No spark VAZ (injector, 8 valves)
The other day, out of the blue, the car (Kalina 1.6, 8 valves) began to shake terribly. Diagnostics showed misfires in cylinders 1 and 4. After a little checking (see how to check correctly here), I came to the conclusion that there was no spark .
And only in cylinders 1-4. Next, in order to find out the reason for the loss of spark, I will go in order.
The first thing to check is the spark plugs. The spark plug looked normal, so I didn’t have much hope that replacing it would fix the situation. And so it happened - the new spark plug still refused to produce a spark.
The second is checking high-voltage wires. They are checked with a conventional multimeter in resistance measurement mode. The resistance should be within 15 kOhm. The wires also turned out to be fine.
Third, and probably most important, is the ignition coil. She, like no one else, is responsible for the spark. Its operability is also checked with a multimeter in continuity and resistance measurement mode. First you need to check the resistance between pins 1-4 and 2-3. It should be about 4 kOhm. If the tester shows infinity, then the coil is broken and must be completely replaced. Next, check the resistance between pins 1a and 1b. There shouldn't be a break here. And the last thing is to check the central contact for breakdown to the housing. The tester should show infinity.
My reel passed the test perfectly. It seems that all the main parts are working properly, so why is there no spark? After digging a little on the Internet, I realized that I still need to check the circuit from the ECU to the coil itself.
A 3-pin chip is placed on the ignition coil, therefore you need to check these 3 wires. The central contact is +12V, which is constantly supplied when the ignition is on. The extreme contacts - 1a and 1b - provide a control signal (negative) at the moment when a spark is needed. How can all this be checked? Very simple - using a regular light bulb.
You need a lamp with a power of 1-2 W or an LED with an additional resistance of 500-700 Ohms.
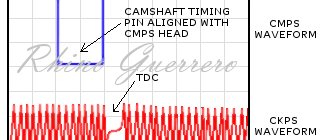
We connect the lamp to the central terminal and contact 1a and ask a partner to crank the engine a little (first remove the fuel pump fuse and relieve the pressure in the rail). When cranking the starter, the lamp should flash. The same procedure must be done with pin 1b - the lamp should also blink.
When I turned on the ignition, the lamp started to light up, just constantly on (pin 1b and central). This means that the control wire has a short to ground somewhere or that the transistor (VT1) in the ECU is broken. To find out, we need to find the ECU, disconnect the wiring harness from it, find the wires we need (1b) and test them for integrity.
Having found the contact diagram, I found out that contact 1b goes to pin 5 of the ECU, 1a goes to pin 2, 3 goes to ground of the ignition circuit. I rang them for integrity - they were all intact. I called ground and everything is fine too. Therefore, you need to check the transistor in the controller itself.
My car has a January 7.2 controller. Inside there are 2 transistors that pass control signals to pins 1a and 1b of the ignition coil. So one of these transistors was broken, i.e. was constantly in the open position.
How to check the transistor for serviceability? It has 3 pins - 2 of which are soldered. It is necessary to ring each outer terminal with the central one. In both cases, the tester should not beep. The contacts must not be closed.
Now all that’s left to do is to unsolder the broken transistor (its marking is gb10nb37lz), solder a new one in its place and rejoice at the spark that appears.
Why is there no spark on the viburnum?
The other day, out of the blue, the car (Kalina 1.6, 8 valves) began to shake terribly. Diagnostics showed misfires in cylinders 1 and 4. After a little checking (see how to check correctly here), I came to the conclusion that there was no spark . And only in cylinders 1-4.
Next, in order to find out the reason for the loss of spark, I will go in order.
The first thing to check is the spark plugs. The spark plug looked normal, so I didn’t have much hope that replacing it would fix the situation. And so it happened - the new spark plug still refused to produce a spark.
The second is checking high-voltage wires. They are checked with a conventional multimeter in resistance measurement mode. The resistance should be within 15 kOhm. The wires also turned out to be fine.
Third, and probably most important, is the ignition coil. She, like no one else, is responsible for the spark. Its operability is also checked with a multimeter in continuity and resistance measurement mode. First you need to check the resistance between pins 1-4 and 2-3. It should be about 4 kOhm. If the tester shows infinity, then the coil is broken and must be completely replaced. Next, check the resistance between pins 1a and 1b. There shouldn't be a break here. And the last thing is to check the central contact for breakdown to the housing. The tester should show infinity.
My reel passed the test perfectly. It seems that all the main parts are working properly, so why is there no spark? After digging a little on the Internet, I realized that I still need to check the circuit from the ECU to the coil itself.
A 3-pin chip is placed on the ignition coil, therefore you need to check these 3 wires. The central contact is +12V, which is constantly supplied when the ignition is on. The extreme contacts - 1a and 1b - provide a control signal (negative) at the moment when a spark is needed. How can all this be checked? Very simple - using a regular light bulb.
You need a lamp with a power of 1-2 W or an LED with an additional resistance of 500-700 Ohms.
We connect the lamp to the central terminal and contact 1a and ask a partner to crank the engine a little (first remove the fuel pump fuse and relieve the pressure in the rail). When cranking the starter, the lamp should flash. The same procedure must be done with pin 1b - the lamp should also blink.
When I turned on the ignition, the lamp started to light up, just constantly on (pin 1b and central). This means that the control wire has a short to ground somewhere or that the transistor (VT1) in the ECU is broken. To find out, we need to find the ECU, disconnect the wiring harness from it, find the wires we need (1b) and test them for integrity.
Having found the contact diagram, I found out that contact 1b goes to pin 5 of the ECU, 1a goes to pin 2, 3 goes to ground of the ignition circuit. I rang them for integrity - they were all intact. I called ground and everything is fine too. Therefore, you need to check the transistor in the controller itself.
