In 2003, the first generation of Mazda 3 appeared. Russian car enthusiasts fell in love with this car almost immediately. The new design, which replaced the appearance of the 323 and 626 popular in the late 90s, turned out to be to the liking of many. And indeed, at that time, the third series seemed to be one of the most attractive models in the small middle class (then simply middle class). Her pretty face and sporty, laconic silhouette stood out among the Focuses, Almeras, Lancers, and Megans of that time. But it’s not just its appearance that makes the “treshka” so popular. These cars have acquired a reputation for being reliable, technologically advanced, and unpretentious. This list can be continued, but now we will be interested in a specific component of this car - the Mazda 3 engine. There are quite a few options in the line of power units of this model, which, by the way, indicates the general demand for the car by a wide audience and the great work done by the company's engineers to satisfy these needs. Different models of engines were intended for different countries, depending, apparently, on demand and service capabilities; in Russia, the most famous are gasoline fours with a volume of 1.6 to 2.3 liters, although there are others, but these are mainly either Japanese or American, but there are diesel ones units intended for the European market, and, less often, Asians. All of them are quite rare.
Mazda 3
Return to contents
Renault Logan 0.9 MT - European version
Another version, which has not yet reached Russia, belongs to the Renault corporation. The French have developed two economical European engines 0.9 and 1.2 liters. We are more interested in the first power unit in our review, since it offers quite adequate technical characteristics. Nobody expects technical breakthroughs from Renault. This is just normal high-quality equipment without any special difficulties in maintenance. But the 0.9 liter engine changed a lot:
- the power unit, despite its quite affordable volume, turned out to be quite powerful - 90 horsepower under the hood helps out in many situations;
- the dynamics turned out to be even better than in the case of the previous participant - the car accelerates to hundreds in 11.1 seconds;
- the maximum speed was limited to 175 kilometers per hour, which turns out to be an excellent achievement for such a unit;
- a manual transmission looks like a logical solution paired with such an interesting and technologically advanced engine;
- fuel consumption in the combined cycle is 5.2 liters - this is a very good indicator considering all the other features of the vehicle.
It must be admitted that Renault has surpassed all its competitors by actively developing modern technologies to save fuel. The corporation's machines meet all quality standards and are quite affordable in price. Interestingly, in Europe, Dacia Logan with such an engine is recognized as the cheapest vehicle. This suggests that modern and high-quality developments turned out to be not so expensive, which is another big plus for the manufacturer. Well, while this Logan is not being imported to Russia, we suggest watching a video of the Kia Picanto with a small power unit:
Is it possible to increase the engine size?
This question is often asked by car owners who want to increase power. There is such a possibility, but it will not be possible to significantly increase the volume. The volume is increased during an engine overhaul, since to restore the shape of the cylinder walls they have to be bored on a special machine (unless, of course, liners are used in it).
The cylinder walls are slowly but steadily ground down from constant friction, which leads to an increase in the volume of the combustion chamber, and boring only helps restore the damaged geometry and correct the discrepancy in the volume of different cylinders.
In Japan, the class of small cars is “kei car” with an engine capacity of up to 660 cc. exempt from road tax
The ability to increase volume is limited by the fact that manufacturers believe that major overhauls are only justified three times, after which the engine must be scrapped. After boring the block, each time you have to buy new pistons of larger diameter, which are called “repair”. There are only three calibers of repair pistons. In this regard, replacing the engine with the same one, but initially having a larger volume, is a much more promising activity in terms of increasing power.
SPIU - Test on the topic “Technical operation of vehicles”
- Full list of completed works on NTETS
- Test for the topic “Road transport”
- Test for the topic “Road Safety”
- Test for the topic “Information support for independent technical expertise”
- Test for the topic “Methodological foundations and provisions for establishing methods”
- Test for the topic “Methodological foundations and provisions for establishing causes”
- Test for the topic “Methodological foundations and provisions of identification”
- Test for the topic “Methodological foundations and provisions for identifying technical damage”
- Test for the topic “General characteristics of independent technical examination of a vehicle”
- Test for the topic “Compulsory civil liability insurance for vehicle owners”
- Test for the topic “Organization and conduct of independent technical examination of a vehicle”
- Test for the topic “Legal support for independent technical examination of vehicles”
- Test for the topic “Theoretical foundations of independent technical examination of a vehicle”
- Test for the topic “Technical operation of vehicles” (current page)
- Test for the topic “Economics of technical operation of vehicles”
You may be interested in the following sections:
What is considered the working volume of an internal combustion engine?
