Where are V-twin engines used?
To be honest, the popularity of such an engine is due to the fact that it can be used in literally any area and installed on any vehicle. Thus, V-engines can be found in the areas of automobile production, ship and aircraft construction. Many “V”s are now placed on powerful motorcycle models.
In general, it all depends on what kind of power is required and for what purpose. But, in most cases, V-engines are ideal for ensuring that the assigned tasks are completed.
It also remains important how many cylinders are in the engine and how they are located, because the strength of vibration during operation, smoothness and balance depend on this.
W-engine in modern automotive engineering
The modern automotive industry is one of the most developed areas of industry, and constantly improving designs of cars and car engines provide consumers with the widest choice of cars with almost any type of engine.
One of the most popular types of engines used in both passenger cars and crossovers and SUVs nowadays is the W-shaped engine, produced by almost all the world's leading automakers.
The W-shaped engine with its layout makes it possible to reduce the height of the car's engine compartment, which has a positive effect on the aerodynamic properties of the body.
The modern W-twin engine is mainly installed on powerful car models. Indeed, in most cases, this type of engine is produced in no less than a six-cylinder version. In addition to six-cylinder engines, eight- and twelve-cylinder engines are installed on cars, allowing them to obtain high torque and maximum power.
W-engines are divided into gasoline and diesel engines, with diesel engines having much higher torque and lower fuel consumption than gasoline engine types.
Despite the fact that diesel engines initially have a higher price, these power units fully justify their cost, because during long-term operation of a car with such an engine, the visible overpayment will be compensated by savings on material costs for fuel.
Most gasoline engines of this type use a direct fuel injection system, with each cylinder having its own separate injector, which allows for significant fuel savings. In addition, for additional savings, fuel afterburning systems are installed on this type of engine, which allow saving up to 5% of fuel.
To increase power, both gasoline engines and their diesel counterparts can be equipped with one or two turbines, which, depending on the compression ratio, can increase engine power by 25-40 percent.
But the W-engine is a complex and expensive power unit to maintain, so all cars with this type of power plant are in a higher price category compared to cars with classic engines.
The V-twin engine is used in most high-performance SUVs, business class cars, executive cars and sports cars, which provides an unforgettable experience of fast driving.
It is also worth noting the fact that recently W-shaped engines have begun to be used in modern hybrid power plants, which has made it possible to significantly reduce fuel consumption when traveling in urban driving.
Types and modifications of V-engine
Most often, the classification of automobile engines is based on the order of operation. When we talk about V-engines, the order turns out to be completely unimportant, since the division into types and classes is based solely on the number of cylinders in the engine and the features of their location relative to each other.
The most common are engines that have a cylinder angle of forty-five and ninety degrees. The sixty-degree angle is also popular. Most often they can be found in production cars and motorcycles.
The main classification of V-shaped engines in modern automobile production is as follows - budget and middle-class production cars use V2 and V6. Among sports car manufacturers, you can most often find a regular or turbocharged V8. There are also "V" 3, 4, 5, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 and 24.
How did this type of engine come about?
The traditional engine is considered to be in-line, and once upon a time, increasing power was achieved only by increasing the volume of the cylinders. But, of course, everything has its limit, just like the size of the cylinders. In this situation, the designers were forced to come up with a new way to increase power, but at the same time, maintaining the dimensions of the engine. And a solution was found: to obtain more power, engines with 6-cylinders were created, which is perhaps the maximum number for a passenger car.
However, this was not enough, so after some time it was possible to make another discovery - an engine in which the cylinders were located at an angle opposite each other, that is, a V-shaped engine. Its design made it possible to save precious space under the hood, and as a result, both the 6-cylinder V-engine and the 8-cylinder engine are widely used, which is the ideal combination between the dimensions and power of the engine.
Development of V-engines
Most experts are confident that in the future the most common engines in all models and classes of cars will be V-engines. Of course, they have shortcomings, but today they are all gradually being leveled out due to new developments by automakers.
Moreover, their design is much more convenient for various modifications - any V-engine that is in use today has not yet been fully developed in terms of using its full potential. That is, from 1905, when the first patent for this type of engine was acquired, to today, when the automotive industry has reached unprecedented heights, the V-twin engine still has a long way to go. The immediate plans include redesigning the design and reducing the cost so that it will be possible to equip even budget production cars from popular manufacturers.