My car has a January 7.2 controller. Inside there are 2 transistors that pass control signals to pins 1a and 1b of the ignition coil. So one of these transistors was broken, i.e. was constantly in the open position.
How to check the transistor for serviceability? It has 3 pins - 2 of which are soldered. It is necessary to ring each outer terminal with the central one. In both cases, the tester should not beep. The contacts must not be closed.
Now all that’s left to do is to unsolder the broken transistor (its marking is gb10nb37lz), solder a new one in its place and rejoice at the spark that appears.
No spark at the spark plugs
Lack of spark on the spark plugs is one of two basic faults most often found on cars (the second is no fuel supply to the engine).
Loss of spark or weak spark from the spark plugs indicates problems in the ignition system. Either in a high voltage circuit or a low voltage circuit. In this case, the car engine will not start at all (both cold and hot), or will start and stall (if there is a spark, but weak). Let's consider the main reasons for the loss of spark on carburetor engines of VAZ 2105, 2107, 2108, 2109, 21099 cars with contact and non-contact ignition systems. Then we remove the central high-voltage wire, insert a working spark plug into its tip and place it on the engine (so that there is contact with ground). While the assistant turns the engine with the starter, you need to visually verify the absence or presence of a spark at the spark plug. A spark has appeared - the spark plugs themselves, the high-voltage wires or the ignition distributor in the distributor are faulty. There was still no spark - problems with the switch, Hall sensor, ignition coil.
Lost spark, reasons for contactless ignition system
- The ignition coil has failed.
Checking the ignition coil. The ignition coil is usually checked for winding resistance and insulation resistance using a tester. For oil-filled coils (27.3705) and dry coils (3122.3707), the resistance is slightly different. Read more: “Checking the ignition coil.” In the absence of a special device for testing, we use the method of replacing our coil with another one that is known to be good.
checking the primary winding of the ignition coil
- The switch is faulty.
Checked with an oscilloscope. Since not everyone has it, we use the replacement method - instead of our switch we install a known good one. You can very roughly estimate the performance of the switch based on the voltmeter readings after turning on the ignition (see “Checking the switch”).
- Hall sensor is faulty.
It is checked with a voltmeter according to a special connection diagram (see “Checking the Hall sensor”). If there is no voltmeter, we use the replacement method.
Hall sensor, check
- Open circuit in low voltage circuit.
Using the diagram, we look through the wires included in the ignition system, and if necessary, “ring” to detect a “break.” See "Contactless Ignition System Diagram".
In the contact ignition system, the list of malfunctions leading to the disappearance of the spark is as follows:
- The mechanical breaker in the distributor is faulty.
Its contacts have oxidized, collapsed or burned. There is no gap between the breaker contacts.
breaker contacts
- The ignition coil is faulty.
- "Open" in the low voltage circuit.
Notes and additions
— To quickly find the reason for the disappearance of the spark on the spark plugs, you need to know the principle of operation of both contact and non-contact ignition systems (for more details, see “The principle of operation of the ignition system”). The purpose of the ignition system is to generate high voltage current at the right moment and supply it to the spark plugs. This is accomplished by interrupting the low voltage current in the primary winding circuit of the ignition coil. In a contactless system, the switch interrupts the current based on a signal from the Hall sensor; in a contact system, a mechanical breaker with contacts is driven by a tetrahedron on the distributor shaft.
No spark VAZ injector video
CHECKING THE IGNITION SYSTEM FOR SPARK
If the engine does not start, first of all you need to check for the presence of high voltage at the output of the ignition coil and at the spark plugs. If the engine is equipped with an ignition coil made as a separate unit, it is necessary to disconnect the coil lead from the central terminal on the ignition distributor cap, connect a spark probe and crank the engine. Read the note “Only a spark probe will give you an accurate answer” later in this chapter. If the ignition system and ignition coil are working properly, then a blue spark will be visible in the spark probe (Fig. 5.15).
Rice. 5.15 . An example of connecting a spark probe in an engine with a non-contact (i.e. without a mechanical ignition distributor) ignition system. The spark plug is grounded to the cylinder head valve cover bolt. The photograph shows the recommended type of spark probe, in which the central electrode is recessed into the surrounding insulator
Using a tachometer
When determining the reason why the engine does not start or runs intermittently, monitor the tachometer readings. If the tachometer does not show the number of engine revolutions when cranking the engine (when the engine does not start) or its readings drop to zero (when the engine is interrupted), then the problem is due to a malfunction of the primary ignition circuit. The tachometer operates using a pulse signal from the primary winding of the ignition coil. Malfunction of the tachometer when cranking the engine may be associated with the following elements of the primary ignition circuit:
• Crankshaft angle sensor.
• Ignition control module.
• Primary winding of the ignition coil.
If the vehicle is not equipped with a tachometer, connect a portable tachometer to the negative terminal of the ignition coil primary winding. Remember:
There is no tachometer reading - this means that the problem is related to a malfunction of the primary ignition circuit.
The tachometer reading is normal - this means that the problem is related to a malfunction of the secondary ignition circuit or a malfunction of the fuel system.
If it is impossible to reach the ignition coil in the ignition system being diagnosed, disconnect the high-voltage wire from one of the spark plugs, connect a spark probe to it and check for the presence of a spark while cranking the engine.
