Gas equipment is increasingly used in the automotive sector. This trend is largely due to the cheapness of gas and the ease of installing special equipment. Despite the relative simplicity of the design, gas equipment (LPG) on a car always has a huge number of components. One of these is the HBO cylinder. We will talk in more detail about its design, structure, types and main characteristics in the material presented below.
History of origin
At the dawn of the formation and development of gas equipment for cars, there was no talk of multivalves. In those glorious times, the following primary tasks were solved:
- gas dosage;
- fuel heating;
- gas supply to the engine.
For this reason, the issue of shut-off valves was postponed. The old cylinders that were used to equip trucks are still preserved. If you look closely, you can see that there is no multi-valve there, but instead there is a set of fittings and valves welded directly into the cylinder.
This situation persisted until the necks of the containers were unified. Only after this did it become possible to develop a unified standard for shut-off valves. This, in turn, led to the creation of the multivalve.
Principle of operation
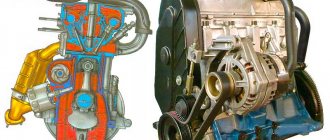
It should be noted that power supply with a gas mixture, the design of the entire gas cylinder system of previous generations is much simpler than the design of a gasoline fuel mixture supply system.
Converting a vehicle to operate on gas equipment and its corresponding conversion looks like this. First, in the luggage compartment, cargo compartment, under the bottom of the car, on the frame, a special container is installed, intended for filling with gas. In the engine compartment (underhood space) an evaporator reducer, additional devices whose functions are related to the supply of a gas mixture to the engine, and fuel adjustment mechanisms are installed.
The cylinders are filled with a liquid mixture of propane and butane. If the pressure corresponds to atmospheric pressure, the fuel is in a gaseous state. If the pressure is higher than atmospheric pressure, the gas is converted into liquid fuel, which can evaporate at household temperatures. Therefore, only sealed containers are used for liquefied gas. The pressure in them can be 2-16 atmospheres.
Gas vapors form pressure, due to which they are supplied to the high-pressure gas pipeline. Refilling the gas cylinder and supplying fuel from it to the main line is done through a multi-valve. To perform refueling, a special remote device is additionally used.
The liquefied gas mixture is directed through a pipeline and passes through a gas valve with a filter element. This additional filtration makes it possible to more effectively purify fuel from resinous compounds and other impurities. This device is also designed to block the supply of the gas mixture when the ignition is turned off or the engine operating mode is switched to motor gasoline.
After filtration, the fuel mixture is sent to the gearbox. Here the pressure of the gas mixture drops to approximately 1 atmosphere. A decrease in pressure promotes the evaporation of the liquid gas mixture. During this process, the gearbox is actively cooled. It is for this reason that it is connected to the cooling system of a car engine.
The heated coolant as a result of circulation through the system prevents the gearbox from freezing. In the cold season, it is recommended to start with motor gasoline, and after pre-warming the engine, it is worth switching its operating mode to gas equipment. This requirement assumes that the engine reaches operating temperature conditions, as well as heating the coolant to the required temperature.
After the gearbox, the vaporous gas is sent to the engine cylinders. The GB system does not have a part that is functionally similar to a fuel pump. The gas mixture is contained in a cylinder under a certain pressure and enters the reducer autonomously; additional pumping is not required for this. Thanks to this, the LPG system is much simpler in design.
A special switch installed in the car interior allows you to switch from gasoline to gas and back. After turning off the ignition, the switch takes the neutral position. Gas equipment can be additionally equipped with the function of shutting off the supply of the gas mixture if there is no spark in the car engine.
Product design and types
A multivalve is a special device installed on a car’s gas system in order to prevent gas leaks and the creation of an emergency. This is a special block consisting of 4 systems:
- Safety;
- Constipation;
- Control;
- Executive.
There are 2 classes of multivalves, which differ in safety measures:
- Class A - these are devices that have a safety valve in their mechanism;
- Class B - this type does not have any safety valves. It is for this reason that such devices are installed only on cylinders whose volume does not exceed 50 liters.
Node characteristics
Today, gas equipment on the market is equipped with a huge number of variations of cylinders. The differences between them are based on two main properties:
- tank shape (cylindrical or toroidal);
- and its technical characteristics.
