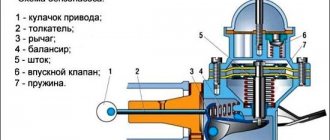
Every car owner knows that diesel fuel can be used in summer and winter. There is also a classification of gasoline based on operating temperature. Fuel grades are specified in GOST 32513-2013, which regulates the characteristics of environmental classes, octane number and explains the difference between winter and summer gasoline. The difference lies in the vapor pressure. This parameter is measured in a completely closed vessel, under conditions similar to a fuel tank. Signs of high saturated vapor pressure (SVP) are well known to everyone - it is this that inflates plastic cans in hot weather and produces a “zilch” when the gas tank cap is unscrewed.
According to GOST, the DNP value for gasoline in the warm season should be 35-80 kPa, and in winter – 35-100 kPa. The saturated vapor pressure must be measured each time fuel is accepted and entered into the documents. Such a small difference in DNP significantly affects other characteristics of gasoline, especially in the off-season. In summer, winter grades of fuel can deform not only the canister, but also the fuel tank if you leave the car in the sun. The critical value of saturated vapor pressure means premature detonation and even the threat of explosion. Summer gasoline evaporates less in cold weather, making cold starting difficult or impossible.
Another difference between gasolines that differ in seasonality is their fractional composition.
What is the difference between “summer” gasoline?
Summer gasoline is gasoline with a heavier fractional composition when compared with “winter” fuel. Due to this, its boiling point is higher: 110 rather than 100 degrees Celsius. This is necessary so that the gasoline completely evaporates and the fuel system does not clog prematurely.
Using such fuel, you can avoid the main problem in the warm season: vapor lock. They do not form even in heat up to +50˚.
In this case, the engine will start without delay at temperatures down to -10-15˚: this is acceptable for early autumn or late spring. And when the morning temperature drops below this mark, you can switch to a “winter” grade of fuel.
During what period and in what territory is summer gasoline offered:
- In central Russia - in the warm season, from April 1 to October 1.
- In hot southern regions - all year round.
Perspective
With proper medical care, minor CNS symptoms will subside as the body eliminates toxins, although it may take several weeks for the kidneys to heal.
If a person washes it off quickly, gasoline usually does not cause significant skin complications.
Severe exposure to gasoline of any kind can be fatal. The long-term consequences of such exposure can be significant. They include:
- lung damage
- renal failure
- vision loss
- severe scars
- intestinal damage
- damage to the food pipe, mouth and throat.
Characteristics of “winter” gasoline
The main difference between this fuel is that it allows you to immediately start the engine in cold weather down to -30 degrees. For this purpose, the proportion of light fractions in the “winter” grade of gasoline is increased, and its boiling point is lower compared to the summer grade.
Where and when is this fuel used:
- In central Russia - in the cold season. Officially, this is the period from October 1 to April 1.
- In the northern regions - all year round.
By purchasing fuel by bank transfer using cards at Rosneft gas stations, you can be sure that you will receive gasoline with the required characteristics. There is no need to specifically select it. If such seasonality is important in your region, “winter” fuel is produced and sold during the cold season, and vice versa.
Features of the 95th
This type of fuel belongs to the “premium” class and is produced by catalytic cracking with the addition of various additives.
The use of 95 gasoline is recommended in high-speed forced engines of modern cars.
Table: characteristics of 95 gasoline
| Characteristic | Standard indicator |
| Octane number | 95 |
| Motor octane number | 85 |
| Boiling temperature | From 33 to 205 °C |
| Amount of lead per dm3 | No more than 0.1 g |
| Sulfur content | No more than 0.05% |
| Manganese content in 1 dm3 | Cannot be detected without manganese anti-knock agent |
| Density (at 15 °C) | 725–780 kg/m3 |
| Availability of resins per 100 cm3 | No more than 5 mg |
| Appearance | Colorless, highly transparent |
| Benzene content | No more than 5% |
Which octane number is preferable?
The relationship between the octane number of gasoline and ambient temperature is one of the main problems that fuel manufacturers around the world are trying to solve.