Only a spark probe will give an accurate answer
The spark probe resembles a spark plug in appearance, but without a side electrode, with a discharge gap between the central electrode and the grounded body. The probe is equipped, as a rule, with an alligator clip attached to the body, with which it can be easily secured in a convenient place in the engine, ensuring contact to the ground of the car. If the ignition system is working properly, it should be able to "pierce" this wide gap under atmospheric pressure. In the absence of a spark tester, a technician who could verify that a normal, grounded spark plug was producing a spark would be able to determine that there was nothing wrong with the ignition system. To break down the discharge gap of a spark plug removed from the engine and under atmospheric pressure, a voltage of about 3000 V is sufficient, no more. In order to penetrate the 3/4-inch discharge gap of a spark probe, a voltage of at least 25,000 V is required. Therefore, a spark in a removed spark plug does not mean that the ignition system is working normally - only a spark probe will give an accurate answer.
Remember, an intermittent spark when cranking the engine should be considered a malfunction of the ignition system, making it impossible to start the engine.
NOTE
An intermittent spark when cranking the engine should be considered a malfunction of the ignition system, due to which the engine cannot be started.
ATTENTION
In most non-contact ignition systems (which do not have a mechanical ignition distributor), the high voltage reaches 40,000 V or higher, and the high-voltage pulse is powerful enough to cause an electric shock to a person. Do not interrupt the secondary ignition circuit in the proximity ignition system to avoid damage and electric shock.
High voltage wire faulty: replace ignition coil
When performing engine tests (for example, testing the compression ratio), be sure to connect the ignition coil winding to ground. Do not allow a high-voltage discharge of the ignition coil to bypass the low-resistance channel to ground, which must be specially created for this. High-power non-contact ignition systems are capable of generating voltages with an amplitude of 40,000 V and higher. In the absence of a low-resistance channel for a high-voltage discharge to ground, an internal arc breakdown of the ignition coil can (and usually does) occur, resulting in a low-resistance channel inside the coil to the primary winding or its steel core (Fig. 5.17). This low-resistance channel is called a breakdown trace and can cause unstable engine operation under load, even if all other elements of the ignition system are functioning normally. Often such traces of breakdown cannot be detected when checking the ignition coil by any means, including flaw detection methods. Since the breakdown trace is a channel of reduced, compared to normal, resistance to the ground, in order for such a defect to appear, it is necessary for the ignition system to operate under load, but even then the defect (unstable engine operation) can either appear or disappear.
Therefore, when turning off the ignition system, to avoid damage to the ignition coil, follow the rules below:
1. Turn off the power to the ignition system to completely stop its operation.
2. In an ignition system with a mechanical ignition distributor, disconnect the ignition coil lead from the central terminal of the distributor cover and connect it with an insulated jumper to vehicle ground. (This way you will provide a channel for discharging the energy accumulated in the secondary winding and eliminate the danger of high-voltage breakdown of the ignition coil).
Hi guys! Let's go straight to the problem, there is no spark on cylinders 1 and 4, I say straight away the spark plugs have nothing to do with it, at first I thought that the ignition module had stopped working, burned out, etc. I don’t know, but I thought there was something wrong with it, I bought it today, moved it, nothing, just once it started, doubled, I checked the spark as it was, cylinders 1 and 4 there is no spark, the explosive wires were transferred from the working machine, it didn’t give any results, I’m racking my brains, what else could it be? Anyone who has encountered this or knows where to go, please help!
A few questions at once: 1) if these are brains, that is, there are a couple of brains from whom you can take a test, but they are from four and ten 8kl, will these brains start up if there is a problem in it? 2) I read on some forums that the BC does not show this kind of error, or rather it does, but it says that there is a misfire, which is understandable, there is no spark, if you take it to computer diagnostics, will it help somehow or is it not worth wasting money and time?
Actually, that’s all and I hope for your help, smooth roads everyone))
Advice from experienced motorists on where the spark goes
Advice from experienced motorists when there is no spark...
Hello dear readers of the blog RtiIvaz.ru. Today I want to talk to you about the spark and where it goes. Experience in operating cars, as well as advice from experienced motorists, shows that this is a fairly common malfunction that causes a lot of trouble for car owners. Today we will look at advice from experienced people that will help many motorists get out of such unpredictable breakdowns on the road on their own. For car enthusiasts who are not well acquainted with the operation of automotive electrical equipment, we will try to give some simple, useful advice from experienced people, considering what to do in various situations. So let's get started. If you lose the spark, immediately determine whether it happened for the first time or whether you have had something similar before.
Auto experience, as well as advice from experienced motorists, indicates that there may be several options for the disappearance of a spark. If you have often had problems with electrical equipment before, namely with the formation of a spark or suspicion that it is weak, i.e. there is no full output of the ignition system, loss of engine power, then these are obvious symptoms of problems with the car’s ignition system.
The engine begins to start poorly, twitches at idle and there is no longer the former throttle response, popping noises in the muffler, this may be caused by burning of the breaker contacts. This, in turn, also has its reasons and, following the advice of experienced people, the culprit may be the distributor capacitor. The capacitor is installed parallel to the breaker specifically to eliminate sparking on them; it takes on excess voltage, which leads to burning of the contact group.
Its failure is now quite rare, but it still happens from time to time. The way out of this situation is not difficult - the capacitor must be replaced properly with a new one. Some facts from history. Did you know that until 1961, the electrical equipment of cars was made according to the plus (+) circuit to ground without a spare capacitor; not a single professional driver went on the road.
Having revised the electrical equipment diagram, linking it with the current path in the circuit by the then Soviet Avtodor, it was decided to take the mass of the car (-) minus and since that time, experienced motorists have forgotten what a capacitor is. And now, if they remember, it’s only when they refuse.
