Servotronic on BMW: what it is and how it works
In 1985, BMW introduced the Servotronic system, designed to adjust steering depending on speed. This system reduces the effort required to turn the steering wheel depending on driving speed or road conditions. Due to its design features, Servotronic can only be installed on vehicles with hydraulic or electric power steering. The presence of such a system has a positive effect on the comfort and precision of vehicle control.
The electric hydraulic booster is designed as follows
The pump unit includes: a hydraulic pump, a working fluid reservoir, and a pump electric motor. Signals are sent from the pump unit to the ECU.
A hydraulic pump can be either gear or vane type, however, gear type pumps are more common.
The actuator mechanism of the GUER (hydraulic electric power steering) is hydraulic. control node. Note that this system allows the power steering to function, and if it fails, the entire power steering will be inoperative. Regulation of force depending on the angular speed of rotation of the steering wheel is ensured by an electronic control system. This power steering is called adaptive power steering.
In the modern world, an electric power steering system called Servotronic has gained momentum.
The executive sensors of such a system are a steering wheel rotation sensor, and such a resistive element is installed only on cars equipped with an ESP system, a speedometer sensor, and a knee speed sensor. shaft
The ECU receives and then processes the signals supplied from the sensors. The next step is to send a signal to the executing mechanism to change the operating algorithm.
In the Servotronic system, where a pump electric motor is installed, the power steering gain is changed by increasing or decreasing the rotation speed of the electric motor.
Design and operating principle of Servotronic
The Servotronic system is divided into three main segments: information, computing and executive. Each of them consists of certain units and components. The data acquisition segment consists of a number of sensors:
- power steering (steering wheel angle);
- Hall sensor on the crankshaft;
- speedometer;
Servotronic sensors collect information about the speed of the car, the angle of rotation of the steering wheel relative to the wheels and other parameters of the car. The collected data enters the computing unit, where it is interpreted into instructions for the actuators.
The actuator segment includes a return piston chamber. The chamber contains an electromagnetic valve controlled by signals from the computing unit. The valve and piston connected to the power steering spool perform the main functions of the system.
When the steering wheel is turned, the spool opens, allowing hydraulic oil to flow into the power steering cylinder. At the same time, the solenoid valve receives data interpreted by the computing unit and fills the return chamber.
So the pressure in the power steering cylinder decreases, the piston in the return chamber, in turn, blocks the spool. The force on the steering wheel increases along with the increase in driving comfort.
In the case of electric power steering, the signals from the computer unit are sent to the servo drive, which is connected to the steering column through the planetary unit. In this case, the mechanical connection of the steering column and rack is preserved. In the event of a failure, the servo drive is blocked, and the ability to control the vehicle remains.
While the vehicle is moving in a straight line, hydraulic oil circulates in the main line between the power steering pump and the storage tank. Turning the steering wheel serves as a signal to change circulation paths. Depending on the direction of rotation, the liquid enters one of the chambers of the power cylinder. From the opposite chamber it is sent to the storage tank. The result is a pressure difference that transmits force to the steering rack. That, in turn, puts pressure on the steering rods and the turn occurs.
The greatest efficiency of hydraulic power steering is observed when operating at low speeds, for example, while maneuvering around the city or parking. This happens due to the inverse relationship between the speed of the hydraulic pump and the speed of the vehicle. The lower the second, the higher the first.
Power steering operating principle
When the car moves in a straight line, the circulation of the working fluid is ensured in a circle.
The torsion bar twists when the steering wheel turns, which in turn rotates the spool around the valve sleeve. In this case, channels open through which the liquid moves into one cavity of the working cylinder, and from the other the process of draining into the tank occurs. The piston allows the steering rack to move, and then the forces are transferred to the steering rods, which turn the hub and, accordingly, the wheels.
When the steering is turned at low speed, the power steering operates at maximum performance. According to the signals from the actuator sensors, the ECU gives a command to increase the rotation speed of the pump motor, and this makes it possible to increase the pump’s performance. Next, the process of reducing the applied force on the steering wheel occurs to achieve the required maneuverability.
As soon as the vehicle speed increases, the pump rotation decreases.
- < Back
- Forward >
Pros and cons of Servotronic
Servotronic is a relatively new and specific technology. It has its adherents and those who express antipathy. The list of advantages and disadvantages below will help you decide on your own opinion.
Advantages
- Servotronic components are spaced apart and do not take up much space in the body. There are no difficulties with the layout or installation of the system.
