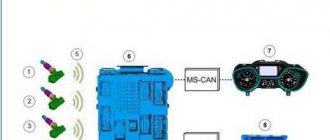
Fuel pressure sensor VAZ 2110: replacement, malfunctions
It is noteworthy that the fuel pressure regulator on the VAZ 2110 is very light in weight and is very cheap compared to many auto parts. But at the same time, this device plays an irreplaceable, extremely important role in the functioning of the entire fuel system.
What can we say, fuel consumption, as well as engine power, largely depend on this sensor. Therefore, VAZ 2110 owners should definitely know how this unit works, what are its main signs of failure, and also how to replace the sensor.
Allowable fuel pressure values for VAZ 2110
- Idle speed - 2.8–3.2 bar (2.8–3.2 atm)
- With the vacuum hose removed, the fuel pressure of the VAZ 2110 may rise by 0.2–0.7 bar (0.2–0.7 atm) . which indicates the serviceability of the pressure regulator.
I changed the mesh and filter, but it didn’t help. I connected the pressure gauge to the ignition fitting. I turn on the pump, it pumps 3 kW, then the car turns off, I don’t start the ignition current, and the pressure immediately drops by 1 atmosphere. And then when you start it at idle 2.5 you get 3.0 gas. at idle I remove the hose from the pressure regulator, the pressure rises from 2.5 to 3.0 at idle
On the forum for 7 years
Added: October 17, 2010 16:37
it drives, it starts normally, not very good
On the forum for 7 years
Auto: 21093i and 21112 barn
Added: October 17, 2010 18:24
I changed the mesh and filter, but it didn’t help. I connected the pressure gauge to the ignition fitting. I turn on the pump, it pumps 3 kW, then the car turns off, I don’t start the ignition current, and the pressure immediately drops by 1 atmosphere. And then when you start it at idle 2.5 you get 3.0 gas. at idle I remove the hose from the pressure regulator, the pressure rises from 2.5 to 3.0 at idle
your injectors are leaking, most likely more than one is why it’s hard to start, and the idle is unstable (over-rich) the pressure in the rail after turning off the fuel pump drops most likely because of them
But how do you find out which injector is running without having to change everything and is it possible to change a set?
It's possible, but not necessary. Change everything 4. If you decide to cut it out, remove the ramp, pour gasoline into it and blow into the supply (compressor pump - choose it yourself). Watch which nozzle gets wet. Change that one. (do you understand the meaning?) You can check the injectors individually. Find a thread about cleaning injectors. You will need a 5cc syringe and a can of carburetor cleaner + injector connector + microphone (toggle switch)) 12 volts from the battery. You can try rinsing it. Mine goes both ways.
Should I try changing the pressure regulator? I'll try it this weekend
Measure the pressure while running. You will find out whether the RTD needs to be changed. If the measurement shows that you need to change, don’t rush. Pinch the return line with pliers for 1 second (you will see more than 5 points on the pressure gauge). Do this a couple of times. Sometimes the RTD starts to work normally as a result of such manipulations. If the pressure pressure does not rise above 5 when the return line is pinched, the pump needs to be replaced (we’re not in a hurry). If it rises slowly, it makes sense to replace the mesh and filter. If replacement does not help, measure the voltage at the pump. If the voltage is normal, replace the pump. if the voltage is low, look for the reason - and it freezes again. _________________ There’s nothing worse than a VAZ.
The fuel pressure regulator is an element of the injection engine power system, which allows you to maintain the required fuel pressure in the fuel injectors at different operating modes of the internal combustion engine. In other words, the overall performance of the injectors and the stability of the engine depend on the serviceability of the fuel pressure regulator (FPR).
Considering that the pressure regulator is actually a diaphragm valve, failure of this element can greatly affect the operation of the engine. In this article we will look at the principle of operation of the regulator, highlight the main signs of its malfunction, and also talk about how to check the fuel pressure regulator.
Read in this article
How the regulator works
Fuel system diagram
The sensor is used to maintain pressure differences regardless of the current engine speed. Fuel injection will not be possible if the pressure in the manifold is equal to or greater than that in the injectors. Injectors are required to have higher pressures.
If everything works well, the following processes are observed:
- The vacuum in the suction cavity of the manifold is reduced during quiet operation;
- In response to this pressure, the fuel in the rail and its supply to the injectors increases.
Malfunctions
Worn rings
If the sensor begins to malfunction, this can be determined by characteristic signs indicating the presence of a breakdown:
- The engine starts to run unstably;
- The engine cannot idle;
- Power disappears, its lack is felt;
- While driving, the speed disappears for a while;
- Fuel consumption increases significantly;
- The level of emissions from the exhaust system increases;
- A car that has been parked for some time is difficult to start, and the starter rotates for a long time.