Burning contacts can be caused by poor engagement of the low voltage circuit, which increases the current and also leads to burning of the wiring. In this case, the contacts must be cleaned, checked, and all low-voltage connections must be tightened, setting the required gap recommended by the manufacturer between the breaker contacts.
We looked at cases when the spark disappears from time to time; its failure is so unexpected for the car enthusiast like thunder from the sky. Now let's look at the most typical case. Complete instantaneous failure of the ignition system on the road. The spark disappears immediately and the engine stalls. There are also several reasons here, but of a different nature.
It could be:
- breakdown of the "woman's" ignition coil
- burnout of the central core of the high-voltage wire coming from the ignition coil
- breakdown of the slider or burnout of its additional resistance
- severe wear of contacts or their almost complete burnout
- wear or damage to the plastic protrusion of the moving part of the contact group, which opens the contacts, as well as the hammer spring
- short to ground low voltage circuit
- break of the negative wire of the contact pair
- breakdown of the distributor cap “crack”
- malfunction of the ignition switch contact group
From auto experience, as well as advice from experienced motorists, these are the most common faults that can cause the spark to disappear in the ignition system. Let's look at them in order:
*if the “woman” ignition coil breaks down, it must be replaced with a new one, according to the rating indicated on the coil body
* if the central armor wire burns out, replace it with a new one
* if the slider breaks down, it is replaced, and if only the additional resistance has burned out, then you can get out of the situation by wrapping it in cigarette foil (after having pulled it out of the slider). The breakdown of the slider is determined as follows: with the distributor cover removed, remove the high-voltage wire from the ignition coil from the cover and hold it at a distance of 1.5-2 mm above the slider, then with the ignition on, open the breaker contacts - a spark that has slipped between the slider and the central wire will show you the breakdown slider
* worn contacts - replace with new ones
* breakage of the contact hammer cover (moving part) is the most difficult fault to detect, since when checking for a spark when the contacts open, there is a spark.
When the distributor shaft rotates, its protrusions cannot open the contacts, since the protrusion is broken off or broken. Although visually this is not noticeable. In this case, when rotating the distributor shaft, you need to make sure that the contacts diverge, i.e. a gap appears. If the hammer pad is broken, the contacts must be replaced, as is the case if the hammer spring breaks.
* short to ground is cleared when detected
* broken negative wiring of the contact group, “snot” must be restored or replaced
* the broken distributor cap is replaced with a new one. On the road, the current crack that appears can be rubbed with a clove of garlic to get home. Garlic will temporarily restore the functionality of the distributor cap.
* a faulty contact group must be replaced, and you can get to your destination by connecting the wires responsible for the ignition to each other and insulating them
We hope that experienced experienced motorists will help YOU get out of difficult situations on the road.
You may also be interested in reading:
What is contactless ignition?
Adjusting the valve mechanism of fret 2107
Advice from seasoned experienced motorists
Advice from experienced motorists when the gas tank leaks
Radiator pipes and their application
Wear of the silent block of the rear beam of a VAZ
Can the engine get hot?
Kalina won't start, the starter won't turn
Possible malfunction
Burnt starter commutator, stuck brushes or severe wear
Open or short circuit in the starter armature winding
| Diagnostics | Remedies | |
| Battery is low | The voltage at the battery terminals with consumers turned off is less than 12V. When trying to start the car, a crashing sound is heard from under the hood. | Charge the battery or replace it with a new one |
| Oxidation of battery terminals or wire terminals, their fit is not tight | When you try to start the engine, the voltage in the on-board network drops much more than at the battery terminals. In this case, a crash may be heard under the hood. | Clean the contacts, lubricate them with petroleum jelly and tighten the terminals |
| The engine or attachments are jammed | Check the rotation of the crankshaft, coolant pump and alternator pulley. | Repair engine, generator, pump |
| The starter is faulty, the starter drive gear or flywheel ring teeth are damaged | Inspect the starter after removal. | Repair or replace starter |
| The starter switching circuit or starter relay is faulty, the wires are damaged, or the ignition switch contacts do not close | When the key is turned to position “II”, the starter traction relay does not operate (a click is not heard under the hood). Check the +12V supply to the control contact of the traction relay. | Replace starter relay, wires, ignition switch |
| The starter traction relay is faulty, there is a short circuit or break in the retractor winding, the relay armature is stuck | When the key is turned to position “II”, the traction relay does not operate (there is no click under the hood), but + 12V is supplied to the control contact of the traction relay. Remove the relay and check its operation. | Replace the traction relay |
| Contacts or wires of the traction relay are oxidized, poor ground contact | When the starter is turned on, a clicking sound is heard under the hood, but the starter armature does not rotate. Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance of the Battery-Starter circuit, as well as the ground wire. If the circuit is in good condition, remove the starter and check the operation of the traction relay by applying +12V to it from the battery | Tighten the terminals, clean the contacts, replace the traction relay |
| Open or short circuit in the holding winding of the traction relay | When you try to start the engine, you hear a crashing sound under the hood. The battery voltage is within normal limits. We check the traction relay with an ohmmeter or by its excessive heating. | Replace the traction relay |
| The starter armature rotates slowly or does not rotate at all. Check the traction relay by applying voltage to the starter contact bolt directly from the battery | Replace starter or armature | |
| Freewheel slipping | When the starter is turned on, the armature rotates, the flywheel is stationary | Replace clutch or starter |
Communities › VAZ: repair and modification › forum › Kalina won’t start
Hello everyone, this morning the car refused to start.
I was late for work, so I didn’t bother to figure it out for a long time and went on my own. The symptoms are as follows: the starter does not turn or click, the fuel pump pumps, the voltage on the battery is 10.4 V, the lamps are on, the radio is playing, the heater seems to work uncertainly (it feels like it’s the first to turn weaker), the check does not light up. Connect the retractor terminal and the one coming to the starter together; if it tightens, then either the ignition switch or the starter relay.
