Problems often arise with the level of engine oil in a car among car enthusiasts who do not fully understand the specifics of the operation of all its systems and do not know how to react to a triggered pressure sensor.
Usually, when the very moment of pressure drop occurs, the burning pressure light causes a stupor in the driver and causes him to panic. Therefore, you should understand what the oil pressure in the engine depends on.
This and other secrets of the functioning of car systems are described in detail below.
Pressure at high and idle speeds
Pressure indicator
Before we figure out what oil pressure should be in the engine and how to check it, let’s figure out how it changes depending on the speed:
- at idle, the engine speed is lower and the oil pressure can be 2 bar or approximately 0.2 MPa;
- at higher speeds the pressure can increase to 4-7 bar.
In the operating manual for each machine, the manufacturer indicates the nominal pressure. For example, on a Lada Priora at XX, a pressure of about 2 bar or 196.2 kilopascals is considered normal, and at 5400 rpm the figure rises to 4.5-6.5 bar (this is the maximum for the engines of these cars).
As for American-made foreign cars, the pressure on them is always indicated per 1000 rpm. On average, 1000 revolutions indicate 10 pounds per square inch, that is, 67 kilopascals. Therefore, at 2000 rpm the norm will be 1.3 bar, and at 5000 - 3.4 bar.
Design Features
Officially, the ZMZ 406 engine became the third after 24D and 402 in the line of power drives of the Zavolzhsky plant. Received microprocessor ignition, DOCH gas distribution circuit with a two-stage chain drive.
The developers still used an in-line engine design with 4 cylinders, but there were two camshafts, they are located on top, inside the cylinder head. The compression ratio of the internal combustion engine was increased by the plant designers to 9.3 in the basic version 4062.10 due to the central location of the spark plug inside the combustion chamber.
Reliability is increased due to a cast-iron cylinder block without liners, a reduction in the piston stroke to 86 mm and the weight of the entire ShPG group. The connecting rods, bolts, crankshaft and piston rings are made from high-strength materials, so major overhauls are required less frequently.
The chain tensioners are automatic, double-acting - preloaded by a spring during hydraulic operation. The degree of oil purification is increased by installing a full-flow disposable filter. A separate V-belt drive is provided for attachments. The ECU firmware corresponds to SOATE, ITELMA VS5.6, MIKAS 5.4 or 7.1 versions
How to measure pressure?
Pressure meter
If you suspect your engine oil pressure is low, you can check it yourself. This should be done on a warm engine - up to 90 degrees. After this, the engine is turned off and the oil pressure sensor is pulled out. Instead, screw in a regular pressure gauge and start the engine again, taking measurements first at idle and then at 4000-5000 rpm. The data obtained must be compared with the parameters specified in the operating manual for the machine.
For each automobile engine, a certain oil pressure is considered the norm. It is influenced by the working volume of the power unit and the number of cylinders. If checking the engine oil pressure reveals reduced readings, you need to go to a service center to diagnose the engine lubrication system.
Pressure and emergency oil pressure sensors for ZMZ 405, 406, 409 engines
In order to monitor the pressure in the lubrication system of the ZMZ 405, 406 and 409 engines, two separate sensors are provided. One of them records the pressure value, and the second reacts to its critical drop.
Characteristics, design and principle of operation of the oil pressure sensor
The oil pressure sensor (OPS) is used to measure the lubricant pressure in the system. ZMZ power plants use MM358 type sensors with the following characteristics:
- working element - rheostat;
- rated voltage, V - 12;
- rated current, A - 0.15;
- operating range, kgf/cm2 – 0–6;
- resistance in the absence of pressure, Ohm - 159–173;
- seat thread size, in inches – ¼.
Pressure sensor MM358
The design of the MM358 pressure sensor consists of:
- housings with fittings;
- membranes;
- pusher
- rheostat;
- rheostat drive elements.
The basis of the sensor design is a rheostat
The MM358 sensor works together with the pressure indicator located on the vehicle’s instrument panel. It has an electromechanical design that responds to changes in sensor resistance.
The oil pressure sensor works in tandem with a pointer located on the dashboard
The operating principle of the MM358 sensor is as follows: when the engine is not running, there is no pressure in the lubrication system. The resistance of the sensor, in accordance with its characteristics, is 159–173 Ohms. When the power unit starts, the pressure increases, and the oil begins to act on the membrane, bending it inside the housing. By bending, it moves the transmission lever through the pusher, which, in turn, moves the rheostat sliders to the right, reducing the resistance of the sensor. The pointer reacts to this decrease by moving the arrow to the right.