All this tells the car owner that something has happened to the fuel pressure regulator; it is necessary to urgently intervene in the situation and solve the problem as quickly as possible.
How to check the pressure in a system with no return?
The VAZ-2110 with a volume of 1.6 liters has constant pressure indicators in the ramp, which, as a rule, vary around 3.6-4 bars.
In addition to the most commonly used measurement methods described above, there are several more unusual solutions:
a) Here we return again to the hose with a pressure gauge, the diameter of which should be 7.5-8 millimeters. Measurements should be taken at the outlet of the fuel pump module. Five to seven atmospheres are normal test results.
b) Remember how the return line is closed on motors with a drain frame. It is recommended to turn off the engine directly at the gasoline pump. Next, you will need to remove the double hose and insert a plug (“The nipple” from an old fuel filter may also be suitable for this task). Now you need to pull a single tube onto the pump fitting. The measurements themselves must be made at the fuel rail.
How to clear a blockage if the fuel supply line is clogged.
One of the reasons for low pressure may be a malfunction of the sensor that regulates the fuel pressure before injection. Low pressure may also be a consequence of a clogged fuel line. By taking proper measurements, you can accurately determine the cause of the malfunction. First, you should check the pressure of the pump and line, then measure the pressure in the ramp. All of the above will help determine the exact cause.
How to clear clogged fuel injectors.
There are several signs to tell you that your fuel injectors are dirty. Let's start in order.
- Difficulty starting the engine.
- Unstable engine operation.
- Dips in the timing of sharp pressure on the gas pedal.
- Loss of power and deterioration in acceleration dynamics.
- Increased toxicity of treated gases.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- The occurrence of detonation.
- Popping sounds in the exhaust system.
- Misfires.
To solve this problem you need to clean the fuel injectors.
Clogged valve. How to identify and fix the problem.
When the valve is clogged, fuel is difficult to pass through, and because of this, it begins to leak everywhere. A significantly increased fuel consumption indicates that it is time to change the regulator, since it is the leading component. Fuel stops being supplied to the supply system if the valve becomes completely clogged.
Examination
If you find characteristic symptoms, first we recommend that you make sure that the problem with the car is related specifically to this sensor.
The inspection is carried out as follows:
- At the end of the ramp block there is a fitting designed to check the pressure indicator;
- It is covered with a plug that you need to unscrew;
- At the bottom of this plug there is a ring that compensates for the distance;
- If there are signs of damage or defects on the ring, be sure to replace it with a new one;
- Now take the cap from the tire and unscrew the spool with its back. It is located in the middle of the fitting;
- Now a flexible hose from the measuring device is connected to the fitting. You can use a regular pressure gauge that you use when inflating tires;
- Clamp the hose with a clamp and start checking;
- Turn on idle, since this is where the vacuum is the lowest and the fuel pressure is the highest;
- Start the engine. The device should show 2.9-3.3 units;
- Now check the readings, only without the vacuum hose;
- Having removed it, the pressure gauge should give about 0.2-0.8 units. If no changes occur, then the regulator is definitely out of order and needs to be replaced.
Replacement
Reset nipple
One way or another, every VAZ 2110 car owner should know about the sequence of replacing the fuel sensor.
- Relieve the load in the fuel system;
- Remove the return mount from the fuel pressure regulator, remove the pipe;
- Unscrew the two bolts responsible for securing the unit;
- Remove the fitting;
- Remove the gasoline hose from the fuel pressure regulator;
- Remove the failed fuel sensor;
- Place a new device in its place;
- During the reassembly process, it is recommended to change the old cuffs. After their dismantling, they usually lose their original working conditions. Therefore, reusing them will not allow them to function as before.
Obviously, the fuel pressure sensor plays a vital role in the functioning of the VAZ 2110, like any other car. Its condition should be treated with increased attention, promptly respond to changes occurring, and take appropriate measures if the regulator fails.
Where is the fuel pressure regulator located?
To find the installation location of the fuel pressure regulator, let’s figure out what it is and what it is needed for. This will help in further searches and diagnostics.
The first thing you need to know is that there are two main types of RDTs - mechanical (old type) and electrical (new type). In the first case, this is a vacuum valve, the task of which is to transfer excess fuel under excessive pressure back into the fuel tank through the corresponding hose. In the second, it is a fuel pressure sensor that transmits relevant information to the ECU.
