Oil pressure in automatic transmission (automatic). What is it and how is it created?
In order for an automatic transmission to function properly, it must have the correct oil pressure. After all, in fact, this is the key to the normal operation of many components, from clutches to the hydraulic plate itself (valve unit). But what is it, or rather its meaning? How many atmospheres, or would it be more correct to say, “BAR”, are created in the automatic transmission in order for it to function normally? Today’s article is useful and I’m sure informative...
THE CONTENT OF THE ARTICLE
This question is not common, but it is also asked by my readers and viewers of my YOUTUBE channel, and, as I understand it, by those who like to delve into the insides of transmissions. Indeed, what kind of oil pressure is created inside the machine so that, say, the clutches are compressed? This is also very useful information for those who want to install an additional cooling radiator, because you need to cut into the oil supply and install special hoses, clamps, and it is important to understand which ones to buy so that they can withstand the pressure. So the information is useful, and I will try to sort it out.
A few words about the automatic transmission device
Before we start talking about oil pressure, we need to understand how an automatic torque converter transmission works.
The oil in it is the working fluid. If you want, this ATF fluid transmits torque from the engine to the transmission and then to the wheels. BUT this is at the level of the torque converter, the pressure there is quite large, but this pressure almost does not come into contact with the main gearbox.
There, pressure is created by a special pump, which pumps oil and delivers it through the hydraulic unit to the necessary channels, thereby forcing the friction rings to close or open, which in turn control the planetary gears - stopping or releasing them. In general, oil pressure in an automatic transmission is a very important process, which controls almost 90% of the operation of the entire transmission. If the pressure inside drops, the box will simply stand up.
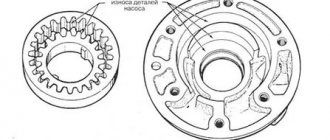
Oil pump
As I already wrote above, there is an oil pump inside the box, which pumps oil pressure into the small channels. It creates pressure inside, there are two types:
- Powered by a chain drive, that is, there is a gear or sprocket on the input shaft that spins the pump shaft so that it pumps oil
- The pump itself is located behind the torque converter, that is, rotations are transmitted directly and ATF fluid is also pumped
In any case, you need to take into account without this pump there would be no oil pressure at all! The automatic transmission would not work. Because there would be no compression or decompression of the friction discs, the gears simply would not shift.
What oil pressure is created inside?
Actually, we now understand that the main purpose of the pump is to compress the clutches and change gears. Oddly enough, much significance is not required here (of course, everything is relative).
The pressure inside the automatic transmission is at the level of 2.5 - 4.5 atmospheres or BAR (in relation to liquid), it rarely happens when it is 4.6 - 5.0 BAR. This is exactly the indicator that is enough to compress disks. Of course, there is no exact value, because there are now dozens (if not hundreds) of machine designs and each manufacturer uses its own design
By the way, earlier on old cars, there were often pressure sensors in the automatic transmission on the panel so that the driver could control this parameter. However, over time it was removed because it was considered unnecessary information (by the way, the same thing happened with the engine oil sensor).
No oil pressure in the automatic transmission - the main reasons
Actually, there are not so many reasons here, although they can be divided into two phases:
- Low blood pressure outside normal limits. In this case, most likely your machine will kick, push and generally not move. This is due to several reasons. Firstly, the oil filter may become clogged; it is simply clogged with wear products due to high mileage (change it urgently). Secondly, the oil itself has become thick (or, conversely, too thin), and has generally lost its properties (also needs to be replaced). Thirdly, the solenoid on the valve body failed. Fourthly, the valve body itself (more precisely, its channels) is clogged. We actually disassemble the box and look for the reason.
- No pressure at all. It's more difficult here. This is most likely the oil pump; it has failed and is not working. There may be several reasons: if it is a chain drive, the chain has broken, if not, then the bushings may have worn out and it is jammed.
In any case, the box needs to be removed and inspected. You can't go anywhere without this. Of course, if you properly service the machine, then such problems might not affect you. At least change the oil and filter correctly, this will be a big plus, watch a short video on the topic.
Actually, this is the information, I hope it helped you, sincerely your AUTOBLOG.
auto-blogger.ru
Automotive portal. Answers on questions
A transmission fluid pressure test is performed to determine the condition of the hydraulic components and whether there are any leaks.
1. Apply the parking brake and chock the front and rear wheels.
2. Run the engine until the gearbox warms up to a temperature of 60~70°C.
3. Before testing, check the levels of all operating fluids and, if necessary, bring them to normal levels.
There is another engine oil warning light, this time there is a dropper and the signal means that the engine oil level is too low and there is a danger of lubricating the engine's mechanical components. If this light comes on, you will need to check your oil level as soon as possible.
The engine oil light shown in the top picture always comes on on the dashboard when you start the car. If there is no problem with the vehicle, the warning light goes out within seconds, but if there is a problem, the warning light remains on.
4. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
5. Remove the mudguard on the left side under the front bumper.
2. Check the engine speed at idle speed and in the “P” selector position.
Engine idle speed:
For Europe and Australia: 750-850 min –1
General: 700-800 min – 1
For specific problems, the engine oil light may only come on during certain events: at high speeds, then during acceleration or braking. The oil warning light, when left on, indicates an anomaly that can be very serious. The spy is represented by an ohler with a drop of pendant.