OK, thank you. I couldn’t do it right away - the tool is in the trunk, but it only opens with a button.
battery... (and no matter how you twist it, the ECU will not give the command to start if there is less than 10V in the on-board network - it simply has a pass-through transistor responsible for powering the chip will not open...) p.s. Also: does the light on the panel light up and is there a signal coming from the APS? if not, then look for the reason in the battery and starter... (possibly a lock...)
As usual there are 3 signals
usually Sinhala 2...
battery... (and no matter how you twist it, the ECU will not give the command to start if there is less than 10V in the on-board network - it simply has a pass-through transistor responsible for powering the chip will not open...) p.s. Also: does the light on the panel light up and is there a signal coming from the APS? if not, then look for the reason in the battery and starter... (possibly a lock...)
Well, the voltage is not less than 10, but 10.4
when starting the starter you will have less... from 6 to 9 V
But for this to happen, the retractor must work.
I’ll just type this out here, maybe it will help...
Diagnostics of the APS-6 immobilizer using a buzzer sound signal and an immobilizer indicator. When the system is in good condition, the immobilizer indicator does not light up and there are no buzzer signals. If, when the ignition is turned on, the immobilizer indicator lights up with a constant light or starts flashing, and after about 10 seconds the immobilizer buzzer sounds and the same signal is repeated after another 10 seconds, this means that the immobilizer is either untrained or there is a malfunction in the immobilizer system. The number of buzzer and indicator signals indicates the type of malfunction.
New Lada: Lada Kalina filling volumes
1. If 1 buzzer sounds and the immobilizer indicator flashes, the diagnosis is “The key cannot be read.” Possible causes: 1.1 Malfunctions of the transponder circuit – this group of malfunctions is characterized by the absence of a “signal about the key being left in the ignition lock” when the ignition is turned off and the driver’s door is open. 1.1.
1 Malfunction in the communication coil circuit of the ignition switch. Measure the resistance of the communication coil between the contacts of the 2-terminal block of black color from the ignition switch, which should be within 6 - 8 Ohms. If the coil resistance is normal, check the continuity of the circuit between the 2-terminal block block to the communication coil and contacts 4 and 5 of connector X2 of the electrical package unit. 1.1.
2 There is no transponder in the key. In the training key, check the presence of the transponder and its designation, it should be PCF7936AS. If there is no transponder, take a “clean” training key and a “clean” engine control system controller (ECSC) and retrain the immobilizer system. 1.1.3 The transponder in the key is faulty, it is detected during pre-sale preparation at the PSSS.
In the training key, you need to take a “clean” training key and retrain the immobilizer system. In a working key with a remote control (RC), you need to replace the remote control with a “clean” one and retrain the immobilizer system. 1.1.4 Malfunction of the input transponder circuit of the APS-6 unit — it is necessary to replace the APS-6 unit and retrain the immobilizer system.1.
2. If 2 buzzer beeps sound and the indicator flashes, the diagnosis is “No connection with KSUD.” Possible reasons: 2.1 Break in the communication line along the W line - restore the circuit between contact “13” of connector X2 of the electrical package unit and contact “71” of KSUD M7.9.7 ( January 7.2).2.2 Malfunction of circuits in the APS-6 or KSUD block on the W line - to identify a faulty product, it is necessary to carry out a trial replacement of them one by one.
If after replacing the product the fault code does not repeat, it is necessary to replace it. 2.3 There is no supply voltage on the APS-6 or KSUD unit. Check for the presence of voltage at the contacts of KSUD M7.9.7 (January 7.2): a) contact “12” - power from terminal “ 30" of the ignition switch; b) contact "13" - power from terminal "15" of the ignition switch; c) contacts "44", "63" - power from terminal "30" of the ignition switch after the main relay.
New Lada: Lada Kalina Hatchback (Lada Kalina) - price, photos, reviews. Technical characteristics of Kalina hatchback
3. If 3 buzzer beeps sound and the immobilizer indicator lights up constantly or flashes - the diagnosis “The code of the read key is not in the APS memory.” Possible reasons: 3.1 If, after turning on the ignition, the immobilizer indicator lights up constantly for 20 seconds and 3 buzzer beeps sound, then The immobilization system is not trained, the system should be trained.3.
2 If, after turning on the ignition with the training key, the immobilizer indicator flashes and 3 buzzer signals sound, then the APS-6 block is “foreign” or the key is “foreign”. , to restore functionality, it is necessary to retrain the system with a “own” training key for the ICS. 3.2.
4. If 4 buzzer beeps sound and the immobilizer indicator flashes, the diagnosis “ACS does not confirm permission to start the engine.” This means that the ICS was previously trained with a different system; it is necessary to replace the ICS with a “clean” one and retrain the immobilizer system.
5. If, after turning on the ignition, the immobilizer indicator lights up for 20 seconds and the buzzer does not sound, then the immobilizer is trained with its keys, but the ACS is not trained. The system should be retrained.
