Signs of a diesel turbine malfunction
A turbine is a complex power-injecting device.
Unlike many other components of a modern car, its malfunction is not critical. However, it must be clarified that in this case there will be no normal operation, and the leakage of expensive oil and fuel will seriously hit the owner’s pocket. What signs of a diesel engine turbine malfunction can you detect on your own? To begin with, it should be noted that the typical manifestations of a diesel turbine failure are very similar to the failure of other units and systems. Therefore, to accurately determine the cause of the appearance of a particular factor, it is necessary to carry out high-quality diagnostics using special stands and measuring instruments. An ordinary car enthusiast cannot do without contacting a service station.
see also
How to check a turbine
Oil leaking from turbine
Intercooler
Turbine check with VCDS program
A car turbocharger, despite the durability (10 years) and wear resistance promised by the manufacturer, still malfunctions, malfunctions and breaks.
Therefore, it is necessary to troubleshoot the turbines of both diesel and gasoline engines from time to time. And in order to identify signs of malfunction in time, you should always pay attention to the non-standard behavior of the car. The turbine fails if :
- there is a feeling that traction has disappeared (power has decreased);
- when the car accelerates, blue, black, and white smoke comes
- when the engine is running, a whistle , noise , or grinding noise ;
- consumption has increased sharply or there is an oil leak ;
- Air and oil often drops
If such symptoms appear, then in these cases a thorough check of the diesel turbine is necessary.
Characteristic signs and possible causes
Often there is a combination of several obvious manifestations of a breakdown, but sometimes only one is observed. The malfunction can be determined by the following phenomena:
- increased oil consumption and leakage;
- change in color and visual increase in the amount of smoke;
- engine noise;
- temporary or permanent overheating;
- noticeable decrease in power and speed of acceleration;
- increased fuel consumption;
- increased emissions of harmful substances from the exhaust system and toxic odor;
- whistling or scratching in the turbine itself;
- floating idle.
The appearance of any of these items requires attention from the owner, prompt diagnosis and repair of the breakdown. The fact is that the lion's share of problems with diesel turbines, one way or another, relates to leakage and oil consumption. When it ends, the work surfaces will begin to wear off. To completely fail this mechanism, it is enough to work for just a few seconds without a lubricant. After this, restoration and repair will become impossible, all that remains is a complete replacement, and this is not cheap.
OlegShakirov › Blog › The main reasons for the breakdown of turbochargers and their repair
Modern environmental regulations are forcing automakers to increasingly use turbocharging designs in engines. And if previously turbocharging was the province of sports cars or trucks, now it can be found under the hood of almost any new car. It is all the more interesting to understand the practice of repairing turbochargers.
It so happens that most repair shops in the event of any problem with turbocharging almost immediately condemn the turbocharger to a complete replacement, since the complexity of the device itself and the impossibility of returning factory characteristics without special equipment have given restored turbines a bad reputation.
Also, many believe that it is better to take a non-original turbocharger made in the Middle Kingdom, but as practice shows, the “Chinese” analog tries to copy the original part only in external form, but not in content, and in the future such savings can affect not only the resource of the unit itself, but also cause the car engine to fail.
Smoke color and exhaust smell
The appearance of smoke in the exhaust system immediately draws attention. This is often accompanied by an unpleasant chemical odor that can be heard even while driving.
Black smoke
This phenomenon means the combustion of the fuel mixture in the turbine. The problem is caused by a lack of air in the fuel system. Need to check:
- tightness of connections of all pipes;
- ECU;
- air filter (most often this is the cause);
- performance of the fuel system;
- engine.
Bluish-gray color
In this case, oil enters the engine. Obviously, the reason lies in the leak. It is necessary to inspect all connections, and the reason lies in problems with the turbine or engine.
Milky white color
Most often this happens when the oil drain line is clogged.
Uncharacteristic sounds
First you need to open the hood and determine the source of the noise. If sounds come from the turbine side, then you need to check the rotor and axle for chips and freedom of movement. Characteristic scratching means deformation and cracking. A whistle indicates air is passing through. Sometimes this happens when the throughput of the oil pipeline deteriorates or foreign objects enter.
Obviously, most of the signs indicate breakdowns in the air supply system, oil lines, ECU, rotor and axle. Sometimes objects get into the system. Diagnostics comes down to checking these elements first.
