Seeing unfamiliar letters, a potential car owner will definitely ask what a CRDI engine is.
You need to know what you are going to buy, what you are paying honestly earned money for, what you will get for it - including, and what problems are planned in the future. What’s interesting is that for some reason such a motor power system is considered almost exotic, and therefore arouses some mistrust. However, this is a misconception: many automakers equip their products with it. They just call the system differently.
For example, Volkswagen calls it TDI, Fiat even has several names: CDTi, TtiD, DdiS, JTD; and General Motors may indicate that the car is equipped with CDTi or VCDi. The names are different - the essence is the same. Another interesting but little-known fact: motors with a similar power supply are widely used in shipbuilding and railway trains. This alone can significantly increase the degree of trust in her.
Content
- The essence of the idea and the principle of its implementation
- What does the CRDI system provide?
- but on the other hand
What a CRDI engine is can be understood simply by deciphering the abbreviation. It stands for Common Rail Direct Injection, which, to a first approximation, should be interpreted as direct (injection) injection of the fuel mixture along the highway. However, the interlinear translation covers little of the technical side of the issue, so let’s figure out what we’re dealing with.
The essence of the idea and the principle of its implementation
The idea is to make the pressure in the entire supply system independent of the frequency at which the crankshaft rotates and also of the volume of fuel supplied. In conventional injectors, diesel fuel is supplied to the nozzles with a lower pressure, which rises during subsequent processes.
CRDI uses a common accumulator to create the required pressure, after which the fuel enters a common rail, also called a common rail. The needle on the nozzle rises not as a result of exposure to higher pressure, but by a special solenoid built directly into the nozzle.
Due to the fact that the two most important processes - creating the required pressure and direct fuel injection - are separated, it has become possible to carry out injection in several phases, and they can be used in parallel during one working stroke. On the first models of this system there was a two-phase injection; in modern, more advanced variations, the number of phases has increased to 9.
1. Description of TDI
1.1.
Properties 1.2. Handling, transportation, storage 1.3. Receipt 2. Application
2.1 Application by industry 2.2 Application by type
Description
The concept of TDI combines three main groups of products: TDI 100, TDI 80, TDI 60.
1.1. Properties of TDI.
TDI is a representative of the class of organic isocyanates (more precisely diisocyanates): substances containing the functional group –N=C=O
, the reactivity of which determines the widespread use of such compounds.
Rice. 1. 2,4′-TDI
Rice. 2. 2.6′-TDI
Toluene diisocyanate
(TDI, TDI), [toluene diisocyanate, toluenediisocyanate]
Toluylene diisocyanates are liquids or crystals (depending on the isomer) from white to yellow in color with a pungent, pungent odor. Toluene diisocyanates are soluble in aromatic and chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons, nitrobenzene, diethyl ether, acetone and other aprotic organic solvents. Reacts with water and alcohols.
TDI has 2 most common isomers: 2,4-TDI and 2,6-TDI.
2,4-TDI
[TDI 100, TDI T-100, pure TDI, TDI 100] – liquid (at room temperature) with a solidification point of 21.8°C, boiling point 250°C. Density (20 °C) 1.2178 kg/l.
2,6-TDI
– liquid (at room temperature) with a solidification point of 8.5°C, boiling point of 120°C. Density (20 °C) 1.2271 kg/l.
Properties of TDI mixtures:
2,4-TDI (80%) + 2,6-TDI (20%)
[simply TDI, TDI 80, TDI, TDI T-80, TDI 80/20, “component B”] – liquid (at room temperature) with a solidification temperature of 13.89 ° C, boiling point 250 ° C. Density (20 °C) 1.2784 kg/l.
2,4-TDI (65%) + 2,6-TDI (35%)
[TDI 65, TDI 65/35, TDI 65] – liquid (at room temperature) with a solidification point of 5°C, boiling point 250°C. Density (20 °C) 1.222 kg/l
1.2. Handling, transportation, storage.
Appeal
During handling and storage, appropriate safety precautions must be observed and special protective clothing must be worn.
