Purpose of the resonator
First, let's figure out what a resonator is for . As mentioned above, it is part of the exhaust system of a car engine. Its main function is to dampen low-frequency sounds that arise during the exhaust process of gases and their entry into the gas exhaust system. There are two reasons why noise occurs in it:
- sound from expansion of gases;
- noise from vibration of exhaust system elements.
Along with a muffler, the tasks of a car resonator include reducing the speed of movement of exhaust gases. This becomes possible thanks to a physical law, according to which gases that move quickly in a narrow pipe, when they enter a large volume, lose their speed and, accordingly, energy. In the gas exhaust system, the resonator is located in front of the main muffler, being, in fact, the first link in the sound muffling chain of the exhaust system. That is, its main tasks are preliminary noise reduction and balancing of exhaust gas flow pulsations.
Some car owners call it the “middle muffler” (due to its physical location approximately in the middle of the bottom of the car) or the “second muffler.” However, this is not true because the exhaust system resonator and muffler have different operating principles.
The resonator of the car exhaust system also performs the function of freeing the engine exhaust from exhaust gases and creating uniform pressure in it. This ensures minimal resistance to the movement of exhaust gases, and it is possible to use almost all the useful engine power.
Parameters of quartz resonators
Rated frequency – frequency Fn indicated on the marking or in the documentation for the quartz resonator (measured in MHz or kHz). Base frequency is the real frequency of the resonator Fo, measured under given operating conditions. As a rule, only climatic conditions are determined, namely the base ambient temperature To (equal to 25 ± 2 ° C for resonators with a cutoff type AT). Operating frequency – the real frequency of the resonator F, measured under real operating conditions (climatic, mechanical and electrical). Typically, only the permissible operating temperature range is defined.
It will be interesting➡ What is a Hall sensor
Frequency setting accuracy is the maximum permissible relative deviation of the base frequency of the resonator from the nominal frequency. It is measured in parts per million of the nominal frequency, designated as ppm (part per m illion) or 1•10 -6. In some rare cases, the value of this parameter is given as a percentage. As a rule, the accuracy value for tuning the frequency of a quartz resonator is selected from the standard range.
Parameters of quartz resonators.
Temperature frequency instability
Relative deviation of the resonator operating frequency from the base frequency. Can be presented as a function of operating temperature T, in accordance with the formula for quartz plates with the AT cut type and formula (4) for quartz plates of other types. Long-term frequency instability (aging) is a systematic change in the base frequency over time due to internal changes in the quartz resonator. The aging parameter is specified as a relative change in the base frequency over a given period of time. This value is expressed in parts per million per year (for example, 3 ppm/year). Frequency drift under the influence of aging is most noticeable during the first 30–60 days of operation, after which the influence of this factor decreases. The standard range of relative frequency deviations for general purpose resonators includes the following accuracy classes: ±5, ±10, ±15, ±20, ±30, ±50, ±75 and ±100 ppm.
Material on the topic: the device of a trimming resistor.
Resonator operating mode (harmonic number)
The operating mode of the resonator is an unchangeable parameter that determines the oscillation frequency. For quartz crystals, not only the fundamental frequency can be used, but also its odd harmonics - overtones. For example, a crystal may operate at a fundamental frequency of 10 MHz, or at odd harmonics of approximately 30 MHz (third overtone), 50 MHz (fifth overtone), and 70 MHz (seventh overtone).
Resonator device
Structurally, the resonator consists of a perforated (drilled along the entire length within the device) pipe placed in a metal casing. The design also has a throttle hole designed to increase the efficiency of damping wave vibrations in the pipe. The internal cavity of the resonator is divided into two or more unequal parts by partitions located in a transverse plane to the pipe. Also, more modern exhaust resonators are designed with thermal insulation and/or sound insulation (often the same material) located under the housing and designed to reduce its temperature and/or sounds emanating from the device.
Internal structure of the resonator
The internal cavities have an unequal volume in order to ensure periodic narrowing and expansion of the flow of exhaust gases, which in turn equalizes their uneven pulsation. That is, each chamber has its own resonant frequency. In addition, they have a slight offset relative to the axis of the body. This is necessary to achieve a change in the direction of the exhaust flow. And internal perforation on the pipe is needed to dampen the large amplitude of sound waves that produce gases.
The efficiency of the resonator is influenced by the following factors:
- the degree of its wear, tightness;
- level of contamination from soot (the cleaner, the more effective);
- diameter (the larger the diameter of the device, the greater its efficiency).
Problems with the resonator
Like any part, a car resonator periodically fails. After all, it passes through exhaust gases having a temperature of several hundred degrees Celsius. And in combination with the aggressive chemical elements contained in the escaping gas mixture, this leads to gradual burning of the metal parts of the system.
The main signs of resonator failure are:
- Deterioration of the muffler and exhaust system . This is manifested by increased sound coming from the exhaust pipe, especially low frequency sounds (roar).
- The appearance of exhaust gases from under the bottom of the car . This is a clear sign of depressurization of the resonator or other parts of the gas exhaust system.
- The presence of a characteristic rattling metallic sound from the resonator . It appears due to the fact that one (or more) of the internal components of the device burns out. Usually in such cases he “hangs out” or breaks away and rumbles in one of the cells.
- Significant drop in engine power . Due to a malfunction, the throughput of the resonator decreases significantly, so it dampens uneven pulsations of exhaust gases worse or not at all. And this gives feedback on the deterioration of the power unit.
If you encounter one or more of the above signs of a resonator malfunction, you need to inspect its operation as quickly as possible
How to check the catalyst?
Engine power depends on the condition of the catalyst. If there are characteristic symptoms of a breakdown, you should definitely check it. This can be done in light (by dismantling) and for back pressure or CO content without removing Read more
Shoots the silencer
Does your car engine need to shoot at the muffler? Then it’s worth checking the ignition system, fuel supply or timing marks. Find out the reasons and how to get rid of popping sounds from the muffler Read more
Replacing the VAZ 2110 resonator
Repairing the exhaust system or replacing the muffler on a VAZ 2110 most often involves replacing the resonator, since welding does not take long to solve the problem of burnout. The main task is to quickly remove the resonator Read more
Checking the resonator
When identifying the problems listed above, every motorist should know how to check the resonator . This will not only normalize the operation of the engine and exhaust system, but also increase the comfort of using the car, including for the people around you.