Signs of a diesel engine turbine malfunction also appear during inept installation and disassembly. An inexperienced craftsman often damages parts, which cost a considerable amount of money. In order to check the turbine, you do not need to remove it - service station specialists do without this, performing the procedure only when necessary. We can confidently attribute inept dismantling to frequent causes of breakdown of this vehicle component.
Signs of a turbine malfunction
OR HOW TO SAVE ON A TURBINE.
Don't rush to change the turbine! Bring the turbine for diagnostics to us, to TigerTurbo, or do the diagnostics yourself.
The first signs that make you pay attention to the operation of the turbocharging system:
- Increased consumption of engine oil (the engine consumes oil). May be accompanied by blue (or gray) exhaust
- Significant loss of engine power. May be accompanied by black smoke from the exhaust pipe (engine smokes)
- Noise during turbocharger operation
So, you have noticed one of the above signs. There is no need to immediately blame the turbine, and even more so, there is no need to run to a service center to change the turbine. The modern original turbine is a very reliable unit. Its trouble-free service life is equal to the engine service life.
According to statistics, 95% of turbines fail for the following reasons:
- Foreign objects entering the turbine through the turbine housing or compressor housing.
- Dirty motor oil
- Turbine oil starvation
- Exceeding the permissible rotor speed (leads to “overcharging” of the engine)
Entry through the turbine housing.
As a rule, destroyed engine elements get through the turbine housing: parts of valves, pistons, piston rings, glow plugs, manifold gaskets.
Entry through the compressor housing.
Occurs, as a rule, due to a damaged filter or a loose or damaged inlet pipe, as well as due to tools or rags left during repairs.
Occurs due to the ingress of coke deposits of oil or abrasive particles as a result of natural wear and tear of engine rubbing parts.
This can happen for several reasons: oil pump malfunction; clogged oil filter, damaged or clogged oil supply tube; sudden engine stop.
Exceeding the permissible rotor speed.
Occurs mainly due to improper operation of the actuator (the bypass valve is stuck in the closed position) or the nozzle apparatus - “geometry” (the blades are stuck in the closed position). The second reason may be increased exhaust gas temperature resulting from incorrect injection - check the fuel equipment.
Try to carry out simple diagnostics of the turbine yourself directly on the car.
Visually check the integrity of the impellers
If technically possible, disconnect the air supply pipes and inspect the impellers on the turbine side and on the compressor side. The impeller blades must not be damaged and must not have nicks or bends.
Let us determine the turbine play - axial and radial.
Mechanical damage to the turbocharger
5.1.Damage to the compressor impeller due to hard objects
Solid objects entering the air supply channel and further into the compressor can cause irreparable damage to it. This could be a washer, nut, or any plastic part that has fallen into the channel as a result of careless repairs. A damaged compressor impeller loses balance, after which the turbocharger completely fails within a short period of time. In the worst case, the rotor shaft may break or the compressor impeller may break (photo 18-20).
5.2.
Damage to the compressor impeller by soft objects
Despite the fact that some objects falling into the compressor are soft, the consequences are no less dire. Dry leaves, a piece of rags, paper or cardboard can get into the compressor, and any of these items causes serious damage to the impeller, after which the entire unit fails. The reason is the imbalance of the rotor, which leads to rapid destruction of spacer bushings and bearings. In the worst case, the rotor shaft may break. Soft objects cause deformation of the compressor wheel blades, and in some cases fatigue failure of the blades occurs (photos 21,22).
5.3.Abrasive damage to compressor impeller blades
Abrasive particles (dust, sand) can enter the turbocharger air line, which gradually wear out the impeller. The shape of the shoulder blades changes, they become smoother and thinner. And although there is no imbalance observed - the surfaces are erased evenly, but the working surface of the wheel decreases, which leads to a drop in the productivity of the unit (photo 23).
The most likely reason for abrasive particles entering the air duct is problems with the air filter. In particular, it can be deformed in such a way that part of the air is not filtered. The cause may also be a leak in the pipe from the air filter to the inlet to the turbocharger. There is a vacuum in this part, and dust and sand are simply sucked inside. Another possible reason is a leak in the crankcase ventilation system.
5.4.
