In the process of driving any vehicle, a huge role is played by the suspension and chassis. Safety and comfort while driving the car will depend on their work. To improve the quality and reliability of the components, manufacturers place metal plates, which are commonly called spacers, in the section from the wheel rim to its hub.
What are spacers for?
First of all, hub spacers are necessary in cases where the wheel rims do not have the required offset. Motorists love to buy flashy, fashionable rims for their cars, but they will be disappointed during installation. If a slight deviation can be allowed in terms of width and diameter, then the overhang value should coincide as much as possible with the specified factory value.
To be able to install those wheels that seem most suitable in design, you cannot do without wheel spacers. The overhang value after installation must be greater than the recommended value. As a result, the wheel offset should be reduced to factory values. It is if this criterion is met that you can count on safe driving and reducing the load on the suspension elements to acceptable parameters. And finally, many car enthusiasts simply use wheel spacers as an extra tuning element.
A situation often arises when the most beautiful wheels may have not only an excessive offset, but also an excessive distance between the mounting studs. Again, you can’t do without spacers - they are first installed on the hub, and then the wheel rims are directly fixed to them with bolts included in the package.
Tuning a vehicle is often difficult to imagine without giving it a sporty or even aggressive appearance. Wider wheels with the help of spacers, in combination with wheel arches and body kits, significantly transform the appearance of the car. They act in exactly the same way when they want to increase the vehicle’s track to improve its cross-country ability.
avtoexperts.ru
Wheel spacers have become a fashionable element of car tuning today. So much so that many people install them without thinking about the consequences. Like, everyone has it, let me get one for myself. Meanwhile, this part has a very specific purpose and should properly be used only when there is a need for it, and not by default, because spacers can be not only beneficial, but also very specific harm. In this material, we examined in what cases spacers can and should be used, and in what cases this is fraught with problems.
Spacers for changing the offset of a disc with bolts
We use
1. Other rims . We're willing to bet that the authors of the spacers came up with them in order to use them to install rims that do not normally fit the car. Any disk has strict parameters for offset, and most importantly for the number and location of mounting bolts. You can’t install another disc, it won’t physically fit, that’s where spacers come to the rescue. And sometimes you really want to install non-standard wheels, for example, you really like a certain model of wheels, but they are not available for a specific type of car. Or even more prosaically - the wheels are leftover from the previous car, you want to save money and not buy again for new sets of wheels and tires. This is where spacers can help.
Hub-mounted spacer
They will not only adjust the offset to factory standard, but also change the bolt pattern. Many spacers are attached to standard places, and allow you to screw the wheels into their holes. It turns out to be a kind of hot dog, in which the role of the spacer is similar to that of a sausage, but this is a completely safe design. The only difficulty is in selecting the right spacer so that, firstly, it fits the hub in terms of mounting, secondly, it matches the mounting dimensions of the new disks, and thirdly, it compensates for the difference in offset. It is not so easy to comply with all the parameters. It is often impossible to find suitable spacers; you have to turn to a turner to make them. But this is different money and questionable reliability. However, if spacers with the required characteristics can be found, then you can use them without fear.
Disk layout
2. Widening the track . Spacers with an increased offset allow you to install wheels wider than they were previously, which quite logically increases the track. In theory, this allows the car to increase stability on the road, reduce the likelihood of rollover, and may slightly improve cross-country ability in some situations. Sometimes they talk about improving handling, but this is a moot point - changing the track can have both a positive and negative effect, the problem is that no one has tested or checked the car with the changed values. The standard version has been thoroughly tested by the manufacturer, but it is difficult to predict what the “homemade” ones will get. If you know exactly why you need to increase the track, then you can take such a step, but we would not recommend doing this without specific reasons.
On the left is a Skoda Octavia A7 with spacers, on the right is a standard one. In addition, the white Octavia has shortened springs.