Kalina won't start, the starter turns
Possible malfunction
| Diagnostics | Remedies | |
| Fuel tank empty | The needle on the fuel gauge is at zero. | Pour gasoline |
| Battery is low | The voltage at the battery terminals with consumers turned off is less than 12V. When trying to start the car, a crashing sound is heard from under the hood. | Charge the battery or replace it with a new one |
| Oxidation of battery terminals or wire terminals, their fit is not tight | When you try to start the engine, the voltage in the on-board network drops much more than at the battery terminals. In this case, a crash may be heard under the hood. | Clean the contacts, lubricate them with petroleum jelly and tighten the terminals |
| Unreliable connection of electrical circuits of engine control and power supply systems | Check the connections of the connectors and the reliability of the contacts in the blocks. | Fix faulty wire connections |
| Increased resistance to rotation of the crankshaft (scores on the shafts, bearing shells, cylinder-piston parts, deformation of the shafts, frozen engine oil, jammed generator, jammed coolant pump) | The crankshaft turns slowly. If the engine is started in severe frost, and the engine was working properly the day before, then most likely the engine oil has frozen. If you hear extraneous noise when starting the engine, check the free rotation of the pump and generator pulleys. | Use the recommended engine oil. Repair the engine. Replace the pump and generator. |
| Malfunction in the ignition system | Check for spark. | Check the circuits and devices of the ignition system. Replace faulty system elements. |
| The high voltage wires are connected in the wrong order or the wire is disconnected | Inspect. | Connect the wires in the correct order |
| The timing belt is broken or the belt teeth are cut off | Open the front timing cover and check. | Replace timing belt |
| Disturbed valve timing | Check the marks on the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys. | Set the correct shaft position |
| Malfunction of the computer (brains), its circuits, crankshaft position sensor or coolant temperature | Check the supply of +12V to the ECU, the sensor circuit, and the absence of damage to the sensors themselves. | Replace ECU, sensors. |
| The idle speed controller or its circuit is faulty | Check the idle air control. When starting the engine, lightly press the gas pedal. If the engine starts and stalls when you release the gas pedal, the sensor is faulty. | Replace sensor |
| The fuse is blown or the main relay of the control system is faulty | Check fuse and relay. | Eliminate the cause of the blown fuse. Replace fuse and relay |
| Fuse blown, fuel pump relay. Circuit, relay or pump is faulty. | When the ignition is turned on, there is no sound of the pump running. Check the fuse. Apply voltage to the pump from the battery. | Clean contacts, replace faulty circuits, replace fuse, pump and relay. |
| The fuel filter is dirty, the water in the fuel line is frozen, the fuel line is damaged | Check the pressure in the fuel rail and the condition of the fuel lines. | Replace the filter, blow out or replace the fuel lines. |
| Insufficient pressure in the fuel rail | Check the pressure in the fuel rail, the pump strainer and the condition of the fuel lines. | Clean the filter. Replace pump, fuel pressure regulator |
| Faulty injectors or their power supply circuits | Check the injector windings with an ohmmeter. Check the chains for breaks. | Replace injectors, replace chains |
| Air leak into the intake tract | Inspect the joints and fittings of the hoses and clamps. During start-up, turn off the vacuum brake booster and plug the receiver fitting. | Eliminate air leaks, replace vacuum booster |
Lada Kalina does not start when cold
- If the crankshaft rotates slowly, the battery may be discharged or the engine oil may be frozen.
- The vehicle's fuel system is faulty. The water in the ramp may have frozen.
- The coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH) of the engine management system is faulty.
- Fuel injectors are leaking.
- Low compression in cylinders.
- The engine control system is faulty. Run diagnostics.
Let us remind you that regular vehicle maintenance will help eliminate engine starting problems.
Checking the ignition system
CHECKING THE IGNITION SYSTEM FOR SPARK
If the engine does not start, first of all you need to check for the presence of high voltage at the output of the ignition coil and at the spark plugs. If the engine is equipped with an ignition coil made as a separate unit, it is necessary to disconnect the coil lead from the central terminal on the ignition distributor cap, connect a spark probe and crank the engine. Read the note “Only a spark probe will give you an accurate answer” later in this chapter. If the ignition system and ignition coil are working properly, then a blue spark will be visible in the spark probe (Fig. 5.15).
Rice. 5.15 . An example of connecting a spark probe in an engine with a non-contact (i.e. without a mechanical ignition distributor) ignition system. The spark plug is grounded to the cylinder head valve cover bolt. The photograph shows the recommended type of spark probe, in which the central electrode is recessed into the surrounding insulator
Using a tachometer
When determining the reason why the engine does not start or runs intermittently, monitor the tachometer readings. If the tachometer does not show the number of engine revolutions when cranking the engine (when the engine does not start) or its readings drop to zero (when the engine is interrupted), then the problem is due to a malfunction of the primary ignition circuit. The tachometer operates using a pulse signal from the primary winding of the ignition coil. Malfunction of the tachometer when cranking the engine may be associated with the following elements of the primary ignition circuit:
• Crankshaft angle sensor.
• Ignition control module.
• Primary winding of the ignition coil.
If the vehicle is not equipped with a tachometer, connect a portable tachometer to the negative terminal of the ignition coil primary winding. Remember:
There is no tachometer reading - this means that the problem is related to a malfunction of the primary ignition circuit.
The tachometer reading is normal - this means that the problem is related to a malfunction of the secondary ignition circuit or a malfunction of the fuel system.
If it is impossible to reach the ignition coil in the ignition system being diagnosed, disconnect the high-voltage wire from one of the spark plugs, connect a spark probe to it and check for the presence of a spark while cranking the engine.
Only a spark probe will give an accurate answer
The spark probe resembles a spark plug in appearance, but without a side electrode, with a discharge gap between the central electrode and the grounded body. The probe is equipped, as a rule, with an alligator clip attached to the body, with which it can be easily secured in a convenient place in the engine, ensuring contact to the ground of the car. If the ignition system is working properly, it should be able to "pierce" this wide gap under atmospheric pressure. In the absence of a spark tester, a technician who could verify that a normal, grounded spark plug was producing a spark would be able to determine that there was nothing wrong with the ignition system. To break down the discharge gap of a spark plug removed from the engine and under atmospheric pressure, a voltage of about 3000 V is sufficient, no more. In order to penetrate the 3/4-inch discharge gap of a spark probe, a voltage of at least 25,000 V is required. Therefore, a spark in a removed spark plug does not mean that the ignition system is working normally - only a spark probe will give an accurate answer.