- Improved steering comfort.
- Safety systems maintain steering control even if Servotronic fails.
- Makes it easier to maneuver at low speeds, for example when parking.
- Increased control accuracy at high speed.
- Economy operating modes.
Flaws
- Leaving the wheels in the extreme position for a long time can lead to system failure due to overheating of the hydraulic oil.
- Reduced steering input when driving at high speed.
Servotronic (SVT)
Servotronic is a lateral dynamics system. Servotronic's job is to continuously adapt the steering assistance depending on the vehicle speed and wheel steering angle. The Servotronic does this by controlling the electrical current of the Servotronic valve, so that the available hydraulic oil flow supports the steering process with varying degrees of intensity. Next, the current steering angle of the wheel is taken into account to harmonize the support through the steering angle. The steering gain is determined using characteristic fields and decreases as the vehicle speed increases, causing the required steering torque to increase.
The steering is power-assisted by a conventional rack-and-pinion steering mechanism with hydraulic booster. The magnitudes and directions of hydraulic auxiliary forces acting on the rack depend on the angle of rotation of the installed torsion bar. The torsion bar is located between the steering shaft and the gear.
The control unit responsible for the servotronic function contains the following parts:
- Output stage for servotronic
- Servotronic software
The servotronic function can be implemented by various control units:
- E70 without active steering as of 04/2010 = Servotronic control unit SVT
- E70 with active steering = active steering (AL)
- E71, E71M and E70M = ICM (= Integrated Chassis Management)
Since 04/2010, Servotronic has been available for the E70 without Active Steering (AL) as an optional equipment. Vehicles without active steering do not have active steering (AL). These vehicles are additionally equipped with an SVT servotronic control unit.
Device and main components
Main components of the electric power steering
The electric power steering Servotronic has three main components: an electronic control system, a pump unit and a hydraulic control unit.
The pumping unit of the electro-hydraulic booster consists of a reservoir for working fluid, a hydraulic pump and an electric motor for it. An electronic control unit (ECU) is installed on this component. Note that there are two types of electric pump: gear and vane. The first type of pump is distinguished by its simplicity and reliability.
The hydraulic control unit includes a power cylinder with a piston and a torsion bar (rod that works to twist) with a distribution sleeve and spool. This component is integrated with the steering mechanism. The hydraulic unit is the actuator of the amplifier.
Electronic control system Servotronic:
- Input sensors – speed sensor, torque sensor on the steering wheel. If the vehicle is equipped with ESP, a steering angle sensor is used. The system also analyzes engine speed data.
- Electronic control unit. The ECU processes signals from the sensors, and after analyzing them, sends a command to the actuator.
- Executive device. Depending on the type of electrohydraulic amplifier, the actuator can be a pump electric motor or a solenoid valve in the hydraulic system. If an electric motor is installed, the performance of the amplifier depends on the power of the motor. If a solenoid valve is installed, then the performance of the system depends on the size of the flow area.
steering column switch center (SZL);
The optical sensor for measuring the steering angle is integrated into the PCB of the steering column switch cluster (SZL). The steering angle sensor is designed as a non-contact optical measuring system. The system consists of a coding disk and an optical sensor. The coding disk is connected via a link directly to the steering wheel. When the steering wheel is rotated, the coding disk moves within the optical measuring system. The steering column switch cluster (SZL) evaluates the steering angle and sends this information via K-CAN2.
The steering angle sensor is installed in the steering column switch cluster (SZL). The steering angle sensor measures the steering angle of the wheel using an optical, non-contact method. The sensor is mounted on a board with an electronic processing unit. The sensor consists of the following components:
- Coding disk
- Optical sensor
The coding disk is connected to the steering wheel through a coil spring cassette. When the steering wheel is rotated, the coding disk moves inside the optical sensor. The coding disk contains various bar codes for analysis.
The steering column switch cluster (SZL) is connected via the chassis CAN bus to the Dynamic Stability Control (DSC). The steering angle of the wheel is transmitted via the chassis CAN bus.
Servotronic control unit (SVT)
The Servotronics control unit (SVT) performs functions that can also be fully integrated into the following control units:
- Integrated Chassis Management (ICM)
- Active steering (ASC)
The following vehicles have an SVT Servotronic control unit:
- E70 with optional Servotronic without active steering
The installation location of the Servotronic control unit (SVT) is located behind the Car Access System (CAS).