3. Improved appearance . Car design is a purely individual thing, but a large number of car enthusiasts believe that rims protruding from the arches are beautiful. We won’t comment, because there are so many people and so many opinions. But if you want to increase the wheel offset, then spacers are the easiest and cheapest way for such an operation. This is precisely why spacers are so popular in the topic of auto tuning - they are, first of all, cheap, and not everyone cares whether they are angry or not.
Left without spacers, right with spacers
We don't use
1. Reducing the suspension life . There is only one situation in which spacers will not affect the suspension in any way - this is when non-standard wheels are used on the car, and the spacers are selected in such a way that, together with the disk, they give the parameters that the standard wheels of the car had. Actually, in such a situation, nothing changes to distribute the load in the suspension. But this doesn’t happen often - as we already wrote above, go find a spacer that perfectly matches the parameters. Most often, the offset changes due to the use of spacers and this makes the suspension feel bad.
Here even people far from physics will understand - the lever has increased, which means that all the loads in the suspension, which is not designed for the new geometry, have increased. The champions in reducing service life when using incorrect spacers are wheel bearings. They break on discs placed behind the arch with enviable regularity, but other elements have a hard time - levers, steering ends, balls, their service life, although not so rapidly, is also decreasing. Those who install spacers “for beauty” should be aware that they will have to pay for this beauty by repairing the suspension.
2. Sandblast the wheels . Typically, engineers calculate the installation of wheels in the arch so that dirt and sand from them do not fly onto the body, because this has a very negative effect on corrosion resistance. Alas, even engineers manage to make mistakes in calculating this issue (hello to the developers of Renault Duster), while installing spacers that increase the offset of the discs inevitably leads to such a problem. Sandblasting will remove the paint from the sills down to bare metal, forming pockets of corrosion and leaving stone chips along the entire side of the body.
After installing the spacers, it gets covered in dirt
We agree that the negative consequences can be partly combated by installing arch extensions or non-standard mudguards, but this, firstly, requires additional expenses and effort, and secondly, does not always help.
3. Changing the behavior of the car . We have already written above that it is difficult to talk about handling using spacers in advance, but it is almost certain that some parameters will worsen, namely, the force on the steering wheel and the turning radius will almost inevitably increase. The first factor can be critical for cars that are not equipped with power steering, the second is negative for those who often have to maneuver in narrow streets or courtyards. Yes, probably, the deterioration will not be catastrophic, but still this factor is also added to the collection of negativity.
Mercedes-Benz C-Class with spacers
4. Reliability of the spacer . Among other things, it is also worth remembering that the spacer is an additional component of the suspension, which can also cause problems - the usual law of physics: the more elements in the mechanism, the higher the likelihood of failure. What in the spacer can break when it is actually a pancake made of metal? And it itself can burst, and the threads collapse, and the mounting holes “break”, but you never know, because on the market there are many cheap products from China or independent “crafts” in makeshift conditions and not with inappropriate equipment. The probability that something could happen to the spacer on the road is, of course, not great, but still it is not zero; such negative cases are known.
Overall, we don't really understand the increased popularity of car spacers. Purely technically, they perform a very specific and not the most common function - installing non-standard wheels while maintaining the parameters of a standard wheel, and in this sense they are good and convenient. But the use of spacers for tuning with a dubious gain in appearance entails a number of very specific problems - a decrease in the reliability, comfort and controllability of the car. Is it worth the “show-off” and illusory improvement in styling? In this formulation, the question seems rhetorical to us.
Skoda Octavia A7 with installed spacers and lowered suspension. Photo — drive2
Types of spacers
Depending on the goals pursued by the car enthusiast, hub spacers can be of different types. The following types are distinguished based on the design principle:
- Equipped with through holes for studs. In this case, standard hub bolts will have to be replaced with longer ones.
- Equipped with holes for hub bolts and for mounting the disc. First, the spacer is mounted on the removed hub, and then the whole thing is screwed onto the disk.
