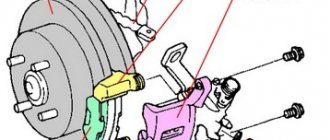
The brakes on your car are designed to help you travel safely on the road. Their serviceability is the key to avoiding emergency operation of the device, preserving the lives of drivers, passengers and pedestrians.
When buying a used car, you need to know the main signs of wear on the brake system in order to protect yourself and others from unforeseen situations.
What you need to visually pay attention to to determine brake disc wear
The main sign of wear on the brake system is indicated by pulsation of the brake pedal and vibration of the car, as well as its body.
- When performing emergency braking (sharply pressing the pedal while driving), creaking, grinding, and other unnecessary sounds are made. This indicates that faulty brake pads are rubbing against the brake rotor, causing wear. It is also possible that the parts do not match the disc due to poor quality brake pads.
- When the speed decreases, the brake pedal feels softer, sinks, or vice versa, it locks. This sign indicates extreme wear of the brake pads.
- A system malfunction is also a long braking distance.
- Vibration and squealing of the brakes indicate increased wear on the brake pads, oval brake drums, or scuffed discs.
- Modern cars are equipped with pad wear sensors. A lit indicator indicates wear on the pads that need to be replaced.
- Changes in the braking torque and steering wheel beating at the same time indicate deformation of the discs.
- When you press the brake pedal at high speed, the car skids to the side, and possibly spins on a dry road.
- The absence of reverse movement of the brake pedal indicates that the pads are burning to the disc, which means there are no brakes. Driving a car in this condition is strictly prohibited.
- If one or more wheels lock when braking, then this sign indicates the presence of scuffs on the brake disc and requires sharpening or replacement.
The serviceability of the rear brake can be checked in this way: put the car in reverse and press the brake pedal. If the car is reluctant to stop, this indicates a problem with the rear brake system.
The listed signs are indirect, visual. The main malfunctions of the disks are revealed by direct inspection and measurement of wear.
When checking the discs, you can detect deformation or misalignment of the part, the presence of deep chips, scratches, a protruding edge along the edge, reduced thickness, or cracking. All this indicates disk wear and requires replacement.
What is the minimum brake disc thickness considered acceptable?
The most vulnerable element of the braking system is the discs. If you do not carry out a technical inspection of the car on time and do not change parts in a timely manner, this can lead to fatal consequences in certain driving situations.
What is the minimum thickness of a brake disc?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to name the minimum thickness of brake discs, since it depends on the car model and brand. Each manufacturer sets its own wear values, which are determined depending on the characteristics of a particular vehicle. Thus, there are no universal evaluation criteria. The wear of the part directly depends on the driving style of the motorist, more precisely on his braking style, and the condition of the roads: if you drive on rocky areas all the time, the brake discs wear out three times faster. Also, premature wear is strongly influenced by the insufficiently large area between the pad and the disc.
To prevent accidents, car manufacturers indicate the nominal and minimum thickness of the part in the form of two marks on the discs themselves. It is worth noting that factories slightly increase the latest figures, indicating the thickness “with a margin”.
Minimum permissible thickness of front brake discs
When you hold the brake disc in your hands, you can see two numbers. The first means the initial thickness of the part, and the second means the minimum allowable thickness. If there are no marks on your disk, then it is “fake”, simply a fake.
Any mechanic at a service station will be able to determine at a glance the condition of your brake disc and tell whether it can be used or should be replaced. How can we determine wear and tear ourselves?
The first step is to measure the thickness of the product. It is measured with an ordinary caliper. Please take into account the fact that the thickness may differ in different areas of the part due to alignment errors.
There are several signs of brake disc wear:
- braking is accompanied by beating of the steering column and vibrations throughout the car. Most often, such “symptoms” are observed during emergency braking. In this case, it is recommended to carry out a complete diagnosis of the vehicle, because such problems can arise not only as a result of brake failure;
- When braking, extraneous noises are heard, mainly “squeaking”. However, this may be a sign of wear on the brake pads, not the discs.
Do not hesitate to replace the part, because if you continue to use it, the manufacturer will refuse warranty service.
Residual thickness of brake discs - possible risks
Using worn brake discs can have many negative consequences. For example, when a driver brakes, a frictional force occurs between the pad and the disc. Once heated to the peak temperature, the part may become deformed. This will result in damage to the entire braking system.
