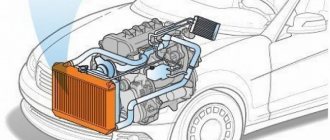
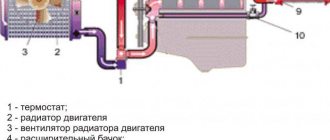
Many characteristics of the power unit directly depend on the effective operation of the engine cooling system (CO). A decrease in pressure in the system and disruption of the normal flow of antifreeze can lead to overheating of the engine and, as a result, its failure.
One of the most dangerous moments is the appearance of air in the engine cooling system. We'll talk about how to remove an air lock from the CO in this article.
What does "air lock" mean?
By ordinary plug we mean an object that prevents the flow or leakage of liquid. The liquid in the cooling system is generally understood to be antifreeze. If air acts as a plug, this phenomenon is called an “air lock”. In addition to cars, this definition can be found in water and heat supply systems.
It is easy to explain this phenomenon physically. Air has a high volumetric compression ratio. In the car's antifreeze circulation system, a maximum pressure of 2 - 3 atmospheres is maintained. Such a relatively low pressure often cannot “push through” the air lock.
The maximum that the water pump can do is move the plug to the highest point of the cooling system, and only if the radiator valve plug is working properly. Some engine CO components may be located above the upper level of the radiator, for example, the interior heater radiator. In this case, the air lock will be “eternal” until measures are taken to remove it.
The worst option is for the plug to move towards the water pump. Once in the area of its blades, the plug will lead to zero pump performance. That is, there is antifreeze in the system, but there is no movement. The engine can overheat in a few seconds. In medicine, this effect is called an air embolism.
How to remove an air lock?
11.12.2012
An air lock in the engine cooling system is one of the main reasons for the engine taking a long time to warm up to operating temperature. Therefore, every driver should be interested in removing air lock from the cooling system of his car.
How to properly remove an air lock from the cooling system?
According to the law of physics, air accumulates in the highest place. In a car, the highest link in the coolant chain is the throttle body. That is why the air must be removed from there. There are several ways to get rid of an air lock. Here's the first one from the bottom:
If you have a 1.6 liter engine, then the first step is to remove the plastic cover on the engine - unscrew the cover on the engine to fill the oil, and then pull out the entire cover. It is seated on rubber seals. After removing this plastic screen, screw the oil cap back on to prevent dirt from getting into the crankcase.
- We find the heating pipes for the throttle assembly (there are 2 of them), see the figure. Pick up any phone.
- Next, unscrew the cap of the expansion tank (coolant reservoir) and cover the neck of the tank with a clean rag.
- We begin to blow into the tank with liquid. We blow until all the air comes out of the hose and antifreeze flows out.
- We quickly put the tube back on and tighten it with a clamp so that no air gets in.
(It is worth noting that depending on the tube that you removed, antifreeze may leak from both the tube and the fitting from which the tube was removed).
The second method of removing air from the cooling system is less perverted. There is no need to blow anything here:
- Warm up the engine to operating temperature.
- Warming up, turn off the engine.
- The expansion tank cap does NOT need to be unscrewed.
- As in the first method, unscrew the clamp of the coolant pipe on the throttle assembly.
- Having removed the heating pipe of the throttle assembly, release the air, and after the antifreeze begins to flow out, immediately put it back on the fitting and secure it well with a clamp.
But be careful and careful! Don't forget that the coolant temperature is approximately 90 degrees.
There is also a simpler, but less effective way to eliminate an air lock:
- We drive up a steep hill so that the radiator cap becomes the highest point of the cooling system.
- Unscrew the expansion tank cap and the radiator cap.
- Let the car warm up to operating temperature.
- Then we accelerate several times and at the same time add coolant into the barrel.
Do this until bubbles stop appearing.
How to remove an air lock on a VAZ with electronic (e-gas)?
Since there is no throttle valve cooling system, you need to bypass this unit. Here you can also set the car up.
I hope that these three methods will help you solve the problem, and that you have found all the answers to your questions on the topic “How to get rid of an airlock?”
Is it necessary to warm up an injection engine?
vaz-2114-lada.ru
Causes
There are many reasons for air locks. They are often due to the characteristics of the engine model and vehicle systems as a whole. The most common reasons are:
1. Incorrect antifreeze filling
.