To check, you will need an inspection hole (if you don’t have one, you can jack up the car). Diagnosis is made using visual inspection. During the process, it is necessary to carefully examine the integrity of both the device itself and the pipes connected to it (especially at their joints).
A clear sign of a problem is the formation of condensation in the cooling resonator, after which it begins to drip to the ground. This means that its body has lost its tightness and must be repaired, or better yet, replaced. You can check for condensation after some time, when you turn off the engine (to allow the resonator body to cool). Note! Some car enthusiasts, when making resonators on their own, specially drill a hole in its body to remove moisture . Therefore, if you bought a car with a similar resonator, then this testing method will not work for you.
Types of automotive resonators
When choosing an exhaust system resonator, you need to know what types they are and what materials they are made from. Currently, automotive resonators made of aluminized steel and stainless steel . The former are distinguished by their low price, but short service life. Their body is made of thin steel, coated with aluminum on top to prevent corrosion. However, this anti-corrosion composition is not durable. Therefore, we do not recommend that you buy an exhaust resonator made of aluminized steel. It is better to buy a car resonator made of stainless steel. This material has a smoother surface (that is, creates a minimum of turbulence in the system), and is also more resistant when working under extreme temperatures.
What types of voice resonators are there?
chest and head resonators
Chest and head voice resonators
Let's look a little at each type of resonator.
Chest resonators
The chest resonators of the voice are located below the vocal folds (cords) and are responsible for how our voice sounds in the lower tones, that is, in the chest (in the chest register, read “Voice Registers”).
Chest resonators:
- Bronchi.
- Trachea.
Chest resonators are called that because they are located in the chest. When we sing with ordinary chest voices, the chest resonators work. This can be checked this way: put your hand on your chest while singing in a chest voice (or just talking) - and you will feel vibration in the chest area. This is how chest resonators work.
But these are physical sensations. And a real vocalist must also develop imaginative thinking while singing. So, when singing with your chest, you need to imagine that the sound is born in the chest and breaks out.
Head resonators
The head resonators are already located above the vocal cords. They are involved in singing in a high voice, head voice (falsetto, see “Head voice. How to sing high notes?”).
The head resonators are located in the head, which is why they are called head resonators:
- Nasal cavities.
- Oral cavity.
- Pharyngeal cavities.
How to check the operation of the upper (head) resonators? It’s very simple: try to sing something or say something in your head voice (falsetto), while placing your hand on the bridge of your nose - it will vibrate.
Again, in this case the vocalist needs to understand not only the physical sensations, but also needs to use imagination. The vocalist should imagine that the sound is passing through the soft palate - and coming out somewhere at the back of the head.
DIY resonator
Before designing and assembling a resonator of your own design, you need to understand one simple thing. The thicker the material from which the exhaust system is made (including the resonator), the more effective the fight against vibrations and resulting noise will be. It is for this reason that the exhaust manifold, which is the first to receive gases from the cylinder head, has such an impressive weight.
However, when choosing a material, you should not overdo it and choose too massive blanks. Otherwise, the mass of the resonator will be significant, and this will affect the dynamic characteristics of the car and the load on its chassis.
There are a number of reasons why car owners make their own exhaust resonators. One of them is to reduce the noise that a standard factory muffler produces. Usually, for this purpose, an additional resonator is installed in the exhaust system. The second reason is the manufacture and installation of a direct-flow car resonator . Its features are as follows:
- reduction in engine power loss (actually insignificant, about 5.10%);
- changing the sound background of the engine and exhaust system (for lovers of low sound).
To make a direct-flow resonator you will need:
- a set of locksmith tools;
- welding machine (it is advisable to use modern semi-automatic machines or inverters);
- angle grinder with a set of cutting and grinding discs.
The design of the resonator will differ depending on the materials used and the imagination of the car owner. We offer you one of the options for self-manufacturing a direct-flow automotive resonator :
- Pre-prepare the pipe that will serve as the internal base of the resonator. It should be the same or slightly larger diameter than the factory one. Make sure that it can be easily welded to the existing system in the future, so do not choose a diameter that is too large (unless it is possible to connect the pipe using a flange).
- Next, you need to drill holes in this pipe, similar to the stock resonator.
- After this, you need to find a pipe with a slightly larger diameter (about 3.5 cm) that will serve as the outer casing. Its length needs to be made smaller (depending on the design, on average by 5.10 cm on each side).
- The plugs necessary to seal the housing at the ends are made. For this, sheet metal is used, where the outer diameters of the large and small pipes are drawn. Afterwards, the blanks are cut out and processed using a grinding machine.
- A pipe with a larger diameter is placed on a pipe with a smaller diameter, and the cavity between them is filled with glass wool (or better yet, modern mineral wool with good heat and sound insulation characteristics).
- Next, you need to weld the ends around the edges of the pipe with a large diameter using pre-made plugs.
- After welding work, clean the seams using an angle grinder. After this you should paint them.
- The last stage is welding the new resonator into the car's exhaust system. After carrying out the work, also clean the welding seams.
DIY resonator
The given algorithm is approximate . There are a wide variety of options for homemade resonators. In some cases, they are simply thrown out of the system, replacing them with a piece of pipe. However, we do not advise you to do this, since you will not receive a significant addition to the car’s power, but an additional roar from the exhaust pipe is guaranteed!
Additional problems
After installing a self-made resonator, the car owner will likely encounter a number of problems that must be solved. First of all, we are talking about increasing the mass of the gas exhaust system, and, accordingly, the car as a whole. This is true if you used heavy metal elements to make the resonator. Therefore, a situation may arise when it is necessary to replace the brackets and/or shock absorbers. That is, strengthen them. Otherwise, the car body will “sag”, and the chassis will experience additional load.
In addition, replacing the resonator entails a change in the ratio of air entering the engine and the amount of exhaust gases. Therefore, it is necessary to empirically determine which optimal settings to choose and make appropriate adjustments in fuel supply and air filtration.
Removing and installing the resonator
Many motorists are interested in a natural question - how to remove the resonator ? The answer to this question will vary depending on the brand of car. However, in general, the algorithm is simple and will be approximately as follows:
- it is necessary to disconnect the resonator pipes at the points of their connection with the exhaust gas removal system (front, on the engine or catalyst side, and at the rear, on the muffler side);
- remove the resonator from its suspensions, with the help of which it is attached to the bottom of the car;
- dismantle the resonator with its pipes.