If the thickness of the disk is already less than permissible, it loses its strength, which in turn threatens to split the part. This phenomenon can only be observed during braking. Failure to stop in a certain situation has catastrophic consequences. It would be good if there were no casualties.
Timely technical inspection of the car is the key not only to its smooth operation, but also to your safety. Once a month, or even more often, check the main elements of the machine for serviceability.
365cars.ru
What to look for when removing a wheel to determine brake disc wear
- When removing a wheel, pay attention to the color of the rim. A blue surface indicates oxidation of the part.
- The presence of cracks, pits, and bumps on the disc is a serious malfunction. Continued use will lead to jamming of the brake system and costly repairs.
- With the wheel removed, spin the disc forcefully. Look at the evenness of its revolutions. If the disc makes oval movements, then we can safely recognize such a defect as warping of the disc.
- The ovality of the drum can be recognized by looking closely at the tire tread. Uneven wear of the pattern (more in one place, less in another, as if the pattern appears in spots) indicates precisely this defect.
Why is it so important to monitor the condition of your brake discs?
Discs and pads are subject to high loads while driving. Like any other car part, they tend to wear out. This in turn can affect the overall safety and reliability of the vehicle. Consequently, every car enthusiast must calculate the most important parameter so that nothing serious happens on the road.
What affects brake disc wear?
Finding out what the permissible wear of brake discs is, at first glance, is not so difficult, because almost every manufacturer prescribes this coefficient for a specific car model. The calculations take into account the weight of the model, engine power and other parameters. However, difficulties arise when predicting the maximum mileage after which discs will have to be changed. All this is influenced by very subjective factors:
- Vehicle operating conditions – constant driving through puddles in wet weather deforms the heated disc and causes uneven wear.
- Using low quality pads.
- Mechanical factors - the service life of the discs will be longer if they are made of ceramic, carbon or steel. Previously, cast iron was used in manufacturing, which was more often subject to wear.
- The driving style of the motorist - a sharp change in braking and acceleration significantly reduces the service life of the discs.
We determine the mileage based on the condition of the disks
Today, cars are sold by so-called resellers, who often deceive buyers. Cars come with low mileage. Many of them only look normal outwardly, but technically they are in a deplorable state. Resellers often change the pads, but simply forget about the discs. And this is in vain - the average mileage of a car can be determined by the condition of the disk.
On average, brake discs are changed every 180-200 thousand kilometers. But this is not true for all cars. Also, different drivers drive differently. Some people manage to drive 150 thousand kilometers until they are completely worn out, and some even 250. But if the mileage of a car is 70 thousand, and the total thickness of the disk is 20 millimeters, this car has probably traveled at least two hundred. It is worth refusing to purchase such a copy.
Here's how to determine mileage based on brake disc wear. But disks can be replaced more than once. And the mileage can be twisted. Therefore, the condition of the discs is just one of a number of signs that you need to pay attention to when purchasing.
How to determine the permissible wear of brake discs?
Personal experiences often help car enthusiasts determine that something is wrong with their braking system. Diagnosis does not always require special tools or a trip to the service center.
Disk wear is indicated by:
- cracks and grooves of significant size on the disks themselves;
- jerks, the presence of grinding noises, vibrations during braking.
If you systematically monitor such manifestations, then it’s time to think about what is the acceptable wear of the brake discs on your iron horse.
Repairs cannot be delayed if, after appropriate diagnostics, external damage is discovered. You also need to be very careful if noises appear at the moment of braking, the car jerks and does not obey.
Certain measurements will help to finally confirm your suspicions. Bring your user manual with you - it should indicate the service life of the disks, as well as recommended parameters. We also take a caliper to check the thickness of the specified disk. We compare the obtained values with the initial ones. Remember the following:
- the size of the cracks should be less than 0.01 mm;
- the difference between a worn and new disk should not be more than 2-3 mm.
Permissible wear of front and rear brake discs
There are two concepts at once - permissible wear of the front brake discs and permissible wear of the rear ones. At the same time, each measurement has its own individual nuances.
In order to find out the permissible wear of the front brake discs, you need to acquire a caliper if you decide to carry out this operation yourself. Then you will need to pinch the discs with the front part. This indicator is measured according to the values indicated in the car manual or on the end. Each manufacturer prescribes this data individually for each brand. The thickness can also be found out at a service station, where they will use a micrometer. The internal distance is used to check the permissible wear of the rear brake discs. It is important to remember that in both cases, measurements are taken at several points, because erasing is often uneven.