When is the oil spy activated?
The lubricating oil enters the engine driven by a pressure pump. The engine oil light comes on when there is not enough pressure to push lubricant to the engine.
Oil light, what to do and what to check
If the oil warning light is on, it is recommended to stop the vehicle immediately to avoid excessive entrapment of the engine's mechanical components, causing damage to the vehicle.
3. Move the selector lever to position “D” and read the pressure value on the pressure gauge.
To prevent damage to the transmission, perform steps 4 and 5 within 5 seconds.
4. Press the brake pedal all the way with your left foot, and smoothly press the accelerator pedal with your right foot.
5. When the engine speed no longer increases, read the pressure value on the pressure gauge and release the accelerator pedal.
How to check engine oil level
Driving with the oil light illuminated is not smart.
What can I check to see if this indicator is on? Before you call a good mechanic, there are some controls that the same driver can do. Caution: Place the vehicle in a suitable location where you can carry out checks in a safe place. Do not obstruct traffic and park on an inclined surface: control of engine oil should be done on the floor. The first thing to do is check the oil level. With the car on the floor this will be enough.
- Park in the floor and allow the engine to cool.
- Open the engine hood.
- Find an oil storage tank.
- Remove the special hub and observe the oil level.
If the level is set to the minimum level, it is necessary to replenish or replace the lubricant.
The lubricating oil should be changed every 1000 km for a petrol car and 000 km for a diesel car. Oil filling or oil changes must be done when the engine is cold. Running the engine at idle speed for at least one minute cools the transmission fluid and prevents deterioration.
Before each subsequent test, cool the transmission for a sufficient period of time.
6. With the engine running, move the selector lever to position N and leave the engine running at idle speed for at least one minute.
What to do when the light is on
The article is an in-depth study of the causes of engine oil light. Car lights are a key indicator of a car's health. Each warning light indicates a malfunction or anomaly that has occurred once or is still ongoing on the vehicle. Knowing your car lights is important, so we provide you with more guidance and a quick guide on the meaning of different car lights.
How to check transmission oil in a car?
Because your engine requires oil to lubricate various components and protect against wear and corrosion, your transmission needs a special fluid called gear oil. Maintaining the proper level of transmission oil is important to ensure smooth operation of the vehicle.
7. Similarly, measure the pressure in all positions of the selector lever:
Transmission fluid pressure, kPa
| Positions | At idle speed | IN modestall test Transmission fluid pressureHow to check transmission oil? The fluid should only be replaced if repaired. Step 2: Locate the fluid level plug if you have an automatic transmission system. Usually its color is red. The instruction manual will help you find the plug. If you're lucky, it will be listed where you can find it.
In the case of front-wheel drive vehicles, the fork is usually located on the driver's side, on one side of the gearbox. |
8. Remove the pressure gauge and close the fitting with a plug.
Tightening torque: 5.0–9.8 N m
Assessing Transmission Fluid Pressure Test Results
| Transmission fluid pressure | Possible fault location If you can't find it, the manual should show you where to look for it. Many cars do not have a transmission test plug. The oil level must be checked by an electrical device or by removing the screw in the gearbox housing. Checking the fluid level in a sealed transmission system is a much more complex process. The average car owner does not have the skills to check the transmission oil level. If your vehicle does not have this plug, please go to your nearest service center to check the level for you. Take the time to do this by changing your engine oil. If your car has this plug, it's a good idea to check your transmission fluid level. Step 3: How to check transmission oil? . Remove the plug, wipe it with a clean cloth, put it back and wait 5 seconds, then remove it again and check the level. Add liquid if necessary. Always use the fluid recommended by the manufacturer. |
| Low pressure in each selector lever position | Worn oil pump Leaks in the oil pump, control valve and/or transmission housing Pressure regulator valve blocked |
| Low pressure in positions D and 2 only Add small amounts, checking the stopper after each addition. It's easy to add transmission fluid, but it can be quite difficult to remove if you add too much. If the transmission needs more than 1 liter or regular refueling, take the vehicle to have it checked for leaks. How to properly test transfer fluid? You can also check the color and smell of the liquid. Color is very important for gear oil. It should not change from its usual light brown, translucent appearance. Automatic transmission fluids are cherry red in color. If the color is dark red or brown, it means you need to change your fluid. | Transmission fluid leaks in the forward clutch hydraulic drive |
| Low pressure in R position only | Transmission fluid leaks in the hydraulic clutch drive front lower gears and reverse or reverse clutch How to check an automatic transmission?If it smells burning or has particles in it, that's also a sign that you should change your oil. Before adding oil to the transmission system, you need to change the transmission filter. What is automatic transmission fluid? Transmission oil is the lifeblood of the transmission. The fluid creates the hydraulic pressure necessary to operate the gearbox. It also cools and suppresses transmission. When the fluid level is low, the pump can introduce air into the system. Air in the hydraulic system interrupts the automatic transmission's normal transmission. |
| Pressure higher than specification | Pressure regulator valve or linear solenoid valve blocked |
Checking pressures in the control system of an automatic transmission of the 722 series from a Mercedes car
Failure can occur very quickly if the transmission fluid level is low. How do we check the oil level in an automatic transmission? For diaphragm gears the procedure is the same as above. Car manufacturers are eliminating these impacts. New transmissions are much more complex than older models, and transmission fluid levels are much more critical. Special procedures are required to check the automatic transmission level of these models.