Another classification is related to the thickness of the metal pancake itself. Each of the varieties, one way or another, is intended for mounting rims with a negative offset indicator:
- thin spacers (from 3 to 10 mm thick. In scientific language they are called “spacers for a hub of small thickness”);
- medium with a thickness in the range of 10-20 mm;
- thick, 20-30 mm., respectively;
- especially thick, the width of which reaches 30-40 mm.
The small overall dimensions of the thin spacers allow them to be mounted simply on standard studs, the length of which should be sufficient. The last 2 of the above varieties are indispensable when tuning hinged wheel arches (for regular cars and SUVs). From the point of view of the laws of physics and mechanics, spacers of medium and large thickness for hubs are necessary only in cases where the recorded offset value is greater than that provided by the manufacturer. The width of the modifying pancake in such a situation is the difference in millimeters between the actual and required overhang.
Spacers with a thickness of over 25 mm have 2 of their own design features. Firstly, bolts can be used that secure this assembly to the wheel hub. The disk itself will be screwed to the washer using standard automotive bolts. As for the other case, we are talking about spacers with built-in studs. The product, designed to correct the offset, is mounted through studs and clamped with nuts directly on the hub. The wheel is hung on the spacer studs and tightened with nuts. In this case, the standard length of the studs will be sufficient.
In addition to the thickness parameter, when choosing spacers for the rear hub, it is important to pay attention to the quality of their manufacture. Even minor errors in the area of the mounting holes or heterogeneity of the alloy used can cause wheel runout. In just a matter of days, this can completely destroy the car's suspension. Critical loads increase under extreme operating conditions, and this directly affects the life and health of many road users.
The quality of factory-made spacers is traditionally higher. When purchasing, you can pay attention to products from brands such as Hofmann, Shiessler, BIMECC, H&R Trac+ and a number of others. Rolled blanks are always more reliable and safe. In contrast, cast products that are not professionally cast may contain many voids. Ultimately, this will negatively affect the performance of the spacer and the wheel imbalance.
Little-known manufacturers often use powder pressing technology for production. The result is a product that is not designed for high loads. Homemade spacers must be balanced on special stands. An unauthorized reduction in the number of fasteners between the spacer, hub and wheel rim is not allowed.
Home → Articles → What are wheel spacers made of?
What are wheel spacers made of?
One of the most frequently asked questions about spacers is related to the quality of the material from which we make our products, as well as its features and differences from various analogues. In this article we will try to briefly explain some related points.
For quite some time now, we have been focusing the attention of buyers on the fact that the quality of wheel spacers and adapters, as well as wheel fasteners, is primarily a matter of safety, and we warn against purchasing cheap products from unknown manufacturers, primarily Chinese. Of course, we shouldn’t lump all Chinese manufacturers with the same brush and talk about complete non-compliance with the quality standards of all Chinese products. This is not so, and the quality of many spacers from China is quite high. Many, but not all. Naturally, the final cost of the product is largely influenced by the cost of the material, so very often, in order to reduce the cost of products, manufacturers use much cheaper silumin instead of reliable, but not cheap duralumin. Silumin, as is known, is an alloy of aluminum and silicon. The peculiarities of this alloy are its high porosity and associated fragility. It is not thermally hardened, therefore it has low mechanical characteristics and can only be used for the manufacture of parts that are not subject to mechanical and thermal loads. It is clear that wheel spacers are subjected to these loads to the fullest and it is impossible to use silumin for their production. However, as already mentioned, many manufacturers nevertheless use it, trying to reduce the cost of their products as much as possible. The photo below shows a sample of Chinese silumin products.
It seems to look good and the price is attractive, but often with even short-term use of these spacers, problems of this kind soon arise:
Or it could all end like this:
If you consider that the car wheels are attached directly to these spacers, it is not difficult to guess what unpleasant consequences the use of such products can lead to.