How to replace a Renault Logan resonator
Installing a new device is done in the reverse order. When removing the resonator, it is important not to damage the O-rings that connect its pipes to the rest of the exhaust system.
As an example, we present to your attention two video instructions demonstrating the replacement of the resonator on popular Renault Logan cars and front-wheel drive VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112, VAZ 2114, VAZ 2115, Kalina, Priore, Grante.
Finally
Partial or complete failure of the car exhaust system resonator is not a critical failure . Diagnosing a resonator failure is not difficult even for an inexperienced car owner. This is indicated by a loss of power, the spread of exhaust gases under the bottom and/or into the cabin, and an increase in background noise when the engine is running. Please note that the car can be used case, however, we still recommend that you do not delay repairs, since driving with a burnt-out resonator can lead to failure of other elements of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
What is a resonator?
One of the main parts of the combustion exhaust system is the muffler resonator. What it is?
The resonator is an important part of the exhaust gas exhaust system of any vehicle, which in appearance is similar to a small muffler. As a result, this part is sometimes called an additional muffler.
This unit itself reduces the noise level of the operating power unit, but this is only a secondary effect of performing its most important function - to ensure an even flow of burnt gases throughout the exhaust system of the vehicle.
During operation of a car engine, regardless of the number of revolutions, intermittent levels of gas pressure appear in the manifold. Their frequency largely depends on the number of cylinders used in the engine and its crankshaft speed. The resonator is precisely designed to eliminate these intermittent levels.
Muffler resonator: device, types, repairs, problems
When any mechanism operates, a characteristic noise is created, and when it comes to a gasoline internal combustion engine, the “sound effects” are distinguished by increased volume, which causes a lot of discomfort both to the driver himself and to other road users, as well as pedestrians. As you know, the role of a noise absorber is played by a standard muffler, which is part of the exhaust system, but few people know why a resonator is needed, which is also an important component of this unit.
From the name it is obvious that this part is responsible for resonating the sound streams that arise during the operation of the car engine. Simply put, the resonator dampens sound vibrations as exhaust gases exit the combustion chamber. Let's take a closer look at the device and features of this element.
What is a resonator?
One of the main parts of the combustion exhaust system is the muffler resonator. What it is?
The resonator is an important part of the exhaust gas exhaust system of any vehicle, which in appearance is similar to a small muffler. As a result, this part is sometimes called an additional muffler.
This unit itself reduces the noise level of the operating power unit, but this is only a secondary effect of performing its most important function - to ensure an even flow of burnt gases throughout the exhaust system of the vehicle.
During operation of a car engine, regardless of the number of revolutions, intermittent levels of gas pressure appear in the manifold. Their frequency largely depends on the number of cylinders used in the engine and its crankshaft speed. The resonator is precisely designed to eliminate these intermittent levels.
What is it for?
In a system that ensures the removal of burnt gases, the resonator ensures the timely removal of the gaseous mixture from the motor chamber.
A significant part of automotive specialists are confident that the level of useful power provided by the power unit largely depends on the quality of this part.
That is why sports cars are always amenable to modernization: the standard model of the resonator, which is included in the basic package, is replaced with a more advanced version.
In order for the main flow of the exhaust mixture from the engine to fall directly on this part, it is placed immediately behind the forward flow. As a result of this, the better quality and functionality the spare part is, the higher the overall driving performance of the vehicle will be.
In addition, the presence of such a spare part significantly reduces the level of emissions of harmful gases into the environment.
Types of resonators
Like many parts, resonators are divided into types that depend directly on the vehicle engines. These parts must fit either a 2-stroke or a 4-stroke engine. With the help of tests, the following results were summed up:
- if the part interacts with the 4-stroke, the engine speed is reduced;
- When the part is removed, the engine speed increases.
In the case of a 2-stroke engine, the opposite happens. If you remove this element, the engine power decreases, which means fuel consumption increases. This waste is groundless; the vehicle owner will be forced to overpay at a lower vehicle speed.
Is it worth changing the resonator?
The answer is ambiguous. Many experts say that if the VAZ muffler resonator has failed, then it is better not to make repairs, but rather just buy the entire system assembled and install it on your car. This is because, having replaced it, after some time you will still be changing either the exhaust pipe or one of the other elements of the system. The same can be said about the resonator of the Lanos muffler. It will be much cheaper to replace the entire system.
How to repair a muffler
There are two ways to solve this problem. In the first case, you can buy a new muffler resonator. The price for it today is quite affordable. The cheapest option can cost about 500 rubles. But there are also mufflers that cost more than one thousand. At the same time, the choice of manufacturers and types of these system elements is quite large.
If you follow the second path, you can also completely modernize the muffler resonator. In this case, it will be quite possible to carry out all the work on your own. When repairing a muffler, it is necessary to take into account the design features of the element, select the appropriate material and maintain tightness. Problems that arise with the resonator can be solved.
To do this, you need to plan the work to be performed. If you have no experience in welding work, then invite a specialist.
What is it for?
In a system that ensures the removal of burnt gases, the resonator ensures the timely removal of the gaseous mixture from the motor chamber.
A significant part of automotive specialists are confident that the level of useful power provided by the power unit largely depends on the quality of this part.
That is why sports cars are always amenable to modernization: the standard model of the resonator, which is included in the basic package, is replaced with a more advanced version.
In order for the main flow of the exhaust mixture from the engine to fall directly on this part, it is placed immediately behind the forward flow. As a result of this, the better quality and functionality the spare part is, the higher the overall driving performance of the vehicle will be.
In addition, the presence of such a spare part significantly reduces the level of emissions of harmful gases into the environment.
VOLUME RESONATORS
to contents resonators volumetric resonator
|
Volumetric resonator
- a device based on the phenomenon of resonance in a volumetric conductive wave cavity, dielectric for electromagnetic waves, elastic for sound waves, limited by walls reflecting waves, in which, due to boundary conditions, the existence of high-quality resonant oscillations in the form of a standing wave is possible at certain wavelengths.
Oscillatory systems in the form of resonant lines are the main ones for decimeter waves, but on centimeter waves the length of the line turns out to be of the same order as its diameter, and it is no longer possible to talk about the line at all. Even at the shortest decimeter waves (10-30 cm), the use of resonant lines often becomes inconvenient.