With such wear, a characteristic beating often occurs. There is a special device that will detect the minimal fluctuations of this phenomenon.
What thickness is already dangerous?
Damaged brake discs can be used up to a certain range. As a rule, there is no minimum thickness for brake discs. You can identify problems that are already growing if you experience jolts and speed surges while driving. You need to remove the disk and take a measurement with a caliper to determine whether the thickness is the same over the entire surface and whether there are any flaws.
If worn or damaged brake discs are not replaced in time, this can damage the entire traffic safety system. First of all, cylinders, CV joints, supports, etc. may fail.
What actions to take
When defects are identified during visual and technical inspection, the discs need to be re-grooved. This procedure allows you to level the entire surface of the product into a single layer. If everything is done correctly, external defects will disappear, and driving comfort will return to normal. In some cases, parts will need to be replaced if the necessary measures are not taken in time.
To avoid any danger while driving, it is important to maintain the functionality of all mechanisms. The braking system deserves special attention, because it is directly responsible for the safety of passengers. When observing even small problems, it is important to conduct a comprehensive inspection to prevent further damage to parts.
If you experience unusual noises and uneven braking of the car, you need to urgently carry out a service inspection. It will allow you to identify problems before they cause harm.
Tips for using brake discs
Problems with the brake system may occur prematurely. And often the driver himself is to blame for this. First of all, analyze your driving style. Perhaps you are a fan of sharp braking, but this is precisely what has an adverse effect on the safety of these parts.
You can try to restore the presented item yourself if the damage is not that significant. A groove will help get rid of small cracks and signs of deformation. On the farm, special equipment replaces the file. Grooving is the removal of a uniform strip of metal from all sides of the disk.
However, it is still worth remembering about the health of your loved ones - large damages endanger both you and your family.
During the operation of the car, many car enthusiasts do not ask themselves what the minimum thickness of the brake disc should be for effective braking. But in vain, because this is an important value on which the safety of the car owner and his passengers depends. Therefore, the question of how to determine the wear of brake discs should be relevant for all drivers.
To clarify this issue, it is worth touching on the design of disks, what causes their wear, how to check it, what are the signs and what factors influence it.
The thickness of the car brake disc: what should it be and when is replacement required?
We all understand perfectly well that the car must move, for this we systematically carry out repairs and maintenance of all its systems: the engine, adding engine oil, chassis, checking the condition of the shock absorbers from time to time, etc.
But, in addition to the fact that the car is moving, we must be 100% sure that we can slow down this movement in a timely and effective manner. And for this, our main task is timely maintenance, diagnostics and repair of all components and parts of the brake system.
Brake discs are no exception; on the contrary, the service life of brake discs and brake pads is almost the main indicator of the performance of the entire braking system.
Brake disc diagnostics
In order to avoid getting into an unpleasant situation while driving, when a brake disc can simply burst and fly into pieces, it is during braking that you need to systematically diagnose the discs.
Take 5 minutes in the garage and, armed with a caliper, simply measure the thickness of the brake disc.
You can determine that it is time for a more serious diagnosis of the brake system using the following methods:
- measuring - this is precisely taking measurements of the thickness of all brake discs. Measurements must be taken at several points on the disk. This is due to uneven wear of the brake disc. So to speak, for the purity of the experiment.
If the average thickness of the brake disc is approaching the minimum, then it’s time to think about regrowing the brake discs and simultaneously replacing the brake pads.
- visual - this is a normal inspection of the condition of the disks. You can see or feel wear on the disc, beads, cracks and chips. It won’t take much time, but it will force you to think and take action, if necessary.
- dynamic - while driving, you will feel the vibration of the steering wheel or brake pedal, and hear a grinding sound. Naturally, it is better not to let the brake discs reach this state.
Based on the results of diagnosing the condition of the brake disc, you yourself make decisions about what to do with it. In principle, there are few options: boring if the minimum thickness of the brake disc allows, or replacing the brake discs with new ones.
Let us remind you that, like brake pads or shock absorbers, brake discs are paired parts, and brake discs are replaced simultaneously on one axle of the car.
What affects brake disc wear?
In order to anticipate questions from motorists about what the acceptable wear of brake discs should or could be, I will answer this way. Each manufacturer has its own digital parameters for the maximum permissible wear of brake discs and pads.