It should be noted that not only Chinese manufacturers are guilty of this kind of thing. Many have already encountered the incomprehensible quality of spacers from one of the Russian manufacturers from the Urals, which often simply crack when they are installed on the hub. This has not yet been seen in any Chinese product. What kind of material is used remains a mystery, apparently melted shavings, but it is a fact that it should under no circumstances be used for the production of spacers.
Another frequently asked question is whether it is better to make spacers from steel, isn’t it more reliable, etc. The answer is no, steel spacers have no advantages, but there are plenty of disadvantages. With the same thickness, the weight of a steel product, as can be seen in the photo, is almost 3 times greater than that of a duralumin product:
Therefore, when using steel spacers, the unsprung weight increases significantly and, as a result, the load on the vehicle’s chassis increases significantly, which can lead to accelerated wear of chassis parts. Plus, steel products are naturally susceptible to corrosion, which is not typical for duralumin products, and the strength properties of D16T duralumin are not inferior in all respects to analogues made from 40X steel.
Well, a little more detail about the material that we use for the production of spacers and adapters - D16T duralumin with aircraft technical acceptance. It is an aluminum-based alloy (up to 94 percent) with copper and magnesium additives, alloyed with manganese, hardened by heat treatment and naturally aged. As a result of hardening, the hardness of the D16T alloy reaches 125-130 HB, which is the maximum among all analogues. These strength characteristics, stable structure, increased resistance to deformation and light weight - all these factors make D16T the most popular in space, aviation, shipbuilding and other types of industries.
The letter T in the name of the alloy brand means heat treatment, which distinguishes it from D16, an alloy without heat treatment, which is correspondingly cheaper, but significantly inferior to D16T in its strength characteristics - its hardness is 75-85 HB. In this regard, we note that we have repeatedly encountered the fact that on the Internet, products made from D16 are offered as made from D16T. In the photo below there are two similar spacers, the first is made of D16, the second of D16T. It is easy to notice the difference in the structure of the material, as well as the fact that a product made from D16 is much more susceptible to scratches, etc.
Basically, this is all I wanted to briefly talk about the materials. We hope this information will be useful to you and help you make the right choice.
Instructions for installing spacers
Even before installation work begins, it should be remembered that it can be carried out for each wheel no more than 1 time. Multiple wheel spacers lead to imbalance and uneven load distribution. Since in this situation the pressure exerted on the bearing increases significantly, it will certainly fail in the shortest weeks and months.
The installation work performed must be carried out with filigree precision. For example, bolts that are placed opposite each other are lightly tightened at first, rather than tightened all the way. A torque wrench is used to tighten. At the stage of tightening the hub mounts, you should clarify the tightening torque value - the vehicle passport or car enthusiast forums will help you do this. It is important to remember that when tightening bolts and studs, the degree of load on other suspension elements also increases.
During further operation of the vehicle, it is necessary to control the tightening torque. According to the recommendations of experts, after 50-100 kilometers you need to not be lazy and tighten the fastenings. If you decide to replace the factory wheels with more branded ones or carry out other tuning of the car, you should not save money by purchasing spacers for the hub assembly of dubious quality and manufacturers.
The life and health of the car enthusiast will largely depend on this, as well as the safety of installation work. If the inserts are made in artisanal conditions, then it is necessary to monitor the load during further operation. It should not lead to accelerated wear of other suspension elements.
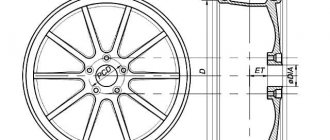
Rules for measuring disc offset
Before selecting spacers, you need to make sure that you really need this element. This can be done by finding out the disc offset (VD).
For this you will need:
- a jack to remove the wheel;
- a rack, the size of which must correspond to the disk radius;
- measuring device (tape measure, ruler);
- tackles;
- key for unscrewing secret bolts.