TDI is highly toxic. Use only in a well-ventilated area. Keep away from heat, sparks and flames. Use explosion-proof electrical equipment. Take precautions against electrostatic discharge. Fumes from burning TDI can be very dangerous. Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing. Avoid ingestion and inhalation. Avoid formation of steam/mist. This substance can cause asthmatic reactions even from a single inhalation of low concentrations. Sensitivity: TDI reacts with water to form carbon dioxide. This gas may cause the sealed container to expand and possibly rupture. If the barrel is sealed, carefully unscrew the cap to relieve the pressure before removing it. Containers of this substance may be explosive if empty. Avoid exposure to cold and direct sunlight. Do not pour the substance into a dirty or wet container. You cannot eat, drink or smoke in the workplace. Equip your work area with hand washing and eye washing stations. Wash thoroughly after handling the substance.
Transportation.
In bulk in tanks, in metal barrels (with a special anti-corrosion coating) for single use with a capacity of 250 kg. Hazard class – 6.1 (dangerous cargo)
Storage (TDI 80)
Recommended storage temperature 15÷30ºС. Possible storage temperature -20÷35ºС (short-term up to 50ºС). During long-term storage above 35ºС, the quality of TDI may change. When stored below 15ºC, TDI crystallizes reversibly. To process it, it must be slowly heated to 15-30ºС and be sure to mix thoroughly, because During crystallization, the distribution of isomers and reactivity are disrupted. Away from heat, flame and all sources of ignition. Away from oxidizing agents. In tightly sealed containers. Store in a closed, well-ventilated area. Avoid exposure to water and moisture, direct sunlight. Once opened, containers must be closed and sealed with nitrogen gas or dry air. When stored outdoors, the container should be covered with waterproof canvas to prevent rain. Guaranteed shelf life 6 months. With proper storage, the period can be increased to 9-12 months.
1.3. Receipt
In general, the technology for producing TDI consists of the nitration of toluene to dinitrotoluene, then the catalytic hydrogenation of dinitrotoluene to diaminotoluene. Next, diaminotoluene is introduced into interaction with phosgene in an inert solvent.
The TDI production chain is described in more detail by the following reactions: It all starts with the base raw material - toluene. From it a mixture of mononitrotoluene isomers is obtained.
Rice. 3 Nitration of toluene
Then there are 2 options for synthesis: isomers can be separated or not separated. 1) From an unseparated mixture of isomeric mononitrotoluenes, a mixture of 2,4- and 2,6-TDI is obtained in a ratio of 80:20.
To do this, the mixture of isomeric mononitrotoluenes is re-nitrated to a mixture of dinitrotoluenes.
Rice. 4 Nitration of mononitrotoluene
The mixture of dinitrotoluenes is then catalytically reduced with hydrogen over Raney Ni to a mixture of diaminotoluenes.
Rice. 5 Reduction of dinitrotoluenes.
Diaminotoluenes can be processed according to 2 schemes:
A) One-stage phosgenation of the latter in a solution of o-chlorobenzene at a molar ratio of phosgene and diaminotoluenes 6:1 (200-210°C, 4.2-5 MPa, residence time in the reactor 40-50 s) according to the reaction:
Rice. 6. Phosgenation of diaminotoluenes.
leads to toluene diisocyanates in 90-96% yield
B) Two-stage phosgenation of diaminotoluenes with a 25-50% solution of phosgene in o-dichlorobenzene proceeds according to the reaction:
Rice. 7. First stage of two-stage phosgenation.
Rice. 8. Second stage of two-stage phosgenation.
With a yield of toluene diisocyanates up to 96%.
2) In the case of separation of isomers by rectification or crystallization from p-nitrotoluene, 2,4-toluene diisocyanate is formed:
Rice. 9. Nitration of p-nitrotoluene
Rice. 10. Reduction of 2,4-dinitrotoluene
Rice. 11. Phosgenation of 2,4-diaminotoluene.
From the o-isomer - a mixture of 2,4- and 2,6-toluylene diisocyanates in a ratio of 65:35.
Rice. 12. Nitration of o-nitrotoluene
Rice. 13. Reduction of dinitrotoluenes.
Rice. 14. Phosgenation of diaminotoluenes.