Servotronic requires the following signals:
- Steering angle of the steering column switch center wheel (SZL)
- Dynamic Stability Control (DSC) driving speed
- Engine status in Digital Engine Electronics (DME) or Digital Diesel Electronics (DDE)
- Contact status in Car Access System (CAS)
The Servotronic valve is only activated when terminal 15 is on and the engine is running.
Servotronic valve
Servotronic adjusts the power steering gain depending on the speed. The fluid flow is regulated differently depending on the activation of the servotronic valve. Throttling depends on the servotronic valve current. The servotronic valve is a solenoid valve.
The Servotronic valve is connected to the Servotronic ECU using a 2-pin plug connection. The Servotronic control unit (SVT) controls the Servotronic valve using voltage and ground.
System functions
Servotronic determines the majority of the steering wheel torque that the driver must generate. The Servotronic function is determined largely by the driving speed and the steering angle of the wheel:
- Low speed range (city, parking) = low steering torque
- High speed range (country road, motorway) = high steering torque
The Servotronic valve is only activated when terminal 15 is switched on and the engine is running. The Servotronic control circuit regulates the current of the connected Servotronic valve. Higher current means more steering gain for the same steering torque. The specified current is determined based on the characteristics field, with the parameters “movement speed” and “wheel rotation angle”. The characteristic field is stored in the coding data and has 10 reference points for the driving speed and 6 reference points for the wheel angle. Intermediate values of the specified current are determined using linear interpolation of adjacent reference points. The value from the graphical characteristic is limited by the function in the range from 0 to 860 milliamps.
Servotronic on BMW: what it is, how it works and how it works
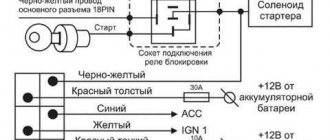
Then I stripped the wires 2 cm before the chip and crashed into it.
At the same time, the insertion site was also filled with liquid plastic... and received a burn. Cool thing, this plastic. As a result, the BMW servotronic repair took place, I was shocked.
The steering wheel on this car has never turned so easily... it’s like feathers. So, if they say that these valves are suitable from other machines, do not believe them.
They are structurally the same, but the chip is located differently. I didn’t resolder it, I bought another one, I was lucky with the same numbers. And there is an opinion that resoldering does not help, but I think I should explain this later. After installing the new unit, hurray, it began to spin easily, and when the speed changed, the force also changed.
But after a year of operation, a problem began to arise, after starting everything works well, but as soon as you drive a couple of meters or more, the steering wheel becomes tighter, BMW servotronic repair after several weeks of operation became completely in the same condition, as if after starting or. I can’t say exactly what error BMW servotronic repair is. After inspecting the comfort unit, it turned out that nothing burned out the resistor in place. So we climb to the valve.
Was immediately purchased used. Testing with a tester showed a resistance of 8 ohms, the one I had also showed 8 ohms.
Well, okay, let's change it. After the replacement, nothing changed, it was just because there was an error.
how to remove and disassemble the servotronic valve
As it turned out, repairing BMW servotronics from the net. Therefore, we connect the computer, reset the error and voila it’s easy to spin. But the joy does not last long, we drive a couple of meters and the steering wheel is tight again. But there are no errors. OK.
I decide to disassemble my valve. This system reduces the effort required to turn the steering wheel depending on driving speed or road conditions.
Due to the design features, the BMW Servotronic Repair can only be installed on vehicles with hydraulic or electric power steering. The presence of such a system has a positive effect on the comfort and precision of vehicle control. Each of them consists of certain units and components. The data acquisition segment consists of a number of sensors: The collected data enters the computing unit, where it is interpreted into instructions for the actuators.
The actuator segment includes a return piston chamber. The chamber houses the electromagnetic repair of BMW servotronics, controlled by signals from the computer unit.
The valve and piston connected to the power steering spool perform the main functions of the system. When the steering wheel is turned, the spool opens, allowing hydraulic oil to flow into the power steering cylinder.
EPS Servotronic: what is it and how does it work?
Electro-hydraulic power steering Servotronic is a car steering element that creates additional force when the driver rotates the steering wheel. In fact, electric power steering (EGPS) is an improved hydraulic booster. The electric hydraulic booster has an improved design, as well as a higher level of comfort when driving at any speed. Let's consider the principle of operation, main components, as well as the advantages of this steering element.
