acquainted with hookah truly believe that a real hookah can only be found in the East. It is for this reason that everything that was brought from popular resorts or Arab countries automatically becomes much better and cooler than what is made in Russia or Europe. It's sad to disappoint, but it's still a little off. And today we are making the first article with a review of oriental and Arabic hookahs. So, Turkish hookahs.
Turkish hookahs. Hookah in Turkey.
What is Türkiye like? A large country washed by several seas and included in the list of one of the most attractive countries in the region for tourists. Since the very image of the country is oriental, and the official religion is Islam, hookah is considered almost a native part of the culture of this country. How much does a hookah cost in Turkey this season (2018)? Most likely, the price will vary from 40 to 60 euros. This is a fairly small price, however, by paying a little extra, you can buy a high-quality hookah in Russia, for which you just need to read our rating of the top 10 hookahs under 10 thousand. If they try to inflate the price of hookah in Turkey, you can safely bargain.
How is a hookah made (slaughtered) in Turkey? The choice of tobacco in Turkey is quite small, so we still recommend taking tobacco with you. The price of a hookah in Turkey to smoke on the beach will be from 5 to 10 dollars. Quite good and very similar to prices in Russia. Unfortunately, this is where the similarities with Russia end. All you can expect from the variety of tobaccos in Turkey is Alfaker. The main disadvantage of hookah in Turkey is the use of a hookah without a purge valve. We will definitely return to this branch of the evolution of hookahs so that together with you we do not understand the meaning of this “improvement”.
The hookah smokes averagely, there is little smoke, and no one even thinks about controlling the temperature. I think that after smoking a hookah in Turkey, all supporters of “traditional” oriental smoking will try to change the subject and dream of flying back to Russia to smoke a normal hookah.
Turkish hookahs. Where's the valve, Karl?
Most often, Turkish hookahs have painted flasks and oriental patterns. In addition, one of the most common materials is copper and brass. Copper is inside and brass is outside, which makes the material quite oxidizable. The main disadvantage of hookahs is the lack of a valve for blowing out the hookah, which is necessary to “smoke” the hookah, lowering the temperature in the cup by periodically blowing air into the flask.
The main manufacturers that produce Turkish hookahs:
- Elmas
- Demirkan
Elmas - left Demirkan - right
These two hookahs are practically no different from each other except that the Elmas hookah has a little more drawings and engraved images. There is a slight difference in the base of the hookah - Demirkan’s is “convex”, while Elmas’s is more similar to the structure of the Pharaoh’s shaft.
Demirkan
Elmas
- El Nefes
- Lotos
- Islemeli
Turkish hookahs Islemeli
- Nargilem is one of the few Turkish brands that make hookahs to Europe, which is why they have a valve.
As you can see, if Turkish hookahs are planned to be produced for the European market, a valve is most often added. When purchasing a Turkish hookah, we recommend ordering exactly these models.
In principle, Turkish hookahs differ not only in that they do not have a valve - this is most often associated with smoking strong tobacco, when smoking which simply does not require blowing. I don’t know how close this version is to the truth, but it seems rather doubtful, since even when smoking strong tobacco, blowing through the hookah helps balance the smoking.
Turkish hookahs - how to plug them? Yes, actually, as usual. The only thing that is advisable to take into account is to make a larger indentation from the foil or caloud, since you will not be able to blow it out if you have a valve - you will not have any differences in blocking from any other hookah.
Turkish hookahs. Difference from others.
Also, Turkish hookahs are distinguished by the handle (mouthpiece) of the hose, which is called marpuch. Marpuche is a long tube, covered with leather, with a wooden mouthpiece that can be changed.
Also in Turkey, it is very common to use an internal hookah cup. In terms of hookahs, this is a slightly strange and not very rational country, relative to how it is customary in Russia.
In terms of smoking, Alfaker or Nakhla (rarely) are most often smoked. Tombak, a strong Turkish tobacco, is actively smoked.
Turkish hookahs. How to choose?
In general, we strongly advise against buying hookahs in Turkey, for the reasons we described above. However, if you cannot resist, then focus on the following hookah criteria:
- price. Don't buy hookahs that cost more than $60, bargain.
- number of tubes. Hookahs with 2 pipes are one of the worst inventions, which forces one of the smokers to plug the hose with his hands to ensure a tight seal.
- condition of the flask. There should be no chips, small cracks or bubbles in the walls of the flask.
- hose. It is advisable not to buy it there at all, unless it is silicone.
- size. Do not buy small decorative hookahs if you intend to smoke them.
- tightness. Assemble the hookah completely, plug the top of the shaft with your hand and try to inhale. If that doesn’t work, the hookah is sealed.
- You can read other tips on how to choose the right hookah by following the link.
Tobacco from Turkey.
Surprisingly, Turkey produces quite a lot of acceptable hookah tobaccos. Of course, many in Russia are not very happy to smoke such tobaccos, because they consider them to be of insufficient quality. In our opinion, this is a clear exaggeration. Adaliya and Sherbetli are high-quality tobaccos that have been delighting with their new flavors for several years now. Unlike many other brands, they continue to develop.
However, in this regard, Adaliya tobacco fails, the taste of which has indeed become very chemical, and the new tastes are almost completely similar to each other. In principle, we didn’t particularly appreciate the other Turkish tobacco Smyrna (Smyrna). Not very smoky and tasteless tobacco.
Compared to Smyrna, Fasil tobacco looks good, which although also does not have particularly cool tastes, but some tops are imbued with a fairly high-quality aroma.