The main type of oscillatory systems for centimeter waves (and partly for decimeter waves) are volumetric resonators, proposed by the Soviet scientist M. S. Neumann in 1939-1940. The theory of operation and calculation of volumetric resonators was developed in the works of M. S. Neumann, G. V. Kisunko and a number of other scientists.
Figure 1 shows the transition from a circuit with lumped parameters to a cavity resonator. Let a circuit of the usual type have a capacitance in the form of a capacitor C formed by two round plates, and an inductance in the form of a rectangular turn L1 (Fig. 1 a). As you know, the quality of such a microwave circuit is very low. If you connect several turns in parallel to a capacitor (Fig. 1 6), then the inductance and active resistance decreases. As a result of this, the natural frequency of the circuit fo and its quality factor Q will increase.
| Fig. 1 - Transition from a conventional circuit (a) to a cavity resonator (c) |
For example, if you turn on 25 turns, then the inductance will decrease by 25 times, and the frequency will increase by 5 times, since
the characteristic resistance of the circuit will decrease by 5 times, which follows from the formula
and the active resistance of the circuit r will decrease by 25 times (if we consider it concentrated only in turns).
Therefore, the contour quality equal to ρ/r will increase by 5 times. Increasing the number of turns connected to the capacitor C, we come to the case when all the turns merge into one common closed metal surface (Fig. 1 b). If this requires N turns, then based on the above example we can assume that the resonant frequency and quality of the circuit will increase by (root) of N times.
Thus, the oscillatory circuit turned into a closed cylindrical metal box, which is a volumetric resonator. In this case, in reality, the quality of the circuit increases not by (the root) of N times, but much more due to the fact that the closed metal surface is a good screen, and therefore the electromagnetic field exists only inside the resonator.
A cavity resonator, like an axial resonant line, is a shielded oscillatory system in which there are no radiation losses and no external field that can create parasitic connections with other circuits. In addition, in a cavity resonator there are no losses in solid dielectrics and the active resistance of the resonator walls is very small due to their large surface. As a result of all this, if energy is not taken from the resonator, then its quality can reach tens of thousands. It is also convenient that the outer surface of the cavity resonator has zero potential and does not carry currents. Therefore, cavity resonators can be mounted without insulation.
| Fig. 2 - Field in a cylindrical cavity resonator |
| Fig. 3 - Types of toroidal resonators |
The oscillatory process in the resonator is essentially standing electromagnetic waves that arise due to the reflection of waves from the walls of the resonator. Figure 2 shows the electric and magnetic field lines in a cylindrical resonator, which is one of the simplest in design. Electric lines of force run from one base of the cylinder to the other, and magnetic lines of force in the form of concentric rings surround the electric field. This field structure is the simplest, but in cavity resonators there can be other types of oscillations that have different field structures.
Historically, one of the first was a toroidal resonator (Fig. 3 a). The electric field in it is concentrated mainly in the middle part between the two disks, and the magnetic field lines are arranged in rings around the electric field. However, the resonator according to Fig. 3 a is difficult to manufacture, and currently resonators of this type are made in a different shape. The most common are toroidal resonators, shown in Fig. 3 b and c, otherwise called coaxial.
Indeed, the resonator (Fig. 3c) is made up of two coaxial cylinders and resembles a coaxial line, short-circuited at one end, and having some capacitance at the other end. But still, it cannot be called a line, since it has the dimensions of the internal cavity of the same order in the radial and axial directions, and the length of the line should be significantly greater than the difference in radii. Of course, it is impossible to draw a sharp boundary between a coaxial cavity resonator and a coaxial line. If the ratio of the height h to the radial size r2 - r1 of a coaxial cavity resonator is increased, then it will gradually turn into a coaxial line.
In some cases, resonators are used, similar to those shown in Fig. 3 b to c, but having a size r2 - r1, significantly larger than the height h. They are called radial line type resonators. Sometimes rectangular-shaped volumetric resonators (in the form of a parallelepiped) are used. It is possible to design resonators and many other forms.
A cavity resonator, unlike a conventional circuit, has not one natural frequency, but many resonant frequencies. This property is characteristic of oscillatory systems with distributed parameters, and we have already encountered it when considering resonant lines. For lines, resonance at a particular harmonic is determined by the number of quarters or halves of a wave that fit along the line.
In volumetric resonators, a different number of standing waves can fit not in one direction, but along any of three dimensions. Since these dimensions can be in any ratio to each other, the resonant frequencies of a cavity resonator cannot be called harmonics. They are not necessarily an integer number of times the fundamental frequency.
A rectangular or cylindrical cavity resonator can be considered as a short waveguide, closed at both ends by metal walls. Traveling waves cannot propagate along it, and therefore a regime of standing waves will occur not only in the cross section, but also in the longitudinal direction. Resonance will be observed at frequencies for which an integer number of half-waves are placed along the waveguide.
For the simplest type of oscillations, it is characteristic that the natural frequency does not depend on the height of the resonator h, but is determined only by its diameter D:
It is also possible to excite other higher-order oscillations, the frequencies of which in most cases are not a multiple of the fundamental (lowest) frequency. The production of oscillations of one type or another in the resonator depends on the frequency of the external oscillations exciting the resonator and on the method of excitation, i.e., on what device is used for excitation. Higher order vibrations are usually not used in practice. However, they can arise as harmful (parasitic) vibrations.
Devices for coupling cavity resonators with other purposes, in particular with other resonators, are implemented in the same way as in waveguides. The coupling elements serve either to excite oscillations in the resonators or to extract energy from them.
| Fig. 4 - Electrical (a) and magnetic (b) connection of the resonator with other circuits and their equivalent circuits (c and d) |
| Fig. 5 - Connection of a resonator with two circuits Fig. 6 - Diffraction coupling of the waveguide with the cavity resonator (through the hole) |
The electrical connection is made using a pin (Fig. 4 a), and the magnetic connection is made using a turn (loop) (Fig. 4 b). Everything that was said about them in relation to waveguides also applies to cavity resonators. These types of coupling are similar to capacitive and inductive coupling in conventional circuits. Figure 4 c and d shows equivalent circuits that highlight this similarity.
Often, electrical or magnetic coupling is used twice in a resonator: once to excite oscillations, and another time to extract energy (Fig. 5).