Damage by foreign objects on the turbine side
As already mentioned, the turbocharger operates at conditions close to the limit. Therefore, even small foreign objects entering the turbine part can lead to catastrophic consequences. This could be scale, carbon deposits, sand particles, or a piston or valve fragment. The most severe case is the separation of the turbine impeller. In variable geometry systems (VNT), the blades can be damaged, which will lead to failure of the control system (photo 24, 25).
The main signs of a turbine malfunction.
The most characteristic and common sign of a faulty turbine is the release of blue smoke from the exhaust pipe and the smell of oil fumes , which is especially noticeable when the car accelerates intensively, and when the engine runs at low speeds, the blue smoke disappears. It is logically clear that the cause of the malfunction is oil entering the combustion chamber, and the consequence may be its leakage from the turbocharger.
Black color from the exhaust pipe and a possible loss of traction indicate the combustion of an over-enriched fuel-air mixture, resulting in an air leak in the injection lines or in the intercooler. The cause may also be a malfunction of the turbocharger control system.
The next sign of a malfunction is the appearance of white smoke from the exhaust pipe . The cause may be a clogged turbine oil drain line.
Traces of oil leaks on the air duct pipes as well as on the turbine itself and naturally increased combustion, frequent addition of oil. The cause is a malfunction of the turbocharger; this could be affected by clogging of the air mixture supply channel, oil drain line, or coking of the axle.
The appearance of any extraneous noise, grinding or surging during operation of a turbocharged engine, the reason may lie in an air leak at the compressor outlet.
A low-quality oil filter can cause low oil pressure , as well as poor flushing, which is popularly called a five-minute flush.
Destruction of the plain bearings will soon lead to irreversible damage to the rotor impeller.
Lack of turbocharger lubrication
4.1.Malfunctions of TC components and parts due to insufficient lubrication, both temporary and permanent
A lack of lubrication in a turbocharger has symptoms very similar to those that occur when the oil is chemically contaminated. In this case, a change in the color of the rotor and sleeve bearings is observed. From silver-white, these parts change color to yellow or even blue-black. Subsequently, if the cause of the lubrication deficiency is not eliminated, destruction of the rotor shaft may follow. The most serious consequence may be a turbine wheel coming off. The spacer bushings and plain bearings are also destroyed (photo 15-17).
Possible causes of TC lubricant deficiency:
— general malfunction of the engine lubrication system, including wear of oil pump parts, malfunction of the oil pump pressure reducing valve, excessive clogging of the oil filter;
— presence in the crankcase pan of large deposits of coked oil and foreign objects (pieces of gaskets, metal fragments, etc.)
In this case, when the engine is idling, the oil pressure in the system is within normal limits. As the crankshaft rotation speed increases, the performance of the oil pump increases, which leads to the contaminants present in the sump being drawn to the oil receiver grid, and this can lead to a significant drop in pressure in the system just at the moment when the engine is running under load and needs lubrication. In this case, the emergency pressure sensor in the lubrication system does not work - the pressure in the system remains above the minimum, but it is not enough to ensure lubrication of the turbocharger, which operates in the most difficult conditions;
— reduction in the amount of oil supplied to the turbocharger due to improper condition of the supply tube. The tube may be clogged with coke deposits or mechanically damaged;
— clogging of the oil passages of the turbocharger housing. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon, and the most likely of them is the ingress of coke particles into the channels from the supply line of the TK lubrication system. When repairing the unit, it is recommended to replace the supply line with a new one. As a last resort, it is enough to thoroughly rinse and blow it to eliminate, if possible, the presence of contaminants in it. The oil channels of the TC housing may be blocked for other reasons. Some models of turbochargers have an additional oil filter, which is a fine mesh in a plastic housing. Plastic may break down during use. and its particles fall into the channels and block them. Also, the plastic housing can be destroyed as a result of improper installation.
Causes of turbine failure.
Let's look at four main reasons for turbine failure.
Oil contamination
Quite often, a seemingly good oil that is too early to change may be contaminated with small particles that cannot be detected visually. Small particles gradually wear out the bushings, causing their edges to become rounded.
Lack of lubrication
This leads to the fact that the turbine shaft wears out very badly, and in addition to it, the bushings wear out and the permissible temperature is exceeded. This can be caused by an oil channel that is loaded with dirty gasket material or sealant.