Learn more about how to change automatic transmission fluid. Drain the transmission fluid: First, disconnect the coolant line that runs from the transmission to the radiator. Connect a piece of rubber pipe by placing the free end of the pipe in an empty container. You can then reconnect the cooling line to the radiator. Remove the bolts holding the drain container to the bottom of the transmission system. Clean the drain container with transmission fluid. Once the filter and seal are in place, put the container back. Hand tighten the bolts for the first few turns to avoid exposing the wire. Then tighten the bolts using a torque wrench. Do not over-tighten the bolts to avoid damaging the threads in the system. Also check the quantity required.
- Start the engine and let it idle.
- The transfer fluid must flow from the cooling line into the container.
- As soon as the fluid stops working, turn off the engine.
This is a really annoying technical problem that can't be described as anything other than a gentle and unconventional solution.
To check the pressure values in the automatic transmission control system, three control plugs are provided to measure the operating pressure, the pressure of the speed regulator and the pressure of the modulator.
Attention:
When measuring operating pressure, modulator pressure and speed regulator, connecting hoses should be routed into the passenger compartment through the front door window so as to prevent them from being pinched. The connecting hoses must not bend or touch the exhaust pipe.
In short, only the fact that the manufacturer apparently decided at the last minute to supply the oil pump module with balance shafts is why we can guess. They are affected by the following engines. New common rail engine generators already have the problematic part of the modified oil pump module, but it is better to check the module with all components when changing the oil.
The whole problem lies in the chosen motion transfer system. So choosing a carrier oil pump that is something we could barely call 10cm thick steel alloy and a counterweight in the balance shaft, more than just a pressed bore, all of which are probably made of soft bronze. After several hundred kilometers - in the range from 000 to 000 km, the driver in the opposite direction of the shaft is pressed and the pressure in the system drops, in other words, we stop lubricating.
Modulator pressure
Attention
: Modulator pressure must be measured at “D” range, driving speed 50 km/h and vacuum line disconnected.
1. Disconnect the vacuum line (10) from the vacuum control unit (60). 2. Set the range selector lever to “D” position, accelerate the vehicle to a speed of 50 km/h and determine the modulator pressure value, which must meet the specifications below.
The lubrication problem is much more striking than it might seem at first glance. When driving, the problem is signaled on the on-board computer by the message “Low oil pressure”. When this message is displayed, the engine will not shut off automatically. This way, the driver can easily give the impression that there is nothing serious. In fact, already at this moment the turbocharger, which is very sensitive to lubrication, is very strongly influenced.
The manufacturer itself does not offer any solutions other than replacing the oil pump, which represents an investment of several tens of thousands, with the same violation after repeated driving. Unfortunately, there are experienced people who have faced the problem from the very beginning and are involved in finding a final but inexpensive solution. As predicted, the problem lies not only in the driver, which is made of hard material, but above all in the quality of the analogue it stores, which is made of soft material and is very susceptible to rolling.
Automatic transmission pressure values in the modulator
| Model | Modulator pressure adjustment 1. Remove the rubber cap on the vacuum control unit. 2. Pull the locking plate out of the locking groove until it can be rotated. 3. The position of the vacuum control unit adjusting screw can be changed using the lock plate. One full turn of the adjusting screw changes the pressure by approximately 0.4 bar. — 4. After adjusting the position of the adjusting screw, press the locking plate back into the locking groove. 5. Reinstall the rubber cap on the vacuum control unit. 6. Remeasure the modulator pressure. 7. Connect the vacuum line. In other words, the jagged hole literally feeds hundreds of thousands of kilometers away. Replacing the oil pump holder will, at best, delay the disaster, or worse, may hasten it because it will pull already worn teeth into the balance shaft. For the situation is not so simple, of course, you can buy a new part, unfortunately, only the oil pump, but not the balancing shaft. While browsing the Internet, a person comes across many modifications, ranging from alternative carriage options to different ways of welding a balance shaft, but there is probably only one person who came up with it with oversight and an emphasis on quality that he cannot see. |
| 300E (3.0l) and 300TE | |
| 300SD Turbo | |
| 350SD and 3S0SDL Turbo | |
| 560SEC and 560SEL |
Operating pressure
Measuring the pressure of the main line needs to be done only in certain cases when the gearbox does not have a rigid connection between the drive and driven shafts. Its measurement is essentially a test of the main pump. 1. Disconnect the vacuum line from the vacuum control unit. 2. Set the range selector lever to the “D” position, set the engine speed to approximately 1000 rpm, measure the operating pressure and compare it with the values in the table below. Note:
The operating pressure of the automatic transmission is not adjustable.