Typically, the fuel pressure regulator is located directly on the fuel rail. Another option for its placement is the fuel return hose of the power system. Another option is to locate the regulator directly in the fuel tank on the pump module. In such systems there is no fuel return hose as unnecessary. Such an implementation has several advantages, including simplified design (no extra pipeline), excess fuel does not enter the engine compartment, fuel heats up less and does not evaporate as much.
How does the fuel pressure regulator work?
Structurally, the old-style valve (installed on gasoline cars) has its own body, inside which there is a valve, a membrane and a spring. The housing has three fuel outlets. Through two of them, gasoline passes through the pressure regulator, and the third outlet is directly connected to the intake manifold. At low (including idle) engine speeds, the fuel pressure in the system is low and it all goes into the engine. As the speed increases, the corresponding pressure increases in the manifold, that is, at the third terminal of the RTD, a vacuum (vacuum) is created, which, at a certain value, overcomes the resistance force of its spring. This creates the movement of the membrane and the opening of the valve. Accordingly, excess diesel fuel gets access to the second output of the regulator and goes back into the fuel tank through the return hose. Due to the described algorithm, the fuel pressure regulator is often called a check valve.
As for the fuel pressure sensor, it is a little more complicated. So, it consists of two parts - mechanical and electrical. The first part is a metal membrane that bends under the influence of force caused by pressure in the fuel system. The thickness of the membrane depends on the pressure for which the fuel system is designed. The electrical part of the sensor consists of four strain gauges connected according to a “Winston bridge” circuit. Voltage is applied to them, and the more the membrane bends, the greater the output voltage from them will be. And this signal is sent to the ECU. As a result, the electronic control unit sends the appropriate command to the pump so that it supplies only the amount of fuel required at the moment.
Signs of breakdown
If for some reason the fuel pressure regulator does not perform its functions, then this can be understood by the following signs:
- The engine's operation has become unstable, it may begin to stall when idling, although it would seem that the fuel level is sufficient and all systems are in working order;
- The crankshaft at idle speed has increased or, conversely, decreased speed;
- The engine, as they say, “loses throttle response”;
- While driving, dips and jerks occur in a running engine;
- Gasoline consumption increases compared to what it was before;
- The content of CO and CH in the exhaust increases;
- The engine starts with difficulty. Although this property does not always appear.
If the regulator has become completely unusable, then an increase in fuel pressure is observed. Instead of the norm for the VAZ 2110, which ranges from 2.5 to 3.3 kg/cm2, it reaches 4 – 5 and even more.
Consequently, the fuel pump supplies more gasoline by volume, which is not completely burned, and overconsumption is guaranteed. Of course, such a regulator needs replacement, and the sooner the better.
If the fuel pressure regulator does not provide the required pressure, or simply does not hold, then the lack of fuel pressure leads to the fact that normal supply does not occur, and the VAZ 2110 “chokes” when you need to increase the speed.
In addition, the starter cannot quickly spin the engine; it has to be turned on many times.
It is quite clear that we first learn about excessive consumption of gasoline by readings from the level sensor. However, sometimes the FLS also starts to lie, and then the true consumption cannot be known.
There may be a situation when you still have half a tank of gasoline, but the FLS says that the fuel is almost empty. That is, the flow sensor itself may confuse you, and before rushing to replace the regulator, make sure that the FLS is working properly, remember that the VAZ 2110 has problems with it very often.
If you notice that it is lying, the fuel sensor may need adjustment or even replacement.
Checking the RTD
So, your sensor is already in order, but there is excessive fuel consumption and other problems indicating that the regulator is acting up. First of all, check it.
This is done like this:
- You need to unscrew the plug of the fitting responsible for controlling the fuel pressure. Look, if the seal ring is torn or simply no longer elastic, it (or even the entire plug) needs to be replaced;
- Unscrew the spool from the fitting, this is done in exactly the same way as in any tire;
- Using a tire pressure gauge secured with a clamp to the fitting, measure the pressure while the engine is running. It should be within normal limits;
- When disconnecting the vacuum hose of the regulator, the pressure should increase slightly (by 0.2 - 0.5 kgf/cm2). If this does not happen, then there is only one solution for your VAZ 2110 - you need to replace the RTD. On average, the price of a standard RTD fluctuates around 300 rubles; an analogue of the SOATE RTD costs about 600 rubles.
Design and operation of RTD
The RTD is a valve with a diaphragm that is installed in the fuel line. When the engine is running, a certain pressure is formed in the system, which must be maintained in the required range, but since the gas pump pumps fuel continuously, the pressure increases. When the pressure increases, the RTD opens the check valve and releases excess pressure into the return system, which communicates with the fuel tank.
