| This article lacks links to sources of information. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You may edit this article to include links to authoritative sources. This mark was set on March 21, 2014 . |
| This article may contain original research. Add links to sources, otherwise it may be set for deletion. More information may be on the talk page. (January 22, 2017) |
| This article needs revision. Need sources, many ORISSA Please improve the article in accordance with the rules for writing articles. There is more information on the talk page. |
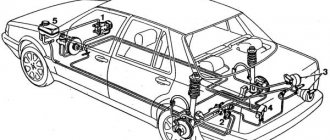
Suspension
car, or
suspension system
, is a set of parts, assemblies and mechanisms that play the role of a connecting link between the car body and the road [1]. Included in the chassis.
The suspension performs the following functions
:
- Physically connects wheels or continuous axles to the vehicle’s supporting system—the body or frame;
- Transfers to the supporting system the forces and moments that arise when the wheels interact with the road;
- Provides the required movement of the wheels relative to the body or frame, as well as the necessary smoothness.
Main elements
pendants are:
- Elastic elements
that perceive and transmit normal (vertically directed) road reaction forces that occur when a wheel hits bumps; - Guide elements
, which determine the nature of the movement of the wheels and their connection with each other and with the supporting system, and also transmit longitudinal and lateral forces and their moments. - Shock absorbers
, which serve to dampen vibrations of the supporting system resulting from the action of the road.
In real suspensions, one element often performs several functions at once. For example, a multi-leaf spring in a classic leaf spring suspension of the rear axle simultaneously perceives the normal reaction of the road (that is, it is an elastic element)
, and lateral and longitudinal forces
(that is, it is also a guiding element)
, and also, due to interleaf friction, acts as an imperfect friction shock absorber.
However, in the suspensions of modern cars, as a rule, each of these functions is performed by separate structural elements that quite rigidly define the nature of the movement of the wheels relative to the supporting system and the road, which ensures the specified parameters of stability and controllability.
Modern automobile suspensions are becoming complex structures, combining mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic and electrical elements, often having electronic control systems, which allows achieving a combination of high parameters of comfort, controllability and safety.
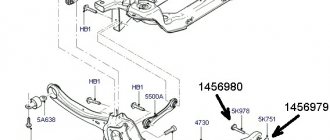
Multi-link suspension device
The chassis of a car is a collection of parts and assemblies. In addition to other classifications, suspensions are divided into subtypes according to the number and location of levers. If the design uses two levers, the suspension is called double-wishbone, if more - multi-link. The levers can be located along, across the longitudinal axis of the machine, or at an angle relative to it. A multi-link suspension is characterized by a complex design and its cost is much higher than a two- or single-link suspension, while the designers managed to achieve close to ideal without deviations in the vertical plane and the effect of “steering” the movement of the wheel. As with any other type of system, guides, damping and elastic elements are used in the structure. Thus, the multi-link suspension device has a number of main components:
- Subframe or frame;
- Cross arms;
- Trailing arm;
- Hub support;
- Shock absorbers and springs.
The independent multi-link that modern cars are equipped with consists of three or five wishbones. The design also uses a stabilizer bar, which prevents swinging of the load-bearing part, reduces the body roll angle when cornering and ensures constant adhesion of the wheels to the road. The subframe (or frame) acts as a load-bearing structural element; transverse arms connected to the hub support are attached to it, which determines its transverse location. Depending on the type of system, shock absorbers and springs can be replaced by a pneumatic strut. The system also contains connecting elements - silent blocks and ball joints, with their help the levers are connected to the subframe.
When installed on a steered axle, the connection to the hub support is made using ball joints, which provide the hub with the ability to change its position angle. Silent block rubber mounts are used on the rear axle, but due to the emerging trend of steering rear wheels, ball elements can also be used. The Multilink suspension is rigidly fixed in relation to lateral and horizontal movement in the longitudinal direction, the car is provided with a smooth ride even on significant road unevenness, as well as excellent cornering. They install a multi-link on both the rear and front axles. In the second case, the levers can be replaced by reaction rods, which are capable of performing the tasks of a stability stabilizer and a lever.
Content
- 1. History
- 2 Basic suspension settings 2.1 Track and wheelbase
- 2.2 Parameters for installing steered wheels 2.2.1 Rolling arm
- 2.2.2 Camber and toe-in.