There are corresponding tables for brands and models of the same brand (this also happens). This is primarily due to engine power, the weight of the car and the ensuing consequences in the form of physical forces acting on the car during braking.
Manufacturing materials. First of all, the factory wear values of brake discs are affected by the material used to make the brake discs.
Traditional brake discs are made of cast iron, but modern technology has also made it possible to make discs from carbon fiber (carbon fiber) and ceramics. This is an objective factor. Next are subjective factors that influence the degree of wear of brake discs.
Mechanical factors: vehicle mileage, availability of high-quality brake pads. Poor quality brake pads lead to uneven wear of the brake disc and the appearance of “scoring” on it. In this case, repair of the brake system is required: grooving the brake disc before replacing the pads.
Vehicle operating conditions. To a greater extent, this is a factor that depends on the driver. For example, during winter operation it is quite possible to cause the brake disc to deform.
When driving, in any case, the disc heats up, and if you drive into a puddle of water, and the temperature outside is still low, then the sudden temperature change causes deformation of the brake disc.
And if this happens periodically, then you cannot avoid regrooving or replacing the brake disc.
Driving style. According to average statistical figures, a brake disc should last 100 - 150 thousand km. mileage But, some drivers already at 6-15 thousand km can safely go to a service station - complete wear of the disk as a result of the so-called. “Schumacher” style: acceleration, braking and the cycle repeats. Emergency braking is a direct path to rapid wear of the brake disc.
How to understand that the thickness of the brake disc has approached a critical level?
Brake discs, as parts that operate in a high range of mechanical stress, are made of fairly durable materials.
But despite this, brake discs are a vulnerable part of the braking system. Important, but vulnerable. Subject to mechanical stress, for example, from faulty brake pads.
In addition, the increase in wear of the brake disc is influenced by the small area in contact with the brake pad. This requires quite a lot of pressure on the contact area, and, naturally, as a result, fairly rapid wear of the brake discs.
To a reasonable question about how to determine the wear of brake discs, the brake disc itself can give you the answer. The service life of brake discs does not have an exact figure in kilometers or years of operation.
Therefore, the frequently asked question about how long brake discs last is incorrect. This figure is simply impossible to determine, since each driver has a purely individual driving style and, accordingly, braking.
But brake disc manufacturers have foreseen this scenario. The permissible thickness of the brake disc is indicated on the end of the brake disc, provided that the disc is made in compliance with the requirements of international standards.
The driver is interested in two numbers indicated on the disc: the initial thickness of the brake disc and the minimum thickness, upon reaching which the manufacturer declines responsibility for further operation of the disc.
Fix or replace?
As soon as the “diagnosis” is made, a completely reasonable question arises: should I fix the old disk or buy a new one?
It is necessary to remember the following feature: sharpening the brake disc is possible if the remainder is at least 4 mm (this applies to ventilated discs).
Many service managers recommend changing the wheels on your car if they are relatively inexpensive. But if the prices are too high for you, you can use the services of a car service and update your old brake discs.
But never forget that the more layers are worn off, the lower the service life will be. Sometimes the groove is done even three times.
It is not recommended to install “contract” discs, since it is not known exactly how and where they were installed, and there is a high probability that they will soon have to be changed or sharpened.
Methods for turning discs
The next question will be the choice of grooving method - on special equipment or on a lathe. By choosing the last method, you can save money; such a groove costs approximately 80 hryvnia per unit.
But there are many disadvantages here. Of course, the craftsmen will do everything in the best possible way, the surface of the disc will be smooth, but when installed on a vehicle, problems may arise again that are associated with beating during braking. This occurs due to the fact that the disk is sharpened not relative to the car hub, but relative to the machine reel.
When sharpening using special equipment, this kind of problem does not arise. In this case, the disc is not removed, it stands firmly on the hub, and the grooving machine is mounted in place of the brake caliper. So, the disc itself remains in its place, and the possibility of a poor-quality procedure is almost reduced to zero.
As for time, you will have to spend about half an hour on grooving. It is done in several passes until the cutter completely processes the entire working surface in one pass. How much metal is removed depends on the condition and wear of the disc.
It should be noted that for high-quality sharpening of discs, serviceable wheel bearings are required, without runouts and backlashes, otherwise this procedure will be carried out poorly.