Characteristics, design and principle of operation of the emergency oil pressure sensor
The emergency sensor is designed to inform the driver about a drop in oil pressure in the system to critical levels. In power units ZMZ 405, 406 and 409, emergency oil pressure sensors of type MM111D or similar are installed, manufactured under catalog numbers 2602.3829, 4021.3829, 6012.3829. These are contact-type devices, the operating principle of which is based on the closing and opening of contacts.
Sensor type MM11D
Characteristics of the MM111D sensor:
- working element - diaphragm;
- rated voltage, V - 12;
- response at pressure, kgf/cm2 – 0.4–0.8;
- seat thread size, in inches – ¼.
A spring-loaded diaphragm is located inside the device body. A contact plate is attached to it, which in the non-operating state is closed with the body (ground) of the sensor. While the engine is running, lubricant under pressure enters the housing through a special hole and pushes back the diaphragm. The contacts are then opened.
The main element of the sensor design is the membrane
The emergency pressure sensor works in tandem with a signaling device, which is located on the instrument panel. It is made in the form of a red butter dish. When we turn on the ignition without starting the engine, the oil can should burn. This indicates that voltage is applied to the sensor, but there is no pressure in the system. 3–5 seconds after starting the engine, the pressure in the system increases and reaches operating values. The oil acts on the diaphragm, the contacts open and the alarm goes off.
Why does oil pressure drop?
Adding oil to the level
What oil pressure should be in the engine and how to measure it we figured out, but why does it usually decrease? First of all, you need to check the oil level in the engine, but this should not be done on a hot engine, but 10-15 minutes after it stops, so that the liquid flows into the crankcase.
While the oil is draining, you need to inspect the engine from all sides for leaks and make sure that there is no damage to the oil sump. Pay attention to the filter - it should sit firmly and not dangle. We also recommend that you learn about the reasons why oil leaks from the engine. After this, remove the dipstick and check the level. If it is at the minimum level, add suitable oil until normal. If adding oil does not solve the problem, how to increase the oil pressure and where to look for the cause of the problem?
- Pump failure. In this case, you will have to buy a new pump and replace it at a service station.
- Wear of engine bearings.
- Clogged oil channels, dirty filter or oil intake screen, or broken oil intake tube. If this is the case, the technicians will replace the filter and clean the channels, as well as remove the crankcase, clean the mesh and replace the tube.
- The pressure relief valve is broken or clogged (oil begins to be squeezed out through the oil seals and other seals).
What to do if the oil pressure light does not go out immediately
As mentioned above, the oil pressure burns for a long time when starting the engine due to the fact that the lubricating fluid leaves the filter element when the engine is idle. This is due to the quality of the oil filter, or more precisely, to the anti-drainage (non-return) valve. An oil filter consists not only of a housing and a filter element, it also has a special gasket called an anti-drainage valve, and its task is to retain oil inside the element.
During operation, or due to poor manufacturing, the check valve may fail. In essence, it is an ordinary rubber band that can crack, tear under pressure, or fly off. Replacing this rubber is not expected, and if the oil pressure burns for a long time, replacing the oil filter will be the solution to the problem.
Please note: The oil filter is often changed at the same time as the oil. If, after the first start of the engine, a problem immediately appears with the pressure lamp fading for a long time, the filter should be replaced. Most likely it was performed poorly, which is why the anti-drainage valve flew off or broke when oil passed through it. Operating such a filter is extremely dangerous for the engine.
Often the problem with the anti-drainage valve occurs on non-original filter elements of low quality. Sometimes it immediately fails to cope with the functions assigned to it, in other situations, after several thousand kilometers the rubber band “sticks”, which is why it stops coping with its tasks.
In order for a car engine to last as long as possible, it is necessary to lubricate it during operation, and even a few seconds without lubrication after the engine starts will significantly speed up the need for major repairs.
( 413 votes, average: 4.62 out of 5)
How to remove broken spark plugs yourself
How to tighten the steering rack
Related Posts
What you can do yourself
The problem of low oil pressure greatly complicates the relationship between lubricant consumption and level drop and the overall pressure in the system. In this case, a number of malfunctions can be eliminated independently.
- If leaks are detected, the problem is quite easy to localize and solve. For example, oil leakage from under the oil filter can be eliminated by tightening or replacing it. The problem with the oil pressure sensor, through which lubricant flows, is solved in a similar way. The sensor is tightened or simply replaced with a new one.
As for seal leaks, in this case you will need time, tools and skills. In this case, you can replace the front or rear crankshaft oil seal with your own hands in your garage with an inspection hole.
Oil leaks from under the valve cover or in the pan area can be eliminated by tightening fasteners, replacing rubber gaskets, and using special engine sealants. Violation of the geometry of the connecting planes or damage to the valve cover/pan will indicate the need to replace such parts.