Operating pressure:
| Models | kPa 30.6 kmH | kPa 90.1 km/h | For vehicles with catalytic converter On vehicles with a catalytic converter, the oil line must be unscrewed to measure the speed regulator pressure. Note: First remove the oil line, then the oil line and the shift valve bracket |
| 300E (3.0 l) AND 300TE | |||
| 300SD Turbo | |||
| 350SD and 350SDL Turbo | |||
| Information is not available | |||
| 210 | |||
Speed regulator pressure
Checking the speed regulator pressure should be carried out at a very specific speed and gear. Accelerate the vehicle to a speed corresponding to the table value and measure the pressure of the speed regulator. If there is no pressure from the speed regulator, remove the regulator and wash it. If the pressure deviates from the table values, the regulator must be replaced.
Checking the vacuum circuit
Vacuum Control Valve (300D and 350SD/SDL Turbo)
1. Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature and check that the throttle actuator is adjusted correctly. Disconnect the vacuum hose and connect a vacuum gauge. 2. Start the engine and measure the vacuum at idle. The vacuum should be 395 - 445 mbar with a red head and 360 - 410 mbar with a black head. Stop the engine and push the throttle actuator against the limiter so that the throttle valve is fully open. The vacuum value should be zero. 3. If the vacuum value corresponds to the required value, then the vacuum control valve is working normally. If the readings do not correspond to the required values, check the wiring of the vacuum hoses. If it is correct, then check the vacuum pump. If pump I is normal, then adjust the vacuum control valve and, if necessary, replace it. Vacuum Booster (300D and 350SD/SDL Turbo) 1. Disconnect the vacuum hose and damper at the vacuum control valve. Open the control valve plug. Disconnect the pressure hoses for the altitude adjustment control (ALDA) on the vacuum booster and connect the tester to the excess pressure side of the disconnected hose. 2. If the vehicle only has one hose, connect the tester directly*/ to the PRE vacuum booster (boost pressure). Apply pressure to 740 mbar. If leaks are detected, replace the vacuum converter. 3. Using a T-piece, connect the tester to the TRA converter (transmission) vacuum hose. Start the engine and measure the vacuum at idle. The vacuum value should be 20-60 mbar. If the vacuum value corresponds to the required value, then the vacuum booster is corrected. Otherwise, check the wiring of the vacuum hoses. If the distribution is correct, replace the vacuum booster.
Overheating of ATF in the automatic transmission and low pressure of transmission fluid - ZF center on DRIVE2
Many automatic transmissions (with the exception of some types of automatic transmissions on budget small cars) have an additional oil cooling radiator. This solution is necessary in order to lower the temperature of the working fluid and maintain its viscosity. In other words, an automatic transmission oil cooler is needed to prevent overheating of the ATF and the entire gearbox. At the same time, the popular hardware automatic oil change in a box under pressure (displacement method) involves connecting a device between the box and the radiator.
On the one hand, this allows you to displace dirty oil and replace it with fresh liquid. However, the disadvantage of this replacement method is that the transmission pan is not removed, the pan is not washed and the magnets are not cleaned of chips, the automatic transmission filter is not replaced, etc.
As a result, the radiator is not washed, dirt and deposits from the pan get into the radiator, and the automatic transmission filter becomes even more clogged. Contaminants also get into the hydraulic unit (hydraulic plate), solenoids (valves) become clogged, etc.
In this case, the full volume of liquid does not pass through the clogged filter and overheating of the automatic transmission occurs due to the low throughput of the thin channels of the oil cooler.
Such a replacement can only be made when the owner is firmly confident that everything inside the box is clean. In practice, it is optimal to alternate hardware replacement with classic replacement, that is, removing the pan, cleaning, replacing the filter, etc.
Drop in oil pressure in the automatic transmission. The cause may be not only contamination, but also problems with the automatic transmission oil pump. In this case, the oil pump in the automatic transmission can be located either behind the hydraulic unit or in the transmission pan. The main task of the device is to create the required operating fluid pressure. If the pump’s performance drops, kicks appear, the machine twitches, noticeable shocks appear
Malfunctions in the operation of the automatic transmission can also occur due to problems with the valve body and solenoids. The valve body is actually an automatic transmission control element. The element consists of thin channels through which ATF fluid passes. If the channels become clogged with dirt and wear products, the valve body will become clogged, the pressure will drop, and the clutches will begin to slip. For this reason, it is very important to prevent contamination of the valve body by promptly changing the transmission fluid and filter, avoid replacement using the displacement method, and avoid overheating of the automatic transmission, which leads to “curdling” of the oil.
Also, special solenoid valves are installed in the valve body. These valves close or open the channels in the hydraulic plate. Solenoids are electric coils with a rod. Voltage comes to the coil, the rod extends, blocking the channel. After the voltage disappears, the spring pushes the rod back, opening the desired channel. This solution allows fluid to be supplied under pressure through the valve body channels strictly to certain gears (the required gear is released or clamped by the clutches). So, solenoids quite often stop working correctly, without closing or opening the channels in the hydraulic plate.
To solve the problem, you will need to remove the valve body, disassemble it, and clean the channels. Then the performance of the solenoids is checked, after which a decision is made to repair or replace the problematic elements.
www.drive2.ru
When to change the transmission mixture?