TDI can be obtained directly from dinitrotoluene by liquid-phase carbonylation in o-dichlorobenzene. This method avoids the use of phosgene, and the waste problem is only the disposal of hydrogen chloride. However, this method has not yet found industrial application.
In the spring of 2011, Bayer announced plans to build a TDI plant in China using new gas-phase phosgenium technology. Bayer representatives believe that this technology is the future of raw materials for polyurethanes, because it is more economical (due to lower heat costs for the separation of substances), more environmentally friendly (due to the reduction of toxic solvents), and also has a number of other advantages compared to the liquid-phase process. This technology can reduce solvent consumption by 80%, energy consumption by 60%, and investment by 20%.
2. Application
TDI is a raw material for the production of various types of polyurethanes.
Polyurethane products have become a part of our lives, so their production will undoubtedly expand in the future.
2.1 Application by industry.
TDI is used mainly to create elastic polyurethane foams used in furniture production, construction and transport. In 2009, they accounted for 66% of global TDI consumption (Fig. 1).
Rice. 15. Structure of world TDI consumption 2009
The most important areas of application of PU are:
1. Furniture, mattresses - various brands of furniture foam rubber. 2. Transport (mainly automobile transport) – seats and other “soft elements” of the interior. 3. Toluene diisocyanate is used to a lesser extent as a component of rigid polyurethane foams. 4. Artificial leather. TDI is the main component of modern high-tech material - polyurethane artificial leather, which is often called “Eco-leather”. A large number of clothes and shoes are made from it. 5. CASE (Coatings, Adhesives, Sealants, Elastomers)
Polyurethane adhesives are used for bonding flexible materials, rubber, textiles and leather. They are used for joining metal products, as well as for gluing metal to rubber and plastic. Polyurethane varnish, the raw material for the production of urethane varnishes and paints, is used to protect a wide range of surfaces. In particular, polyurethanes provide good gloss and scratch resistance to automotive paint. Polyurethane elastomers are used in thick film coatings, filters and shoe soles. Vibration-damping parts, rollers, wheels, and tires for roller skates and skateboards are made from them. Polyurethane sealants have a number of unique properties. TDI is also used as a crosslinker for nylon-6.
2.2 Application by type of TDI:
The following types of TDI are used commercially:
TDI 80 TDI 100 TDI 65 Modified TDI
The types differ in the content of isomers (2,4-TDI and 2,6-TDI) and additional modification.
TDI 80
— Furniture, mattresses, transport, sealants, paint varnishes.
TDI 100
– CASE (Coatings, Adhesives, Sealants, Elastomers)
TDI 65
— Transport, rigid polyurethane foams.
Modified TDI
– CASE, artificial leather.
Rice. 16. Structure of world consumption of isocyanates (MDI and TDI) by industry
What does the CRDI system provide?
Thanks to all the engineering tricks described, an engine with such an injection has a number of advantages.
- Requirements for the environmental cleanliness of motors are becoming more stringent every year. CRDI fuel distribution provides the ability to fully comply with these regulations;
- A fine spray of diesel fuel allows you to spend significantly less fuel on engine operation. Savings reach 25% for some engines;
- Precise, dosed injection ensures an increase in engine power by 40%;
- A side, but very pleasant consequence of using common rail injection was a noticeable reduction in engine noise - studies conducted by automakers showed a 10% reduction in background noise.
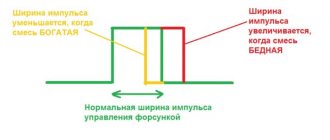
In conventional fuel injection pumps, when changes in fuel consumption occur, pulsating pressure waves appear in the channels leading to the injectors.
This forced the designers to limit the pressure on the injectors to 300 bar, which affected the power of the unit. And at the same time it did not always save: the fuel lines were still destroyed. Maintaining a constant high pressure (and in CRDI it reaches 2000 bar) eliminated the possibility of damage to the fuel lines: all the work happens inside the injector, there are no external fluctuations. In a word, the system had a beneficial effect on many engine characteristics.
Line defect detector TDI-MA (receiver)
The TDI-MA line flaw detector is a universal device that allows you to locally determine the location and direction of cable lines and metal pipelines, as well as determine the location of their damage (break, short circuit, damage to the protective shell, corrosion, decreased insulation resistance).