- If the coolant gets into the engine oil, then you can remove the cylinder head yourself and replace the head gasket, while following all the recommendations regarding the removal and subsequent re-covering of the cylinder head. An additional check of the mating planes will indicate whether the cylinder head needs to be ground. If cracks are found in the cylinder block or head, repairs are also possible.
As for the oil pump, if this element wears out, it is better to immediately replace it with a new one. It is also not recommended to clean the oil receiver, that is, the part is completely changed.
- In the case where the problem in the lubrication system is not so obvious, and you have to repair the car yourself, then at the very beginning you should measure the oil pressure in the engine.
To solve the problem, as well as taking into account an accurate understanding of where the oil pressure in the engine is measured and how it is done, additional equipment must be prepared in advance. Note that there is a ready-made device for measuring engine oil pressure available for free sale.
As an option, a universal oil pressure gauge will “Measure”. This device is quite affordable and comes with everything you need. You can also make a similar device with your own hands. To do this, you will need a suitable oil-resistant hose, pressure gauge and adapters.
To measure, a ready-made or home-made device is connected instead of an oil pressure sensor, after which the pressure readings on the pressure gauge are assessed. Please note that ordinary hoses cannot be used for self-production. The fact is that oil quickly corrodes rubber, after which the detached parts can get into the oil system.
When the engine heats up, the oil pressure lights up: consequences for the engine
Let's start with the fact that any problems with lubricant pressure mean that the power unit is experiencing oil starvation. Simply put, the rubbing surfaces do not receive enough motor oil and their wear begins to increase. Oil also plays the role of a cleaner and cooler, washing away wear products and lowering the temperature in the area where the surfaces of rubbing pairs work.
This means that if there is not enough lubrication or the pressure is weak, then there is also a high probability of local overheating and damage to the loaded rubbing surfaces by wear products (metal shavings, etc.). It is not difficult to guess that in such cases, scoring on the cylinder bore may form in the engine, and sliding bearings and other important elements may fail.
Also, when the efficiency of the oil system decreases, knocks and noises appear in the engine, which subsequently lead to more serious damage or even engine seizure. In this case, jamming may well be accompanied by a “fist of friendship,” which greatly complicates the repair of the damaged unit and increases the overall costs of restoring the internal combustion engine.
If we talk about the situation when the oil pressure light comes on when the engine heats up, in this case you need to take into account that there are several main reasons:
- reduced lubrication level in the engine;
- motor oil is not suitable for the engine;
- the lubricating fluid has lost its properties;
- malfunctions of the lubrication system and internal combustion engine;
First of all, if the oil pressure is on, it is highly not recommended to operate such an engine until the problems are identified and completely eliminated. So, let's start with the simplest reason. We are talking about a banal decrease in the level of lubrication in the engine. Oil can leak out for various reasons, ranging from a broken oil pan to increased fuel consumption, oil leakage in the turbine area, etc.
Also, the unit itself may be worn out, that is, the engine “eats” oil and emits oil smoke due to problems with the CPG or valve stem seals. One way or another, if you do not monitor the lubricant level, if it drops before the power plant warms up, the oil remains thicker and the “cold” light may not light up.
However, after reaching operating temperatures and heating the lubricant, the material naturally liquefies and becomes more fluid. It is also worth remembering that the gaps between the mating parts in the engine are somewhat reduced, and it becomes more difficult for the oil pump to maintain the required pressure while pumping liquid oil through the system.
If we add to this a partial lack of lubrication, then it becomes clear why the pressure lamp begins to light up after the internal combustion engine has warmed up. To solve the problem, you need to add oil to the engine.
Then you can continue to add lubricant to the level for some time or immediately eliminate the leak (replacing oil seals, valve stem seals, piston rings) depending on the specific situation. If the engine is very worn out, then it is better to immediately undertake a comprehensive overhaul.
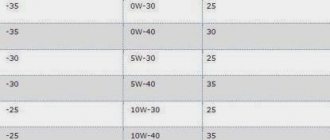
- Let's move on. In many cases, the cause of low pressure may be the oil itself. For example, if a lubricant is poured into the power unit, which according to SAE does not correspond to that recommended by the car manufacturer according to the manual (for example, the driver filled in 0W20 instead of 5W40), then after warming up the lubricant will be very liquid.
In such a situation, it is quite likely that even serviceable engine oil seals and gaskets will leak, which naturally leads to a decrease in the oil level, and the pressure in the oil system will be lowered. To prevent this from happening,
oil must be selected correctly
by viscosity and a number of other important characteristics.
It is also important to consider that the lubricant may lose its properties for other reasons. For example, a significant increase in the planned replacement interval (instead of 10-15 thousand km, the lubricant worked for 20-30 thousand).