The connection between volumetric resonators and waveguides is often done by diffraction—through a hole, and diaphragms are usually installed for matching (Fig. 6). In some radio devices, communication with the resonator is carried out using an electron flow. To allow this flow to pass through, holes are made in the walls of the resonator.
The quality of cavity resonators connected to other circuits is significantly lower than in the absence of communication. The removal of energy from the resonator is equivalent to an increase in losses in the resonator.
Therefore, it is always necessary to distinguish between the quality of the resonator itself, which has no connection with other circuits, and the quality of the loaded resonator.
Volumetric resonators can be tuned to the required frequency range by changing their volume. Figure 7 shows various ways to change the volume of resonators. The movable plunger Fig. 7a is arranged in the same way as in a coaxial resonant line, and has the same disadvantages. A frequently encountered design is Fig. 7 b, in which the inner cylinder of the resonator can be screwed in and out.
| Fig. 7 - Setting up a cavity resonator by changing its volume. |
| Fig. 8 - Setting up a volumetric resonator using a variable capacitor of variable capacitance |
This method is convenient and gives a wide range of settings.
If the inner cylinder is completely unscrewed, then the resonator will be cylindrical and its frequency will be the highest. As the cylinder is gradually screwed in, the resonator turns into a coaxial one, and its natural frequency decreases. Sometimes an elastic corrugated wall is made at the resonator, which can be bent using a pressure screw (Fig. 7 c).
Another tuning method is shown in Fig. 8a, including a variable-capacitance capacitor in the resonator. The simplest design is shown in Fig. 8 b. Moving a screw with a plate inside the resonator also gives some change in volume, but the main effect on the frequency is exerted by a change in capacitance at the antinode of the electric field or near it. An increase in this capacitance results in a decrease in the natural frequency of the resonator. Changing the frequency within small limits by screwing screws into the resonator is often used to adjust to the desired frequency. Sometimes this is done by turning a short closed loop of a magnetic field antinode or a metal disk near it. This method increases the natural frequency, and it will be greatest in the case when the plane of the coil or disk is perpendicular to the magnetic lines of force.
Literature on cavity resonators
- Vainshtein L.A., Electromagnetic waves, 2nd ed., M., 1988;
- Lebedev I.V., Microwave technology and devices, 2nd ed., vol. 1, M., 1970;
- Jackson J., Classical Electrodynamics, trans. from English, M., 1965;
- Katsenelenbaum B. 3., High-frequency electrodynamics, M., 1966;
- Nikolsky V.V., Nikolskaya T.I., Electrodynamics and propagation of radio will, 3rd ed., M., 1989.
to contents resonators volumetric resonator
Did you know,
that relativism (SRT and GTR) is not a true science? — True science necessarily relies on causality and the laws of nature given to us in physical phenomena (facts). In contrast, STR and GR are built on axiomatic postulates, that is, fundamentally unprovable dogmas in which the followers of these teachings are obliged to believe. That is, relativism is a form of religion, a cult, inflated by the political machine of the mythical authority of Einstein and his faithful followers, elevated to the rank of saints of relativistic physics. Read more in the FAQ on ethereal physics.
| FORUM NEWS Knights of Aether Theory | 06/09/2020 - 19:25: ECOLOGY - Ecology -> Biological safety of the population - Karim_Khaidarov. 06/09/2020 - 19:24: WAR, POLITICS AND SCIENCE - War, Politics and Science -> The problem of state terrorism - Karim_Haydarov. 06/09/2020 - 19:23: EDUCATION, ENLIGHTENMENT, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> Enlightenment from Plamen Paskov - Karim_Haidarov. 06/09/2020 - 19:17: EDUCATION, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> Enlightenment from Andrey Fursov - Karim_Khaidarov. 06/09/2020 - 18:26: ECONOMY AND FINANCE - Economy and Finances -> COLLAPSE OF THE WORLD FINANCIAL SYSTEM - Karim_Haidarov. 06/09/2020 - 18:13: WAR, POLITICS AND SCIENCE - War, Politics and Science -> WE ARE WATCHED - Karim_Khaidarov. 06/09/2020 - 06:30: ECOLOGY - Ecology -> ECOLOGY FOR ALL - Karim_Haydarov. 06/09/2020 - 06:04: CONSCIENCE - Conscience -> RUSSIAN WORLD - Karim_Khaidarov. 06/08/2020 - 18:18: WAR, POLITICS AND SCIENCE - War, Politics and Science -> DISHUMANITY. WHO NEEDS THIS? — Karim_Khaidarov. 06/08/2020 - 18:14: EDUCATION, ENLIGHTENMENT, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> Enlightenment from Vladimir Vasilyevich Kvachkov - Karim_Khaidarov. 06/08/2020 - 18:08: EDUCATION, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> COMPUTER AND NETWORK SECURITY FOR ALL - Karim_Haydarov. 06/08/2020 - 07:32: WAR, POLITICS AND SCIENCE - War, Politics and Science -> JUSTICE.NET - Karim_Haidarov. |
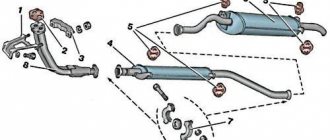
Resonator device
Structurally, the resonator consists of a perforated (drilled along the entire length within the device) pipe placed in a metal casing. The design also has a throttle hole designed to increase the efficiency of damping wave vibrations in the pipe. The internal cavity of the resonator is divided into two or more unequal parts by partitions located in a transverse plane to the pipe. Also, more modern exhaust resonators are designed with thermal insulation and/or sound insulation (often the same material) located under the housing and designed to reduce its temperature and/or sounds emanating from the device.
Internal structure of the resonator
The internal cavities have an unequal volume in order to ensure periodic narrowing and expansion of the flow of exhaust gases, which in turn equalizes their uneven pulsation. That is, each chamber has its own resonant frequency. In addition, they have a slight offset relative to the axis of the body. This is necessary to achieve a change in the direction of the exhaust flow. And internal perforation on the pipe is needed to dampen the large amplitude of sound waves that produce gases.
The efficiency of the resonator is influenced by the following factors:
- the degree of its wear, tightness;
- level of contamination from soot (the cleaner, the more effective);
- diameter (the larger the diameter of the device, the greater its efficiency).