- 2.2.3 Caster (king pin caster angle)
- 2.2.4 Kingpin lateral inclination angle
- 3.1 Elastic characteristics
- 4.1 Forces acting on the wheel
- 6.1 On a transverse spring
- 7.1 With oscillating axle shafts
Principle of operation
The functioning features of the suspension give the car such important characteristics as handling, stability and smoothness, which generally determine the level of safety. When performing various maneuvers, accelerating, braking, as well as overcoming uneven road surfaces, the system is activated. The ability of the hub to change its position in the horizontal plane, resulting in excellent performance when cornering and other conditions, is a distinctive feature of the design. The independent multi-link suspension is nothing more than the result of the evolution of the double-wishbone suspension. It is more difficult to design a chassis of this type, so it is designed using computer modeling. As a rule, the rear axle is equipped with a chassis with multiple levers, while there are also options where it is used for the front part, and the multi-link suspension scheme involves connecting one of the levers to the steering rack.
There are many chassis options based on the degree of rigidity. The most informative control is provided by a stiffer suspension, but the level of comfort is reduced. A soft suspension, on the contrary, while providing maximum comfort, is inferior in handling, which is why it is so important to implement these necessary qualities in one design. Independent suspension implies the implementation of autonomous operation of the wheels, so the upper and lower arms, independent of each other, are fixed on the body and on the hub, and each of the elements performs its own task, forming the character of the system, be it a change in lateral movement or camber.
The operating principle of a multi-link suspension remains the same as that of a double-wishbone suspension. The displacement of the wheel in the up and down directions relative to the body is ensured by transverse arms, while the trailing arm is responsible for preventing longitudinal movement. Under the influence of damping devices, the rigidity of the movement of the elastic elements is softened and the transmission of the impact force created by the wheel hitting a road unevenness to the body is minimized, which determines the smoothness of the ride. At the same time, the stabilizer performs a function that prevents swaying of the body and rolls. The system, like other components and assemblies of the machine, requires periodic maintenance, and the more complex the design, the more troublesome the maintenance. Suspensions operating in harsh operating conditions will have to be repaired more often.
The main advantages of a multi-lever
Many car models offer either excellent handling or comfort, but the implementation of several levers in the design allows you not to choose between two important characteristics, excluding one of the concepts from the list of advantages of the car. Of course, there are no ideal solutions, just as there is no limit to perfection, so multi-link suspension has its pros and cons. The excellent combination of convenience and ease of control made Multilink a very popular system, despite its shortcomings. It is not for nothing that chassis of this type are used on premium cars. The main advantages of a car with multi-link suspension are as follows:
- The wheels of one bridge are not dependent on each other (for example, only the lever of the wheel that falls into the hole is activated). In the case of a beam, force is transmitted to the adjacent hub;
- Excellent handling, including at high speeds and in conditions of extreme, emergency driving;
- Softening of the hard suspension is achieved due to swinging springs, which absorb the impact of road imperfections, while no shocks are felt in the cabin;
- Stability, excellent grip on the road surface, which ensures a high level of safety;
- Keeping the wheel perpendicular to the road, which ensures an increase in the contact surface and improved traction on the road surface;
- Weight reduction due to the use of aluminum elements in the structure of the system;
- Transverse and longitudinal adjustment of the hub position;
- Protection from noise and vibrations;
- Chassis versatility, it can be used in cars with front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive.
Rear dependent suspensions
In front-wheel drive passenger cars, the design of the rear chassis is much simpler and more reliable than the front. The reason is the absence of rotating elements and drive axles. The most suitable option for such cars is a semi-independent suspension with a swinging or torsion beam.
A semi-independent swing beam design is common on budget cars equipped with front-wheel drive. The system includes the following parts:
- all-metal beam attached to the body on hinges;
- springs inserted between the body cups and special areas on the beam;
- shock absorbers are installed inside the springs or separately;
- lateral stability rods and reaction rods that hold the rear axle under the influence of longitudinal forces.
Article on the topic: Choosing the best SUV within 500 thousand rubles
The system works as follows: during movement, the lever beam swings on hinges, supported on the other side by rods and shock absorbers. Irregularities are smoothed out due to the spring. The wheel hubs are rigidly attached to the rear axle and rotate on bearings.