ATF fluid needs to be changed periodically, because this will increase the service life of not only the transmission, but also the car as a whole. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out systematic measurements of the oil level. The replacement period is affected by:
- vehicle mileage;
- terms of Use;
- driving style.
Professionals recommend changing transmission oil after every 20-25,000 km. Therefore, such an operation is performed no more often than once every 24 months.
The procedure should be entrusted to specialists at a service station, where there is all the necessary equipment that will allow you to change the oil. After all, you can only drain part of the ATF yourself; a significant part remains in the box. With the help of technical devices, professionals will also be able to rinse or replace the filter.
Loss of oil pressure in automatic transmission
The automatic transmission is designed in such a way that, thanks to oil supplied under pressure to the actuators, gears are changed, as well as torque is transmitted through the torque converter from the engine to the gearbox. Loss of pressure in the hydraulic system inevitably leads to most problems with the automatic transmission. The car stops moving normally, acceleration dynamics suffer, slipping occurs, etc. And in some cases this can lead to a complete stop of the car.
The oil pressure in the automatic transmission hydraulic system is created by the oil pump. Its failure is not uncommon, but this is not always the main reason for the loss of pressure. The most common source of this problem is worn sealing elements and contamination of oil passages and valves.
Despite the fact that the mechanics of the automatic transmission are made with high precision, many of its components and parts cannot do without gaskets, seals and cuffs, which are designed to prevent oil leakage and maintain pressure. Unfortunately, these details do not last forever. Made from elastic materials, they are forced to work in an aggressive environment. They are exposed to high temperature, chemically active oil components, high pressure and friction of mating parts. Because of this, they become rougher, wear out and cease to perform their main functions - to ensure tightness. The decisive factors that shorten their service life are overheating of the box and saturation of the oil with wear products, which act on them as an abrasive. When the oil level is low, these parts interact with the metal “dry”, which also does not add to their service life. Restoring pressure when seals, oil seals and cuffs in an automatic transmission are worn out is only possible during the overhaul of the box by completely replacing them.
Another reason for a drop in pressure in the hydraulic system is its clogging with wear products. Many oil channels in the hydraulic system have a small cross-section or a complex configuration. This creates favorable conditions for the formation of wear debris deposits. If the oil in the box works for a long time at the limit and without replacement, then it becomes dirty very quickly, and the insides of the automatic transmission become overgrown with dense oil deposits. When changing the oil, these deposits may be washed away, but not dissolved. Pieces of dirt picked up by the liquid easily clog the oil channels and valves, and the pressure drops. The valve body suffers the most from this. Problems with oil pressure in the valve body can be resolved by flushing it with a special liquid. The solenoids also undergo a procedure of disassembly and cleaning, and in critical conditions, replacement.
Replacing oil seals and cuffs, as mentioned above, is a labor-intensive process, but inevitable and vital. Therefore, replacement of sealing elements is always included in the overhaul of the box.
For more information on automatic transmission repair, see here....
akpp.one
Why does the automatic transmission get very hot?
Despite the fact that a manual transmission is still considered the most reliable and durable, many drivers prefer automatic transmission. It allows you to drive the vehicle in a more comfortable mode and actually takes on some of the tasks.
However, due to the fact that the automatic transmission is a more complex unit, it is not without its drawbacks and often fails. If you ignore the first problems with this unit, you may face serious financial costs (changing a gearbox is not a cheap pleasure).
Overheating of the machine can also lead to destruction of friction discs, solenoids and wiring.
If we talk about the average value, it ranges from 60 to 90-95 degrees. Of course, some transmission components can withstand more severe temperature loads, but if we are talking about the entire system, then you should not exceed the limitations specified by the manufacturer. The maximum temperature that the most modern and expensive automatic transmissions can withstand is 130 degrees.
If the ATF fluid overheats more, it will cause sediment, which will clog some parts of the assembly. In addition, overheating negatively affects the lubricating functions of the oil, which will also accelerate the wear of the automatic transmission. It is impossible to determine the difference in temperature conditions by eye, but there are several methods and recommendations that will help to identify the problem in a timely manner.
The easiest way to determine the occurrence of problems is by characteristic signs. Overheating is most likely to occur if:
- The gearbox began to “kick” with each gear change (the driver feels quite strong jerks).
- Gears begin to shift untimely. Sometimes they may not work at all. There are often situations when it is possible to move from second gear only to fourth.
- A symbol appears on the dashboard indicating that the system is overheating (a check or A/T lights up on the car’s dashboard).
- An unpleasant burning smell appears in the cabin, which comes from transmission oil.
On modern cars, the on-board computer allows you to obtain all the information about the temperature conditions of all necessary components. Therefore, it is worth trying to find information about the fluid in the automatic transmission. If its temperature exceeds 100 degrees, then this indicates obvious overheating.
If the car does not have a function for checking the fluid temperature, then in this case you can buy a simple diagnostic device (the same, Chinese ELM 327) and check the standard indicators of the car via a mobile phone.
Important! If the automatic transmission starts to operate in emergency mode, then it only takes 20-30 minutes for the entire unit to fail. Therefore, when the first suspicion of overheating appears, you need to establish its cause and take appropriate measures.