Replacing the RTD
Replacement is carried out in the following order:
- It is necessary to reduce the pressure in the fuel system, then unscrew the nut securing the fuel pipe to the RTD;
- Unscrew the bolt with a 10mm wrench securing the oil level indicator guide tube and remove it;
- Unscrew the bolts securing the RDI to the ramp;
- Remove the fitting from the fuel rail, remove the RTD;
- When installing a new regulator, experienced car owners advise lubricating the O-rings with gasoline.
In the future, do not forget to look at the fuel level sensor. If a large flow rate is detected, you may suspect that the replacement was not carried out entirely correctly, and it needs to be carried out more carefully.
How to check the fuel pressure on a VAZ-2110?
Fuel pressure is an important parameter that needs to be given special attention and kept under control. Its value directly affects the efficiency of the engine, its power, and behavior in different modes. Therefore, a good driver should check the pressure from time to time. All that remains is to find out how to do it correctly.
Features of measuring fuel pressure on a VAZ-2110
I would like to immediately note that this parameter can be measured in several ways. One of the most popular is to purchase a special kit, which includes a special adapter for connection, a pressure gauge (it is with this that the measurement is made), as well as a drain. You will have to allocate about 1,500 rubles to purchase such devices. You can do it differently - go to a service station, where specialists will carry out the necessary measurements for 300-500 rubles.
But there is a more sophisticated method that does not require additional costs - measuring fuel pressure using a regular pressure gauge, which is used to check tire pressure. In this case, for measurements it is better to use pressure gauges with a minimum limit (about 6-7 atmospheres). In this case, the error will be minimal.
But how to check? The sequence of actions will be as follows:
- Prepare a pressure gauge with a limit of 6-7 atmospheres and wind the foam directly under the pipe.
- Prepare an oxygen tube with a diameter of 9 mm and put it on top.
- Secure the fasteners on both sides with clamps.
- Cover the generator with something to prevent fire.
- Reduce fuel system pressure to a minimum. It's easy to do. Remove the fuse that powers the fuel pump (in the “ten” it is located under the trim near the control unit, on the far left side), start the engine and wait until it stalls.
- Twist off the plastic cap installed on the fuel rail.
- Look inside the cap - there will be a standard hole and nipple. Take the cap from the car wheel and unscrew it. Be prepared for a slight surge of fuel (this is caused by residual pressure).
- Now put the second edge of the hose onto the ramp outlet and then secure it with a clamp.
- Remove the “protection” from the generator and start the engine (don’t forget to put the fuse back in place).
Pressure regulators VAZ 2110 - design and operation
A fuel pressure regulator (FPR) is needed to maintain gasoline pressure in the fuel system at a constant certain level, regardless of engine operation. It is installed in the injector rail and is a diaphragm valve connected to the fuel supply channel to the injectors, the drain line and the air tube supplied from the intake manifold.
The RTD valve is affected by fuel pressure, on the one hand, and, on the other, by air pressure in the tube and spring force, adjusted to certain operating parameters in the system. When the engine is running, a serviceable RTD maintains the following indicators in the system: 2.9–3.3 kgf/cm 2 (284–325 kPa).
Why do you need a fuel pressure regulator?
As mentioned above, this regulator maintains the required fuel pressure necessary for normal operation of the injectors, taking into account one or another operating mode of the power unit. In other words, the RTD affects the amount and intensity of the fuel supply that enters the engine cylinders through the injectors.
Simply put, the amount of fuel supplied to the engine at the time of injection depends on the pressure that is created inside the fuel rail (rail), as well as on the pulse duration for opening the injector and the vacuum in the intake manifold.
For more accurate dosing and maintaining constant pressure, a diaphragm valve-regulator is used, which experiences fuel pressure on one side, and a spring force on the other. RTD is used in power systems where there is a so-called “return”. The regulator is installed at the fuel rail. Also, this element can be located in the fuel tank, while such systems do not have a return line.
- Let's first look at the common design in which the regulator is located in the fuel rail. The element operates on the following principle: the fuel pump forces fuel from the fuel tank along the line. The resulting fuel pressure acts on the regulator. The device itself has two chambers (a spring chamber and a fuel chamber), which are separated by a membrane. On one side, the membrane is pressed by fuel, which enters the regulator through special inlet holes, and on the other side, there is spring pressure and intake manifold pressure. If the fuel pressure turns out to be stronger than the spring force and the pressure in the inlet, then the regulator opens slightly, resulting in some of the fuel being discharged into the return line. The fuel returns through the return line to the fuel tank.