Extreme loads on the turbine
“As they say, if you love to race, you also love to fix.” The most typical failure is the plain bearing on the bushings as a result of torsion, overblowing and high temperature of the turbine. As for the shaft, it bends as a result of the load, and the burnt oil cokes it. Torque of the turbine leads to breakage of parts of the turbine shaft blades.
Damage from foreign bodies
This malfunction can be immediately determined by looking at the compressor volute; such a malfunction often leads to an overhaul or replacement of the engine, and it will not be possible to stop only at repairing the turbine.
Causes of breakdown and failure of the turbocharger.
There may be several reasons for a turbine to fail, however, if you follow all the technical regulations for car maintenance, oil changes and carry out vehicle maintenance on time, then the turbocharger installed on the car will serve you for many years and the car’s mileage is 200-250 thousand km with one a turbine is not uncommon, but simply paying close attention to your car and complying with the requirements for its long-term and trouble-free operation.
We recommend that you watch a video from Garrett dedicated to problems with turbines and proper handling of them:
Now let's talk about the problems in more detail:
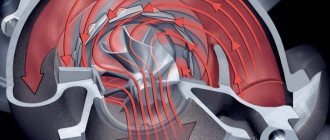
How does it work
The operating principle of a turbocharger is quite simple: the turbine rotates by using the energy of the exhaust gas flow. The turbine is connected to the compressor by a rigid axis. The compressor draws in fresh air through the air filter, compresses it and then pressurizes it into the engine intake manifold. The more air supplied to the cylinders, the more fuel can be burned, which increases engine power.
Despite the fact that more fuel is required to supply more air, a turbocharger, compared to engines of similar power but without a turbocharger, does not “eat up”, but saves fuel. In addition, the engine with a turbine is smaller in weight and dimensions than usual. Perhaps the only drawback of this system can be considered changes in the thermal balance of the engine. If the turbine processes excess heat, pulsation and back pressure (the so-called turbo effect) can serve as a factor due to which the turbine housing will burst, followed by bearing failure, oil leakage and the engine, as they say, “die”. This is very important to consider for proper engine operation!
How to check a removed turbine
The skills of checking whether a turbine is working will come in handy when buying a used spare part at a disassembly. So, you need to know:
Cooler play
During the process of dismantling the pipe, it makes sense to check the play of the installed cooler. Please note that a distinction is made between transverse (radial) and longitudinal (along the axis, axial) play in relation to the housing. So, longitudinal play is not permissible, but transverse play is not only permissible, but will always be there. Transverse play can be checked without removing the turbine, but longitudinal play can only be checked by dismantling the unit.
To check the cooler axis, you need to gently shake it with your fingers towards the walls of the turbine circumference. There will always be transverse play; when the turbine is in good condition, its range is about 1 mm. If the play is significantly greater, the turbine is worn out. And the greater this play, the greater the wear. In parallel with this, it is necessary to assess the condition of the turbine walls. In particular, look for traces of the cooler blades on them. After all, if it wobbles a lot during operation, then its blades will leave marks on the turbine body. Repairs in this case can be expensive, so it is better to refuse the purchase.
Blade condition
In addition to checking for marks, you also need to check the condition of the blades themselves. New (or remanufactured) turbines will have sharp edges. If they become dull, it means the turbine has problems.
However, the edges of the blades can become dull for another reason. In particular, sand or other small debris flew into the turbine with air, which over time wore down the blades. This could happen for various reasons. The most common of them is that the air filter was not changed on time. Using a turbine with worn blades can result in a loss of vehicle power and increased fuel consumption.
However, the most important nuance when blades wear out is imbalance . If any of the blades, due to grinding, have less mass, this will lead to the emergence of a centrifugal force, which will gradually break the cooler bearing, which will significantly reduce the overall life of the turbine and quickly disable it. Accordingly, it is not recommended to buy a turbocharger with worn blades.
Presence of mechanical damage
It is imperative to inspect the turbine housing for mechanical damage, in particular dents. This is especially true if a car owner wants to buy a used turbine, removed from a car that has been in an accident. Or a turbine that was simply dropped on the floor and a small dent appeared on its housing. Not all dents are critically dangerous, but it is desirable that there are none at all.