What is urea for a diesel engine
An automobile internal combustion engine is a complex engineering device that includes multiple systems, electronic and mechanical components, attachments and additional equipment.
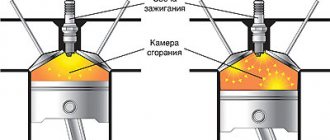
The principle of operation is to supply a fuel-air mixture to the combustion chambers of the power unit, where this mixture is ignited under pressure by spark plugs or glow plugs.
As a result of combustion (which is a micro-explosion), a large amount of energy is released, which moves the piston located in the cylinder. The piston acts on the crank mechanism, and the energy is converted from translational to rotational. With its help, the crankshaft of the engine rotates. Next, the torque from the crankshaft is transmitted to the transmission, and from it to the drive axle (or axles) of the car. The axle shaft rotates the wheel - the car moves.
The above process is repeated until the driver turns off the engine or until fuel is supplied and there are no problems preventing the normal functioning of the engine. The part of the cylinder in which the fuel combustion process occurs is the combustion chamber. Its volume is called working volume. To find out the engine volume, add up the working volumes of its combustion chambers (roughly speaking, the sum of the cylinder volumes). Liters are used to express engine volume, and cubic centimeters are used for combustion chambers.
As an example, consider the commonly used two-liter four-cylinder gasoline engine. Without pretending to be accurate, let's assume that each of its combustion chambers has a working volume of 499 cm3. This engine has four cylinders, the total volume of the combustion chambers is 1996 cm3. To express in liters, round this figure to the nearest whole number - 2 liters.
Features of operation of large cars
Compared to small-displacement engines, large-displacement engines are characterized by smoother operation and less noticeable wear, since they are much less likely to have to operate at the power limit. An engine with a large combustion chamber produces its maximum capabilities only when it participates in racing, i.e. in sports competitions. When driving in normal mode, the engine retains a reserve of power, so it does not wear out. Fuel consumption, of course, remains higher than that of small-displacement engines, but it can be reduced by properly adjusting the gearbox. A powerful engine, which is rarely used in hard conditions, is capable of driving up to a million kilometers without the need for major repairs. Therefore, the costs incurred when purchasing a powerful large car are subsequently recouped by the long-term operation of the car.
Is it possible to increase the engine size?
This question is often asked by car owners who want to increase power.
There is such a possibility, but it will not be possible to significantly increase the volume. The volume is increased during an engine overhaul, since to restore the shape of the cylinder walls they have to be bored on a special machine (unless, of course, they are used in it). The cylinder walls are slowly but steadily ground down from constant friction, which leads to an increase in the volume of the combustion chamber, and boring only helps restore the damaged geometry and correct the discrepancy in the volume of different cylinders. In Japan, the class of small cars is “kei car” with an engine capacity of up to 660 cc. exempt from road tax
The ability to increase volume is limited by the fact that manufacturers believe that major overhauls are only justified three times, after which the engine must be scrapped. After boring the block, each time you have to buy new pistons of larger diameter, which are called “repair”. There are only three calibers of repair pistons. In this regard, replacing the engine with the same one, but initially having a larger volume, is a much more promising activity in terms of increasing power.
V6 engine today
Modern six-cylinder V-engines have a crankshaft with six cranks (offset crank pins). They provide a uniform ignition interval of the fuel-air mixture. And the first order moment of inertia is stabilized using a balancing shaft.
Sports cars most often use a large, 120-degree camber. This motor is wider compared to its analogues. However, its main advantage is its low center of gravity. This has a positive effect on the maneuverability and controllability of the car.
There are two connecting rods on the crankpin. This configuration is characterized by a high first-order moment. Therefore, the design necessarily uses a balancing shaft. Thanks to it, not only vibration is reduced, but also ensures high smooth running of the power unit.
On the topic: methodological developments, presentations and notes
Open lesson on the discipline: "Car Maintenance" in the 3rd year vocational education group. Topic: Organization of maintenance and repair posts at service stations.
basic terms and concepts used in studying the discipline Automotive Maintenance.
basic terms and concepts used in studying the discipline Automotive Maintenance.
Contents Topic 1. General design and mechanisms of engines Topic 2. Engine systems Topic 3. Electrical equipment Topic 4. Transmission Topic 5. Body, chassis and control mechanisms Topic 6. .
Test No. 1 Design, operation and maintenance of automobiles.
Test No. 2 Design, operation and maintenance of automobiles.
IDC work program. 01.02 “Design, maintenance and repair of vehicles” PM 01. “Maintenance and repair of vehicles” for profession 2.