Car wheel rim offset
First you need to measure the rear offset, which can be designated by the letter A. To do this, remove the wheel and place it face down. Place the rack on the inside (its ends should be in contact with the rim of the disc, not the rubber). Then measure from the mating disk surface to its bottom edge. Record all results obtained during measurements in millimeters.
After this, measure the frontal setback B, turning the wheel “face” up. The edges of the rack must be in contact with the rim (not with the spokes or other components). Measure the distance from its bottom edge to the mating disk plane.
Next, the calculation is carried out using the following formula:
Example: ID = (143+43)/2 - 43 = 50 mm.
You also need to remember that when mounting the wheels on the hub, you will need to control the number of nut turns when fully tightened.
It will be useful: How to improve engine compression?
How to make the right choice
In addition to making spacers with your own hands, there are products that are manufactured in the factory. Their quality is guaranteed by the plant and confirmed by relevant documents. The most popular companies in this area are foreign proven companies BIMECC , Schiessler , Hofmann , H&R TRAK+ . For home-made products, it is recommended to use rolled or forged blanks.
You need to know that cast blanks for the manufacture of spacers can contain a large number of voids if casting is of poor quality or unprofessional, which will lead to unbalance of the final product.
Consequences of poor-quality wheel spacers
Do-it-yourself spacers for increasing wheel rim offset
Almost any car wheels you like can be installed on your own car.
Even if the fasteners do not always match, spacers will come to the rescue to increase the disc offset. With their help, you can adjust the installation of the selected wheels. The vehicle's track thus widened will help increase the stability of the vehicle. Also, these additional pancakes can be an indispensable addition for mounted tuning, when plastic modifiers are attached to the car.
How to install spacers
There are several recommendations and schemes for installing wheel spacers. Here is the basic generally accepted procedure.
- Carefully remove dirt and corrosion from the hub surface using a wire brush.
- Place the part on the disk and check that it fits tightly with the centering protrusion and chamfer to the surface.
- Check that it fits tightly to the surface of the hub with the internal chamfer and centering belt.
- Remove the mounting bolts, clamps, and centering pins (if any).
- Inspect the installation bolts, comparing them with the factory ones. In this case, the thread length should be greater by the size of the spacer thickness. The seat cone must exactly match the mating surface. If the stock wheel bolts have a movable spherical or conical surface, then the extended bolts should have one too.
- Secure the spacer to the hub with long bolts, aligning the mounting holes in advance.
- After installation, check that the mounting bolts do not touch the internal elements of the hub or caliper.
- The tightening torque of the mounting bolts is 100 N*m.
Installation must be done carefully so as not to damage the parts or strip the threads of the vehicle fasteners. First, you need to tighten two opposite bolts on the wheel, and then the rest.
Attention! Tighten the bolts with a torque wrench; an impact driver will not accurately create the required tightening force.
After installation, rotate the wheels in a suspended state and check whether the wheels are touching the body parts. After driving 100 km, it is recommended to check the tightness of the bolts and tighten them if necessary. Self-processing of parts is prohibited.
Wheel spacers are a tool for tuning and installing non-standard wheels, widening the track and giving the car a sporty look. But an important point is the careful selection of these elements, taking into account our recommendations.
Main categories of spacers
Two other groups of materials are more popular:
- Spacers 12-25 mm thick. Their use will help you forget about such difficulties as vehicle imbalance while driving. One of the design elements of these wheel spacers is the hub. Immediately after installing such a part, you will notice an increase in the wheelbase. This solution is often used by tuning enthusiasts who want to make the appearance of their car as dynamic as possible. Such products often help maintain the original appearance of the car after installing aerodynamic body kit elements.
- Spacers for wheels with a thickness of 25-50 mm. They, in turn, are divided into two categories. The first category includes products with bolts, with which the spacer is attached to the standard hub (standard bolts connect the wheel to the spacer). The second includes products equipped with studs that are attached to regular ones. Only after this are they connected to the product using standard wheel nuts. This option is more preferable for off-road vehicles, as well as vehicles whose rims are secured with nuts.