For example, after an impact, some threaded connections inside the turbine may become loose. And during engine operation, especially at high speeds and power of the turbocharger, the mentioned connection can completely unwind, which will certainly lead to significant damage not only to the turbine, but also to the engine.
Checking the turbine actuator
Actuators are valves that control the mechanism for changing the geometry of turbine exhaust gases. Returning to mechanical damage, it is worth noting that dents should not be allowed on the actuator body. The fact is that if its body is damaged, there is a high probability of a decrease in the stroke of its rod. In particular, it will not reach its highest position. Accordingly, the turbine will not work properly and its power will decrease.
How to check a turbine actuator
The peculiarity of actuators is that they are very sensitive to corrosion. However, the problem is that without dismantling it is not possible to examine the presence of rust. Accordingly, when checking, you should always pay attention to the presence of corrosion at the base of the rod. It shouldn't be there at all!
If there is rust on the base, then the inside of the valve will be rusty. And this is almost guaranteed to lead to the fact that the rod will jam, due to which the turbine will not operate in normal mode and its power will decrease.
The main thing is proper operation
Turbines have one serious problem - they begin to operate in extreme conditions for the engine. Truck turbines rotate at breathtaking speeds (70 - 100 thousand revolutions per minute). With this rotation and exposure to exhaust gases, the turbines quickly heat up. Overheating, large amplitude of temperature fluctuations and malfunctions in the lubrication system are the main enemies of turbochargers.
To prevent these enemies from overpowering the turbine, it is necessary to properly monitor the condition of the engine and operate it correctly. The operating rules are quite simple, you just need to remember about them.
It is believed that the operating life of a turbocharger is equal to the operating life of the engine, however, the turbine is very sensitive to its operating conditions, so the “life” of the turbine ends, as a rule, earlier than the “life” of the engine. Vitoldas Sakalauskas, head of service at Volvo Lietuva, says that with proper operation, turbochargers of trucks operating on international routes can withstand at least a million kilometers. The service life of turbochargers is greatly influenced by climatic conditions, terrain and route complexity. Kestutis Chapas, a car mechanic, says that sometimes cars with a mileage of 1.5 million kilometers come to the service center, and the turbines of such cars are in excellent condition. In such cases, only the repair kit is replaced, and the car can move on.
In a commentary on engine life, V. Sakalauskas mentioned that he had encountered trucks whose mileage was 2.5 million kilometers.
Preventing turbine breakdowns
To extend the life of your turbocharger, follow these simple rules:
- Change air filters promptly.
- Fill with original oil and high-quality fuel.
- Completely change the oil in the turbocharging system after every 7 thousand km .
- Monitor the boost pressure.
- Be sure to warm up a car with a diesel engine and turbocharger.
- After a long drive, allow the hot engine to cool down by idling for at least 3 minutes before turning it off. There will be no carbon residue that harms the bearings.
- Carry out regular diagnostics and ensure professional maintenance.
Malfunctions in the lubrication system are the reason for the breakdown of half of the turbines
Experts say that almost half of the turbines fail due to faults in the lubrication system. Approximately 40 percent. turbines deteriorate due to small foreign objects entering the turbine blades - as a rule, they enter the turbines from the engine or air supply system. The remaining 10 percent breakdowns occur for other reasons (due to overheating, design defects, etc.).
The bearing is the part of the turbocharger that is under constant load. To ensure that the bearing does not fail, a sufficient amount of lubricant is necessary. Engine oil performs this function - it not only lubricates, but also cools the bearing. If foreign objects get into the engine oil, friction will begin on all lubricated surfaces, which will accelerate the wear of these surfaces. Reducing the pressure in the engine oil at freewheeling will not cause damage to the engine, but at high speeds it can cause a decrease in engine life.
In order to avoid such troubles, you need to promptly change the engine oil and filters, and keep the lubrication system clean. When it comes to oil, it is best to choose the oil recommended by the truck manufacturer. Speaking of cleanliness, any foreign object that enters the turbine through the air filter can cause premature wear of this unit, or, worse, melting of all parts of this system. Therefore, V. Sakalauskas reminds not only about timely replacement of engine oil, but also about replacing the air filter. Solid particles can enter the turbine through the air supply system, causing impact marks on the compressor blades; over time, the blades can lose balance and break. Similar problems can arise if air hoses are cracked.