We’ll talk about the shapes of cylinders separately in the next paragraph of the article, but now let’s pay attention to the technical characteristics of these LPG elements. Today, the following properties of gas cylinders stand out:
- Weight and dimensions. Perhaps the most understandable division, which occurs due to the use of cylinders of different capacities and types of production;
- Volume. This characteristic is one of the most important for gas cylinders. For ordinary cars, tanks with a capacity of 20-90 liters are actively used, for SUVs - 150 (plus several additional ones - 30 liters each), for medium-sized vehicles (for example, gazelles) - 300, for trucks - up to 1000. Many people want to install gas equipment on their car, people often ask the question “What volume is best to install cylinders?” There is an answer to it, and it is confirmed by practice. For passenger cars, the optimal option is 25-30 liters, and for all others – 100, of course, per tank, of which an unlimited number can be used in the LPG design;
- Possibility of verification. Note that most modern HBO cylinders are perfectly diagnosed through the equipment control unit, so this type is used quite often. Nodes that do not have a verification function are now almost never used;
- Type of gas used. Today, only two types of cylinders stand out in this regard. The first are propane, because they are intended for storing gas of the same name, while others are installed on gas equipment with methane, respectively, operating exclusively on it;
- The need for installation at a service station, systematic certification, inspection, opening a technical passport, undergoing pressure testing or compliance with other formalities. Fortunately for the majority of car drivers, they do not need to use such cylinders, because it is enough to register the entire LPG. However, for owners of gas "heavy" gases, they will most likely have to tinker with the certification of cylinders and their inspection. It is worth mentioning that at the legislative level, mandatory inspection of all cylinders separately from the LPG itself has long been considered, but so far no such measures have been officially taken. Many will say that this already exists, because once every 2 years gas equipment is checked without fail, but it is worth noting that the government wants to greatly modify the inspection procedure with an emphasis on detailed diagnostics of cylinders separately from other components of gas equipment.
Otherwise, there are no divisions at the gas tanks. However, the provisions presented above are quite a lot for organizing the most flexible selection of a cylinder, right?
Purpose of multivalves for HBO
Installation of such a block of fittings is carried out on the neck of the cylinder. It plays the role of a locking device, which implies the following aspects:
- Prevents cylinder overfilling - the valve cuts off further fuel supply at the gas station after the cylinder is 80% filled with the liquid phase of gas. 100% filling is unacceptable, because liquefied gas has a very high coefficient of expansion (volume), so excess liquid gas in the cylinder is dangerous and extremely undesirable. Expansion occurs when there is a sudden change in temperature (for example, when a car drives from the street into a warm garage in winter). In such situations, it is possible for gas to expand to its limit, which provokes an emergency release of its excess. As a rule, this happens when the pressure reaches 25 atmospheres. To avoid this, it is necessary to install a multi-valve, which simply does not allow the cylinder to be filled to capacity, leaving about 15% “in reserve”.
- Limiting the gas outlet speed - this is the responsibility of the high-speed valve integrated into the gas system. It controls the rate of gas supply to the engine compartment and prevents its leakage in the event of a main pipeline break.
- Protection from possible destruction - this safety measure is fully justified in the event of a fire in a car equipped with gas cylinder equipment. If there is significant heating and the permissible pressure in the tank is exceeded, an urgent release of excess gas occurs, which is removed outside the machine through a ventilation unit. The emergency (safety) valve is responsible for resetting.
- Gas level - this sensor allows you to control the amount of “blue fuel”.
- Non-return valve - this device does not allow gas to escape from the cylinder when the clamp is disconnected at the gas station.
- 2 shut-off valves - they are installed for forced (manual) shutdown of the filling and main pipelines.
Tomasetto class A multivalve R-01
Classification of gas cylinders
In addition to the division based on the product’s own dimensions, they differ in shape. If we discard highly specialized models and heavy cargo equipment, then there are two types of propane cylinders: cylindrical and toroidal, designed for installation in automobile gas equipment.
Cylindrical version
Today it is considered a rather outdated version, more suitable for earlier generations of HBO, but still does not lose its relevance. It is gradually being replaced by toroidal shapes as more practical in general.
Structurally, it is a very ordinary cylindrical cylinder; installation by most experts is recommended in the trunk of a car with a sedan-type body.
There are ways to place it along and across the center of gravity of the car. The disadvantage of this method of placement is that the useful cargo space is cluttered - the installation seems to divide the trunk in half.
Unfortunately, installing it in a corner does not lead to anything good; the cylinder unevenly loads the axles. For large cars, it is possible to install a small container of 20 - 35 liters under the hood, a suitable option for a reserve gas supply for a long journey.