- In systems without a return line, the regulator is usually located directly in the tank. The advantages include the absence of an additional pipeline. The injectors are supplied with the required amount of fuel directly from the tank, that is, excess fuel does not enter the engine compartment, and there is no need to deliver it back to the tank. This also allows us to talk about less heating of the fuel and provides a number of additional advantages in the form of less intense evaporation.
Types and symptoms of regulator malfunction
The types of RTD malfunctions are as follows. The valve does not hold - fuel begins to circulate freely throughout the fuel system, the pressure in which decreases because of this. As a result, the engine does not have enough fuel when the speed increases, and its power decreases; The pressure in the system should not change after stopping the engine, but since the valve is not able to hold it, when starting the engine, you have to work with the starter for a long time to create the required pressure.
A completely inoperative valve means fuel is not discharged into the tank, and because of this, the pressure in the system increases. As a result, the amount of fuel supplied to the combustion chambers through the injectors increases - there is overconsumption and incomplete combustion of gasoline.
Signs of a faulty RTD are the following engine operation:
- unstable;
- stalls at idle;
- insufficient pickup;
- cannot develop full power;
- the crankshaft rotates at idle speed with a reduced or increased frequency;
- dips and jerks while the machine is moving;
- difficult starting - not always;
- the content of CO and CH in the exhaust gases significantly exceeds the permissible standards;
- excessive consumption of gasoline.
Fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
Problems in the engine power system can vary. For this reason, during diagnosis it is necessary to look for certain signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator. Most often, the main symptoms are considered to be when the engine does not pick up speed and does not develop full power, and also stalls in different operating modes. In the list of main signs, experts note:
- unstable operation at idle, the unit stalls at idle;
- loss of power, noticeable increase in fuel consumption;
- slow reactions to pressing the gas pedal;
- jerks and dips during acceleration, at the moment of throttling;
- the car does not accelerate, does not gain momentum;
Note that the malfunction of the RTD on gasoline cars is similar in symptoms to common problems with the fuel pump or its strainer. For this reason, when determining faults in the power system, a mandatory check of the fuel pressure regulator is necessary.
In other words, if the car stalls at idle, the engine power is lost, dips appear, the car jerks during acceleration or when changing gears, significant fuel consumption is noted, then the problem may not only be in the fuel pump grid, the motor or its relay, but also in the fuel pressure regulator.
Regulator malfunctions usually come down to the fact that the spring loses the required force, as a result of which the fuel is prematurely drained into the “return”, and the engine simply does not have enough fuel when you press the gas and increase the speed, as well as in transient modes. It turns out that the pressure in the fuel rail when the fuel pressure regulator spring is faulty is low, as a result of which the engine runs unstably, engine power decreases, the ECU is not able to correctly adjust the mixture composition for different operating modes, etc.
Failures in the operation of the RTD are also possible when the pressure regulator in the fuel rail begins to jam at certain intervals. In such cases, pressure drops occur in the fuel supply system, and the car begins to twitch. Let us add that the most common reasons for regulator failure, which results in signs of malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator on a diesel or gasoline car, also include wear and tear of the materials inside the device, that is, the valve simply wears out its service life over time. The service life and condition of the regulator are affected by the quality of the fuel and the content of various impurities in it, long periods of vehicle downtime without starting the engine, etc.
How to check and replace the VAZ 2110 regulator?
To check the operation of the RTD, you will need a 24mm wrench, a 5mm hexagon and a pressure gauge (for example, a tire gauge):
- We unscrew the plug of the pressure control fitting on the end surface of the injector ramp.
- Using the metal tire valve cap, unscrew the spool valve from the fitting.
- We connect the pressure gauge to the fitting through a hose, the ends of which are secured with clamps, and start the engine.
- We check the pressure - disconnect the vacuum hose from the RTD.
The pressure gauge readings should increase by 0.2–0.7 kgf/cm2 (20–70 kPa). Otherwise, the RTD must be replaced.
Replacing the regulator: relieve pressure in the fuel line; unscrew the nut securing the fuel return pipe to the RTD; unscrew the 2 bolts securing the RTD to the injector ramp; carefully remove the RTD fitting from the ramp hole; Having disconnected the fuel pipe from the RTD, remove it; We install the new RTD in the reverse order, first moistening the rubber sealing cuffs with gasoline (we replace inelastic and torn rings).
How to check the fuel pressure regulator of a VAZ 2110
24.01.2019The intended purpose of the VAZ 2110 fuel pressure regulator is to maintain a regular pressure in the injectors for petroleum products. The RDT is influenced from two planes - by a spring, which has a special valve, and by gasoline. Its essence boils down to the following - the unit maintains equal performance during various functioning processes. When the load decreases, it returns excess fuel. This saves fuel and maintains correct characteristics in the fuel supply system.