The turbine may begin to overheat due to low-quality fuel or improper engine adjustment. The fact that the turbine is overheating is indicated by pale spots on its body. If this problem is not corrected in time, through cracks may appear in the turbine wheel housing. The oil that lubricates the turbine can “burn out” due to high temperatures and turn into coke, and this will lead to corrosion of the shaft, its seals and even bearings.
In order to extend the life of the turbine, it is recommended to start driving the car at least one minute after starting the engine. This is important to remember during the cold season when the oil thickens. In such cases, it takes time for the oil to reach the bearings, so in cold weather, do not rush to move.
Another rule is to let the engine idle before stopping the engine. It is very important not to forget about this after a long flight when the engine was operating under high load. The engine and turbine must cool down - otherwise carbon deposits will appear on the hot turbine, and this, in turn, reduces the life of the seals, bearings and turbine housing.
Turbocharger malfunctions
Often, the dismantling of the turbocharger is carried out regardless of whether the engine has been tested to identify faults. Meanwhile, testing makes it possible to save the car owner from the useless procedure associated with replacing the turbocharger. Based on this, you should know the main malfunctions caused by improper operation of the turbocharger:
- the engine does not develop full power;
- smoke coming from the exhaust pipe is black or blue;
- oil consumption increases;
- The operation of the turbocharger is accompanied by excessive noise.
Black smoke and reduced engine power The symptoms listed in the headline may indicate a problem associated with a decrease in the volume of air entering the engine. The main reasons in this case can be considered air leakage from the pipelines, the heat exchanger of the ONI or the turbocharger connections. It is also possible that the air supply channel becomes clogged. If the area where the engine and the turbocharger output connect is considered problematic, then you must keep in mind that often a defect of this type can be identified by the whistle emitted by the air that rushes out. In addition, you should always check the condition of the air filter and the channel supplying air to the turbocharger. In the event that these measures do not lead to a positive result, the exhaust manifold and seals, as well as pipelines should be checked for clogging. In this case, it is necessary to exclude the presence of cracks, weak tightening of bolts, and possible damage to connections and gaskets. The rotation of the turbocharger rotor must be easy, so it is necessary to monitor compliance with this condition. In a standard situation, the rotor is caused by the presence of slight play, but if the turbine wheel touches the housing during rotation, then we can say that the bearings are seriously worn out. In the event that checking all components of the turbocharger did not reveal any malfunctions, you should look for problems directly in the power unit.
Blue Smoke and Excessive Oil Consumption If oil leaks, oil combustion may produce blue smoke. In this case, you should first check the air filter. If the air flowing to the compressor encounters an obstacle on its way, this could be the reason leading to an oil leak. This condition is associated with the appearance of a vacuum area behind the compressor wheel, which implies the flow of oil located in the bearing housing directly into the compressor itself. At the next stage, it is necessary to check the free play of the rotor to prevent the wheels from touching the inner surface of the turbocharger housing. In certain cases, oil leakage is possible when the turbocharger is working properly. In this case, it is the compressor turbine that can become a problem area, for example, the oil line is clogged or there is an increase in pressure in the oil crankcase of the power unit.
Excessive noise Interruptions in the operation of the turbocharger due to excessive noise can be caused by loosening of bolts, nuts and clamps, which are fasteners for pipelines under pressure. In this regard, the reliability of connections in the gas pipeline and exhaust systems should be checked. As in previous cases, it is necessary to prevent the wheels that are part of the rotor and compressor from touching the device body. If this fact occurs, then the turbocharger should be replaced. To ensure that the malfunctions discussed above occur as rarely as possible, do not forget about timely and regular engine maintenance. In particular, checking the tightness of the system, for example, gaskets, hoses and flange connections, will avoid air and exhaust gas leaks, which greatly affect the optimal operation of the turbocharger. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically check the reliability of all fastenings of the turbocharger elements.
The main causes of damage to turbochargers Basically, problems with a turbocharger arise in three cases:
- low oil volume;
- high level of oil contamination;
- presence of foreign components in the oil.