Operating principle of VR motor
VR is a new engine designation for in-line units. “VR” are two German words, where V-shaped and R-row. The V-twin engine with a small extreme angle of 15° and the in-line engine is developed by the German and represents a symbiosis of the engine. The V-shaped engine has six cylinders at a camber angle of 15°. The standard and traditional 60° or 90° V-twin motor is different from the VR motor. The VR engine is more compact, smaller in width than a six-cylinder V-twin and shorter in length than an in-line six-cylinder. Installed on Sharan, Volkswagen Passat, Vento, Corrado, Jetta, Golf cars since 1991. Thanks to the small camber angle, the VR engine can reduce the lateral and longitudinal size of the unit. VR5 and VR6 have gained popularity. (R) in-line engine - a layout in which the cylinders are located on the same plane. When the number of cylinders is small, use (R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6). The six-cylinder inline engine is easy to reduce vibrations, but it is quite long. The engine is V-shaped, in which the cylinders are located in two planes so that they resemble the Latin letter V. And therefore this angle between the planes is called the camber angle of the engine with the designation of the Latin letter V. A V-shaped engine always has an even number of cylinders, with this arrangement The length of the engine decreases and the width increases. V4, V10, V12, V16 engines are rare. The most common are V6 and V8 engines.
The uniformity of the alternation of working strokes in V-shaped four-stroke engines is influenced not only by the location of the crankpins of the crankshaft, but also by the angle between the axes of the cylinders. To obtain optimal uniformity of running of a two-row engine, this angle, called the camber angle, must be 2 times less than the angle between the connecting rod journals:
γ = δ/2,
where b is the camber angle between the cylinders. In this case, the angle of alternation of working strokes is determined by the formula
φ = 720/(2i)
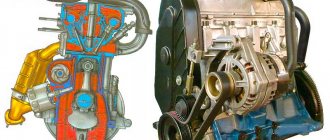
Six-cylinder V-shaped engines (Fig. 2.8, a)
with a camber angle of 90° and angles between the crankpins of 120°, the operating order is 1-4-2-5-6-3. A special feature of the engine is the mounting of two connecting rods on one crankpin. In this case, strokes of the same name in the cylinders alternate unevenly at 90 and 150°. On such engines, to improve the smoothness of running, flywheels with an increased moment of inertia are installed (60...70~% greater than that of an in-line engine). An example of such an engine is the YaMZ-236M engine of the MAZ-5335 car.
Eight-cylinder V-shaped engines (Fig. 2.8, b
) cars GDZ-53-12, ZIL-431410. KamAZ-5320 (Fig. 2.9 and 2.10) are made with a camber angle of 90°. Consequently, the alternation of working strokes is carried out through 90 ° and two connecting rods are attached to each crankpin. The crankpins of the crankshaft are arranged crosswise at an angle of 90°. In an eight-cylinder four-stroke engine, eight power strokes are made per two revolutions of the crankshaft. The overlap of the working strokes in this case is 90°, which ensures uniform rotation of the crankshaft. The operating order of the cylinders of such an engine is: 1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8.
The operating procedure largely determines the design of the engine, in particular the design of the gas distribution mechanism, the ignition system in a carburetor engine and the fuel equipment in a diesel engine.
Rice. 2.8. Diagram of four-stroke V-engines:
A
— six-cylinder;
b
- eight-cylinder
Rice. 2.9. Longitudinal section of the KamAZ-740.10 diesel engine of the KamAZ-5320 car:
1
-fan;
2
— hydraulic coupling of the fan drive;
3
— generator;
4
—manual fuel priming pump;
5
— high pressure fuel pump;
6
— compressor;
7
— fine fuel filter;
8
— fuel pump drive gear;
9
— camshaft;
10
— crankshaft;
11
— flywheel;
12
— connecting rod journal of the crankshaft;
13
— oil receiver;
14
— pallet;
15
- oil pump
Rice. 2.10. Cross section of the KamAZ-740.10 engine of the KamAZ-5320 car:
1—
pallet;
2 —
full-flow oil filter;
3
— crankshaft;
4
— connecting rod of the right (in the direction of the car) row of cylinders;
5
— piston with piston rings;
6
— cylinder head;
7
—nozzle;
8 —
rocker arm;
9
— inlet pipeline;
10
—manual fuel priming pump;
11
— high pressure fuel pump;
12
— exhaust valve;
13
—exhaust pipeline;
14
— piston pin;
15
— camshaft;
16
— connecting rod of the left (in the direction of the car) row of cylinders;
17
- oil pump
Topic No. 3
KShM.