The cost of a “technical” disk update depends on the class and make of the car and varies greatly. For example, for an SUV, diagnostics and tuning costs approximately 500 hryvnia, for minivans - a little cheaper, 400 hryvnia, and the owner of a sedan will have to pay 300 hryvnia rubles.
The price depends not only on the time spent setting up and installing the machine, but also on the area of the brake disc, or rather its working surface. The larger the car, the more difficult it is to adjust the equipment and sharpen the brake disc.
And now the groove is made. What's next? Do I need to change the brake pads now? Experts unanimously declare that this is simply a must, otherwise, when braking the car, the same problems may arise as before the disk update.
Signs that brake discs should be replaced
— Grinding noise when braking;
— noise and beating when driving a car;
— locking the brakes when you press the brake pedal;
— reducing the thickness of the brake disc plane below the permissible level;
— cracks on the disks;
— a protruding rim along the outer edge of the disk;
— deep scratches and chips on the disc;
- deformation, distortion of the disc, uneven, wavy surface;
— increase in braking distance;
- increasing pedal travel;
— decrease in brake fluid level.
Of course, in order to avoid the appearance of the above symptoms, it is necessary to use brake discs, as well as other elements of the braking system, which should be purchased only from trusted places.
Subscribe to our feeds on Facebook, Vkontakte and Instagram: all the most interesting automotive events in one place.
Was this article helpful?
auto.today
Design features
The bulk of the front and rear discs are made of cast iron. Its popularity was facilitated by its low cost and good friction properties. But the trouble is that during the braking process this material heats up. This can lead to warping, changing the shape of the working surface and ultimately uneven erasing. To minimize these phenomena, manufacturers began producing front and rear discs with internal ventilation. They also began to cut grooves on their surface and perforate this product. This made it possible to significantly reduce overheating and increase their operating time.
Effective adhesion between the pads and the disc begins only after they are ground in. At this time, you should not press the brake sharply, but stop smoothly. This usually happens with a mileage of no more than 1000 km. You can check the effectiveness of lapping on a special stand.
Factors affecting wear
Each manufacturer itself prescribes the permissible wear rate for the wheels of the car brand it produces. These parameters are calculated based on engine power, machine weight, and other things. But it is difficult to take into account the maximum mileage after which it will be necessary to change the brake discs. After all, this is influenced by factors that cannot be taken into account:
- Driving style. If there is extreme driving, in which acceleration is replaced by sharp braking, then the wear life can be significantly reduced.
- Conditions in which the vehicle is operated. If you constantly drive through puddles in slushy weather in winter, then moisture falling on a heated disc can cause its deformation and, as a rule, uneven wear.
Determination of erase thickness
To find out what the permissible maximum thickness of a disk is, you should pay attention to its end or look at the car’s manual. There are two values there - the initial and minimum thickness of these elements of the brake system. These numbers vary depending on the manufacturer of both the machine and the parts themselves.
If the disc wears down to a point where the maximum thickness does not allow effective braking, you should immediately change them. You can measure the thickness at a service station using a micrometer.
Or, by independently determining this with a caliper, in this case we measure the thickness of the front discs by clamping them with the front part of the tool.
They need to be changed when a check shows maximum wear or if the discs have different thicknesses. These values must be checked at different points of a given brake element. This is due to the fact that its abrasion occurs unevenly.
The drum-type rear disc is checked not by thickness, but by the internal distance (diameter) from one side to the other, also at several points.
Uneven wear, which causes runout, can be checked with a special device that detects fluctuations in hundredths of its values.
Identified errors: uneven wear or different thicknesses can be corrected by turning the brake discs. But a warped or cracked element definitely needs to be replaced.
When do you need to change brake pads?
In addition to the mileage of the car, manufacturers also indicate the minimum permissible thickness of the friction lining at which replacement is necessary. After all, it often happens that you have already driven 20-30 thousand km, and the pads are like new, or, on the contrary, they have driven a little, and the wear is already critical.
The weight of the car also matters. The less the car weighs, the slower the pads wear out and vice versa. But in most cases, the minimum thickness of brake pads on different brands is almost the same and is 2-3 mm.
Sometimes critical wear can be seen visually without even removing the wheel. In this case, you can stock up on a set for one axle in advance. If the corresponding icon on the dashboard lights up (this option is not available on all cars), it means that the electronic sensor that determines the minimum permissible thickness of the friction linings has been activated.