Oil contamination, as well as its lack, are the reasons why turbocharger bearings become unusable. In turn, this circumstance leads to imbalance, and this causes friction between the turbocharger wheels and the housing walls, which can cause mechanical damage to the rotor shaft. In accordance with this, it is necessary to promptly replace filter elements and oil, based on the brands recommended by the manufacturer. It is also advisable to follow certain driving rules, which must be correlated with the operating characteristics of an engine equipped with a turbocharger. In particular, stopping an engine operating at high speeds leads to the fact that the turbocharger rotor does not stop rotating, and no lubricant is supplied to it at this time, since the oil pressure in the engine comes to almost zero. This puts both bearings and O-rings at risk of damage. Based on this, stopping the engine, which was previously running under load, should be carried out with a preliminary setting of the idle mode for at least three minutes. The same rule applies in reverse, when the engine must idle for about five minutes before applying full load. As for the entry of foreign objects, for example, into the intake channel of a turbocharger in the form of fragments of the same piston rings, this is quite possible and can cause damage to the rotor or wheel. At the same time, even small particles such as sand and dirt can wear off the edges of the wheel blades if the air supply route is not sealed, which causes the penetration of abrasive materials of this type. Such wear of the blades will unbalance the rotor and trigger further damage. In particular, even a small imbalance in combination with high rotor speeds will not only damage the bearings, but will also harm other components of the turbocharger. When carrying out maintenance, you should always check the ease of movement of the turbocharger rotor. To do this in practice, it is necessary to dismantle the exhaust pipe that serves to remove exhaust gases. After this, check by hand the freedom of rotation of the rotor in the extreme axial and radial positions. The rotation of the rotor should be easy to move without any contact with the turbocharger parts related to the static elements of the system. Technical maintenance regulations determine the need to dismantle the turbocharger at least once during a two-year period to carry out general diagnostics and cleaning of the centrifugal compressor.
Cleaning the centrifugal compressor The turbocharger must be removed without disconnecting the exhaust manifold. To do this, first remove the part of the oil line that is attached to the compressor adapter, and then disconnect it from the manifold. In this case, cleaning the centrifugal compressor must be carried out in compliance with the following stages of work:
- remove the fasteners in the form of bolts that hold the compressor housing. Using a hammer, directly disconnect the compressor housing. To do this, you need to make light blows on the structural elements in the form of bosses. Then inspect the condition of the sealing ring located in the groove of the cover. If defects are diagnosed, the sealing ring should be replaced;
- assess the condition of the compressor wheel, in particular its blades. If traces of contact of the blades with the compressor body are detected, replace them or contact a specialized service for repairs, if this is economically justified;
- Proceed directly to cleaning the internal cavity of the housing using a rag, which must first be moistened in diesel fuel. As for cleaning the inter-blade surfaces, the optimal tool here is a hair brush, also dipped in diesel fuel;
- check the ease of movement of the rotor;
- proceed to the assembly process, taking into account the alignment of the marks applied to the end surfaces of both the compressor housing and the cover. In this case, the O-ring must be lubricated with engine oil and the bolts must be tightened using a torque wrench.
When the assembly is completed, you should check again how freely the rotor rotates. The rotor wheel must not in any way come into contact with the housing parts. It should be borne in mind that the work of balancing a turbocharger rotor is a high-precision process that can be carried out at a high-quality level only if special equipment, appropriate tools and professional personnel are available, and this is ensured exclusively at specialized enterprises. Seasonal maintenance involves removing condensate from the ONV heat exchanger. This can be implemented in practice by turning the heat exchanger over so that the pipes face down, which will allow not only the remaining condensate to drain, but also the oil. After this, it is necessary to use compressed air to blow through all rows of heat exchange plates in turn, avoiding any deformation. If the heat exchange plates are too dirty, then hot water can be used for washing, which involves two methods of implementation. First, a method of dipping this turbocharger element into a bath of hot water. Secondly, placing it under running hot water and then cleaning it with a hair brush. The last stage involves blowing with compressed air and drying under hot air streams.