Most often this happens for several reasons, for which inattentive car owners are to blame:
- Due to untimely change of ATF fluid. The service life of the highest quality trains cannot exceed 150,000 km. It is recommended to change the ATF fluid at intervals of 100,000 km. If we are talking about a modern automatic transmission, then it is better to reduce this value to 80,000 km. A lot also depends on your driving style. If the car owner prefers to press the gas pedal to the floor, often skids, uses a heavy trailer or tows the car, then the transmission oil is changed after 50-60,000 km.
- Due to burnout additives. This leads to the formation of special compounds, which, under the influence of elevated temperatures or loads, begin to interact with metal parts, forming a film of iron sulfide and various combustion wastes on them. If you want to extend the life of the working fluid, then it is better to purchase synthetic oils (they cost several times more) that have improved anti-wear and extreme pressure properties.
- Due to increased loads on the car. When purchasing a car, it is recommended to immediately find out its exact weight and how large trailers or cars can be towed on it. If the towed object exceeds the standard requirements, this can easily cause overheating and rapid wear of the gearbox. Of course, if we are talking about SUVs, then they can easily transport trailers or vehicles weighing up to 2 tons. However, even in this case, the automatic transmission oil will overheat (perhaps to a lesser extent, but there will still be a negative impact). However, if we are talking about a passenger car, then you need to be especially careful.
- When slipping. If a car starts to slip at high speeds on ice, snow or mud, this will certainly lead to severe overheating. Some perform such manipulations on the asphalt intentionally to attract attention, but such a “show” can end disastrously for the automatic transmission. Strong heating will occur in the gearbox, causing the friction discs to burn.
- If problems arise with the gearbox radiator. If it is clogged with dust, dirt, fluff, midges, etc., it will not be able to cope with its main function - cooling the transmission fluid. Therefore, it is important to remember that the radiator must be cleaned at least once a year. Often, car manufacturers combine a cooling element for the engine and gearbox. Such a “joint” radiator does not always cope with its task. Therefore, many install an additional element to cool only the automatic transmission.
- Due to aggressive driving. If your car has an automatic transmission (especially when it comes to old or too cheap cars), then you should not make sharp turns, press the gas pedal to the floor, drift and engage in other manipulations that can easily lead to overheating. Some cars have a special sensor that reduces the supply of gasoline when driving too aggressively. It is designed to limit driving speed and thereby save the driver’s life, and to give the automatic transmission time to “digest” the torque being squeezed out.
Read more: Signs of a faulty manual transmission
Regardless of the reasons for the overheating of the machine, you should never operate the car in this condition. It is best to call a tow truck, since replacing the entire box will cost much more.
In the future, it is worth more closely monitoring the condition of the automatic transmission, checking it for possible leaks, checking the “freshness” of the oil and how well the cooling system works.
You need to take care of your car and not “force” it to work under extreme loads if it is not designed for this.
But they have several weak points, and if you do not follow the operating rules, then you can very quickly “ruin” this transmission, and the cost of a new one or repairing this one is simply HUGE money! One of the destructive reasons is overheating.
This is exactly what I want to talk about today in more detail. As usual there will be a text version of the video.
Overheating can very quickly damage your automatic transmission, and overheating may not even be noticeable and at low speeds in the city (for example, driving in gentle modes), you won’t even notice it, and when the automatic transmission starts to kick, it will be too late. Today we will talk about the causes and symptoms, and the consequences too.
The machine heats up from the transmission oil (it is special, called ATF fluid).
This fluid is a transmission link - in simple words, it transmits torque from the engine to the wheels.
All this happens in a torque converter, when one turbine (turbine wheel), conventionally tied to the engine, transfers the oil pressure to another turbine, which is tied to the transmission.
As you understand, it is the oil that heats up, and not the automatic transmission itself, and this heat heats up everything else.
In order to level out excess heating of the liquid in the machine, it is passed through a cooling radiator, which is precisely why destructive heating does not occur.
It is worth noting that the normal temperature of the oil inside an automatic transmission is between 65 and 95 degrees Celsius. If the temperature exceeds 100, and even more so 110 degrees, then you already need to think and watch. Otherwise, breakdowns are nearby
Now let's think about what could be the reasons why the machine overheats.
Causes of overheating
The reasons are often trivial and anyone can encounter them:
- The cooling radiator is clogged. Usually it is separate, located next to the main engine cooling radiator. Over time, it can become clogged with lint, dirt, insects, etc. IMPORTANT! Clean it every year (at least wash it with not very strong streams of water)
- The oil hasn't been changed for a long time. Let's say we rode 150 - 200,000 km and never got into an automatic transmission. A VERY large amount of dirt accumulates, and it can also clog the cooling radiator from the inside. ATF fluid will not circulate, so you have overheating
- Towing a car or trailer. A large traction mass can also lead to overheating and greater wear.