The desire to speed up the process forces drivers to use wide funnels. When refueling through the radiator, the fill area is literally choked by the flow of liquid. Along with the antifreeze, air enters the radiator and then into the system, which may remain in non-stock cavities. The mistake is to seal the lid too quickly when the air has not yet escaped in the form of bubbles.
Video - how not to air out the cooling system when filling with antifreeze:
2. Incorrect refilling of antifreeze
.
The reasons are the same as in the previous paragraph. Even if topping up occurs through the expansion tank, but at high speed, there is a high probability of air getting into the engine cooling system.
3. Poor CO tightness
.
Antifreeze can escape through micro-slits in the connections of pipes, hoses, fittings, and tubes. Its place is taken by air, which, having accumulated, combines into an air plug. This phenomenon is especially often observed during parking in the cold season, when the daily temperature difference is large. In this case, the linear dimensions of the connections change significantly. Before starting the engine in winter, experienced drivers check that there are no drops of antifreeze under the car.
4. Malfunction of the radiator cap valve or expansion tank cap
.
In this case, during heating and cooling of the engine, first part of the antifreeze that has increased in volume during heating will go into the expansion tank. Air will flow back into the system during cooling.
Video - airing of the cooling system due to a faulty expansion tank cap:
5. Burnt out cylinder block gasket
.
It may be so slight that the driver will not notice a change in engine performance. Under pressure, air can enter the cooling system, and in large quantities.
6. Malfunction of the interior heater radiator, pipes leading to it, gaskets
.
In this case, antifreeze may not be discharged under the car: it will gradually accumulate in the passenger compartment or on the air conditioner cooler tray.
7. Pump seal malfunction
.
Air can enter the system directly through the water pump.
8. Using low-quality antifreeze
.
The operating temperature of modern engines often exceeds 100 degrees Celsius. If you pour low-quality antifreeze, it can boil even with increased pressure in the system. This leads to gas formation.
9. Thermostat is not working properly
.
If the thermostat is stuck in the neutral position, this can lead to the simultaneous operation of the large and small circle of the recirculation system. The efficiency of the cooling system decreases, boiling of the coolant and gas formation occurs.
Blockage in the cooling system, reasons for the formation of a blockage
The reasons that cause an air lock to occur are quite different. We will tell you about the most common ones:
- The tightness is too weak in the places where the tubes connect to the pipes and fittings. As liquid passes through the tube, reduced pressure occurs in the inner wall of the tube and the places where the liquid comes into contact. If there is a defect at the connection, air is drawn into the system.
- Such a plug may occur when replacing coolant or adding fluid to the system.
- If the air valve in the expansion tank has failed. If this valve malfunctions, it does not release excess pressure, but works to let in air, which subsequently enters the system.
- The seal of the pump is broken, which as a result sucks in air from outside.
- The occurrence of defects in the outer shell of heating and cooling radiators, which cause leakage.
- Possible defect in the cylinder block gasket. Liquid leaks from under the head, the exhaust pipe emits white steam, coolant appears in the oil sump, and excessive bubbling occurs in the expansion tank.
- When a polymer material is deformed.
- In case of mechanical damage as a result of an accident.
Signs of the presence of air in CO
The presence of air in the engine cooling system cannot be detected by direct (visual) method. The following indirect signs may indicate this fact:
- increase in coolant temperature above normal values;
- whitish tint of exhaust gases (a sign of the presence of water);
- drops of antifreeze under the car;
- bubbles under the removed radiator cap and in the expansion tank;
- uneven heating of the cooling radiator;
- pump whistling;
- poor heating of the interior heater;
- sweetish smell of antifreeze in the cabin.
How to remove a plug from the system, the first method, detailed instructions
- First, you need to drive the vehicle into an inspection hole or a flat surface, then squeeze the handbrake and engage neutral gear.
- Next, we raise the front of the car with a jack forty centimeters from the surface.
- After this, open the cap of the expansion tank. Care must be taken here as there is a risk of burns.
- Now you should start the engine and radiator at maximum temperature.
- Then we begin to carefully add coolant to the expansion tank to the maximum.
- Next, we increase the engine speed to 3000 rpm.
- We wait for the thermostat to open and squeeze the lower pipe that leads to the radiator with our hand. The procedure must be carried out wearing gloves, with extreme caution, observing the necessary safety rules.