This unit is characterized by low weight and budget cost. Due to its important functions in a vehicle, Lada drivers must have knowledge of the principles of operation, the main causes and symptoms of failure, and changing techniques.
What does the sensor consist of?
Before discussing the question “ how to check the fuel pressure regulator of a VAZ 2110 ”, it is important to understand what it contains. Understanding this process will help you more effectively change the unit if it breaks down.
The regulator has 2 parts - fuel and vacuum. In the internal vacuum part there is a membrane, the purpose of which is to respond to the level of air influence coming from the power unit. Fuel compartment - high pressure gasoline.
The level of exposure to gasoline is counteracted by special valve equipment. When the indicators increase, the excess amount of fuel begins to be discharged.
Principle of operation
RTD monitors and stores the difference in influence on the membrane on both sides (both cavities). Only if these conditions are met can the car engine operate normally. The sensor’s task is to constantly maintain pressure surges, regardless of engine speed. This indicator in the injectors should always be at a high level, especially in comparison with the manifold. If not functioning correctly, injection problems will occur.
When the RTD is functioning correctly, the following is noted: the vacuum decreases in the manifold at minimum engine speeds, and the fuel pressure sensor in the VAZ 2110 ramp reacts to changes and increases performance and injects fuel into the injectors.
Symptoms of a problem
Let's look at the existing options for unit breakdowns. If the valve does not hold, gasoline begins to move freely throughout the system, and the impact is reduced. Subsequently, the engine does not have enough oil in the process of increasing speed, and, accordingly, the power decreases. The pressure level should not change when the engine is stopped, but due to the fact that the piston is not able to hold, during ignition it is necessary to perform prolonged actions with the starter. This will increase the pressure to the desired level.
If the piston is completely out of order, excess fuel does not return to the gas tank and therefore the impact increases. The result is an increase in the amount of gasoline entering the combustion chamber, which means excessive consumption of the petroleum product and its incomplete combustion.
The main symptoms that indicate sensor failure are the following processes in the functioning of the motor:
- unstable;
- stops at idle;
- inability to develop sufficient power;
- crankshaft revolutions with reduced or increased frequency at idle;
- jerks while driving the vehicle;
- periodic difficulty starting;
- increased fuel consumption;
- the exhaust vapor contains an excess amount of CH and CO;
- insufficient pickup.
The most common failures of the fuel pressure regulator are:
- loss of influence. Because of this, the fuel begins to return, which means that the car cannot be started;
- piston clogging. Here, complete or partial blockage is possible. When full, gasoline does not function in the fuel system. If partial, fuel leakage is noted. The last situation is the most important malfunction;
- a decrease or increase in impact, that is, its unevenness. Most often this happens due to a stuck piston. Therefore, the vehicle moves unevenly (the engine stalls or the movement is jerky).
We sorted out the answer to a frequent request - “ VAZ 2110 fuel pressure regulator, signs of malfunction .” It should be noted that not all types of breakdowns can indicate a valve, therefore it is important to be able to check the unit and then draw the right conclusions and engage in repair work.
How to check and replace the RTD on a Lada?
In most cases, piston failure is caused by spring sagging and wedging. This occurs due to natural wear and tear of the steel. Another reason may be prolonged downtime of transport. To prevent this from happening more often, you need to use it. Also, a malfunction may occur due to the use of low-quality petroleum product. Many companies dilute gasoline with water to increase income, so you need to refuel your “iron horse” exclusively at proven stations.
If necessary, the sensor can be checked and replaced by following the following process:
- turn the fitting plug, the function of which is to control the fuel pressure and is located in the end plane of the ramp. The plug itself contains a sealing ring. If the material has become inelastic and has also lost its integrity, it must be replaced separately or all the equipment;
- Next you need to unscrew the spool from the fitting. A steel tire valve protective cap will help you with this;
- then connect the pressure gauge and the fitting, secure them with a clamp. You can apply the model to tires. The operating characteristics must be checked with the engine running. Ideally, it should show values ranging from 284 to 325 kPa or from 2.9 to 3.3 kgf/cm squared;
- Next, you should disconnect the vacuum hose. After this manipulation, you will notice an increase in device performance by a minimum of 20, maximum of 70 kPa or 0.2-0.7 kgf/cm squared. If no changes are detected, a complete change of the unit will be required;
- the next step is to reduce the pressure in the power supply system. Turn the nut securing the fuel pipe towards the sensor;
- turn the two securing bolts towards the ramp;
- Using smooth manipulations, remove the fitting from the ramp hole;
- separate and remove the unit from the tube with the oil product;
- for installation - first lubricate the sealing ring with petroleum product and perform the indicated steps in reverse. It is imperative to renew rings that have lost their shape or integrity.
