The interchangeability of motor oils is of interest to car owners from a practical point of view: gasoline must be purchased, and diesel can be obtained from familiar employees of large transport enterprises. But many people don’t know whether it is suitable for a carburetor engine.
There are big differences in power plants, therefore, lubricants also have different characteristics, which relate primarily to additives. There is no clear answer to the question about the possibility of pouring diesel oil into a gasoline engine; many factors should be taken into account.
Main characteristics and types
Tolerances serve as a guide when choosing motor oils. The vehicle's technical documentation or special catalogs and tables will help determine the brand of lubricant. Some car enthusiasts prefer the most popular and expensive brands, but at the same time find it difficult to choose based on quality indicators. The wide range of fuels and lubricants on the market complicates the task. But everyone knows that both diesel and gasoline oils are characterized by viscosity grade, a certain additive package and a number of other indicators.
The SAE indicator indicates the viscosity properties of the lubricant and its seasonality. The letter W means that it is suitable for use in winter and is considered all-season. Numerical values show the temperature range.
Viscosity indicators indicate the rate of fluid supply to the surfaces of parts and mechanisms experiencing friction. The same indicator determines the resistance force at the moment of rotation. The first digit of the marking indicates negative temperature indicators, the last - the maximum temperature.
The SAE standard marking is universal for all types of oils, distinguished by base and area of use. Thus, from this designation it is impossible to determine for which type of internal combustion engine the oil is intended.
The belonging of the lubricating fluid to the type of motor is indicated by the API standard indicator. According to this standard, lubricants are divided into products for gasoline engines - designated with the letter S, and for diesel engines - designated with the letter C. If both letters are present, printed in the form of a fraction, the product is universal and suitable for both types of engines.
API classification subcategories:
- SS - for naturally aspirated and slightly supercharged engines;
- CD - for highly supercharged engines operating in extreme conditions, high sulfur percentage;
- CE - such lubricants are produced for turbocharged units manufactured before 1983;
- CF-4 - for four-stroke engines manufactured after 1990;
- CG-4 - for modern power units. It has high environmental performance;
- CD-11, CF-2 - for two-stroke engines.
European manufacturers have created their own ACEA classification, according to which they are divided into 4 groups and distinguished by energy saving class. The symbolism of this standard means:
- A - for gasoline;
- B — diesel engine oil;
- C - for both units, characterized by similar particulate filters;
- E - for high-power truck engines.
The numbers 1 and 5 in the marking, located after the letter designation, indicate energy saving (for example, B1 or B5). Such products make it possible to reduce fuel consumption and, accordingly, the emission of harmful substances. Numbers 2, 3 and 4 indicate standard oils.
As for the basics, the main selection criterion for most motorists is cost. Mineral oil for diesel is relatively inexpensive, but semi-synthetic and synthetic oils are more stable and significantly increase the service life of the power unit. It should be noted that synthetic motor oils show high stability in winter temperatures, which makes them different from others.
The trade brand is not of fundamental importance. Therefore, choosing expensive products is not justified in every case. It must be taken into account that when changing the oil, the liquid is not completely drained. When adding another brand of lubricant, deposits may form due to the interaction of additive components.
What is the difference between oil for gasoline engines and oil for diesel engines?
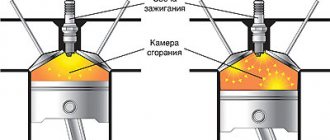
Let's start with the fact that both types of engines operate on a similar principle, burning a fuel-air mixture in the cylinders. It is also well known that the main task of oil in any engine is to lubricate loaded friction pairs. Taking into account this information, at first glance it may seem that any oil will cope with its functions, regardless of which engine it is poured into. At the same time, until recently, lubricants for gasoline and diesel fuel units were more clearly differentiated by scope of application. The main reasons for this division can be considered:
- individual characteristics of each type of internal combustion engine (method of ignition of the mixture, maximum crankshaft speed, loads at the interfaces of parts, temperature, etc.);
- different types of fuel used (gasoline and diesel fuel), which differ in their composition and properties;
Diesel oil additives
Additives in the lubricating fluid play an important role: they allow you to cope with those tasks that the basic base cannot do. With the help of additional components, the replacement period, engine life and other operational characteristics are significantly increased.
Synthetic metal conditioners are used as an additive component, which are designed to reduce the coefficient of friction and thereby reduce engine wear. For diesel oils, additives are used that prevent the formation of soot and soot, as well as components with antioxidant properties.
Each manufacturer uses a unique additive package. For diesel, the alkalinity number (not lower than 1.3) and ash content (not lower than 11.5) are considered optimal.
What are universal oils
On sale you can find specialized oils for diesel or gasoline engines, as well as universal options. They can be poured into both of the engines under consideration, which is achieved through proven compositions. In such oils there is no excess of alkali, and oxidation is neutralized, partially, with the help of additional additives. At the same time, universal oils can operate in wide temperature ranges, which is necessary for their use in two types of engines at once.
We can say that universal engine oils are the ideal solution, and they do the job perfectly. However, they have one significant disadvantage - cost. Due to the complexity of producing such oils, their price is usually 50-100% higher than specialized oil for a diesel or gasoline engine. Most often, universal oils are fully synthetic.
Article on the topic: Causes of cracking
Selecting oil for a diesel engine by marking
The product label will tell you which oil should be poured into a diesel engine. According to the SAE standard, lubricant is selected within a range of certain temperatures. For example, the designation 5W-40 indicates high temperature viscosity. It is able to retain its basic properties from -25 in winter, which makes cold starting easier. The last digit indicates the maximum temperature. And the letter W indicates suitability for work in winter.
Diesel oil is designated C (according to API category), or B (ACEA classification), modern samples may be designated CG-4. The technical documentation for internal combustion engines usually contains recommendations for selecting the necessary oils.