- Slipping. Stuck in mud, sand or snow. If you are slipping in one place, the speed is high, the automatic transmission is thoroughly warming up. Many cars even have an overheating protection system, it turns off the machine after critical heating, and you have an indicator on the dashboard
There is another reason, but this is what I call planned aging. The point here is this - on some cars the automatic transmission radiator and the main radiator for the engine are combined. BUT often now motors can be high temperature, which
As long as you don't haul trailers behind you or skid in the mud. Then it is important for you to flush the radiator and change the oil inside on time
Are the consequences most dire for an automatic transmission? Let's go through the points again:
- Oil (or ATF fluid). Its operating temperature (the best one) is up to approximately 130 degrees Celsius. If the heating goes higher, then it simply loses its properties and may even burn. And from such burning, sediment may form, clogging many working parts - solenoids, valve body, etc. At a minimum, the performance of your box will be impaired
- Friction discs (or clutches). I already wrote about them here, they are both hard (usually metal) and soft (can be pressed cardboard and other impregnated types of special paper). So, “soft” clutches can simply collapse from excessively high temperatures.
- Solenoids. In simple terms, these are specialized valves that open the flow of oil to a package of one or another package of friction discs, closing or opening them. So now solenoids can be 50% plastic, and high temperatures can simply destroy them
- Wiring. Often, special control wires can go to the solenoids, but from high temperatures, they can also melt and collapse.
Automatic transmission radiator?! Pressure in the automatic transmission?! Help! — Community “All about automatic transmission” on DRIVE2
Guys, I ask for your help! I have a LA4A-EL (cd4e) transmission - a Ford one. It’s leaking from the breather, yesterday the torque converter oil seal was squeezed out (I discovered that my standard automatic transmission radiator is clogged, I blow into its hose with my mouth, it barely blows (very, very hard) , I’m straining all my lungs.
Tell me, what is the maximum ATF pressure on the cooler?
The automatic transmission repair instructions say that the test lines have the following pressure: in position D, at idle, from 3.7 to 4.3 kg/cm2; in position D, with an engine speed of 2100 rpm, it ranges from 9.2 to 10, 7 kg/cm2 in position R, at idle from 5.4 to 7.2 kg/cm2 in position R, with an engine speed of 2100 rpm it ranges from 14.4 to 16.8 kg/cm2. But about the speed of 5000 -7000 rpm is not stated in the manual in mode D, there are also kick-downs) Could you tell me the pressure at such a load? The following question is also of interest:
Will the radiator withstand oil (engine oil)? If in the engine at high speeds the oil pressure is about 6.5 bar. Or maybe the heater radiator or intercooler? What alternatives can you choose?
additional radiator
Hayden radiator
In our city, finding an external radiator for an automatic transmission (like Hayden, etc.) is very difficult, it takes a long time to order, and the machine is desperately needed, it’s sitting in a pit (
Thanks a lot!
www.drive2.ru
How is pressure formed?
Let's try to figure out what causes increased pressure to be created and maintained in the engine cooling system. After you start your car's engine, it will begin to heat up and the coolant temperature will rise.
Accordingly, steam is formed, and due to it, the pressure level begins to increase. A valve is installed in the radiator cap or expansion tank that maintains it at the required level.
If we talk about digital parameters, then depending on the manufacturer it is from 1.2 to 2 bar. Typically, when the pressure rises above 1.5 bar, the safety valve is activated and the excess steam generated is released into the atmosphere.
Why is ATF so expensive?
But really, why can a liter reach a price of 700–800 rubles, while a vending machine often requires about 8–10 liters? But as you understood from above, this is the most technologically advanced liquid, and it evolves every year.
It is much more advanced than motor oil, and even more so than regular transmission oil, hence the prices. However, again, I repeat, it works in an aggressive environment and for a fairly long period of time, 60 - 70,000 kilometers.
This is what ATF oil is, I think you liked the article. Read our AUTOBLOG, subscribe to updates.
Similar news
- Automatic transmission clutches. What are they, how do they work and why do they burn?
- Double clutch. What is it, the basic principle of operation. Plus …
- CVT (variable gearbox): what is it, the principle of…
Where to get “not original”
From the buyer’s point of view, it would seem that everything is simple - you need to find out which “non-original” oil is approved for use on a specific automatic transmission and when replacing it, buy only it.
However, in practice it turns out that not everything is so simple - in Russia there is a rather specific market for the sale of cars and spare parts for them, which makes its own adjustments.
Firstly, information about the tolerances of a specific “non-original” oil for a specific automatic transmission model, as a rule, contains many indicators intended for people who understand the kinematic viscosity, density and flash point of transmission fluids.
An ordinary buyer who does not understand anything about this has to rely on all sorts of “experts” - such as sales assistants in stores or service technicians. Whether you can trust these people with your automatic transmission - each car owner decides for himself.
Secondly, in our country, not only car manufacturers, but also official dealers, for whom the sale of spare parts is one of the main sources of income, are trying to make money on expensive original spare parts.
Therefore, providing car owners with accurate information about “non-original” spare parts and oils that have manufacturer approvals is not in the interests of the dealer, unless he himself is engaged in the sale of such “non-originals”.
Thirdly, oils sold in Russia are very often counterfeited. Even if the car owner manages to find out which “non-original” oil can be used in his automatic transmission, he does not have many guarantees that the purchased oil will not be counterfeit.
Therefore, in order to use “non-original” oil in his automatic transmission, the car owner must first absolutely find out whether it can be used in his automatic transmission, and then find a store where they will sell him this particular oil, and not some other filled into “someone else’s” packaging.