Defects detected on turbochargers produced by KAMAZ-Diesel OJSC Extraneous noise. The most frequent complaints from drivers, as well as employees of auto centers, are related to extraneous noise that occurs during the operation of turbochargers from this manufacturer, which often turns into a whistle. Typically, this type of noise is caused by foreign objects getting on the wheel blades or by the blades touching the internal parts of the compressor or turbine housing. In addition, the reason may be a lack of tightness or the presence of deformation in the routes used to supply and exhaust air (gas), and the appearance of extraneous noise is influenced by the air filter if it is heavily soiled. In this case, complaints are rejected by the manufacturer in cases where the design dimensions of the turbocharger are met, compliance with control parameters is observed and there is no contact between the compressor and turbine blades of the static elements of the housing. Large rotor play. They are also distinguished by the consistency of complaints from drivers and dealers of auto centers due to the presence of large axial and diametrical play of the rotor. The occurrence of this condition is determined by the design nuances of the Kamaz family of turbochargers and usually it correlates with the permissible values that guarantee the operation of the supercharging unit. Oil leak. A remark of this kind is quite common and is often included in claims. If the operating rules are fully observed and the rotor parts, as well as the housing cavity seal assembly, comply with the requirements of the design documentation, then practically no oil leakage is observed. Otherwise, the reasons affecting the occurrence of oil leakage include:
- high percentage of engine CPG wear;
- poor performance of engine crankcase ventilation;
- the air filter is too dirty;
- problems associated with the supply and exhaust routes for gases, air and oil, which may be contaminated or deformed;
- excessive contamination of the wheels and turbocharger housing;
- unbalance of the rotor, which can jam;
- wear and breakage of seal rings;
• a transport plug installed on the oil drain hole, which must be removed when installing or replacing the turbocharger. In any case, you should follow certain operating modes of a turbocharged engine to protect yourself from unnecessary problems. In particular, shorter idle operation of the power unit will avoid oil leakage from the turbocharger and, accordingly, its entry into the flow parts of the internal elements of the turbocharger, as well as into the engine cylinders. If this condition is not met, then coking of the piston rings will occur, and the turbine in its flow path will become dirty and carbon deposits will appear on it. In cases where the operation of the power unit at idle is a forced necessity, for example, warming up or pumping air into cylinders related to the brake system, you should control the frequency at which the crankshaft rotates (not lower than 1000 rpm) . If the engine was operating under high load, before stopping it, you should go to idle speed, which should correspond to a minimum time of three minutes. This will avoid overheating of the bearing and coking of the rotor. In principle, instantly stopping an engine that was previously operating under high load is an incorrect action on the part of the driver.
Compliance with safety rules 1. The turbocharger must be installed exclusively on the power unit that is intended for this purpose. 2. The turbocharger and engine may be damaged if misused, unauthorized modifications are made, or the intake/exhaust and fuel delivery systems are altered. 3. Touching a running turbocharger, or immediately after it has stopped, is prohibited, since rotating parts and hot surfaces are factors that can lead to possible injuries. 4. Installation of the turbocharger must be carried out on the basis of the instructions and recommendations received from the engine manufacturer, in particular:
- When installing a new or repaired turbocharger, it is imperative to change the engine oil, air and oil filters, of course, if they have not been replaced relatively recently. At the same time, in technical terms, filters must meet the requirements put forward by the engine manufacturer;
- it is necessary to ensure that all plugs are removed;
- the pipelines connected to the turbocharger must be clean, since any foreign object that gets into them will inevitably lead to breakdown;
- The gaskets used must be checked for compliance. The use of paste or liquid for sealing is strictly prohibited;
- fastener elements due to the presence of threads must correspond to the values given in the manufacturer’s documentation;
- Starting the engine should be accompanied by checking the turbocharger connections for leaks. Before putting a load on the power unit, you should idle it for three minutes.
Signs of trouble in the turbine
The dream of any driver is not to encounter unexpected malfunctions during a trip, so any potential problems must be prevented. What signs indicate the impending “demise” of the turbine?
K. Chapas says that malfunctions in the turbine are indicated by the appearance of extraneous sounds, an increase in smoke, an increase in oil consumption, and sometimes a decrease in thrust. In this case, fuel consumption may remain unchanged.
One of the signs of a turbine malfunction is an unusual sound, similar to a whistle. As a rule, this means that cracks have appeared in the seals or in the turbine housing, and exhaust gases or air pass through these components, as they say, “with a whistle.”
Another sign of turbine damage may be an oil leak. You can determine this problem yourself - to do this, you need to turn off the engine, remove the intake air duct and inspect the condition of the blades. There should be no damage to them. The blades should rotate easily and smoothly, without getting stuck anywhere. The bearings should not wobble.