Resonator: purpose, device and types
The resonator is one of the components of the exhaust system of a car. Visually it resembles a smaller muffler, but it is not one - these are two different parts with overlapping functionality.
The product may be considered an important element of the exhaust, but sometimes there are layouts where there is no resonator. If you take the engine as the starting point and head towards the exit of the exhaust tract, then the muffler will be located at the very edge. And the resonator is located before it, closer to the motor.
Purpose
The main functions of this part, despite the external similarities with the muffler, are not obvious:
- ensuring timely removal of combustion products from the engine to create space for the working mixture to enter;
- reducing the temperature of the exhaust gases (from the initial 700-800 degrees Celsius to 300-400). This way, the service life of the muffler, which experiences lower thermal loads, is extended;
- compensation of impulses arising from fuel combustion - gases are discharged in a stream, encountering a minimum of resistance (hence the name “resonator”).
In addition to the above, the product reduces the noise level emanating from a running motor. But it mainly suppresses low frequencies - if you remove the resonator and start the car, “bass notes” will appear.
Structure
The shape, exact configuration and dimensions of this element vary depending on the specific vehicle. All parameters are selected individually so that fuel consumption, noise and engine power are in balance.
However, it is possible to generally describe the structure of the resonator - it is a hollow tube encased in a sealed metal casing (can/cylinder). The gaseous mixture enters from one end, and from the other, passing through the multi-level structure of the part, it is redirected to the muffler. The pipe is drilled along its entire length within the “can.” Perforations are necessary to separate the gas flow.
The internal space is divided by transverse partitions into several or more chambers. They differ in volume, due to which periodic expansion/constriction of the flow of combustion products is performed, compensating for pulsations.
Varieties
The main method for classifying resonators is the type of engine for which they are intended. At the same time, it allows you to roughly determine the degree of practical usefulness of the part:
- Two-stroke - the resonator in this case is an important part of the exhaust system. In its absence, the engine power characteristics will decrease and fuel consumption will increase.
- Four-stroke - the presence of this product for such power mechanisms is a limiting factor that limits the maximum technical capabilities of the engine. When dismantling the resonator, the power will increase by 2 percent, but in return the damage to the environment will increase - the emission of harmful substances will increase.
It is worth noting that this method of dividing into categories is quite vague. After all, the resonators differ from each other in configuration and size.
Functionality check
When a resonator fails or functions incorrectly, the following phenomena are often observed:
- exhaust smell in the cabin;
- the appearance of characteristic noise;
- the appearance of gases from under the bottom.
If one or more of the above signs of problems are detected, you need to check the resonator. The most basic and simplest way to detect/remove the most common faults is inspection. You drive the car into a pit or otherwise gain free visual access to the desired element (for example, by using a jack). Now you should carefully look for traces:
- rust caused by exposure to aggressive environments - corrosion often causes the resonator to malfunction;
- thermal damage - unburned fuel falling on the body contributes to the “burning out” of the metal, ultimately forming through holes;
- dents and other external mechanical damage - occur due to contact of the surface of the element with the road surface.
If a visual inspection does not produce any results, but you hear the rumbling of the resonator or observe other unambiguous signs of a breakdown of this part, then you cannot do without the help of specialists. They will diagnose the exhaust system and figure out the root of the problem, including “hidden” options:
- clogged resonator cavity;
- destruction of the internal structure of the structure (violation of the position of the walls, etc.).
However, you will have to contact the service station employees in any case, even when you independently discover external damage, but you will not be able to fix it yourself. This will require special equipment that car services have.
Note! Sometimes it is impossible to restore the functionality of an element - if the damage is too critical, you will need to replace the faulty part. The service station will advise you on which replacement resonator to buy and install it.
TYPES OF RESONATORS
Like many parts, resonators are divided into types that depend directly on the vehicle engines. These parts must fit either a 2-stroke or a 4-stroke engine. With the help of tests, the following results were summed up:
- if the part interacts with the 4-stroke, the engine speed is reduced;
- When the part is removed, the engine speed increases.
In the case of a 2-stroke engine, the opposite happens. If you remove this element, the engine power decreases, which means fuel consumption increases. This waste is groundless; the vehicle owner will be forced to overpay at a lower vehicle speed.
Signs of a malfunctioning muffler resonator
Any malfunction of the resonator can lead to a decrease in motor power and also affect the noise level. Most often, car enthusiasts encounter the following signs of deterioration in the performance of the additional muffler:
- The volume of the exhaust system sound has increased.
- A metallic rattling noise appeared in the place where the resonator was installed. The reason for this may be that one of the internal parts of the resonator has burned through.
- Engine power began to drop. This is a consequence of the reduced capacity of the additional muffler.
If you notice one or more characteristic signs, repair or replace the resonator.
Checking the resonator
When identifying the problems listed above, every motorist should know how to check the resonator . This will not only normalize the operation of the engine and exhaust system, but also increase the comfort of using the car, including for the people around you.
To check, you will need an inspection hole (if you don’t have one, you can jack up the car). Diagnosis is made using visual inspection. During the process, it is necessary to carefully examine the integrity of both the device itself and the pipes connected to it (especially at their joints).
A clear sign of a problem is the formation of condensation in the cooling resonator, after which it begins to drip to the ground. This means that its body has lost its tightness and must be repaired, or better yet, replaced. You can check for condensation after some time, when you turn off the engine (to allow the resonator body to cool). Note! Some car enthusiasts, when making resonators on their own, specially drill a hole in its body to remove moisture . Therefore, if you bought a car with a similar resonator, then this testing method will not work for you.
Also, the integrity of the resonator body can be determined by the presence of exhaust gases leaving it. This also indicates depressurization and the need to replace it. This fact can be checked with the car engine running by looking under the bottom. To be sure, you can ask an assistant to “turn on the gas” at the same time so that more exhaust gases pass through the system. Also, suspicion of depressurization is caused by the appearance of smoke from under the bottom of the car while driving or when parked with the engine running.
How to repair a muffler
There are two ways to solve this problem. In the first case, you can buy a new muffler resonator. The price for it today is quite affordable. The cheapest option can cost about 500 rubles. But there are also mufflers that cost more than one thousand. At the same time, the choice of manufacturers and types of these system elements is quite large. If you follow the second path, you can also completely modernize the muffler resonator. In this case, it will be quite possible to carry out all the work on your own. When repairing a muffler, it is necessary to take into account the design features of the element, select the appropriate material and maintain tightness. Problems that arise with the resonator can be solved. To do this, you need to plan the work to be performed. If you have no experience in welding work, then invite a specialist.