What do we end up with?
As a result, the serviceability of the gearbox directly affects the quality of the engine, as well as the functioning of the entire vehicle . If certain signs of failure of a given unit are detected, you should immediately begin diagnosing it in order to understand exactly where the problem lies. The diagnostic procedure should be performed very carefully, following all the steps described above. This way you can determine as accurately as possible what is the reason for the incorrect operation of the automatic gearbox.
And then a video about how to check an automatic transmission:
Catalog of ROLF transmission oils for automatic transmissions
More details
ROLF ATF II
Fluid for automatic transmissions that require the use of oils with a specification not lower than DEXRON IID. It has extended replacement intervals, stable viscosity over a wide temperature range, and due to its high viscosity index, it ensures reliable operation of the gear shift mechanism even if the oil pump is worn.
More details
ROLF ATF III
High-quality ATF fluid designed for heavily loaded transmissions of passenger cars and trucks. Due to its increased heat capacity, it effectively cools the torque converter, clutches and brake mechanisms of the box, and ensures reliable transmission of torque by friction clutches. In addition to the DEXRON IIIG requirements, it meets the approvals of ZF, Allison, Volvo, Voith. Received approvals from Mercedes-Benz, Caterpillar, MAN.
More details
ROLF ATF Multivehicle
A high-class synthetic transmission fluid developed to meet the widest range of requirements of automakers in the Asian and American markets. It can be used in automatic transmissions of Toyota, Nissan, Honda and Mitsubishi, and meets MOPAR, Allison, Ford approvals. Approvals received from Volvo and ZF.
How does ATF fluid work?
I have already touched on several aspects of the work, but now I would like to talk in detail about how it works.
Temperature
The average operating temperature of the fluid is about 80 - 95 degrees Celsius, although at some moments, for example in traffic jams in the summer, it can heat up to 150 degrees. But why? It's simple - the automatic machine does not have a rigid transmission of torque from the engine to the wheels. Therefore, sometimes the engine provides increased power, which the wheels do not need to overcome road resistance - the excess energy must be absorbed by the oil and spent on friction, hence the heating in traffic jams is simply enormous.
Foaming and corrosion
Large masses of oil that move under enormous pressure create a favorable environment for ATF fluid to foam. And in turn, this process leads to oxidation of the oil itself, and metal parts. Therefore, the liquid must have the necessary additives to minimize these processes. Moreover, the additives selected are different each time; there are no identical ATF oils.
Liquid life
As you understand, this liquid is essentially unique; it works in very unfavorable conditions, but even at such temperatures it can work for many thousands of kilometers. Its resource is approximately 50 - 70,000 kilometers. However, do not forget that it does not last forever, and after 70,000 kilometers its properties are lost, replacement is required.
Evaporation
Not many people know, but ATF oils can evaporate, so some manufacturers install dipsticks (to measure the level) on their machines. The level may drop due to the release of vapors through the ventilation system of the automatic transmission cavities, in simple words through the “breather”. Therefore, it is important to monitor the level, this is a kind of mandatory practice.
When checking the automatic transmission oil level, they look at its color, transparency, smell and foaming. You can check the purity of ATF using the “rag test”, by dropping a drop from the dipstick onto a white paper napkin. Good oil will be absorbed quickly. Remains of solid particles, shavings, crumbs indicate contamination of the liquid.
Black and opaque oil needs to be changed urgently. A burning smell along with contamination indicates overheating of the box - diagnostics with a complete overhaul will be required.
How often should you change the oil?
The viscosity and condition of transmission oil is an important diagnostic sign. A dark color with a specific odor indicates slippage and overheating of the clutches; insufficient control pressure can indicate both mechanical breakdowns and aging of the lubricant itself or its insufficient level.
Read more: Replacing the release bearing on a VAZ 2110 with your own hands: video instructions
When changing the oil in an automatic transmission, you must adhere to the deadlines established by the manufacturer, or reduce them when operating in difficult conditions (aggressive driving style, hot climate, off-road use). There are two replacement technologies: draining or pumping. In the first case, the procedure is faster, requires a smaller volume of fluid, but does not allow a complete oil change (primarily in the torque converter). Therefore, it is preferable to replace with pumping, when part of the oil is drained under pressure while the engine is running, and losses are replenished.
In any case, control of the amount of oil must be carried out in accordance with the service documentation for the vehicle. Usually the temperature at which the level is checked with the engine running and the selector lever in the “parking” position is indicated. Long-term operation of an automatic transmission with a low oil level is unacceptable, as it accelerates wear of the gearbox mechanisms.
How to choose oil
Automatic transmission oil must be selected in compliance with all requirements specified in the service documentation. If the manufacturer indicates only the DEXRON classification, you can purchase any product of the corresponding class. If there are specific requirements (primarily for Japanese cars, as well as heavy trucks of European or American production), it is important to comply with the requirements of the corresponding approvals.
As a rule, such automakers market transmission fluids under their own brand, guaranteeing their compatibility with transmissions of cars of their brand. For such cases, ROLF Lubricants GmbH creates a universal oil, the composition of which meets the requirements of the largest number of global automakers.
Read more: Ways to solve problems with automatic transmission in a BMW car reasons