- We continue to carry out the operation until clear liquid, without air bubbles, begins to come out of the expansion tank.
- Now we check the lower part of the pipes with our hands - they should be hot.
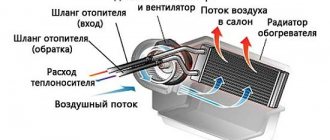
- After this, we start the heating radiator. Check to see if there is hot air flowing into the vehicle interior.
- We lower the car from the jack and secure it with wheel chocks for safety.
- Then add the missing amount of coolant, but its level should not reach the upper mark, as it may overflow through the cap. Over time, antifreeze particles can corrode the vehicle's paintwork.
- If the airiness is severe, the procedure can be repeated.
Possible consequences
The worst consequence of air locks is engine overheating, associated with the need for major repairs. At speed, the driver may not notice the moment the engine boils. This is when maximum boiling occurs, which is easy to determine. If the antifreeze boils away significantly, the driver can drive several more kilometers until the problem is detected. Therefore, it is important to always keep the coolant temperature indicator under control.
A less terrible outcome is damage to the cylinder head gaskets and cooling system. But this is also associated with high costs and lengthy repairs.
When boiling, a leak in the radiator of the engine cooling system is likely. Replacing it is not so labor-intensive, but quite expensive in monetary terms.
Also dangerous are hidden problems that appear some time after partial or complete overheating:
- violation of compression in the cylinders;
- improper operation of the throttle valve;
- injector malfunction;
- failure of the interior heater;
- malfunction of engine control system sensors, etc.
How to remove a plug from the system, the second method, detailed instructions
- We drive into a viewing hole or a flat surface, again squeeze the handbrake and engage neutral gear.
- In this case, the engine does not need to be turned off. It must be heated to a temperature of 90 degrees Celsius so that the thermostat opens and the liquid begins to circulate in a large circle.
- We do not open the expansion tank cover.
- We turn off the engine.
- Then you need to loosen the clamp in the throttle body pipe and remove the pipe. Be extremely careful and careful, wear rubber gloves when working, as the temperature is quite high (90 degrees).
- After removing the rubber hose, you need to wait a while until all the air along with the antifreeze comes out.
- Now you need to put the pipe back on and tighten the clamp.
- At the final stage, we start the engine and test the vehicle. To double-check the system in full, it is advisable to drive it at both low and high speeds.
A simple method for removing air
This method of removing an air lock from the cooling system is relevant for those machines that have the ability to disconnect the heating hose of the internal combustion engine power system unit. You must proceed as follows:
- we provide access by removing protective covers and other interfering parts;
- disconnect the heating hose clamp and remove it from the fitting;
- Having unfastened the tank cap, we blow it with our mouth until we see a flow of coolant;
- We immediately return the hose to its place and return all the disconnected elements to their places.
How the system works
In order to find out how an airlock affects the functioning of the entire system, you need to consider the principle of operation. Antifreeze circulates in small and large circles. They differ only in that when the liquid moves in a large circle, the main radiator of the system is switched on.
Until the engine temperature reaches 80 degrees, the antifreeze moves only in a small circle and enters the interior heater radiator. As soon as the temperature reaches 80 degrees, the valve begins to open and the liquid enters the channels of the large circle. In this case, the antifreeze passes through the radiator honeycombs and is effectively cooled to operating temperature.
Professional advice on how to prevent air locks in the cooling system
You need to know that in order to prevent the appearance of air locks in the cooling system, you should promptly and systematically carry out a technical inspection of the vehicle, as well as properly care for it. Usually, the common cause of traffic jams is a coolant leak, so you need to look under the hood and under the bottom of the car as often as possible in search of characteristic spots.
Low-quality antifreeze can also cause traffic jams because it cannot cope one hundred percent with the task, which contributes to channel blockages.
Most experts recommend installing additional filters on antifreeze for more efficient filtration. It is recommended to completely replace the component after 5,000 kilometers. However, it is much more practical and cheaper to buy high-quality refrigerant, rather than diluted powder with water, which costs pennies on the car market. With this approach the car will not go far.
This is where we end this article and sincerely hope that our advice will help many motorists in gaining experience in troubleshooting breakdowns in the vehicle’s cooling system.