Repair
The muffler resonator can only be repaired if holes form in it. For this you will need:
- piece of tin;
- metal screws for attaching a tin “patch”;
- sandpaper;
- drill and metal drill bit;
- putty and hardener.
The operating procedure is as follows:
- Cut a plate from tin that is larger in size than the damage that is supposed to be repaired.
- Clean the surface on which the patch will be installed.
- Drill several holes in the body and plate.
- Using putty and hardener, install the plate in place.
- Secure the patch using self-tapping screws.
- You can start operating the car after the putty has hardened.
Removing and installing the resonator
Many motorists are interested in a natural question - how to remove the resonator ? The answer to this question will vary depending on the brand of car. However, in general, the algorithm is simple and will be approximately as follows:
- it is necessary to disconnect the resonator pipes at the points of their connection with the exhaust gas removal system (front, on the engine or catalyst side, and at the rear, on the muffler side);
- remove the resonator from its suspensions, with the help of which it is attached to the bottom of the car;
- dismantle the resonator with its pipes.
How to replace a Renault Logan resonator
Installing a new device is done in the reverse order. When removing the resonator, it is important not to damage the O-rings that connect its pipes to the rest of the exhaust system.
As an example, we present to your attention two video instructions demonstrating the replacement of the resonator on popular Renault Logan cars and front-wheel drive VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112, VAZ 2114, VAZ 2115, Kalina, Priore, Grante.
Partial or complete failure of the car exhaust system resonator is not a critical failure . Diagnosing a resonator failure is not difficult even for an inexperienced car owner. This is indicated by a loss of power, the spread of exhaust gases under the bottom and/or into the cabin, and an increase in background noise when the engine is running. Please note that the car can be used case, however, we still recommend that you do not delay repairs, since driving with a burnt-out resonator can lead to failure of other elements of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
The first, intermediate, middle muffler is how this component of the exhaust system is called. But in all cases we mean a resonator. Let's look at what this device is, what it does and how it works.
Purpose, principle of operation and design of the resonator
If you ask any motorist who has the slightest understanding of the structure of a car about the purpose of a resonator, he will answer that this element reduces the noise level. In principle, this statement is true. But what most of us don't realize is that this exhaust system component has other functions as well. In addition to reducing sound, the resonator is also responsible for reducing the system’s resistance to the movement of exhaust gases (and this happens by smoothing out pulsations) .
This is confirmed by the fact that the exhaust system without a resonator on many cars does not work entirely correctly. The noise naturally increases, and at the same time, many motorists who decided to take a rash step and voluntarily removed the resonator, replacing it with a piece of pipe, complain that the car does not maintain XX speed. And this happens precisely due to the fact that the back resistance of the system increases, and there is no smoothing of pulsations (exhaust gases do not arrive simultaneously from all cylinders, but, so to speak, in “batches”). Therefore, a pipe instead of a resonator is “not good”: this is, in principle, possible, but you need to trust such a modification to professionals who will carry out the necessary calculations and do everything correctly. Also in this element there is a decrease in the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases and a decrease in their temperature (about 300-400 degrees at the outlet versus 700-800, or even more, at the input of the resonator).
Design, principle of operation and repair of the muffler resonator
On the road, each mechanism of the car makes a lot of sounds, especially loud noise is typical for internal combustion engines - a muffler was created in order to reduce the noise level.
See all photo news >>
It remains the key link in the exhaust system, and the muffler itself consists of a number of components, one of which is a resonator.
Muffler resonator
The main role in dampening the noise that occurs after combustion of the working mixture in the engine is played by the resonator. The dimensions of this spare part depend directly on the amount of noise produced; its shape also matters.
Due to a breakdown of the resonator, the entire exhaust system works worse - there is a smell of exhaust gases inside the car and there will be a lot of noise while driving.
How does a resonator work?
It itself consists of a mass of layers, where each is responsible for carrying out specific tasks. As soon as the hot exhaust gas enters the resonator, it passes through the reflectors. Particles of the produced gas flow through two different streams. The intake and exhaust resonators do the same amount of work as they move the exhaust through the entire system.
Due to the fact that the resonator and the exhaust system as a whole are regularly affected by extremely high temperatures, these machine parts often break. To prevent breakdowns, you need to regularly inspect and maintain the exhaust system.
You should know that the operation of the resonator depends on:
• the state of cleanliness of the muffler; • the quality of the catalyst; • the size of the pipe in diameter.
From the outside, the resonator resembles a small muffler. For excellent operation of the system, the pressure must be evenly distributed. It is thanks to this that the exhaust system has less resistance, which does not in any way affect the reduction in engine output.
Resonator repair
Depending on the engines, there are different types of resonators - for example, there are resonators for a two-stroke engine and a four-stroke one. They are divided depending on size and appearance.
How to understand that there is a breakdown in the resonator: if it is faulty, then noise will appear when the motor is running or the output of the engine will be reduced.
Basically, holes appear in the resonator and rust appears. You can do the repairs yourself, or call a professional.
So, to fill holes you need:
• cut a sheet of tin to cover the hole. It should be noted that the size of the “patch” needs to be made larger so that it is not butted;• then you need to rub the repair area with sandpaper;• then several holes are drilled for fastening on the resonator and the plate;• to fix the plate on the resonator you will need to take putty and hardener; • after installing the plate, screw the screws through the holes; • you do not need to start the engine immediately - the putty needs to harden.
Thus, it will be possible to repair the hole in the resonator and it will be able to work for another couple of years.
How to replace a muffler resonator with your own hands
The resonator is usually replaced in the garage, since a pit is needed.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
• treat the surface of the connection of the resonator bolts with anti-rust spray WD-40, then unscrew the connecting bolts. • Disconnect the special clamp securing the resonator, and after disconnecting the pipes, remove the seal. • Disconnect all fasteners with O-rings and completely remove the resonator. • Installation of a new resonator is carried out in reverse order.
When installing the resonator, you should check the connection to the muffler - there should be no gaps. If they appear during assembly, the efficiency of the resonator will become noticeably lower and the noise will be loud.