Also, loss of properties often occurs after mixing oil with antifreeze. In this case, it is appropriate to talk about a serious breakdown when coolant enters the oil system. This is often caused by cracks in the cylinder block and cylinder head, malfunctions and breakdowns of the head gasket, etc.
The problem can be quickly diagnosed by an increase in the oil level and a decrease in the level of antifreeze in the expansion tank, as well as by the presence of an emulsion under the oil filler cap and on the oil dipstick.
Fuel, which penetrates in excess from the combustion chamber into the crankcase pan, can also change the properties of the lubricant. Often, the problem does not arise on its own, since a violation of the combustion of the mixture in the cylinder leads to engine tripping (the cylinder does not work and the mixture does not burn).
There are many reasons for engine tripping (malfunctions in the power supply system, low compression, lack of spark on the spark plugs, etc.). Also, the injectors can “flow” even when the engine is turned off. In this case, the unit does not move during operation, but fuel still gets into the lubricant. In any case, gasoline in the oil can greatly dilute the lubricant, which will inevitably lead to pressure problems.
It should also be added that adding different types of lubricants, which led to
mixing engine oil
(e.g. synthetics and mineral oil) can also lead to loss of properties of the bulk of the lubricant. The same can be said about the use of various additives and additives (detergents, viscosity agents, stabilizing agents, protective agents, etc.).
Before adding oil or using any additive in the engine, you must take into account all possible risks and effects on the base lubricant.
- Now let's move on to engine and oil system malfunctions. As already mentioned, significant wear on the CPG and an increase in gaps often lead to the oil pressure lamp coming on at idle, on a cold engine, or after the engine has warmed up.
You should also remember that the oil receiver strainer may also be clogged. If a sufficient amount of lubricating fluid does not pass through the filter, then oil starvation of the engine will begin with all the ensuing consequences.
The fact is that washing allows such deposits to peel off, but does not dissolve them. As a result, even a working oil pump is not able to pump the lubricant, and the oil pressure burns. To solve the problem, you need to remove the crankcase oil pan, after which the oil receiver mesh is cleaned mechanically or using active solvents. After such an operation, the difficulties in passing oil through the filter mesh will be eliminated.
Reasons causing a sharp decrease in engine lubricant pressure
Many car owners wonder why the oil pressure dropped in a warm engine. Insufficient oil pressure can occur due to various reasons, both related and unrelated to the breakdown of the engine itself:
- The need to change the engine oil, because its beneficial properties have been lost and the viscosity of the lubricant has decreased.
- Oil filter clogged.
- Malfunction of the oil pump, which does not cope well with pumping lubricant.
- Failure of the pressure relief valve, causing low pressure in the lubrication system.
- Increasing gaps in working units, which cause a drop in engine oil pressure.
- Defects in the oil receiver tube.
- Lubricant leaks through cracks in the engine sump.
- Faults in the electrical wiring of the car.
- A sensor malfunction causes the lamp to light up.
Failure to comply with the mandatory rule of regularly changing lubricants reduces the viscosity of the oil. The oil pump is not able to provide the required pressure when low-quality lubricating fluid is pumped into the system. A situation arises when the oil pressure drops on a warm engine. An oil change should be done after 8–15 thousand kilometers of the vehicle.
When engine elements wear out and the oil filter and pump mesh are heavily clogged, the pressure in the lubrication system may also be lost.
The activation of teeth in the gears of the oil pump, large gaps, and valve failure can be the reason for disassembly and subsequent overhaul of the power unit.
Violation of the tightness of the pan leads to leakage of lubricants. As a result of leaks, the oil pickup tube is unable to capture the required amount of lubricant to be supplied to the system.
Cracks in the oil receiver tube, formed as a result of increased vibrations, prevent the normal intake of lubricating fluid; with such defects in the part, the lubricant pressure may drop.
The integrity of the electrical wiring and the serviceability of the pressure sensor must be checked first.
To additionally check the pressure, the sensor is removed and a pressure gauge is installed in its place. The lubricant pressure is measured at idle engine speed. Pressure gauge readings of 0.6–0.8 bar indicate normal operation of the power unit. Data that goes beyond the specified limits in any direction serves as the basis for subsequent repair of the motor.
Location in power units ZMZ 405, 406, 409
In ZMZ motors, the location of both sensors is identical. You will find them in the upper left part of the cylinder head (as viewed from the interior) above the exhaust manifold. And while the emergency sensor may not be immediately visible, the oil pressure sensor is instantly identified by its barrel-shaped body.
Pressure and emergency oil pressure sensors are located in the upper left part of the cylinder head
Both sensors are screwed into one forked fitting (tee), which is screwed into the cylinder head and connected to one of the oil channels of the lubrication system. Power wires are connected to the sensors.