Such manipulations help in diagnosing and replacing the fuel pressure regulator VAZ 2110 8 valves . The procedure is actually not complicated and is guaranteed to save your home budget. These actions involve close contact with elements containing gasoline residues. Therefore, it is not recommended to carry out work during painful sensations in the head, dizziness and other ailments. Because fumes can further harm your weakened immune system.
Good luck on the roads and no breakdowns in your vehicle.
Fuel pressure regulator VAZ 2110 - check and replacement
Fuel pressure is one of the most important indicators used in diagnosing the operation of a car engine. The efficiency and usefulness of all parts that make up the fuel system depend on it. That is why it is necessary to maintain the correct pressure, regardless of the functioning of the engine. This task is precisely performed by the RTD in the VAZ 2110. Every motorist must remember that it is the pressure regulator that affects gasoline consumption and engine power. A faulty regulator will not allow the engine to operate normally and should be replaced.
How to check the fuel pressure of a VAZ 2110 1.6 engine without return flow, check diagram (step by step)
On a VAZ 2110 with a volume of 1.6, the pressure indicators in the fuel rail are unchanged and vary between 3.6-4 bars. In this case, measurements are often carried out according to the same principles as described above. However, there are several other non-standard methods.
- We prepare the above-described structure - a hose at the end with a pressure gauge.
- The diameter of the hose should be approximately 8 millimeters.
- Measurements are taken at the outlet of the fuel pump module.
- The normal parameter is considered to be a pressure of 5-7 atmospheres.
- Remember how the return line is closed on engines with a drain ramp. In this case, it is better to turn off directly at the fuel pump.
- The double hose should be dismantled and a plug inserted (instead of the plug, you can use a “nipple” from the fuel filter).
- Pull the single pipe onto the pump fitting. Measurements are taken directly on the ramp.
It is important to remember that problems with the fuel system, as a rule, manifest themselves as sudden “dips” when reaching high engine speeds. In addition, when driving, the car can jerk, it stalls when accelerating, and so on. In this case, you need to check the pressure. Only after this can the main causes of the problems be discovered - the fuel pump, injectors, filters, and so on.
On the VAZ 2110, the fuel pressure regulator is designed to maintain constant pressure in the fuel system in any operating mode.
The RTD is a diaphragm valve that is installed in the fuel rail. On one side, gasoline pressure is exerted on it, on the other, springs and air from the intake manifold.
Symptoms of a problem
Before moving directly to the process of replacing the regulator, you need to mention the signs of its malfunction.
The main one is problems in the operation of the valve, especially when the valve does not hold well, i.e. fuel circulates freely. This in turn provokes a decrease in pressure. As a result, the engine power decreases, because it does not have enough fuel to increase speed. When you turn on the engine, it becomes necessary to work for a long time with the starter (i.e., a device that spins the engine shaft in order to start it) in order to create the required pressure. If the valve is completely inoperative, fuel stops being discharged into the tank. This provokes an increase in pressure. As a result, there is excessive consumption of gasoline, as well as incomplete combustion.
In addition, there are other signs indicating a malfunction of the RTD in the VAZ 2110:
- the engine stalls at idle;
- the motor does not work at full power;
- unstable engine operation;
- the content of CO (carbon monoxide) and CH (methane) significantly exceeds the established standards;
- jerking while driving.
Purpose of the regulator
A device such as the VAZ 2114 fuel pressure regulator is designed to maintain the same level and, if necessary, correct the gasoline pressure in the system. Structurally, it is a mechanism of a membrane and a valve located inside the fuel rail (also known as the fuel supply rail). On one side, the pressure of gasoline presses on the regulator membrane, and on the other, a spring.
If the fuel pressure in the system is too high, the valve opens and excess gasoline is dumped back into the gas tank, after which the pressure returns to normal.
RTD in the fuel rail
If the turbocharger becomes jammed, releasing gasoline (and with it excess pressure) becomes impossible. As a result, the total pressure in the fuel system increases by 2 or more times, which entails severe excess fuel consumption.
In a situation where the valve completely stops holding the fuel pressure, there is a constant discharge of gasoline and its free circulation through the system. This, in turn, leads to a sharp drop in pressure and, as a consequence, a strong drop in engine power. For the same reason, starting the engine (especially after a long stay) becomes difficult; you have to spin the starter for a long time before the engine starts.