Toroidal cylinders
The advantage that has ensured the popularity of this form of gas storage tank in a car is its successful imitation of a car’s spare tire, as a result of which these parts have the same dimensions and are accordingly interchangeable. In the case when the installation takes place on a hatchback or liftback type body with remote placement of the spare tire, the entire working space of the trunk is completely preserved and the propane is as far away from the passenger compartment as possible.
A naturally arising question is that drivers decide what to do with the spare tire itself in three ways:
- Store the wheel in the trunk or interior. For this, it is very appropriate to purchase a special portable and outwardly solid case.
- Place a container of gas on the hood. This is a more practical option than the one similar to the cylindrical one: toroidal cylinders, having the same volume of 20 -35 liters, are flatter and such a high vehicle clearance is not needed for successful installation.
- In general, abandon the spare tire in favor of a compact and practical repair kit that quickly and reliably repairs a rupture of almost any severity. However, do not forget - this is not a full-fledged replacement for changing a tire; situations can be very unpredictable.
Ventilation unit
The multivalve is inextricably linked with the ventilation box, since the device diagram implies its placement in the so-called. ventilation box. Special hoses come out of it (into the atmosphere).
The gas cylinder equipment of the car is equipped with this block in order to prevent gas leakage into the car interior in the event of depressurization of the multivalve itself.
At the moment, there are 3 designs for the ventilation system mounted on cylindrical cylinders:
- A cylinder is a metal device welded directly to the body of the container. Equipped with a steel cover (removable);
- Housing and plastic (transparent) cover - in addition, the kit includes 2 flanges with ventilation hoses;
- Silicone cap.
As for toroidal cylinders, in this case, schemes with the installation of silicone or plastic blocks are possible.
Protective silicone case for multivalve
Due to the fact that the inner neck of the toroidal container has a steel cap that covers the entire internal space of the cylinder, a hole in the body acts as ventilation. It is through this that the supply and filling tubes approach the multivalve.
A few words about the purpose of HBO cylinders
Gas equipment used on cars involves the use of liquefied gas - propane or methane - to power the engine with fuel. The standard design of the gas equipment consists of three main elements:
- fuel distribution system (injectors, control unit);
- overpasses (hoses, filters);
- container or containers for storing fuel.
The cylinder belongs to the last class of HBO elements. That is, this unit is an ordinary tank that helps store and transport the gas that powers the car’s engine.
Gas cylinders have no specific features, except for the requirements for their use. In particular, it is not allowed to store liquefied gas from the LPG system in tanks:
- with a wall thickness of less than 3 millimeters;
- with broken seal or shape;
- without basic gas distribution and supply systems.
Ignoring the noted requirements and using cylinders that do not comply with them is a huge danger for both the driver and his passengers, because such tanks can explode at any moment.
How to remove the multivalve
To diagnose and identify the cause of the malfunction, remove the “cartoon” from the gas cylinder.
- You should proceed with dismantling only when there is no gas left in the cylinder.
- First, you should loosen the fastening of the gas main pipes and bleed off the remaining gas.
- After all the gas has completely left the cylinder, we begin dismantling the multivalve. To do this, unscrew all the mounting bolts. This should be done extremely carefully, since breaking the fastening bolt does not threaten anything good. If one or more bolts do not budge, treat them with penetrating lubricant and wait a few minutes.
Unscrew all the bolts and carefully remove the multivalve from the cylinder
It is best to show the removed “multiple” to a specialist, who will determine whether it is possible to get by with a repair kit for the multivalve or whether this unit should be completely replaced with a new one. If you decide to replace the multivalve, you should reassemble in the reverse order.
What types of multivalves exist and how do they differ?
"Mults" are divided into protection classes. There are two main classes: “A” and “B”. The first differs from the second only in that it has in its design an excess pressure valve, which releases the vapor phase into the outside if the pressure in the cylinder increases. “B” class “cartoons” do not have an overpressure valve, so they can be installed on gas cylinders with a capacity of no more than 50 liters.
- During installation, the multivalve for cylindrical cylinders is equipped with a ventilation box to which a corrugated hose Ø 30 mm is connected. This hose removes gas fumes from the trunk of the car.
- A multivalve for toroidal cylinders with an internal arrangement is installed in a cylinder, which is mounted in a recess under the “spare tire”.
- “Mult” for toroidal cylinders with an external location is mounted in the cylinders, with the neck extending outward.