What to remember when changing diesel engine oil
Using domestically produced diesel fuel, oil changes should be made a little more often than recommended in the documentation. This is explained by the high percentage of sulfur. The process itself is not particularly difficult; you can fill in the lubricant yourself. It is important to monitor the quality of the oil; if clots form on the cap, this is one of the signals to replace the lubricant.
Remember that mixing mineral water and synthetics is unacceptable. The so-called coagulation of components occurs, which can lead to failure of the internal combustion engine.
Experts believe that oil changes in diesel units must be carried out after 6-8 thousand kilometers. The reason for this is low quality diesel fuel.
What is required from motor oils?
The specifics of fuel and engines determine the requirements for lubricants:
- Significant content of heavy fractions and the volume of air in the mixture, increased combustion temperature, and the method of ignition due to compression lead to incomplete combustion of components and the formation of ash residue (soot) and soot in diesel engines in much larger quantities than in engines running on gasoline.
- A high compression ratio leads to an increase in the amount of gases entering the crankcase. The consequence of this is intense oxidation of lubricants, the likelihood of which in diesel units exceeds that of gasoline engines. The concentration of sulfur compounds has the same effect.
- Among the most important indicators of oils for high-speed engines are the indicators of dynamic and kinematic viscosity and their stability.
Accordingly, diesel engine oil must have oxidation resistance, improved cleaning properties, and contain elements that prevent intensive aging. Based on these considerations, additive packages are selected. They should have an increased content of anti-ash components and improved cleaning properties to combat soot. At the same time, the alkaline number of the oil should increase, as a guarantee of slowing down oxidative processes.
The set of additives in lubricants for gasoline engines is mainly focused on ensuring efficient operation at high speeds.
Differences between diesel fuel and gasoline affecting the specifics of motor oils
The advantages of diesel engines over gasoline engines are high efficiency, efficiency, and durability. The fundamental aspect is the formation of the air-fuel mixture and the ignition process itself. Despite the disadvantages of diesel, such as significant weight, vibration and noisier operation due to self-ignition of the fuel and high pressure in the cylinder, more and more motorists prefer diesel engines. They are an order of magnitude more durable and sometimes more reliable than most of their gasoline “brothers.”
Diesel resource is 400-600 thousand km. Thanks to modern innovations, it has been possible to reduce the noise and vibration that accompany the operation of diesel engines. But many car enthusiasts still put efficiency first. In addition, diesel fuel is cheaper than high-octane gasoline.
Both units have a similar type of operation. The difference between a diesel engine and a gasoline engine is the ignition method, load, shaft speed and other indicators. The main difference is the use of fuel.
Due to incomplete combustion of the mixture in a diesel engine, there is a high risk of oxidation. In this case, soot is formed, the oil thickens and deteriorates the quality of engine operation. Another drawback is the sulfur content. If gasoline contains no more than 0.03%, then in diesel fuel this figure is different - it is 10 times higher.
What fundamentally distinguishes diesel oil from a similar product for gasoline is, first of all, the additional components. For diesel, the alkaline number and ash content are much higher; this type of oil also requires additives that actively resist oxidation.
Torque affects accessory components. Motor oils for a gasoline engine must contain additives that reduce the load at high speeds, which is fundamentally unimportant for a diesel engine.
Whether it is possible to pour diesel oil into a gasoline engine in some cases is of interest to most car enthusiasts. Additives used for a diesel engine may not work, and even be harmful, in a gasoline engine. But in small quantities and in exceptional cases this is permissible, no more than 0.5 - 1.5 liters. But adding oil for a gasoline internal combustion engine to a diesel engine is unacceptable. The consequence will be high formation of soot and soot. Such a step is justified only in the most extreme cases, for example, in case of a breakdown on the road in order to get to a service center.
Pour diesel oil into a gasoline engine. Consequences and reviews
- Reduced average speed. A diesel engine rarely spins up to 5000-6000 thousand rpm. While on gasoline this crankshaft speed is achieved quite often.
- Increased ash separation. Due to the sulfurous nature of diesel fuel, sulfur oxides are formed in a diesel engine, which partially penetrate into the oil.
There are a few other, less significant differences. But we will not consider them, since they have almost no effect on the requirements for engine oil.
Modern standards of diesel oils
Brands of motor oils for modern diesel engines are quite widely represented on the market and in retail chains. What general recommendations can be given for selection? It would be preferable to use a special lubricant created for a diesel engine, which provides for all the design and operation features of such an engine. It will also not be a big mistake to fill in a universal product that is suitable for all types of engines. When purchasing, pay attention to the alkaline number and ash content. Select oil according to the tolerances recommended by the manufacturer.
Features of universal motor oils.
Increasingly, fuel and lubricant manufacturers are actively promoting products on the market that can be used in the lubrication systems of both gasoline and diesel internal combustion engines.
Universal solutions are especially widespread in European countries. Today, many official dealers of automakers literally force their use as part of warranty programs.
The use of such lubricants can be justified from an economic point of view in the case where the owner has a fleet of gasoline and diesel cars.
The versatility of such lubricants is determined by a precisely selected additive package that will provide:
- high-quality removal of carbon deposits;
- oxidation resistance;
- ability to bind ash residue;
- protection when operating at high speeds.
However, most materials are designed for high-quality fuels, which are widely used in Europe. In Russia, both diesel fuel and gasoline, for the most part, do not comply with European standards, which creates difficulties in the use of universal lubricants.
The universal version is developed taking into account the performance of an abstract averaged internal combustion engine, and on specific car brands and models it can demonstrate characteristics that differ from those declared.
In short, motor oil, intended for use in power units of a certain type, is a universal product of similar quality in terms of significant performance indicators.