Location of the regulator in the VAZ 2114
As you can see from the above, a jammed or, conversely, weakened pressure regulator valve cannot lead to anything good. That is why, at the first sign of a malfunction, the entire device should be replaced. We’ll talk about how to do this correctly below, but first let’s say a few words about checking the device yourself.
How to check the RTD of a VAZ 2110?
If you want to check the fuel pressure regulator 2110, you must first unscrew the special plug that closes the fitting for checking the pressure.
You should look for the fitting on the ramp block, from the end. After you have unscrewed the plug, you need to unscrew the spool from the fitting. Use the back of a metal tire cap for this.
After the completed operations, attach a pressure gauge to the fitting using a hose. You can take a regular pressure gauge that you use to measure tire pressure. Secure the ends of the hose with clamps. Now you can start checking - turn on the engine. We continue to check the pressure - it is necessary to disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator. After removing the hose, the correct pressure gauge readings should be in the range of 0.2 - 0.7 cm 2. Other data indicates the need to replace the RTD.
How to check the pressure in the fuel rail of a VAZ 2110
There are several ways to check pressure. This article will describe the most commonly used of them.
To do this, you will need to purchase a special kit, which includes:
- Special adapter for connection;
- Pressure gauge;
- Drain.
All this will cost you approximately 1,500 rubles. You can also turn to specialists (service stations) for help, who will perform an inspection for 300-500 rubles.
Pressure gauge
But there is a more interesting method that will allow you to do without extra costs. Fuel pressure can be measured with a tire pressure gauge to check tire pressure. To do this, it is better to use pressure gauges with a minimum limit (6-7 atmospheres). This will reduce the error as much as possible.
Now let's take a closer look at how to do this:
- First, you need to prepare a pressure gauge and wind the fum tape directly under the pipe.
- Secondly, you will need an oxygen tube with a diameter of 9 millimeters, put it on top.
Next, we fix the fasteners on both sides with clamps. To avoid fire, the generator should be covered with something.
Now you need to reduce the pressure to a minimum. This is not difficult to do. To do this, remove the fuse that powers the fuel pump (in the case of the VAZ 2110, it is located near the control unit, on the left under the trim).
How to replace the regulator?
Below you will find step-by-step instructions for replacing the fuel pressure regulator in a VAZ 2110 car. Follow this plan and you will definitely succeed.
- Step 1: Relieve pressure in the fuel line, i.e. in the tubes through which fuel is transferred from the gas tank to the carburetor and back.
- Step 2. Unscrew the nut securing the fuel return pipe (injector hose) to the RTD and remove the pipe.
- Step 3. Remove the two bolts securing the RTD.
- Step 4. Carefully remove the RTD fitting from the ramp hole.
- Step 5: Disconnect the fuel pipe.
- Step 6: Remove the regulator.
- Step 7: Remember to wet the rubber seals with gasoline. If you notice that the rings are inelastic or torn, replace them.
- Step 8. Install a new regulator. To do this, follow these instructions in reverse order.
Ready!
Any motorist knows that a car cannot go without breakdowns. It is only important to notice their first signs and replace the faulty spare part in time. You should also not panic if there is no car service nearby. Follow the step-by-step instructions and you will succeed. Good luck on the roads!
How does the fuel pressure regulator work?
Internal structure of the fuel pressure regulator: 1 - housing; 2 - cover; 3—pipe for vacuum hose; 4 - membrane; 5 - valve; A - fuel cavity; B - vacuum cavity
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm valve, which in systems with fuel recirculation is installed on the fuel rail. Well, in systems where such recirculation is not provided, the RTD is placed directly in the fuel tank.
On the one hand, the fuel pressure regulator is affected by a special spring, as well as pressure in the intake manifold. On the other hand, it is pressed down by the fuel supplied by the pump. When the fuel pressure begins to exceed the spring pressure and the pressure acting on the valve from the intake manifold, the diaphragm valve opens, letting in the required amount of fuel, and as soon as the pressure of the supplied fuel decreases, the pressure regulator diaphragm closes.
In simplified form, it all looks like this. There are two chambers, fuel is pumped into one, and the spring is located in the other. The chambers are covered by a membrane, which opens at pressure values exceeding the action of the spring. It should also be said that in car models of recent years, such a regulator may not exist. Its functions are performed by a special electronic sensor that measures the voltage in the electric pump that supplies fuel. This solution allows you to optimally maintain the required pressure and regulate the fuel supply by directly controlling the pump. But, although such a system is more accurate, nevertheless, it is often a mechanical RTD that is much more reliable and lasts much longer than an electronic sensor, which is subject to various negative influences.