Be sure to follow the manufacturer's recommendations. If the instructions for the car indicate strictly one octane number of fuel, then only this can be poured into the tank at any time of the year. If the manufacturer allows a range of values, you can experiment with varieties. It is better to start in winter to reduce the risk of high evaporation. It is believed that high-octane gasoline contains more ethers and alcohols, so they ignite worse, but in any case, in the cold, the probability of detonation is almost zero, so in winter, as an experiment, you can try pouring AI-92 gasoline into the tank instead of AI-95. During the first kilometers, evaluate the dynamics, performance of the car engine, and estimate the consumption. In the spring, you can switch to high-octane gasoline again.
Many leading automakers offer the ability to select the octane number. For example, for Volvo S60 models, fuel with an octane rating ranging from 91 to 98 is recommended, with priority for 98 in the hot season. Sports cars also allow the use of AI-98 and AI-95 gasoline, but owners of such cars rarely pay attention to this.
About temperature and freezing
The oil itself becomes thick already at -25 - 30 degrees Celsius, but gasoline is its, if you want a volatile compound, it has a much lower freezing level.
For the middle zone, where the frost is about -20 - 35 degrees, you don’t have to worry about anything; freezing gasoline in the tank in the cold is simply physically impossible here.
There is still no accurate information about freezing! There is a very high dependence of fuel on the additives in it, the method of production and purification. However, there is such generally accepted information - popular brands such as AI - 92, AI - 95 and AI - 98 have fairly low freezing thresholds: they start from - 72 degrees Celsius! If they can freeze, it is only at the poles of our planet. According to other information, especially pure gasolines (at EURO 6 level) have a freezing threshold of -118 degrees Celsius. At this temperature, gasoline does not become solid, it looks like liquid rubber or molten paraffin - a thick jelly-like substance.
To be honest, in the Arctic, there is a special gasoline, it is called “Arctic”. Its threshold is even lower, so with the help of a special formula and additives it remains liquid up to -150 degrees Celsius, which is more than enough, yet there are practically NO such temperatures on earth!
But freezing of the fuel is not the worst thing - it needs to leave behind the possibility of ignition, otherwise it will be of little use, the so-called viscosity! Thus, Russian GOSTs (GOST R 51105-97 and GOST R 51866-2002 - “as amended”) characterize not only the sulfur content in the fuel, but also the minimum temperature at which a flash should occur in the engine cylinders, now it is 62 degrees. That is, at this temperature, gasoline of popular brands should ignite and not thicken.
How to prevent gasoline poisoning
People can usually prevent exposure to gasoline vapors by avoiding areas where they may be exposed to gasoline vapors.
Persons who regularly work in a manner that exposes them to gasoline should always take appropriate precautions, such as wearing protective clothing or masks.
Those who work with gasoline can follow good safety practices at the site and when handling or storing gasoline, such as:
- avoiding standing near exhaust pipes
- wearing gloves and protective clothing or masks when handling gasoline for long periods of time
- Wash your hands thoroughly as soon as gasoline comes into contact with your skin.
- storing gasoline and gasoline products in a safe place out of reach of children
- avoiding intentionally sniffing or inhaling gasoline.
- regular booking of regular petrol pipe inspections and services
- avoiding using gasoline-powered machines such as cars or power tools in an enclosed area without proper ventilation.
- Observe safety rules when handling or storing other products containing hydrocarbons, such as motor oils, kerosene, incendiary fluid and diesel fuel.
Many people don't know if they have gasoline lines running through their property. People can access the National Pipeline Mapping System through the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration website.
People who work with gasoline should talk to their doctor about ways to reduce the risk of long-term health effects. People should also report any symptoms of overexposure to their doctor as soon as they develop.
Shelf life
As mentioned above, the shelf life of fuel, depending on conditions, is 1-5 years. If the requirements are completely neglected, the shelf life is further reduced. First of all, we are talking about those cases when gasoline is stored in the open sun and in an open tank. These are the approximate storage times for gasoline depending on the tank:
- The tank of the car is six months.
- Canister - one year.