The TDI-MA line defect detector replaces the following devices: TI-03M, TI-05, TI-05-2, TI-05-3, TDI-02M, TDI-05M, TDI-05M-2, TDI-05M-3, TI-05C .
Purpose
The TDI-MA fault detector is designed for the following types of work on cable lines and metal pipelines:
- determining the location of the route;
- determining the direction of the route;
- determining the depth of the route.
- determining the location of the route damage (break, short circuit, insulation damage, etc.);
Application area
The TDI-MA line flaw detector is used for monitoring during installation and operation of the following types of cable lines and pipelines:
- copper-core communication cables (TPP, ISS, etc.);
- signaling and control cables (SBPZAVpShp, etc.);
- power cables (ASB, VVG, etc.);
- television and radio frequency cable lines (RK-75, etc.);
- optical armored cables (DPS, SPS, DAS, SAS, etc.);
- water supply, gas pipeline, oil pipeline;
- in construction organizations to prevent the possibility of damage to communications during excavation work.
Features of the device
- fully electronic mode control;
- LCD display showing operating modes;
- digital signal filtering – allows you to increase the noise immunity and selectivity of the receiver by an order of magnitude;
- additional suppression of industrial interference (50-100Hz) allows operation near overhead railway lines and in other unfavorable conditions in which operation of previous models of routers was impossible;
- fully automatic selection of the required gain within 5 decades;
- the presence of a 7 Hz channel, which makes it possible to separate capacitive and galvanic leakages and filter out stray currents;
- the ability to work both using headphones or a built-in speaker, and according to readings on the LCD display;
- a high-speed charger combined with a Li-Ion battery allows you to not only fully charge the battery in 2 hours, but also quickly recharge it in 15-20 minutes without any adverse consequences (Li-Ion battery does not have a “memory” effect);
- microprocessor monitoring of the battery condition allows you to promptly turn off the device in automatic mode, protecting the battery from destruction by overcharging;
- splash-proof film keyboard;
Specifications
| Search methods | induction and contact |
| Operating frequencies, induction method | 50 Hz, 893 Hz, 2430 Hz, 8930 Hz |
| Operating frequencies, contact method | 7 Hz, 50 Hz, 893 Hz, 2430 Hz, 8930 Hz |
| Active filtration | analog, digital |
| Information output | LCD display 98x32, built-in speaker, headphones |
| Time of continuous operation of TDI-MA from a rechargeable battery | at least 8 hours and depends on the condition of the battery. |
| Operating temperature range | -20°С…+40°С |
| dimensions | 350 x 850 x 260 and 300 x 400 x 250 mm |
| Weight of TDI-MA with battery | no more than 2.5 kg |
| Generators compatible with signal parameters | source of probing pulses IZI-6M or IZI-100 |
Contents of delivery
| TDI-MA receiver: measuring unit | 1 PC. |
| Disc search antenna | 1 PC. |
| Leak detection pin | 2 pcs. |
| Power supply (charger) | 1 PC. |
| Manual | 1 PC. |
| Bag for accessories | 3 pcs. |
Additional equipment
- source of probing pulses IZI-6M or IZI-100
- headset
Certificates and reviews
- Included in the accounting register as a type of product in Test St. Petersburg
- Feedback on testing TDI-MA at JSC Russian Railways
Documentation
but on the other hand
Everything cannot be completely good. Therefore, the CRDI injection system also has certain disadvantages.
The main thing that can confuse a car owner is the demanding nature of CRDI when it comes to fuel. Diesel fuel should be almost perfect, but in our open spaces it is not always possible to fill it with at least a good one.
Spare parts for the system cost a quarter more than for more modest options. Here you can complain that CRDI uses a catastrophically large number of sensors - and this is its weak point. In addition, not everywhere there are car services with sufficiently trained technicians. The system is of little use for independent repairs: the work requires special equipment.
Of course, knowledge of what a CRDI engine is and what problems it can bring to its owner cannot be regarded as an obstacle to buying a car with such a unit. However, it is still worth asking whether there are competent specialists in your area, and looking for a reliable gas station in advance: such actions will either prevent possible problems, or, if they give negative results, will make you think about another car.