The second type of semi-independent suspension has a split beam with a torsion bar in the middle. When one of the wheels falls into a hole, this element twists and tends to return to its previous position. Thanks to this effect, torsion bar suspension creates more comfortable conditions for car passengers .
The car's fully dependent suspension is equipped with a solid beam with a built-in gearbox and axle shafts that drive the rear wheels. The structure is supported by a reaction rod system and rests on springs with shock absorbers. Unlike the previous version, the chassis is designed for rear-wheel drive vehicles.
In trucks and commercial vehicles, the rear springs are replaced by a package of springs - elastic steel plates. The middle of the spring assembly rests on the beam, and the ends rest on body brackets. The design is designed to transport heavy loads: the more sheets are used in the spring package, the higher the vehicle's load capacity.
Interesting fact. The popular Mercedes Sprinter minibus is equipped with a single front spring mounted across the body. Moreover, the original part is made of plastic.
Disadvantages of multi-link car suspension
Despite all the numerous advantages, the high cost of a car equipped with a multi-link suspension, which is caused by the complexity of the design, is disappointing. As a rule, the more complex the device, the higher its price, the more expensive it is to maintain and repair. The structural features of the suspension entail another drawback - the level of reliability decreases, since all these hinges, silent blocks, as well as other components wear out and require periodic replacement. The suspension serves regularly up to 100,000 kilometers, but in difficult conditions the period is significantly reduced, bringing the date of replacement of elements closer. The front multi-link suspension is more expensive than the rear, so it is not always advisable to purchase a car specifically in this version. Adding levers with ball joints increases the cost of the entire chassis design. The high cost of components and repairs is justified only in the case of a luxury car. It is precisely these inconveniences that are responsible for the fact that the Multilink suspension has bypassed most of the car market and is not installed on the majority of cars. The suspension for the rear axle has gained the most popularity; it is structurally simpler, the manufacturing cost and the final price are lower.
It is impossible to say unequivocally that one type of suspension is better or worse than another; different systems offer their own advantages of use, so it is more likely that the suspension equipment of a certain type is adapted for the specific purpose of the car. At the same time, each driver has his own requirements for the car, so there is no objective opinion on this matter.
Ford Focus 2 replacement of rear levers: we will tell you in detail
The second generation Ford Focus car is modern and very reliable, both in terms of suspension, engine, transmission, etc. The suspension, by the way, can even cope with our roads and serve for quite a long time.
It should be noted that one of its disadvantages is the complexity of repairs, which is quite difficult to carry out on your own. However, if you have the necessary skills, knowledge and tools, then the process is quite feasible.
Replacing the front and rear suspension arms requires several hours of time, and we will tell you later how to do this correctly on a second-generation Ford Focus.
Damage to the rear suspension arms leads to strange and unusual knocking noises in the lower part of the car, the angles of the rear wheels are disrupted, and the tires wear out much faster. Replacing Ford Focus 2 levers will require you to have the following tools:
- Ties.
- Set of sockets, screwdrivers and wrenches.
- Jack.
- Body supports.
- Pliers.
- Wheel stands.
Replacing the lower arm of the rear suspension is mandatory if it is deformed or the silent block has received any mechanical damage, for example, ruptures, damage to the integrity of the rubber, etc.
Before you start working, you need to drive the Ford Focus 2 onto an overpass or into a viewing hole. It is also advisable to have an assistant, since replacing the levers yourself will be more difficult and time-consuming.
It should be noted that if you are unsure of your abilities, then it is better to entrust the replacement to professionals, because the safety of FordFocus 2 depends on the condition and correct installation and adjustment of the suspension.
Replacing the upper Focus arm
Replacing the upper arm of the Ford Focus rear suspension is carried out when there is mechanical deformation or wear of the silent blocks (cracked rubber, peeling, etc.) To remove the arm, we will need a platform or hole, ties for removing the rear spring and an adjustable stop for the lower arm.
We remove the spring using zip ties, remove the wheel, install an adjustable stop or hydraulic jack under the lower rear arm at the junction of it with the trailing arm, and use the stop to raise the arms so that the rear suspension is in the “car on wheels” position.