Design and operating principle of Servotronic
The Servotronic system is divided into three main segments: information, computing and executive. Each of them consists of certain units and components. The data acquisition segment consists of a number of sensors:
- power steering (steering wheel angle);
- Hall sensor on the crankshaft;
- speedometer;
Servotronic sensors collect information about the speed of the car, the angle of rotation of the steering wheel relative to the wheels and other parameters of the car. The collected data enters the computing unit, where it is interpreted into instructions for the actuators.
The actuator segment includes a return piston chamber. The chamber contains an electromagnetic valve controlled by signals from the computing unit. The valve and piston connected to the power steering spool perform the main functions of the system.
When the steering wheel is turned, the spool opens, allowing hydraulic oil to flow into the power steering cylinder. At the same time, the solenoid valve receives data interpreted by the computing unit and fills the return chamber.
So the pressure in the power steering cylinder decreases, the piston in the return chamber, in turn, blocks the spool. The force on the steering wheel increases along with the increase in driving comfort.
In the case of electric power steering, the signals from the computer unit are sent to the servo drive, which is connected to the steering column through the planetary unit. In this case, the mechanical connection of the steering column and rack is preserved. In the event of a failure, the servo drive is blocked, and the ability to control the vehicle remains.
While the vehicle is moving in a straight line, hydraulic oil circulates in the main line between the power steering pump and the storage tank. Turning the steering wheel serves as a signal to change circulation paths. Depending on the direction of rotation, the liquid enters one of the chambers of the power cylinder. From the opposite chamber it is sent to the storage tank. The result is a pressure difference that transmits force to the steering rack. That, in turn, puts pressure on the steering rods and the turn occurs.
The greatest efficiency of hydraulic power steering is observed when operating at low speeds, for example, while maneuvering around the city or parking. This happens due to the inverse relationship between the speed of the hydraulic pump and the speed of the vehicle. The lower the second, the higher the first.
SAFETY
Even in the event of a failure of the vehicle's electrical network or failure of its individual elements, the steering drive remains fully operational. In emergency situations, Servotronic 2 operates by forcing the mechanical opening of the converter valve with maximum hydraulic counteraction (high speed characteristics).
In the event of an unexpected lack of signals while driving, for example, a broken contact or failure of the tachometer, a high-performance microprocessor in the electronic control unit is able to calculate the flow value based on the last received signals. Therefore, error-free steering operation is ensured until the engine is turned off. The next time the engine is started, maximum hydraulic backlash is ensured according to the high speed characteristic.
SPECIAL EQUIPMENT
In order to optimize the operation of the control system and adapt it to different kinematic conditions and different power units, Servotronic 2 can be equipped with a number of additional equipment options.
VARIABLE GEAR RATIO
In addition to a constant gear ratio, Servotronic 2 can have a variable gear ratio. In this case, the teeth of the rack may differ in shape and engagement angle. Due to this, on the one hand, the response of the steering wheel during straight-line movement remains the same. On the other hand, when the steering wheel is turned at a significant angle (right and left), the gear ratio decreases, and the control becomes more active. The difference between the maximum and minimum gear ratio should not exceed 35%. This results in an extremely low ratio between steering rotation (up to two full turns) and the movement of the rack engagement.
Servotronic 2 with variable gear ratio is used to equip mid-size cars, light trucks and sports cars. The system ensures precise, fast steering when driving at high speed, eliminating the risk of “over-twisting” the steering wheel, as well as optimal control when parking and turning on narrow sections of the road and safely passing sharp turns.
DAMPING AT END OF STROKE
If car manufacturers deem it necessary, the Servotronic 2 system may have polymer elements as part of the travel limiters. The work of the damper before the end of the stroke is felt in the form of noise at maximum wheel turn.
Advantages and disadvantages
First, about the advantages of the EGU R: compact design; driving comfort; operation with the engine switched off/not running; ease of maneuvering at low speeds; precise control at high speeds; efficiency, reduced fuel consumption (turns on at the right time).
Disadvantages: risk of power steering failure due to the wheels being delayed in the extreme position for a long time (oil overheating); reduced information content of the steering wheel at high speeds; higher cost. Servotronic is a trademark of AM General Corp. EPS Servotronic can be found on cars of such companies as: BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Volvo, Seat, Porsche. The Servotronic electro-hydraulic power steering undoubtedly makes life easier for the driver, making car trips more comfortable and safe.