- Tank or barrel - two years.
- Special fuel tank - up to three years.
- A special tank buried underground - up to five years (maximum period).
Under ideal conditions, gasoline retains its properties and can be used without loss of efficiency for five years. However, few people use special tanks for storing fuel, and even in a buried state. Most often, drivers stock up on gasoline in cans, storing them in their garages. In this case, the fuel can be stored for only one year.
Does gasoline burn in the snow?
On the eve of winter, many romantically inclined people were interested in whether gasoline would burn if it was poured onto the snow and set on fire. After all, if so, you can write a pleasant wish to your loved one very beautifully and effectively. The answer to this question is yes. In the snow, fuel will be able to burn, and the higher the air temperature, the better this process will be, since the vapors necessary for combustion will be released more actively.
But, now knowing whether gasoline burns in the snow, do not rush to organize a fire show. Take safety first. For this:
- Thoroughly clear the required area.
- Make sure the fire will not cause any damage or spread to nearby trees or vehicles.
- Just in case, bring a bucket of sand with you, which can be used to put out a fire if something happens.
Also, do not forget that gasoline fumes are extremely toxic, and inhaling them is dangerous to your health. In addition, gasoline burns out very quickly, so the spectacle will not last long.
A simpler, safer and, moreover, longer-burning alternative can be ordinary candles, for which you will have to make small lampshades from plastic bottles so that a sudden wind cannot put them out. This will, of course, take more time, but the effect will be achieved even better - due to a longer burning time.
Shelf life depending on capacity
As we have already found out, according to GOST, fuel is stored for five years under ideal conditions. If you bury the tank in the ground, the storage conditions will be close to ideal. In other cases, gasoline will deteriorate faster.
How long fuel will be stored depending on the tank:
- The tank of the car is six months.
- Metal canister - 1 year.
- A tank or barrel located in the basement - about two years.
- A special tank that sits on a plot of land in the shade for about three years.
- A special tank completely buried underground - up to five years.
Therefore, if you do not have a special tank, then there is little point in stocking up on fuel. It is also worth considering that many gas stations in Russia sell far from the highest quality gasoline, which may not comply with GOST at all. Its shelf life is reduced already upon purchase.
The fuel supply is frozen, what should I do?
Now let's move on to our everyday life and questions from readers, why is gasoline not supplied to the injector or carburetor from the tank? What's frozen? Of course not! All the fault here is as fuel, sometimes the owners themselves.
SO : Now I won’t criticize all gas stations, but now there are more or less conscientious ones. However, in many, especially “unnamed” gasoline, they are mercilessly “fueled” - sometimes with diesel, sometimes with water, but you never know what, you can even find fuel oil and oil.
What's happening? In summer and warm weather, water and other “bad stuff” float at the bottom of the tank, sometimes falling on the filter mesh, but it does not let them through. This way they remain “filtered” and your engine runs clean without problems.
But with the onset of frost the situation changes dramatically. Water freezes already at 0 degrees, diesel, if it is not “winter”, also begins to thicken, and other petrochemical products too. Thus, a dense film forms on the mesh of your fuel filter, which does not allow fuel to flow through the line, it seems that it is working, but no fuel is flowing! This happens all the time, no one is immune from it.
You just need to remove the fuel filter and clean it; it is also advisable to clean the tank from “deposits” at the bottom. Then performance will be restored in 90% of cases. This malfunction manifests itself precisely in severe frosts - remember this!
I also pointed out that sometimes the drivers themselves are to blame - why? It’s also simple - water can get into the tank when refueling a car in rainy or snowy weather, or when pouring gasoline from a canister through a regular funnel, and who knows what’s in that canister at the bottom! So when pouring gasoline into the tank from a canister, use a funnel with a mesh, there will be fewer problems in winter.
Now let's watch the video version.
This is the information I think was useful to you. Read our AUTOBLOG, subscribe to VKONTAKTE groups.
Similar news
- How gasoline is made from oil. How much can you get from a liter + per...
- Octane number and compression ratio. Plus a detailed table and video
- Plastic gas tank - main pros and cons