Remember, an intermittent spark when cranking the engine should be considered a malfunction of the ignition system, making it impossible to start the engine.
NOTE
An intermittent spark when cranking the engine should be considered a malfunction of the ignition system, due to which the engine cannot be started.
ATTENTION
In most non-contact ignition systems (which do not have a mechanical ignition distributor), the high voltage reaches 40,000 V or higher, and the high-voltage pulse is powerful enough to cause an electric shock to a person. Do not interrupt the secondary ignition circuit in the proximity ignition system to avoid damage and electric shock.
High voltage wire faulty: replace ignition coil
When performing engine tests (for example, testing the compression ratio), be sure to connect the ignition coil winding to ground. Do not allow a high-voltage discharge of the ignition coil to bypass the low-resistance channel to ground, which must be specially created for this. High-power non-contact ignition systems are capable of generating voltages with an amplitude of 40,000 V and higher. In the absence of a low-resistance channel for a high-voltage discharge to ground, an internal arc breakdown of the ignition coil can (and usually does) occur, resulting in a low-resistance channel inside the coil to the primary winding or its steel core (Fig. 5.17). This low-resistance channel is called a breakdown trace and can cause unstable engine operation under load, even if all other elements of the ignition system are functioning normally. Often such traces of breakdown cannot be detected when checking the ignition coil by any means, including flaw detection methods. Since the breakdown trace is a channel of reduced, compared to normal, resistance to the ground, in order for such a defect to appear, it is necessary for the ignition system to operate under load, but even then the defect (unstable engine operation) can either appear or disappear.
Therefore, when turning off the ignition system, to avoid damage to the ignition coil, follow the rules below:
1. Turn off the power to the ignition system to completely stop its operation.
2. In an ignition system with a mechanical ignition distributor, disconnect the ignition coil lead from the central terminal of the distributor cover and connect it with an insulated jumper to vehicle ground. (This way you will provide a channel for discharging the energy accumulated in the secondary winding and eliminate the danger of high-voltage breakdown of the ignition coil).
No spark at the spark plugs
Lack of spark on the spark plugs is one of two basic faults most often found on cars (the second is no fuel supply to the engine).
Loss of spark or weak spark from the spark plugs indicates problems in the ignition system. Either in a high voltage circuit or a low voltage circuit. In this case, the car engine will not start at all (both cold and hot), or will start and stall (if there is a spark, but weak). Let's consider the main reasons for the loss of spark on carburetor engines of VAZ 2105, 2107, 2108, 2109, 21099 cars with contact and non-contact ignition systems. Then we remove the central high-voltage wire, insert a working spark plug into its tip and place it on the engine (so that there is contact with ground). While the assistant turns the engine with the starter, you need to visually verify the absence or presence of a spark at the spark plug. A spark has appeared - the spark plugs themselves, the high-voltage wires or the ignition distributor in the distributor are faulty. There was still no spark - problems with the switch, Hall sensor, ignition coil. Lost spark, reasons for contactless ignition system
- The ignition coil has failed.
Checking the ignition coil. The ignition coil is usually checked for winding resistance and insulation resistance using a tester. For oil-filled coils (27.3705) and dry coils (3122.3707), the resistance is slightly different. Read more: “Checking the ignition coil.” In the absence of a special device for testing, we use the method of replacing our coil with another one that is known to be good.
checking the primary winding of the ignition coil
- The switch is faulty.
Checked with an oscilloscope. Since not everyone has it, we use the replacement method - instead of our switch we install a known good one. You can very roughly estimate the performance of the switch based on the voltmeter readings after turning on the ignition (see “Checking the switch”).
- Hall sensor is faulty.
It is checked with a voltmeter according to a special connection diagram (see “Checking the Hall sensor”). If there is no voltmeter, we use the replacement method.
Hall sensor, check
- Open circuit in low voltage circuit.
Using the diagram, we look through the wires included in the ignition system, and if necessary, “ring” to detect a “break.” See "Contactless Ignition System Diagram".
In the contact ignition system, the list of malfunctions leading to the disappearance of the spark is as follows:
- The mechanical breaker in the distributor is faulty.
Its contacts have oxidized, collapsed or burned. There is no gap between the breaker contacts.
breaker contacts
- The ignition coil is faulty.
- "Open" in the low voltage circuit.
Notes and additions
— To quickly find the reason for the disappearance of the spark on the spark plugs, you need to know the principle of operation of both contact and non-contact ignition systems (for more details, see “The principle of operation of the ignition system”). The purpose of the ignition system is to generate high voltage current at the right moment and supply it to the spark plugs. This is accomplished by interrupting the low voltage current in the primary winding circuit of the ignition coil. In a contactless system, the switch interrupts the current based on a signal from the Hall sensor; in a contact system, a mechanical breaker with contacts is driven by a tetrahedron on the distributor shaft.
Immobilizer
If the car refuses to start, then this is one of the possible reasons. You can notice problems in the operation of this system yourself. If the corresponding icon blinks on the dashboard and a characteristic beeping sound is heard, then you should read the operating instructions. If the Lada Kalina does not start, the immobilizer is a common problem. The problem is not easy to fix. In the instructions for the car, the manufacturer indicates the decoding of sounds and blinking lights - the car owner needs to count the time between flashes, the number of buzzer signals, and then read what the manufacturer writes about this.