How a resonator works and works
The operation of this element is based on the following physical processes:
- Expansion and contraction of exhaust gas flow. This is achieved through the use of multiple cameras in the element in question.
- Suppression of mid- and high-frequency pulsations. Exhaust resonators for cars have pipelines inside for this purpose, located offset relative to each other.
- Interference of sound waves. Due to this, the total amplitude increases, and, consequently, the oscillation frequency decreases. This is achieved through the use of chambers of different volumes, as well as using perforations on the pipes inside the resonator.
- The use of closed chambers in which gases accumulate. Gases entering through the perforations are released at a certain point in time.
Also, depending on the design, the middle part of the muffler (or resonator) may have several chambers. The latter, to reduce noise, can be made using special soundproofing material. As for the body, the original or universal exhaust system resonator can be made of stainless steel, or so-called aluminum steel (coated with a layer of aluminum to protect against corrosion). The first option is more expensive, but it is characterized by better corrosion resistance.
Microwave
English Microwave cavity
Accelerating microwave cavity in the linear accelerator of the Australian Synchrotron. In the center of the resonator there is a vacuum chamber of the linear accelerator. Possible configuration of electric and magnetic fields in a microwave resonator.
An electromagnetic resonator in which the energy of electromagnetic oscillations is accumulated in a volume limited by well-conducting surfaces. A cavity resonator has a spectrum of natural oscillation frequencies and corresponding oscillation modes (types of oscillations). Each mode is determined by its structure of electric and magnetic fields. In the simplest volumetric resonators based on sections of a waveguide limited at the ends by conducting walls, the following are distinguished: H-type oscillations, which have longitudinal (along the waveguide axis z) components only of the magnetic field Hz (electric field component Ez=0); E-type oscillations having longitudinal components only Ez (Hz=0).
Excitation of oscillations in cavity resonators, as well as in radio waveguides, is carried out using loops, pins, slots, electron flows, etc. Volume resonators are widely used in microwave electronics devices (klystrons, magnetrons, etc.) and microwave technology devices (wave meters, filters, etc.). In volumetric resonators used in electronic devices to interact with electron flows, the main types of vibrations are most often used. In this case, the main characteristics of a cavity resonator - resonant frequency, quality factor and characteristic impedance - are identified with the characteristics of the equivalent oscillatory circuit.
According to Maxwell's equations, an alternating electric field generates an alternating magnetic field, and vice versa. There is a continuous exchange of energy between the electric and magnetic fields. If you somehow limit a certain volume of space with reflective walls that prevent the loss of energy from this volume due to radiation, then electromagnetic oscillations can be excited in this volume at certain wavelengths determined by the size of the device. If a hollow resonator is formed by metal walls, then it is also often called a closed resonator. Volumetric microwave resonators can also be filled with a dielectric. There are also open dielectric resonators, without metal walls, in which the wave is reflected from the boundaries of the dielectric due to the effect of total internal reflection - resonators with “whispering gallery” modes. Due to the fact that electric and magnetic fields hardly extend beyond the boundaries of the cavity resonator, their quality factor is extremely high (10,000 or more).
Direct flow resonator
One of the varieties of the exhaust system element under consideration is a direct-flow (or sports) resonator. Its difference from the “regular” one is that there is a lower reverse resistance. And it turns out to the detriment of smoothing pulsations and reducing sound. Such a resonator, as a rule, does not have chambers and does not change the direction of movement of the exhaust gas flow. In essence, this is a smooth “tunnel” with perforated walls. This means that, given the problems discussed above that can be caused by pulsations, you need to choose such an element for your car very carefully. It’s better to entrust this matter to professionals. So, we figured out what a resonator is for and how it works. If you need repair or replacement of this element (including installation of a direct-flow element), contact GSAvto specialists.
What is a resonator and how do they differ from each other?
Welcome! Resonator - before we begin to understand what is the difference between them, let’s say a few words about them, firstly, this unit has a lot of other names, by the way, the most common names for this unit are a resonator and just an additional car muffler, let’s go over everything a little closer to this topic.
Note! At the very end there is an interesting video, if you are really interested in what a resonator is, then watch it, it says a lot about this unit!
What is a resonator? (In details)
Firstly, you must understand that this unit is the main part of the exhaust system and therefore it is present on almost all cars of the VAZ family, it acts as a kind of pipe that is located in the very middle of the car and therefore, as such, an additional muffler has a much greater chance of getting into under attack than, for example, the same intake pipe, and by the way, it is mainly the tank or tanks of the resonator that come under attack (More on this a little later) and generally the deformed tanks of the additional muffler are very noticeable on the so-called lowered cars, otherwise on low ones, for In order for you to have at least some idea about this additional muffler, then in this case, look at the photo prepared especially for you, in which the arrows indicate the resonator itself, as well as the places where it is attached to the exhaust pipe (Blue arrow) and to the rear part muffler (Green arrow).
Note! This photo above was taken under the bottom of a VAZ 2106 car; on other cars of the VAZ family, the additional muffler is located almost the same way!
Types of resonators:
At the moment, there are many different types, as they say, each car has its own, and in fact, almost every car of the VAZ family uses its own resonator, but they are all very similar to each other, for example, let’s take an additional muffler from a classic. On classic cars, and this is the VAZ 2101-VAZ 2107 line, two types of resonators are used, namely an additional muffler with one and two tanks, let's look at them in more detail:
Single barrel resonator - its main feature is that it costs less, unlike an additional muffler with two barrels. In size, both types of resonators are almost similar to each other, the only peculiarity in them is that another so-called additional tank is welded to the free space in the resonator with one barrel, and thus an additional muffler with two barrels is obtained.
Resonator with two barrels - let's start with the fact that its cost is slightly higher than that of a resonator with one barrel, but its main feature is that the engine runs quieter with it and thus you drive in a quiet car and can freely enjoy music and not be distracted constantly to the sound of the engine, since on a car where this unit with one barrel is installed, the engine, namely its exhaust system, is louder, which creates some discomfort.
Note! When choosing a resonator, you should pay attention to its dimensions, because not every resonator can fit perfectly into the bottom of the car, and also not every given unit can seamlessly fit into the exhaust pipe of your car and the rear part of the muffler, so when choosing, be careful and pay attention pay special attention to this!
Link! How to replace the resonator - on a classic? How to replace an additional muffler on Samara family cars?