Problematic case: the speedometer does not work on the Lada Kalina
Very often you can hear the same phrase from Lada owners: the speedometer on Kalina does not work. The main reason for the failure of the speedometer installed on the Lada Kalina, judging by the reviews of car owners, is the incorrect operation of the speed sensor (DS). This malfunction is characterized by a variety of symptoms. Sometimes the speedometer needle on Kalina just calmly shows zero, sometimes it jumps like crazy.
In some cases it starts to freeze. This can happen both when the car is moving and at rest. For such a breakdown, the mileage is not at all important. Sometimes the EUR signal may come on. Most often, this means that the electric power steering in the Lada Kalina car has failed. It would seem that the steering wheel and speedometer readings are completely incompatible things. But the speed of a car has been measured electronically for a long time.
All readings are carried out by a speed sensor operating on the basis of the Hall effect. The controller receives electromagnetic pulses from this sensor. They are the basis for measuring the speed of a car. This sensor also saves fuel. If the car is coasting and the speed exceeds 20 km/h, the controller, reading the sensor readings, stops the fuel supply.
How and why the immobilizer fails
Let's dwell on this topic in a little more detail. The thing is that the ECU controller on this model is located under the heater radiator. In second-generation models, the controller was moved.
First of all, when exposed to liquid, the output switch burns out. The chip can be re-soldered, but after such repairs the problems will go away for literally two months, and then they will appear again. The heater radiator will need to be replaced. If this problem exists, then experts recommend installing a new controller between the engine compartment partition and the stove.
Now about the immobilizer - in Kalina cars the manufacturer installs APS-6 immobilizers. In very rare cases, these devices fail on their own. Often, the problem is hidden in the wiring or control panel. The key fob body is held together with one self-tapping screw - the screw can be overtightened or undertightened. A crack appears on the remote device chip between the transponder contacts. In this case, if the Kalina does not start, only a spare or training key, or replacing the remote control will help.
What to do if the speedometer on the Lada Kalina does not work
The problem of a non-working speedometer is very common among Lada Kalina car owners.
Most often, this problem is encountered as a result of incorrect operation of the speed sensor. In this case, the needle does not necessarily have to be on o; it can constantly jump from one indication to another. Sometimes it even happens that it simply freezes (it doesn’t matter whether the car is running or stationary). This article will tell you what to do if the speedometer on the Lada Kalina does not work. A speed sensor is a device that sends a pulse to the controller, which provides information about the movement of the vehicle on the display. Often the car itself shows its owner that it has faults. This can be expressed as follows:
- interruptions in engine operation;
- excessive fuel consumption for no particular reason;
- impossibility of developing the full power of the machine's power apparatus;
- disruption of the vehicle's driving dynamics and sudden stalls.
If the Lada Kalina is equipped with an on-board computer, then most likely, if the speedometer breaks down, error number 24 will be displayed.
Many car owners are sure that mileage is the cause of speed sensor failure, but this is not always the case. The fact is that if the electric power steering fails, all readings are transmitted precisely by the speed sensor, since the speed limits of the cars are set electronically.
Several types of speed sensors can be installed on a Lada Kalina car. Their seat is the same, but if the sensor fails, then it is no longer possible to determine the speed, which can affect the operation of the motor.
Starter
The immobilizer has been checked and does not give any alarms, but the engine still does not want to start. Another reason for this behavior is the starter. It’s easy to notice a problem with the starter – you won’t hear the characteristic sound of the engine starting. The mechanism simply does not spin, which means the engine will not be able to start. Everything is clear here - you need to remove and check the starter.
If the Kalina does not start, the starter does not turn, then the first reason may be the battery. It may simply be discharged. If the lights in the cabin and on the dashboard are not lit, the driver will be able to immediately notice this. However, it often happens that everything is in order, but the starter still does not work. For diagnostics, turn on the high beams and get out of the car. Dim headlights are due to the battery. It is discharged, but only to a critical level, when there is not enough power to turn the starter.
If the Kalina does not start, the starter does not turn, the best way out of this situation is to charge the battery. But if the headlights are bright in high beam mode and are not going to dim, then you will have to look for the reason elsewhere.
Starter or wiring problems
You can use a multimeter to test the wiring. The red wire is connected to the starter contact, the black wire to ground. In a normal situation, the device will show from 12.5 to 14.5 V. If the reading is less or even zero, then there is something wrong with the wiring.
The first step is to clean the contacts, check the integrity of the wires and fuses.
This is another popular problem when Kalina does not start. ECUs are the “brains” of the car; they themselves are quite reliable, and if you don’t touch them, then no problems will happen. However, most often the ECU is flooded.
This often happens when antifreeze leaks. This has already been discussed in the section on the immobilizer. When installing an alarm system or when pulling car wires, they forget to install the plugs - water gets into the ECU. Repairing an electronic unit is a futile task.
Gasoline pump
The vagaries of the fuel pump are often observed, especially in winter. The starter works, but the Kalina car refuses to start, the fuel pump cannot be heard, and an exclamation mark may flash on the dashboard.
First of all, check the pressure in the fuel system. To do this, open the hood and look for the cap on the ramp with the injectors. You can see the nipple there - if you press it, fuel should spray out. If it splashes, then the problem is not with the fuel pump.
Another reason is the relay. There is a cover in the transmission tunnel on the passenger side. It contains power coils. To eliminate the malfunction, just knock or warm them up.
If the fuel pump does not work, then you need to get to it and check the voltage. If the multimeter shows about 12 V, then the fuel pump is working. If not, then it is worth checking the fuses, as well as the relays.